数组
Go语言数组,声明有如下几种方式:
var arr1 [10]int
arr1[0] = 10000
var arr2 = [10]int{0:0,2:2}
var arr3 = [...]int{1,2,3}
其中arr1只是进行声明,数组在声明时,内存空间已经被开辟过,所以可以赋值。arr2是声明的同时赋值,arr3是用…语法糖自动推断数组的长度。
数组作为参数传递或赋值时都是值拷贝,即——修改数组的copy不会对原数组造成任何影响。
数组的长度 <= 4时,会被分配在栈空间,否则分配在堆空间,这部分内容需要看Go编译器前端的源码,暂时略。
切片
原型
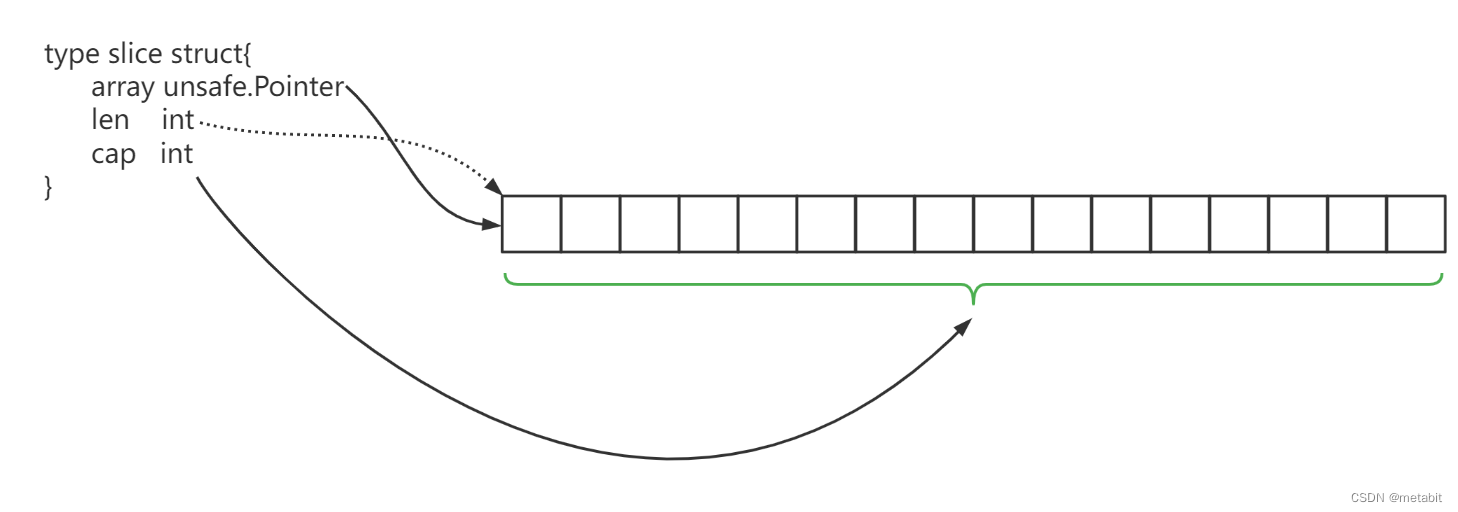
Go语言中,切片(slice)是对数组的一个"封装",他的底层结构如下:
src/runtime/slice.go
type slice struct {
array unsafe.Pointer
len int
cap int
}
slice 结构体中
- array 字段保存的是一个指向数组的指针
- len 字段保存的是当前切片中元素的数量
- cap 字段保存的是当前切片底层数组的长度
当然,如果好奇一个切片类型的变量占用多大的内存空间,可以使用unsafe.Sizeof()函数查看一下,代码如下。
你会发现,64位机器上,切片类型变量占用的空间为64字节(内存对齐后)。array:8字节,len:8字节,cap:8字节。
var slice []int
fmt.Println(unsafe.Sizeof(slice)) // 24
切片的使用
var slice []int
slice[1] = 100 //panic: runtime error: index out of range [1] with length 0
切片在通过index访问时,必须先初始化,只声明便使用是不被允许的,如上边的代码,产生了panic
切片的初始化
var s0 []int = []int{}
var s1 = []int{}
var s11 = []int{1,2,3,4,5} // 初始化并赋值
var s12 = []int{0:0,2:2,99:99}
var s2 []int = make([]int,10)
var s3 = make([]int,10) // len = 10, cap = 10
var s4 = make([]int,0,10) // len = 0, cap = 10
s5 := make([]int,10,10)
使用append()方法对未初始化的切片进行追加时,是被允许的。
切片的原理
array指针指向底层数组
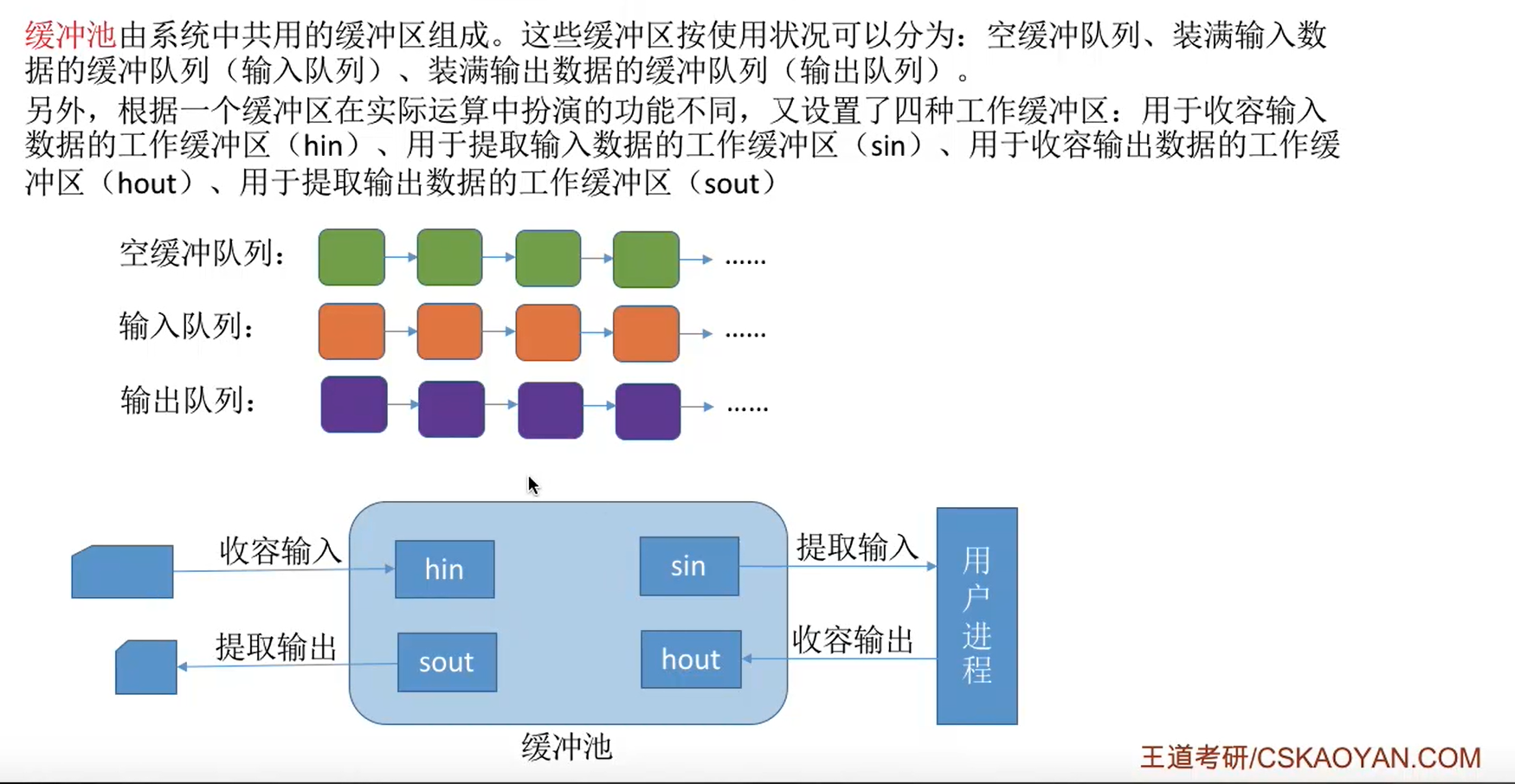
以下图为例,详细讲解切片操作。
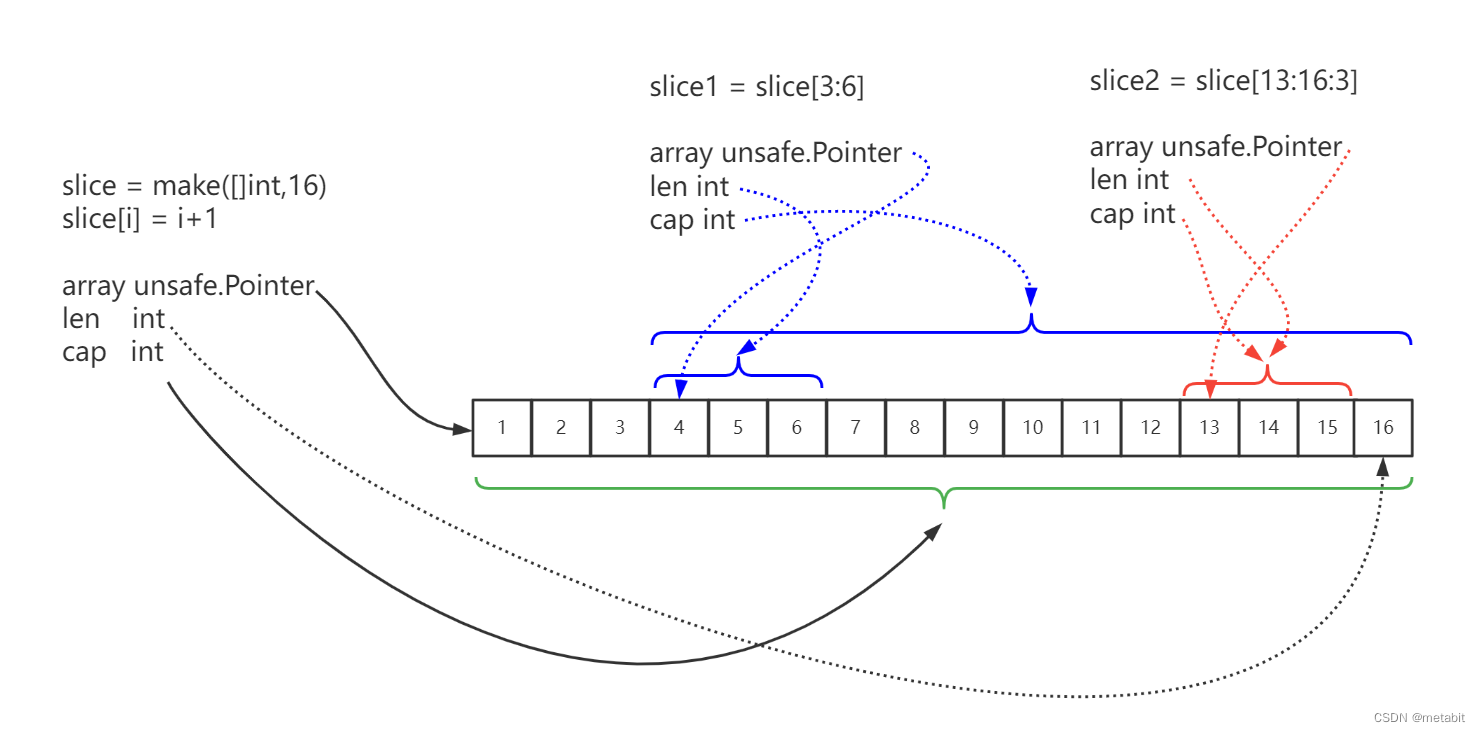
slice 是一个底层结构中array字段指向长度是16的int类型数组,len字段为16,cap字段为16的切片。使用for循环对切片进行赋值,切片的底层数组中存储了[1,2,3…16]共16个值。
slice1 = slice[3:6]是对slice[3,6)位置的元素进行截取,创建一个新的切片,slice1的array指向了slice底层数组的第4个空间的地址,slice1的len = 6 - 3 = 3,slice1的cap = 16 - 3 = 13 (与slice的cap后半部分重叠)。因为slice1与slice共用了底层数组[3,5]的空间,所以slice与slice1中任何一方修改底层数组(slice[3,6],slice1[0,3])的数据,slice 与 slice1 的数据都会受到影响。当slice1使用append()函数追加数值时,slice底层数组相应位置的元素将被覆盖。
slice2 = slice[13:16:3]是对slice[13,16)位置的元素进行截取,同slice1不同的是,其指定了slice2的cap = 3,而不是像slice1与slice共享cap的公共部分(16 - 3 = 13)。而对slice2使用append()函数进行追加数值时,会另外开辟新的底层数组,赋值给slice2的array指针。不会对原slice的array造成任何影响。
若不想让切片变量的操作对原切片造成任何影响还可以使用copy(dst,src)函数,对其进行复制。
s0 := []int{1, 2, 3}
var s1 []int = make([]int, len(s0))
copy(s1, s0)
fmt.Println(s1) // [1 2 3]
s1[2] = 99
fmt.Println(s0, s1) // [1 2 3] [1 2 99]
copy(dst,src) 在运行时调用slicecopy()函数 copy(slice, string or slice)
src/runtime/slice.go
// slicecopy is used to copy from a string or slice of pointerless elements into a slice.
func slicecopy(toPtr unsafe.Pointer, toLen int, fromPtr unsafe.Pointer, fromLen int, width uintptr) int {
if fromLen == 0 || toLen == 0 {
return 0
}
n := fromLen // 计算将要拷贝数据个数
if toLen < n {
n = toLen
}
if width == 0 {
return n
}
size := uintptr(n) * width // 计算将要拷贝的数据所占的空间
if raceenabled {
callerpc := getcallerpc()
pc := abi.FuncPCABIInternal(slicecopy)
racereadrangepc(fromPtr, size, callerpc, pc)
racewriterangepc(toPtr, size, callerpc, pc)
}
if msanenabled {
msanread(fromPtr, size)
msanwrite(toPtr, size)
}
if asanenabled {
asanread(fromPtr, size)
asanwrite(toPtr, size)
}
if size == 1 { // common case worth about 2x to do here
// TODO: is this still worth it with new memmove impl?
*(*byte)(toPtr) = *(*byte)(fromPtr) // known to be a byte pointer
} else {
memmove(toPtr, fromPtr, size)
}
return n
}
- 计算将要拷贝的数据的个数,在目标切片的长度和源切片的长度中取其小者
- 如果数据长度为1,则直接使用*(*byte)(toPtr) = *(*byte)(fromPtr)的方式进行赋值而不开辟新空间
- 如果数据长度不为1,使用memmove,对内存中的值进行拷贝
make & copy 连用时,调用运行时makeslicecopy()函数
[1]
// makeslicecopy allocates a slice of "tolen" elements of type "et",
// then copies "fromlen" elements of type "et" into that new allocation from "from".
func makeslicecopy(et *_type, tolen int, fromlen int, from unsafe.Pointer) unsafe.Pointer {
var tomem, copymem uintptr //目标存储空间大小, 源数据存储空间大小
if uintptr(tolen) > uintptr(fromlen) { // 目标数组长度 > 源数组长度
var overflow bool
tomem, overflow = math.MulUintptr(et.size, uintptr(tolen)) // 返回二者乘积,和是否溢出
if overflow || tomem > maxAlloc || tolen < 0 {
panicmakeslicelen()
}
copymem = et.size * uintptr(fromlen)
} else {
// fromlen is a known good length providing and equal or greater than tolen,
// thereby making tolen a good slice length too as from and to slices have the
// same element width.
tomem = et.size * uintptr(tolen)
copymem = tomem
}
var to unsafe.Pointer
if et.ptrdata == 0 {
to = mallocgc(tomem, nil, false)
if copymem < tomem {
memclrNoHeapPointers(add(to, copymem), tomem-copymem)
}
} else {
// Note: can't use rawmem (which avoids zeroing of memory), because then GC can scan uninitialized memory.
to = mallocgc(tomem, et, true)
if copymem > 0 && writeBarrier.enabled {
// Only shade the pointers in old.array since we know the destination slice to
// only contains nil pointers because it has been cleared during alloc.
bulkBarrierPreWriteSrcOnly(uintptr(to), uintptr(from), copymem)
}
}
if raceenabled {
callerpc := getcallerpc()
pc := abi.FuncPCABIInternal(makeslicecopy)
racereadrangepc(from, copymem, callerpc, pc)
}
if msanenabled {
msanread(from, copymem)
}
if asanenabled {
asanread(from, copymem)
}
memmove(to, from, copymem)
return to
}
计算 tomem(目标存储空间大小), copymem(源数据存储空间大小)
为to分配内存,使用memmove(to,from,copymem)拷贝copymem大小的数据从from到to中
返回to
make
func makeslice(et *_type, len, cap int) unsafe.Pointer {
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(et.size, uintptr(cap)) // 计算所需要内存空间 类型占用空间 * cap,判定是否溢出等
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc || len < 0 || len > cap {
// NOTE: Produce a 'len out of range' error instead of a
// 'cap out of range' error when someone does make([]T, bignumber).
// 'cap out of range' is true too, but since the cap is only being
// supplied implicitly, saying len is clearer.
// See golang.org/issue/4085.
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(et.size, uintptr(len))
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc || len < 0 {
panicmakeslicelen()
}
panicmakeslicecap()
}
return mallocgc(mem, et, true)
}
func makeslice64(et *_type, len64, cap64 int64) unsafe.Pointer {
len := int(len64)
if int64(len) != len64 {
panicmakeslicelen()
}
cap := int(cap64)
if int64(cap) != cap64 {
panicmakeslicecap()
}
return makeslice(et, len, cap)
}
- 切片类型的变量实际上是一个指针,只是在写代码的时候,其表现形式让你无法知道其底层类型
- makeslice 先计算创建变量所需要内存空间大小,判定空间大小是否溢出等
- 交给mallocgc去分配可被回收的空间,同时对空间置类型的零值
- makeslice64只是len,cap 两个参数的类型是int64,该函数它包装了makeslice函数
append 切片的扩容机制
// growslice handles slice growth during append.
// It is passed the slice element type, the old slice, and the desired new minimum capacity,
// and it returns a new slice with at least that capacity, with the old data
// copied into it.
// The new slice's length is set to the old slice's length,
// NOT to the new requested capacity.
// This is for codegen convenience. The old slice's length is used immediately
// to calculate where to write new values during an append.
// TODO: When the old backend is gone, reconsider this decision.
// The SSA backend might prefer the new length or to return only ptr/cap and save stack space.
func growslice(et *_type, old slice, cap int) slice {
if raceenabled {
callerpc := getcallerpc()
racereadrangepc(old.array, uintptr(old.len*int(et.size)), callerpc, abi.FuncPCABIInternal(growslice))
}
if msanenabled {
msanread(old.array, uintptr(old.len*int(et.size)))
}
if asanenabled {
asanread(old.array, uintptr(old.len*int(et.size)))
}
if cap < old.cap {
panic(errorString("growslice: cap out of range"))
}
if et.size == 0 {
// append should not create a slice with nil pointer but non-zero len.
// We assume that append doesn't need to preserve old.array in this case.
return slice{unsafe.Pointer(&zerobase), old.len, cap}
}
newcap := old.cap
doublecap := newcap + newcap
if cap > doublecap {
newcap = cap
} else {
const threshold = 256
if old.cap < threshold {
newcap = doublecap
} else {
// Check 0 < newcap to detect overflow
// and prevent an infinite loop.
for 0 < newcap && newcap < cap {
// Transition from growing 2x for small slices
// to growing 1.25x for large slices. This formula
// gives a smooth-ish transition between the two.
newcap += (newcap + 3*threshold) / 4
}
// Set newcap to the requested cap when
// the newcap calculation overflowed.
if newcap <= 0 {
newcap = cap
}
}
}
var overflow bool
var lenmem, newlenmem, capmem uintptr
// Specialize for common values of et.size.
// For 1 we don't need any division/multiplication.
// For goarch.PtrSize, compiler will optimize division/multiplication into a shift by a constant.
// For powers of 2, use a variable shift.
switch {
case et.size == 1:
lenmem = uintptr(old.len)
newlenmem = uintptr(cap)
capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap))
overflow = uintptr(newcap) > maxAlloc
newcap = int(capmem)
case et.size == goarch.PtrSize:
lenmem = uintptr(old.len) * goarch.PtrSize
newlenmem = uintptr(cap) * goarch.PtrSize
capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap) * goarch.PtrSize)
overflow = uintptr(newcap) > maxAlloc/goarch.PtrSize
newcap = int(capmem / goarch.PtrSize)
case isPowerOfTwo(et.size):
var shift uintptr
if goarch.PtrSize == 8 {
// Mask shift for better code generation.
shift = uintptr(sys.Ctz64(uint64(et.size))) & 63
} else {
shift = uintptr(sys.Ctz32(uint32(et.size))) & 31
}
lenmem = uintptr(old.len) << shift
newlenmem = uintptr(cap) << shift
capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap) << shift)
overflow = uintptr(newcap) > (maxAlloc >> shift)
newcap = int(capmem >> shift)
default:
lenmem = uintptr(old.len) * et.size
newlenmem = uintptr(cap) * et.size
capmem, overflow = math.MulUintptr(et.size, uintptr(newcap))
capmem = roundupsize(capmem)
newcap = int(capmem / et.size)
}
// The check of overflow in addition to capmem > maxAlloc is needed
// to prevent an overflow which can be used to trigger a segfault
// on 32bit architectures with this example program:
//
// type T [1<<27 + 1]int64
//
// var d T
// var s []T
//
// func main() {
// s = append(s, d, d, d, d)
// print(len(s), "\n")
// }
if overflow || capmem > maxAlloc {
panic(errorString("growslice: cap out of range"))
}
var p unsafe.Pointer
if et.ptrdata == 0 {
p = mallocgc(capmem, nil, false)
// The append() that calls growslice is going to overwrite from old.len to cap (which will be the new length).
// Only clear the part that will not be overwritten.
memclrNoHeapPointers(add(p, newlenmem), capmem-newlenmem)
} else {
// Note: can't use rawmem (which avoids zeroing of memory), because then GC can scan uninitialized memory.
p = mallocgc(capmem, et, true)
if lenmem > 0 && writeBarrier.enabled {
// Only shade the pointers in old.array since we know the destination slice p
// only contains nil pointers because it has been cleared during alloc.
bulkBarrierPreWriteSrcOnly(uintptr(p), uintptr(old.array), lenmem-et.size+et.ptrdata)
}
}
memmove(p, old.array, lenmem)
return slice{p, old.len, newcap}
}
扩容机制
如果新申请的容量 cap > 2 倍旧容量, 新容量 = cap
如果新申请的容量 cap <= 2倍旧容量
- 如果旧容量 < 256 那么新容量 = 2 倍旧容量
- 如果旧容量 >= 256 且 <= 2倍旧容量 则 新容量newcap += (newcap + 3*threshold) / 4,直到大于等于2倍旧容量
Reference
[1] https://www.51cto.com/article/677993.html
Todo
makeslicecopy *具体使用场景待考证


![[激光原理与应用-53]:《激光焊接质量实时监测系统研究》-4-激光焊接系统软件设计](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/61218c58769a4948be184f50b294810f.png)