Tensorrt operators docs:
Activation
Apply an activation function on an input tensor A and produce an output tensor B with the same dimensions.
import numpy as np
from cuda import cudart
import tensorrt as trt
# 输入张量 NCHW
nIn, cIn, hIn, wIn = 1, 1, 3, 3
# 输入数据
data = np.arange(-4, 5, dtype=np.float32).reshape(nIn, cIn, hIn, wIn)
np.set_printoptions(precision=8, linewidth=200, suppress=True)
cudart.cudaDeviceSynchronize()
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.ERROR)
builder = trt.Builder(logger)
network = builder.create_network(1 << int(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH))
config = builder.create_builder_config()
inputT0 = network.add_input('inputT0', trt.DataType.FLOAT, (nIn, cIn, hIn, wIn))
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------# 替换部分
# 这里演示使用 ReLU 激活函数
# 也可以替换成你想用的激活函数
activationLayer = network.add_activation(inputT0, trt.ActivationType.RELU)
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------# 替换部分
network.mark_output(activationLayer.get_output(0))
engineString = builder.build_serialized_network(network, config)
engine = trt.Runtime(logger).deserialize_cuda_engine(engineString)
context = engine.create_execution_context()
_, stream = cudart.cudaStreamCreate()
inputH0 = np.ascontiguousarray(data.reshape(-1))
outputH0 = np.empty(context.get_binding_shape(1), dtype=trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(1)))
_, inputD0 = cudart.cudaMallocAsync(inputH0.nbytes, stream)
_, outputD0 = cudart.cudaMallocAsync(outputH0.nbytes, stream)
cudart.cudaMemcpyAsync(inputD0, inputH0.ctypes.data, inputH0.nbytes, cudart.cudaMemcpyKind.cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream)
context.execute_async_v2([int(inputD0), int(outputD0)], stream)
cudart.cudaMemcpyAsync(outputH0.ctypes.data, outputD0, outputH0.nbytes, cudart.cudaMemcpyKind.cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream)
cudart.cudaStreamSynchronize(stream)
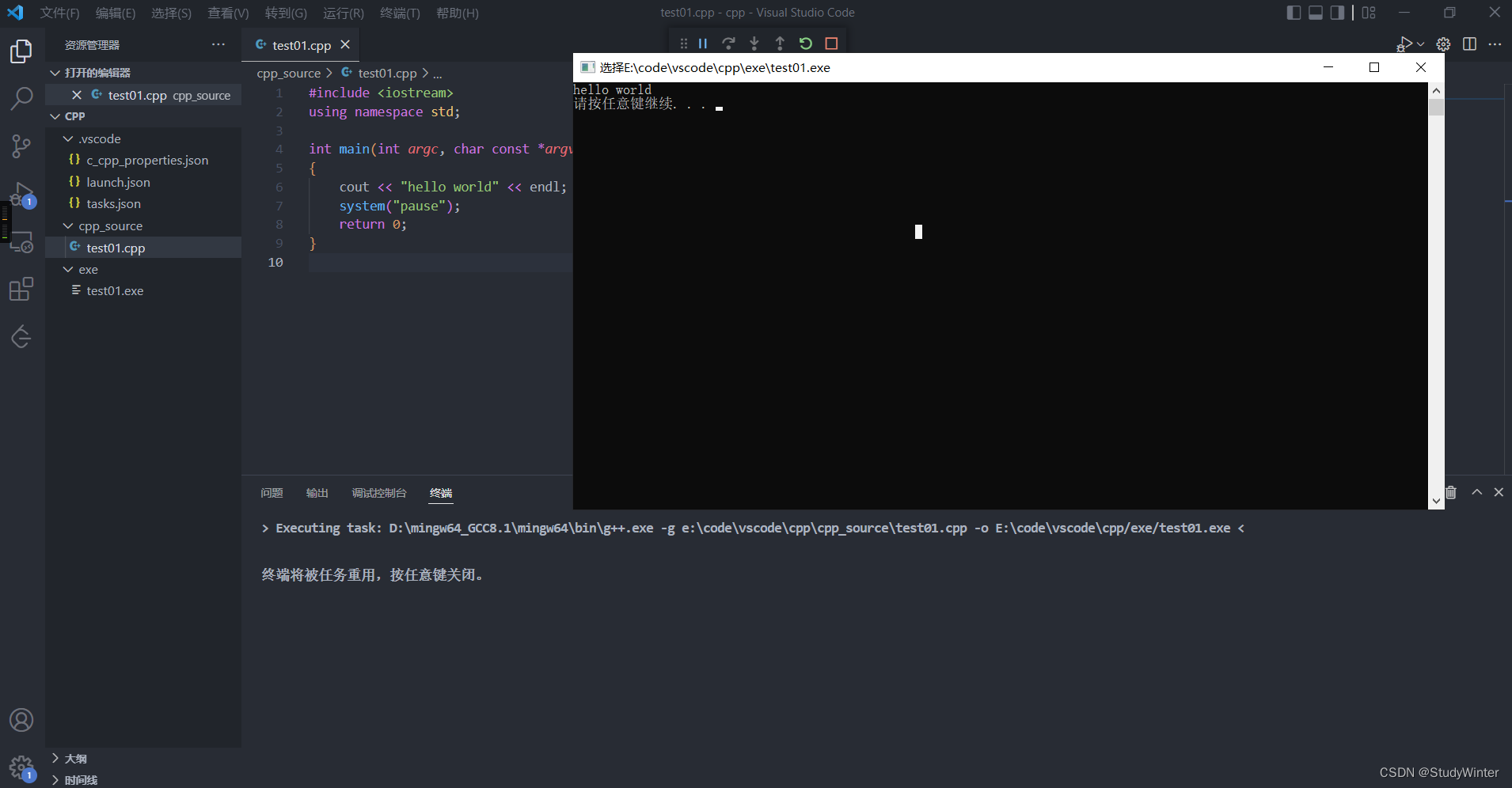
print("inputH0 :", data.shape)
print(data)
print("outputH0:", outputH0.shape)
print(outputH0)
cudart.cudaStreamDestroy(stream)
cudart.cudaFree(inputD0)
cudart.cudaFree(outputD0)
其中:data是一个形状为(1, 1, 3, 3)的4D NumPy数组,表示一个1x1通道的3x3输入图像。它的数据范围从-4到4。
np.set_printoptions()是NumPy库中用于设置打印数组选项的函数。它允许您设置NumPy数组的打印输出的格式,如精度、行宽和是否使用科学计数法。 precision=8: 设置浮点数的打印精度为 8 位小数。这意味着打印浮点数时,会显示小数点后 8 位数字。对于超过 8 位小数的浮点数,将四舍五入保留 8 位小数。
import numpy as np
# 创建一个包含小数的 NumPy 数组
data = np.array([0.123456789, 1234.56789, 123456.789], dtype=np.float32)
# 默认打印输出
print("默认打印输出:")
print(data)
# 设置打印选项
np.set_printoptions(precision=2, linewidth=20, suppress=True)
# 使用设置后的打印输出
print("\n使用设置后的打印输出:")
print(data)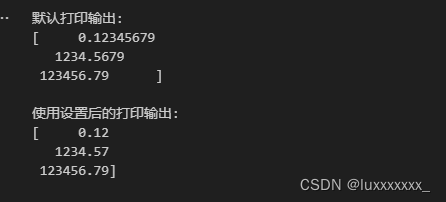
其中输入
inputH0 : (1, 1, 3, 3)
[[[[-4. -3. -2.]
[-1. 0. 1.]
[ 2. 3. 4.]]]]
outputH0: (1, 1, 3, 3)
[[[[0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1.]
[2. 3. 4.]]]]
(<cudaError_t.cudaSuccess: 0>,)