书接上文 MyBatis – 执行流程
我们通过SqlSession获取到了UserMapper对象,代码如下:
// 获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 执行查询操作
try {
// 获取映射器接口
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 调用映射器接口的方法执行查询操作
List<User> users = userMapper.getAllUsers();
// 处理查询结果
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user.getId() + " - " + user.getName());
}
} finally {
// 关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
我们看到,往 sqlSession.getMapper 传入UserMapper接口后,得到的是一个 userMapper 对象,这是怎么做到的呢?
查看SqlSession源码发现,SqlSession有两个实现类,在正常情况下使用的当然就是默认的 DefaultSqlSession
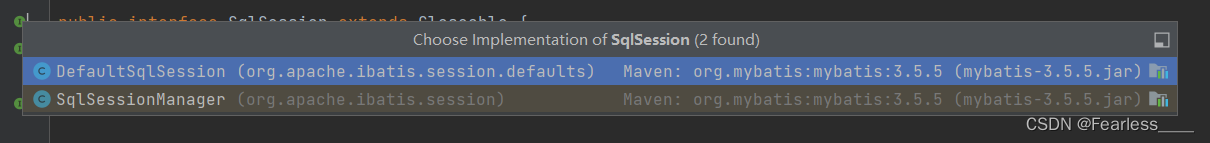
DefaultSqlSession中有以下属性,其中最重要的两个属性是 Configuration 和 Executor
private final Configuration configuration;
private final Executor executor;
private final boolean autoCommit;
private boolean dirty;
private List<Cursor<?>> cursorList;
什么是Configuration
查看SqlSessionFactory的默认实现类 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 发现,其内部只有一个属性,就是Configuration
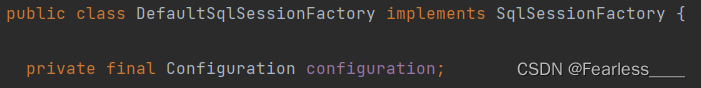
那DefaultSqlSessionFactory的Configuration从哪里获取到的值呢?那就得追踪到SqlSessionFactoryBuilder,在上文中,我们通过如下方式创建SqlSessionFactory对象
// 创建 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
// 加载配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
// 构建 SqlSessionFactory 对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = builder.build(inputStream);
// 关闭配置文件流
inputStream.close();
查看SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的源码(实际上SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 的所有方法就是多个重载的build,以下仅展示我们使用到的),如下:
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) {
return build(reader, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
我们调用了 build(Reader reader) 方法,而该方法内部调用了 build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) 方法,其中只传入了一个reader参数,另外两个参数是null,reader参数保存的是核心配置文件 mybatis-config.xml 的信息
通过reader获取到XMLConfigBuilder对象,我们不知道这个对象到底是什么,但是我们知道它的作用仍然是保存 mybatis-config.xml 的信息
接着return 了 build(parser.parse()) 方法,该方法源码如下
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
发现调用了DefaultSqlSessionFactory的构造方法,并传入携带 mybatis-config.xml 信息的config
该构造方法源码如下:
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
将config赋值给了 DefaultSqlSessionFactory对像 的 configuration 属性
然后我们调用如下代码获取到SqlSession 对象(即 DefaultSqlSession对象),其中sqlSessionFactory引用指向的就是DefaultSqlSessionFactory对像
// 获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
查看 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 中的 openSession() 方法源码,如下:
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
发现调用了openSessionFromDataSource方法,继续跟踪
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
我们终于看到了真正创建SqlSession的方法,该方法调用了 DefaultSqlSession 的构造方法,并直接传入DefaultSqlSessionFactory 的 configuration,到此我们就知道了,DefaultSqlSession 中的 Configuration 属性就是记录着 mybatis-config.xml 的信息,其中包含着 数据源信息 和 Mapper 映射文件地址等
executor
从上面我们知道,创建 DefaultSqlSession 的方法是 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 对象中的 openSessionFromDataSource方法,源码如下:
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
我们发现在调用 DefaultSqlSession 构造方法时,不仅传入了 configuration 对象,还传入了executor对象,并且是通过 configuration 的 newExecutor 方法获得,查看 newExecutor 方法源码
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
大概上可以看出,该方法是通过 executorType 参数来构造不同类型的构造器,查看ExecutorType源码,发现是个枚举类
public enum ExecutorType {
SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH
}
其中的枚举值的含义如下:
- SIMPLE:简单执行器,用于执行简单的查询操作,不支持事务的提交和回滚。
- REUSE:重用执行器,用于执行重复的查询操作,可以重用缓存的查询结果,提高性能。
- BATCH:批处理执行器,用于执行批量的数据操作,如插入、更新和删除操作。它可以一次执行多个SQL语句,并支持事务的提交和回滚。
当我们调用 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 的无参 openSession 方法时,而openSession 方法又调用openSessionFromDataSource方法,并传入的参数configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(),我们不断跟踪.getDefaultExecutorType方法,发现最后返回的是ExecutorType. SIMPLE ,而 openSessionFromDataSource 又把这个参数传给了newExecutor 方法,因此此时的executor是简单执行器对象,创建的是 SimpleExecutor 对象
我们查看 SimpleExecutor 类的源码发现,其继承了 BaseExecutor,如下 ,实际上每个Executor都继承了BaseExecutor
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor
查看 BaseExecutor 源码(源码太多不加入文章),发现其实现了Executor接口,Executor接口中的方法几乎覆盖了对数据库的所有操作,如下,包括事务的操作和增删改查的操作
public interface Executor {
ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null;
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException;
List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException;
void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException;
void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException;
CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql);
boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key);
void clearLocalCache();
void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType);
Transaction getTransaction();
void close(boolean forceRollback);
boolean isClosed();
void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor);
}
因此SqlSession依靠Executor属性就能完成所有的SQL操作
最后看 SqlSession 是如何生成 Mapper
查看 DefaultSqlSession 中的 getMapper方法 源码
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
传入了Mapper接口的类对象,以及 DefaultSqlSession 本身
追踪 getMapper 方法,最后来到了 MapperRegistry 类的 getMapper 方法
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
该方法的大致过程就是 通过动态代理生成了 Mapper 实例的代理对象,并且这个代理对象还“整合”进了sqlSession对象
当调用代理对象的Mapper接口方法时,代理对象将拦截这个方法调用,并获取对应的方法信息(参数返回值等),然后交由 sqlSession对象 对象中的 Executor对象,执行真正的SQL操作,而Executor对象 在执行SQL时需要用到的信息就来之DefaultSqlSession对象中的configuration属性(包括数据源信息和Mapper映射文件信息等)