常用shell命令
管道命令
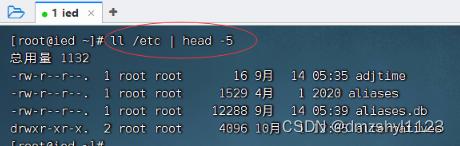
查看/etc目录信息前5行信息
执行命令:ll /etc | head -5
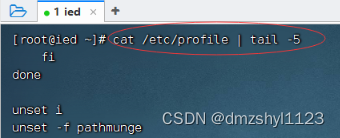
查看/etc/profile文件后5行信息
执行命令:cat /etc/profile | tail -5
grep命令
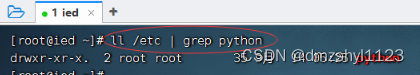
抓取/etc目录下的python信息
执行命令:ll /etc | grep python
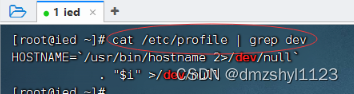
抓取/etc/profile文件里的dev信息
执行命令:cat /etc/profile | grep dev
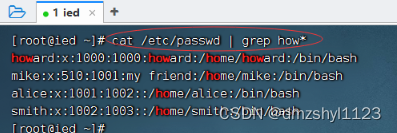
抓取用户数据文件中以how打头的信息
执行命令:cat /etc/passwd | grep how*
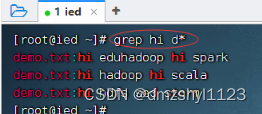
显示所有以d开头的文件中包含hi的行
执行命令:grep hi d*
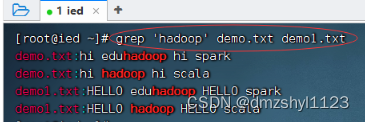
显示两个文件匹配某个字符串的行
执行命令:grep 'hadoop' demo.txt demo1.txt
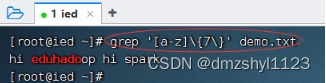
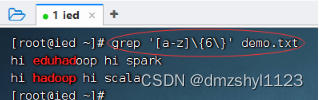
显示文件中至少有n个连续小写字符的行
执行命令:grep '[a-z]\{7\}' demo.txt / grep '[a-z]\{6\}' demo.txt
find命令
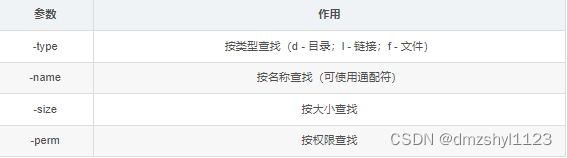
按类型查找
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -type 'd'
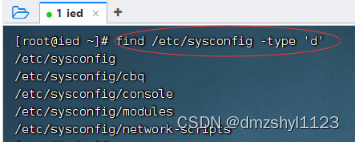
按名称查找
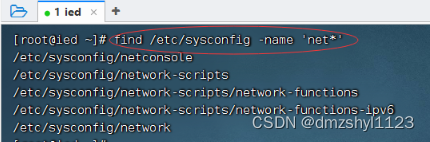
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -name ‘network’
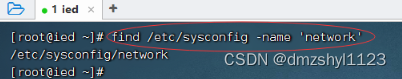
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -name 'net*' (可使用通配符)
按大小查找
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -size 15c(等于15字节)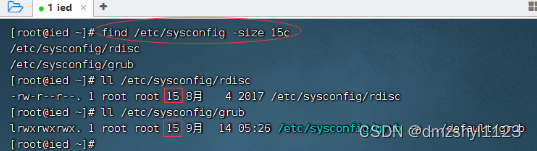
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -size +10k(大于10240个字节)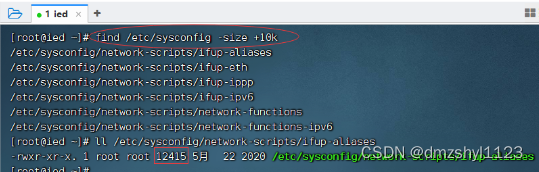
find /etc/sysconfig -size -20c (小于20个字节)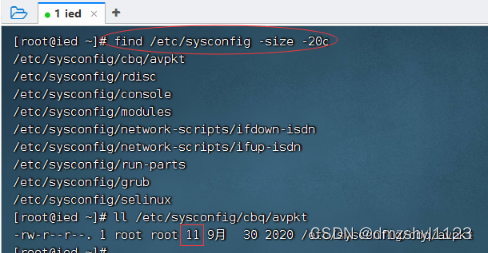
按权限查找
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -perm '777' (权限字符串:rwxrwxrwx)
find /etc/sysconfig -perm '755' (权限字符串:rwxr-xr-x)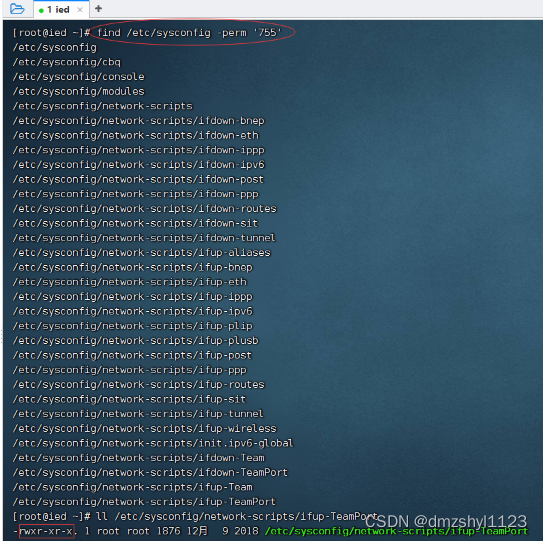
sed命令
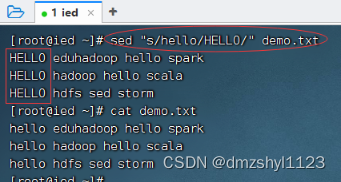
将所有行的第一个hello替换成HELLO
执行命令:sed "s/hello/HELLO/" demo.txt
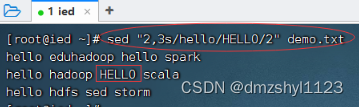
将第2行到第3行的第2个hello替换成HELLO
执行命令:sed "2,3s/hello/HELLO/2" demo.txt
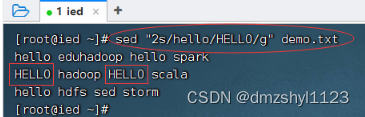
将第2行的hello全部替换成HELLO
执行命令:sed "2s/hello/HELLO/g" demo.txt
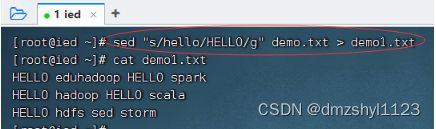
将全部的hello替换成HELLO后生成新文件
执行命令:sed "s/hello/HELLO/g" demo.txt > demo1.txt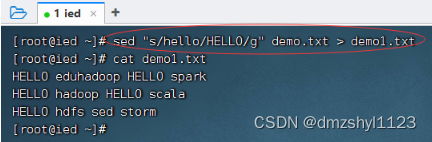
将全部的hello替换成hi,要求修改原文件
执行命令: sed -i "s/hello/hi/g" demo.txt
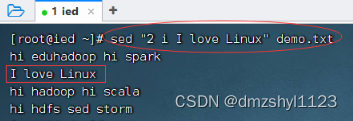
在第2行之前插入一行新内容
执行命令:sed "2 i I love Linux" demo.txt
在第2行之后插入一行新内容
执行命令:sed "2 a Linux is fun and I love it" demo.txt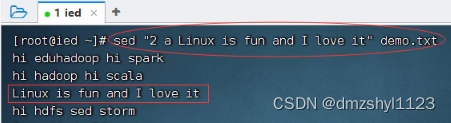
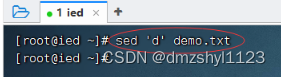
删除第2行
执行命令:sed '2d' demo.txt
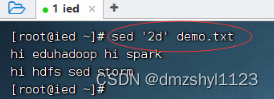
删除第2行到第3行
执行命令: sed '2,3d' demo.txt
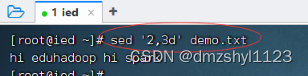
删除文件所有行
执行命令:sed 'd' demo.txt
删除包含指定字符串的行
执行命令:sed '/scala/g' demo.txt

tail命令
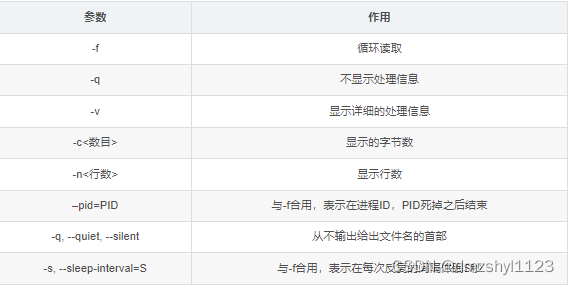
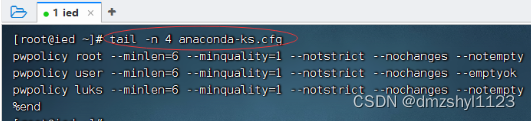
显示文件最后4行内容
执行命令:tail -n 4 anaconda-ks.cfg
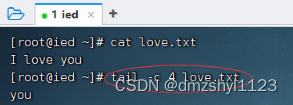
显示文件最后4个字符内容
执行命令:tail -c 4 love.txt
显示文件修改行
tail -f filename 显示文件修改的内容。
说明:监视filename文件的尾部内容(默认10行,相当于增加参数 -n 10),刷新显示在屏幕上。退出,按下CTRL+C。
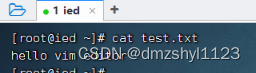
查看test.txt内容
修改test.txt,在末尾增加10换行内容,然后存盘退出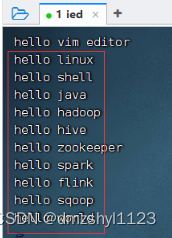
sort命令
案例演示
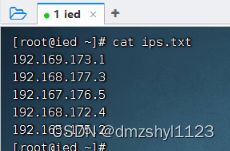
预备工作:创建ips.txt文件
对文件按行排序
执行命令:sort ips.txt,按字典排序法升序排列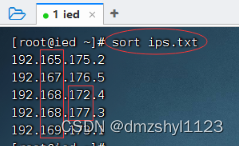
执行命令:sort -r ips.txt,按字典排序法降序排列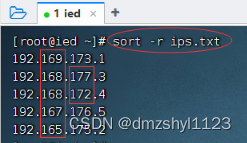
对文件按第4节排序
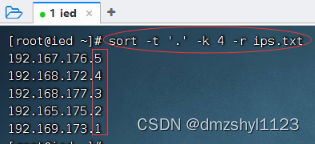
执行命令:sort -t '.' -k 4 ips.txt,升序排列

执行命令:sort -t '.' -k 4 -r ips.txt,降序排列
cut命令
提取ips.txt文件第7列字符
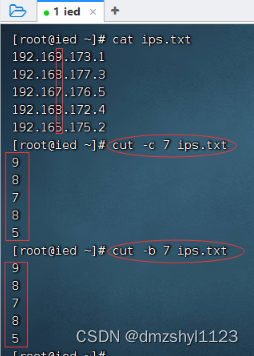
执行命令:cut -c 7 ips.txt
执行命令:cut -b 7 ips.txt
提取ips.txt文件第4节内容
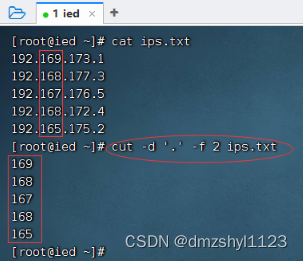
执行命令:cut -d '.' -f 4 ips.txt,提取第4节内容

执行命令:cut -d '.' -f 2 ips.txt,提取第2节内容
history命令
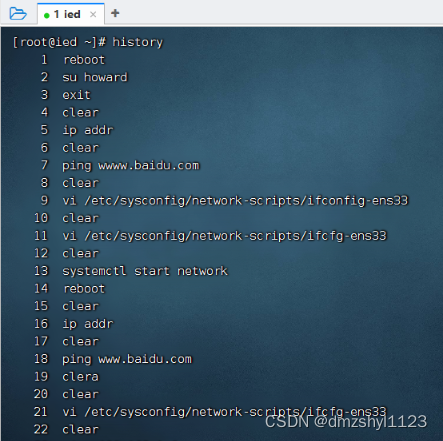
查看历史操作记录
执行命令:history
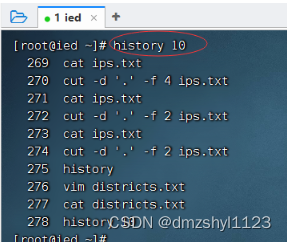
查看最近10条历史命令
执行命令:history 10 (写成history -n 10也是一样效果)
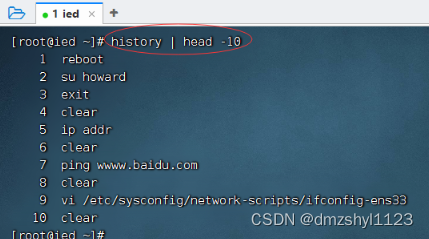
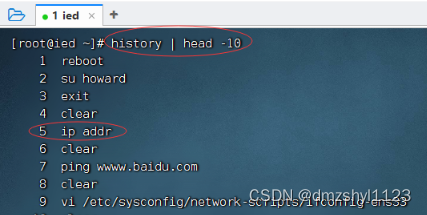
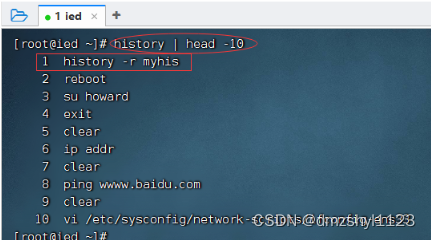
查看最开始10条历史命令
执行命令:history | head -10
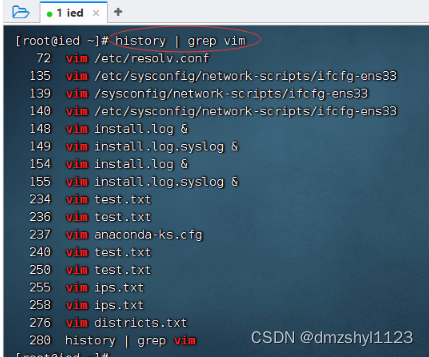
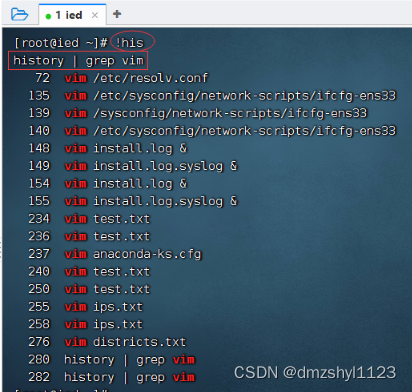
曾多少次使用vim编辑文本文件?
执行命令:history | grep vim
执行历史第5条命令
查看历史第5条命令
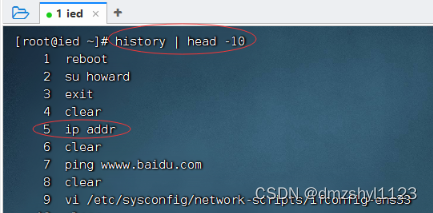
执行命令:!5
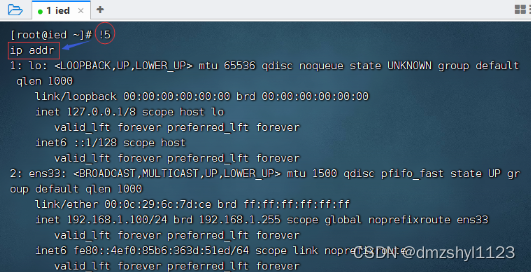
执行上一条命令
执行命令:!!
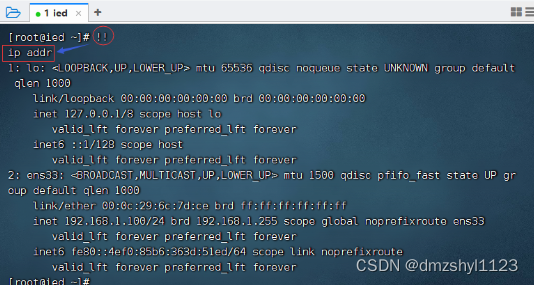
执行最后一次以his开头的命令
执行命令:!his
将当前历史命令缓冲区命令写入历史命令文件中
执行命令:history -w myhis
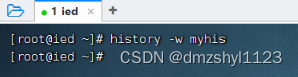
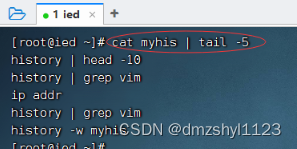
执行命令:cat myhis | tail -5
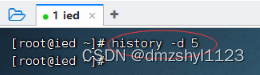
清除第5条历史命令
查看第5条历史命令
执行命令:history -d 5
清除所有历史命令
执行命令:history -c

将历史命令文件中的命令读入当前历史命令缓冲区
执行命令:history -r myhis
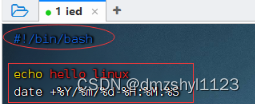
shell脚本
执行shell脚本
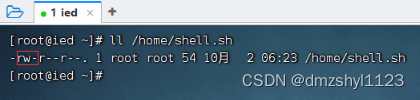
创建脚本文件,执行命令:vim /home/shell.sh
此时,shell.sh对于所有者而言,只有读和写的权限,并不是可执行的脚本
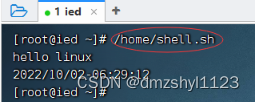
绝对路径方式执行脚本
执行命令:/home/shell.sh
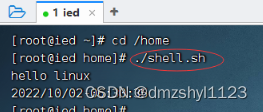
相对路径方式执行脚本
执行命令:cd /home
执行命令:./shell.sh (.表示当前目录)
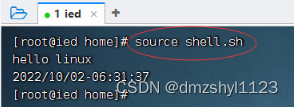
利用source命令执行脚本
执行命令:source shell.sh
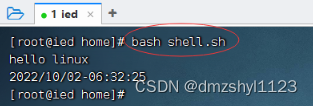
利用bash或sh命令执行脚本
执行命令:bash shell.sh
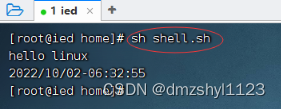
执行命令: sh shell.sh
shell脚本案例
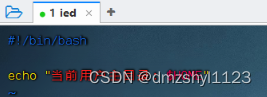
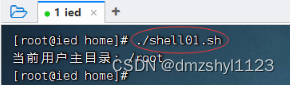
任务1、显示当前用户主目录
编写脚本
执行命令:vim shell01.sh
设置权限
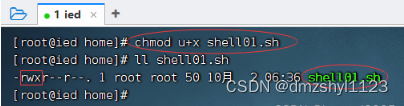
执行命令:chmod u+x shell01.sh,增加可执行权限
执行脚本
执行命令:./shell01.sh
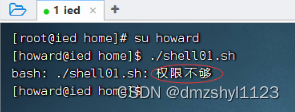
切换到其他用户,看一看是否能够执行该脚本呢?
设置权限
执行命令:chmod u+x shell02.sh
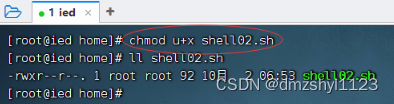
执行脚本
执行命令:./shell02.sh
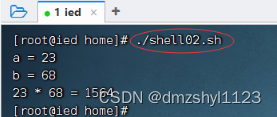



![[附源码]Nodejs计算机毕业设计基于web的小说浏览系统Express(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e7a8fda3901141158c8d216957a92d03.png)






![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计动物保护资讯推荐网站Django(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9f0fcde6dd024dc3ae41a1d00bf9ba82.png)