Javaweb学习
- 一、Maven
- 1.1 Maven概述
- 1.2 Maven简介
- 1.3、Maven基本使用
- 1.4、IDEA配置Maven
- 1.6、依赖管理&依赖范围
- 二、MyBatis
- 2.1 MyBatis简介
- 2.2 Mybatis快速入门
- 2.3、解决SQL映射文件的警告提示
- 2.4、Mapper代理开发
- 三、MyBaits核心配置文件
- 四、 配置文件的增删改查
- 4.1 Mybatis案列
- 4.1.1 环境的准备
- 4.2 查询所有数据和结果映射
- 4.3、查看详情单个查询
- 4.4、条件查询
- 4.4.1、多条件查询
- 4.4.2、动态条件查询
- 4.4.3、单条件动态条件查询
- 4.5、添加
- 4.6、修改功能
- 4.6.1、修改全部字段
- 4.6.2、修改动态字段
- 4.7、删除功能
- 4.7.1、删除单个字段
- 4.7.2、批量删除
- 4.8、参数传递
- 4.9、注解开发
一、Maven
1.1 Maven概述
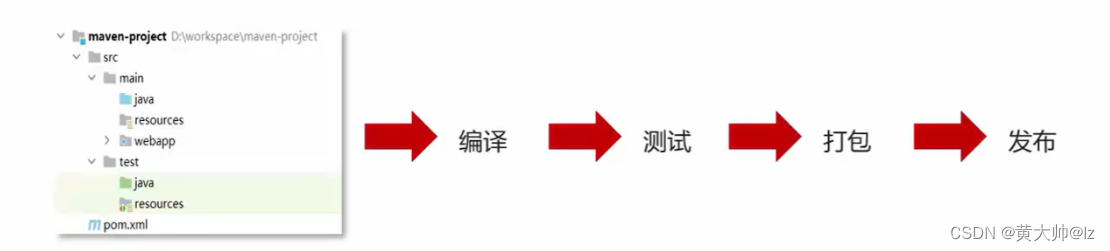
Maven是专门用于管理和构建Java项目的工具,它的主要功能有:
提供了一套标准化的项目结构

Maven提供了一套标准化的项目结构,所有IDE使用Maven构建的项目结构完全一样,所有IDE创建的Maven项目可以通用
-
提供了一套标准化的构建流程(编译,测试,打包,发布.....)
-
提供了一套依赖管理机制

1.2 Maven简介
Apache Maven是一个项目管理和构建工具,它基于项目对象模型(POM)的概念,通过一小段描述信息来管理项目的构建、报告和文档
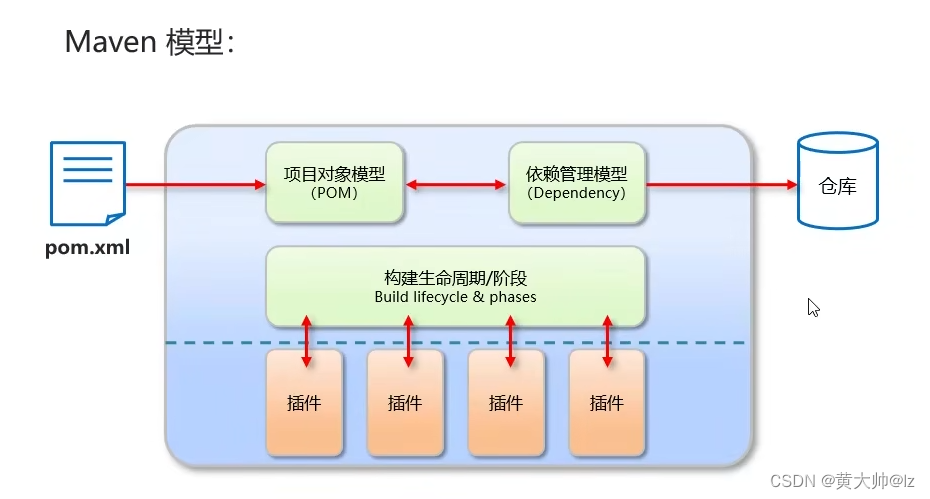
- 项目对象模型(Project Object Model)
- 依赖管理模型(Dependency)
- 插件(Plugin)
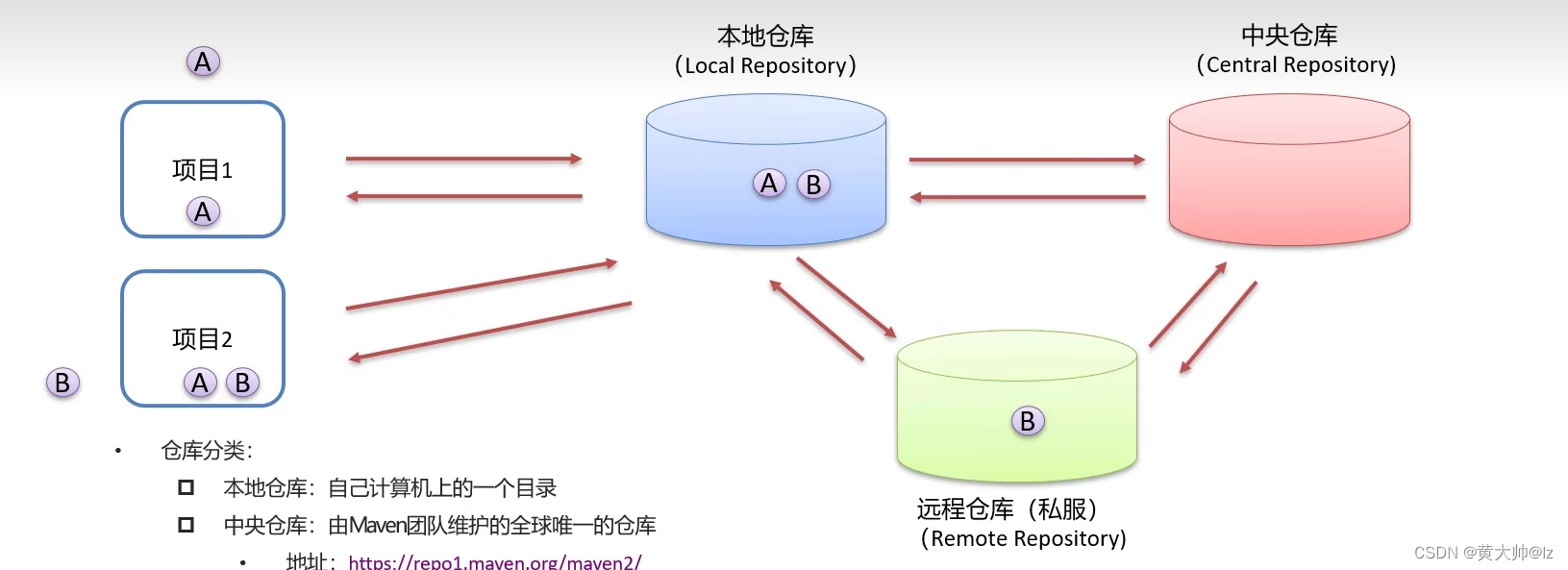
- 仓库分类:
本地仓库:自己计算机上的一个目录
中央仓库:由Maven团队维护的全球唯一的仓库
地址: 中央仓库地址
远程仓库(私服):一般由公司团队搭建的私有仓库 - 当项目中使用坐标引入对应依赖jar包后,首先会查找本地仓库中是否有对应的jar包:
如果有,则在项目直接引用;
如果没有,则去中央仓库中下载对应的jar包到本地仓库。
还可以搭建远程仓库,将来jar包的查找顺序则变为:本地仓库→远程仓库→中央仓库
1.3、Maven基本使用
常用命令
compile :编译
clean:清理
test:测试
package:打包
install:安装
生命周期
- Maven构建项目生命周期描述的是一次构建过程经历经历了多少个事件
- Maven对项目构建的生命周期划分为3套
clean:清理工作
default:核心工作,例如编译,测试,打包,安装等
site:产生报告,发布站点等
同一生命周期内,执行后边的命令,前边的所有命令会自动执

1.4、IDEA配置Maven
步骤:
- 选择IDEA中 设置
- 搜索maven
- 设置IDEA使用本地安装的Maven,并修改配置文件路径
Maven坐标详解
什么是坐标?
Maven 中的坐标是资源的唯一标识
使用坐标来定义项目或引入项目中需要的依赖Maven 坐标主要组成
groupld:定义当前Maven项目隶属组织名称(通常是域名反写,例如: com.itheima)
artifactld:定义当前Maven项目名称(通常是模块名称,例如order-service、goods-service)
version:定义当前项目版本号
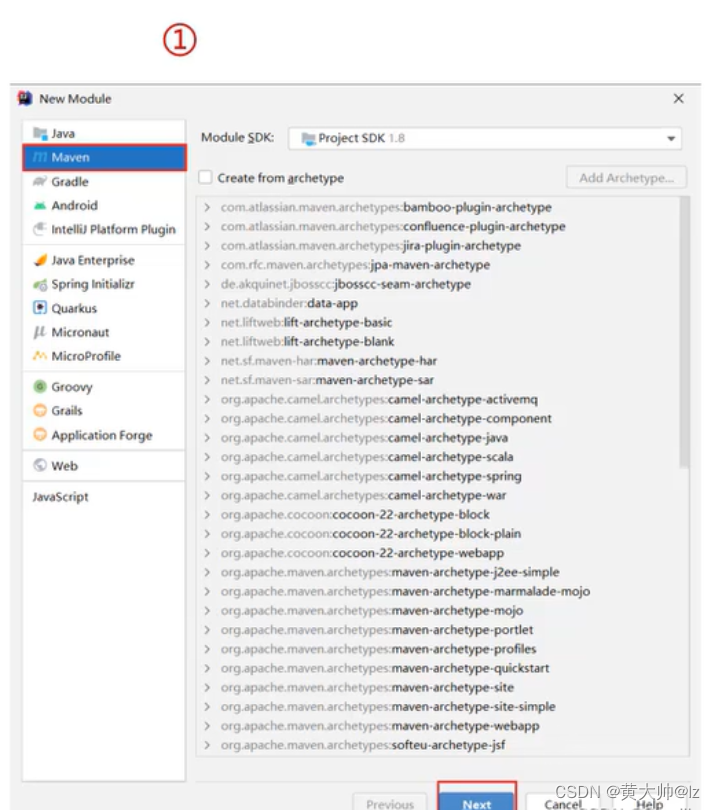
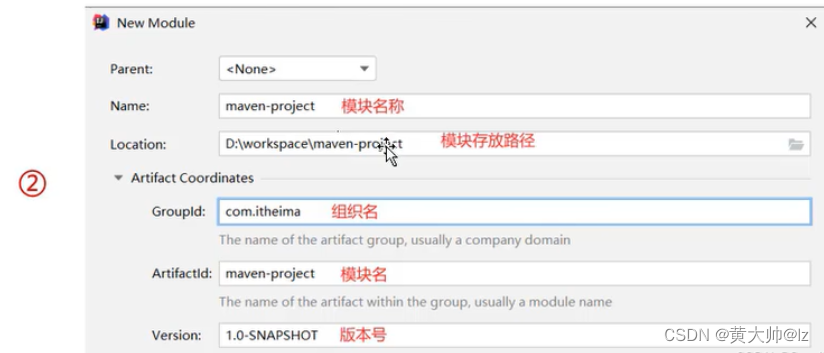
IDEA创建Maven项目
- 创建模块,选择Maven,点击Next
- 填写模块名称,坐标信息,点击finish,创建完成
- 编写HelloWorld,并运行
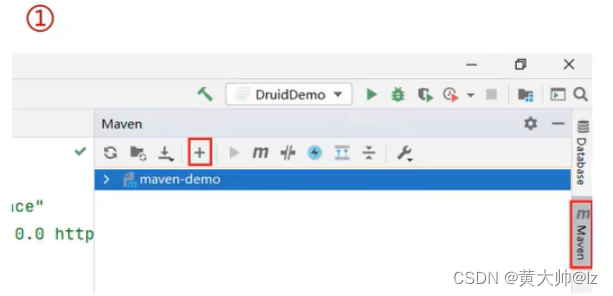
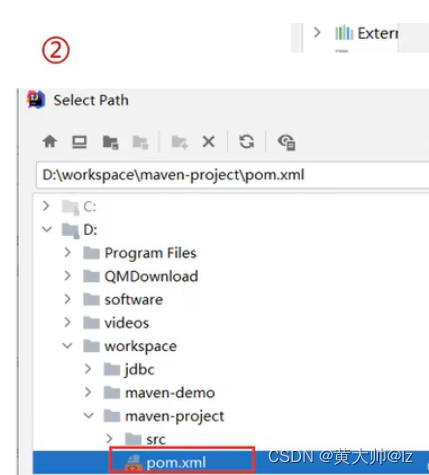
IDEA导入Maven项目
- 选择右侧Maven面板,点击+号
- 选中对应项目的pom.xml文件,双击即可
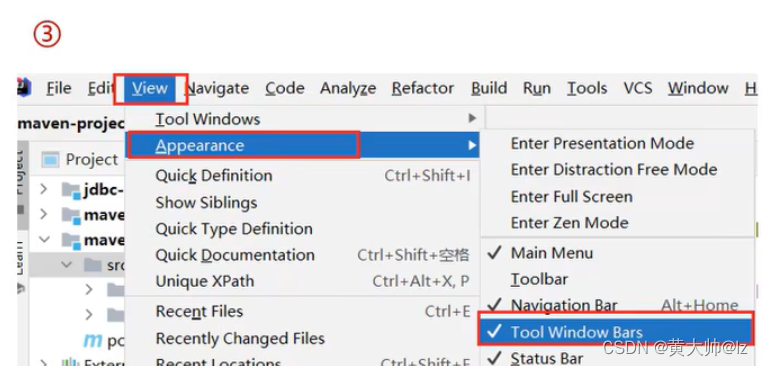
- 如果没有Maven面板,选择
View→Appearance→Tool Window Bars
配置Maven-Hepler插件
- 选择IDEA中 File --> Settings
- 选择Plugins
- 搜索Maven,选择第一个Maven Helper,点击Install安装,弹出面板中点击Accept
- 重启IDEA
1.6、依赖管理&依赖范围
依赖管理
- 在
pom.xml中编写<dependencies>标签 - 在
<dependencies>标签中使用<dependency>引入坐标 - 定义坐标的
groupld,artifactld,version - 点击刷新按钮,使坐标生效
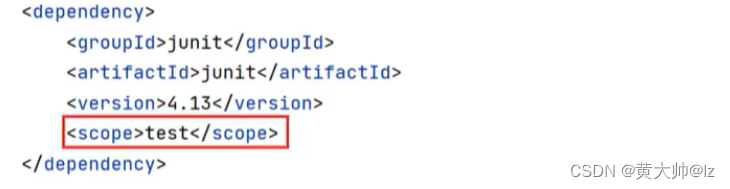
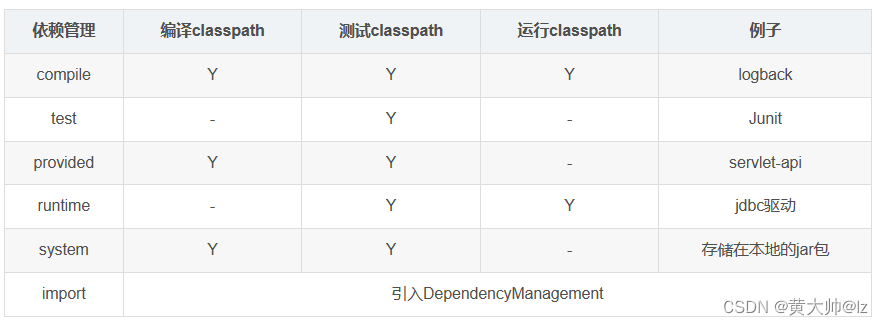
依赖范围
通过设置坐标的依赖范围(scope),可以设置对应jar包的作用范围:编译环境、测试环境、运行环境
<scope> 默认值:compile
二、MyBatis
2.1 MyBatis简介
什么是MyBatis
- MyBatis是一款优秀的
持久层,框架,用于简化JDBC开发- MyBatis本是 Apache的一个开源项目iBatis, 2010年这个项目由apache softwarefoundation迁移到了google code,并且改名为MyBatis 。2013年11月迁移到Github
- 官网: MyBatis官网
持久层:
- 负责将数据到保存到数据库的那一层代码
- JavaEE三层架构:
表现层、业务层、持久层
框架
- 框架就是一个半成品软件,是一套可重用的、通用的、软件基础代码模型
- 在框架的基础之上构建软件编写更加高效、规范、通用、可扩展
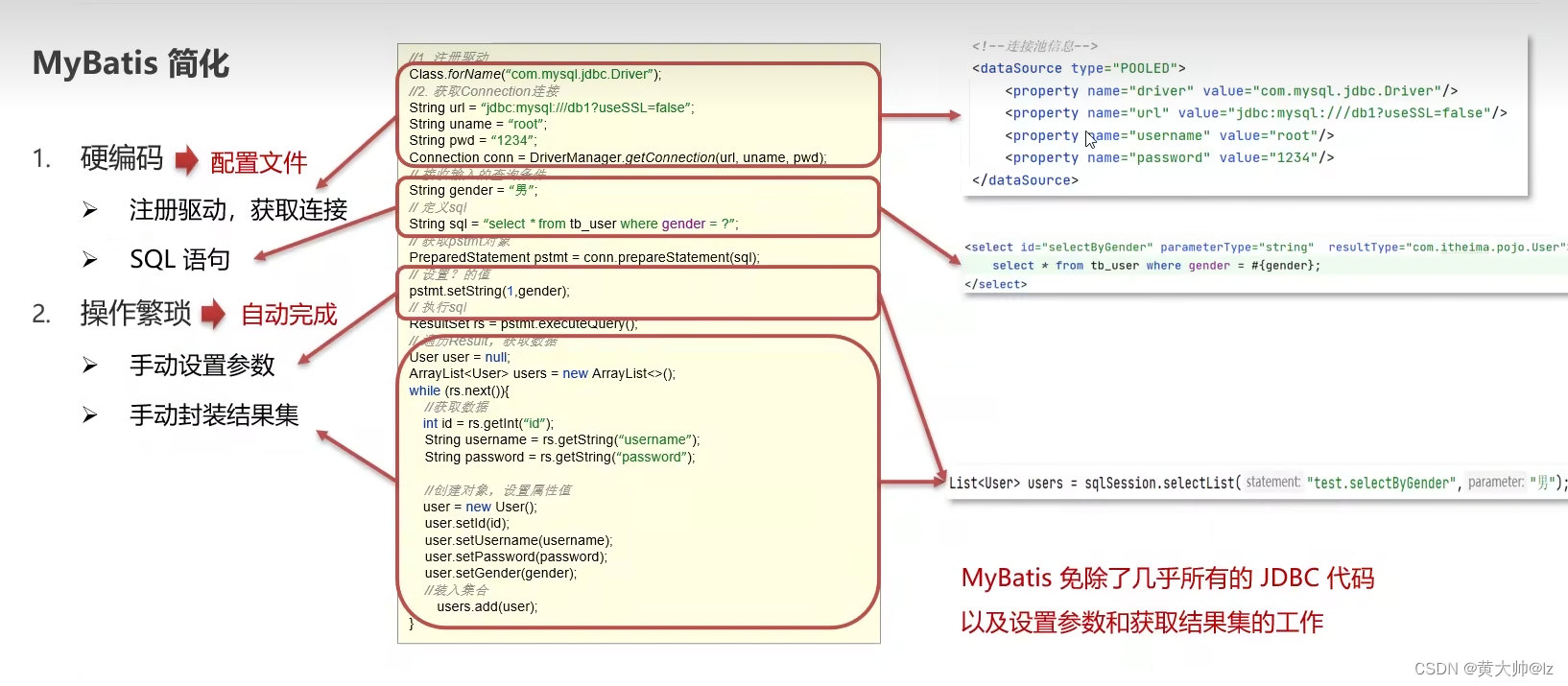
JDBC缺点:

由于JDBC的缺点,所以出现了MyBatis
2.2 Mybatis快速入门

2.3、解决SQL映射文件的警告提示
产生原因:Idea和数据库没有建立连接,不识别表信息
解决方式:在Idea中配置MySQL数据库连接
第一步:
首先在设置当中去下载
Database Navigator
第二步:
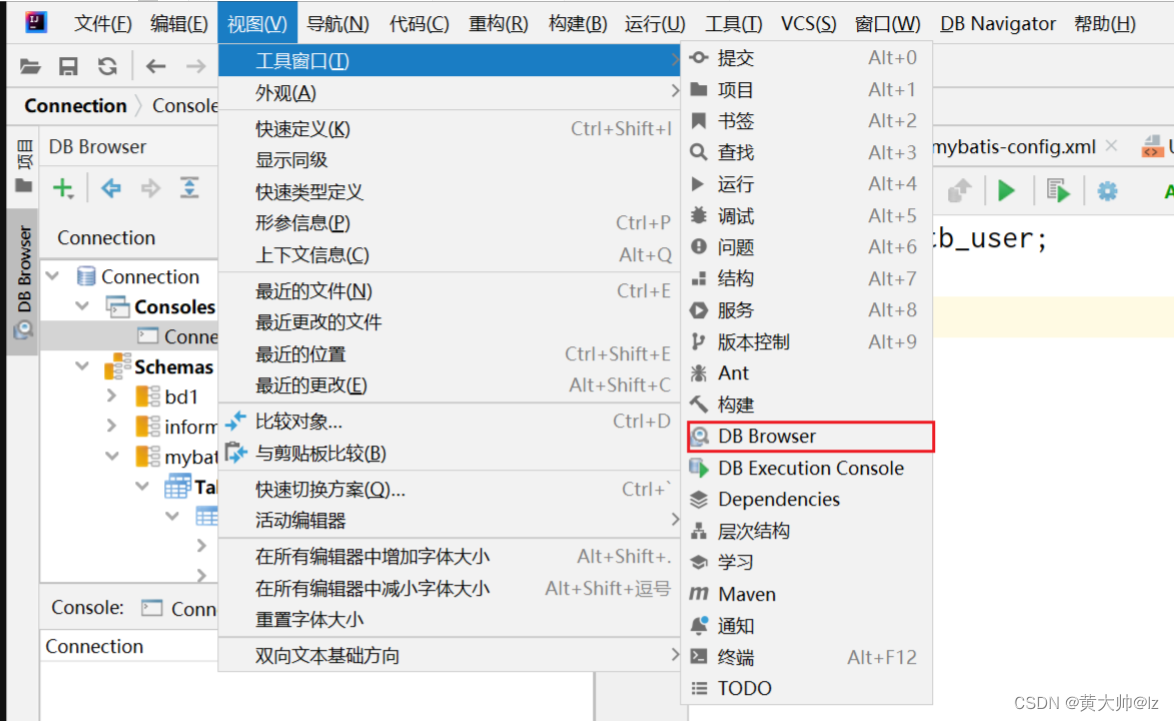
第三步:
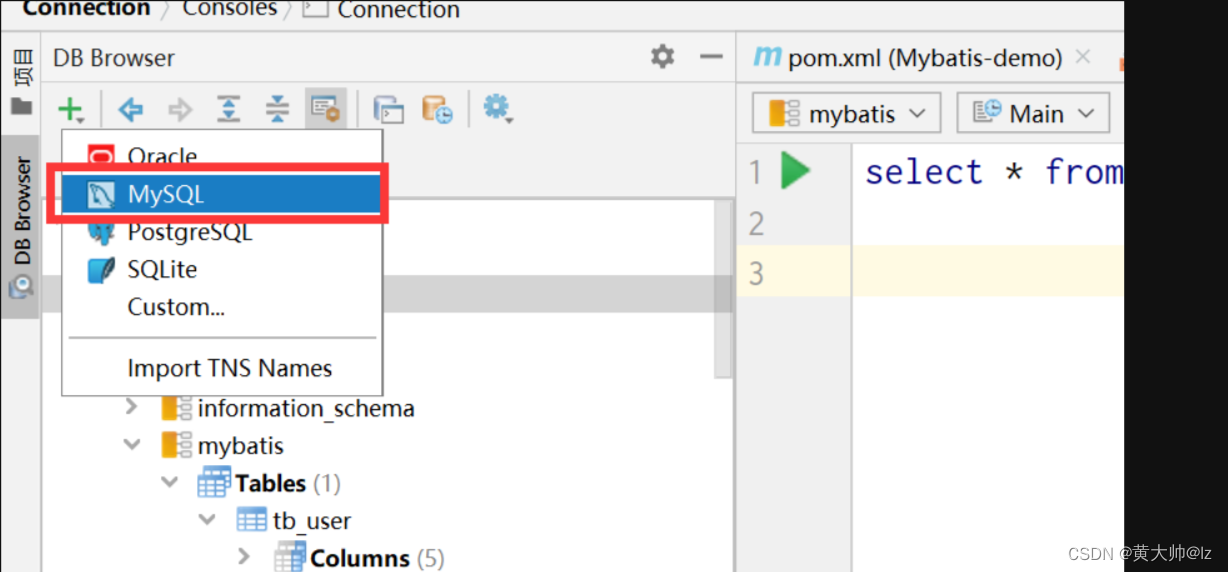
第四步:
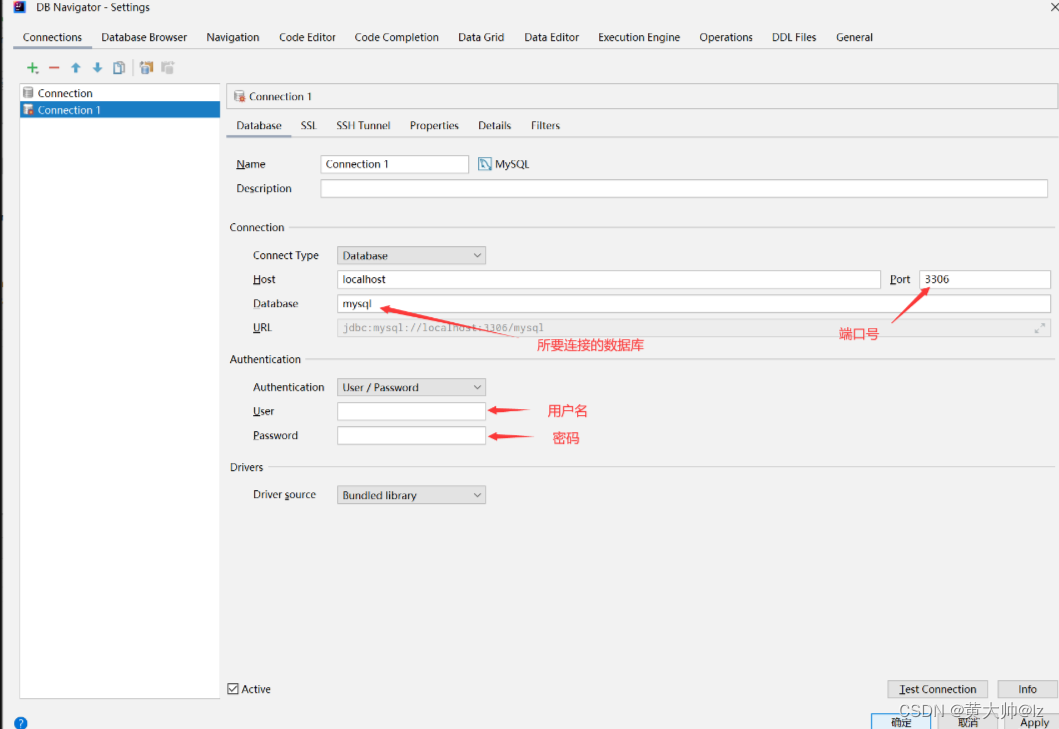
2.4、Mapper代理开发
目的
- 解决原生方式中的硬编码
- 简化后期执行SQL
使用Mapper代理方式要求
-
定义与SQL映射文件同名的Mapper接口,并且将
Mapper接口和SQL映射文件放置在同一目录下 -
设置SQL映射文件的namespace属性为Mapper接口全限定名
-
在Mapper接口中定义方法,方法名就是SQL映射文件中sql语句的id,并保持参数类型和返回值类型一致
-
编码
- 通过
SqlSession的getMapper方法获取Mapper接口的代理对象- 调用对应方法完成sql的执行
细节:如果Mapper接口名称和SQL映射文件名称相同,并在同一目录下,则可以使用包扫描的方式简化SQL映射文件的加载
package com.Smulll;
import com.Smulll.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.Smulll.pojo.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
/*
* 代理开发
* */
public class MybatisDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1,加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取sqlSessFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SqlSession对象,用它来执行SQL
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3.执行sql语句
//List<Object> Users = sqlSession.selectList("test.selectAll");
//获取UserMapper接口的代理对象
UserMapper usermapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> users = usermapper.selectAll();
//打印
System.out.println(users);
//关流
sqlSession.close();
}
}
核心配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--
environments:配置数据库连接环境信息,可以配置多个environment,通过default属性切换不同的environment,即通过这个改变其数据库的不同
-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--数据库连接信息-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!--加载SQL的映射文件-->
<mapper resource="com/mybatisDom/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
mapper代理
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
namespace: 名称空间
-->
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper">
<!--statement-->
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.User">
select * from tb_user;
</select>
</mapper>
接口文件
package com.itheima.mapper;
import com.itheima.pojo.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> selectAll();
}
三、MyBaits核心配置文件
MyBatis核心配置文件的顶层结构如下:

<!--
用这个就可以省略前面的包名目录了
-->
<typeAliases >
<package name="com.itheima.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
细节:配置各个标签时,需要遵守前后顺序
四、 配置文件的增删改查

4.1 Mybatis案列
4.1.1 环境的准备
4.2 查询所有数据和结果映射
- 编写接口方法:Mapper接口
参数:无
结果:List - 编写SQL语句:SQL映射文件
执行方法,测试
测试:
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.mapper.BrandMapper;
import com.itheima.pojo.Brand;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class MyBatisTest {
@Test
public void testselectAll() throws IOException {
//1.获取sqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SQLsession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4.执行方法
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectAll();
System.out.println(brands);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
接口文件:
package com.itheima.mapper;
import com.itheima.pojo.Brand;
import java.util.List;
public interface BrandMapper {
public List<Brand> selectAll();
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
namespace: 名称空间
-->
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.BrandMapper">
<!--statement-->
<!--
数据库表的字段名称 和 实体类的属性名称 不一样,则不能自动封装数据
起别名:对不一样的列名起别名,使其和实体类的属性名一样
缺点:每次查询都要定义一次别名
sql片段
缺点: 不灵活
resultMap
1.定义<resultMap>标签
2.在<select>标签中,使用resultMap属性替换resultType属性
-->
<!--
id:唯一标识
type:映射类型,支持别名
-->
<resultMap id="brandResultMap" type="com.itheima.pojo.Brand">
<!--
id:完成主键字段的映射
column:表的别名
property:实体类的属性名
result:完成一般字段的映射
column:表的别名
property:实体类的属性名
-->
<result column="brand_name" property="brandName"/>
<result column="company_name" property="companyName"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select
*
from tb_brand;
</select>
<!--
<sql id="brand_colum">
id,brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName ,ordered,description,status
</sql>
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.Brand">
select
<include refid="brand_colum"></include>
from tb_brand;
</select>
-->
</mapper>
核心配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--
environments:配置数据库连接环境信息,可以配置多个environment,通过default属性切换不同的environment
-->
<typeAliases >
<package name="com.itheima.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--数据库连接信息-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!--加载SQL的映射文件-->
<mapper resource="com/itheima/mapper/BrandMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
实体类属性名和数据库表列名不一致,不能自动封装数据
起别名:在sql语句中,对不一样的列名起别名,别名和实体类属性名一样
可以定义片段,提升复用性
resultMap:定义完成不一致的属性名和列名的映射
4.3、查看详情单个查询
- 编写接口方法:Mapper接口
参数:id
结果:Brand - 编写SQL语句: SQL映射文件
执行方法,测试
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.mapper.BrandMapper;
import com.itheima.pojo.Brand;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class MyBatisTest_selectById {
@Test
public void testselectAll() throws IOException {
//1.获取sqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SQLsession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4.执行方法
Brand brand1 = brandMapper.selectByID(1);
//打印结果
System.out.println(brand1);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
接口文件:
public interface BrandMapper {
Brand selectByID(int id);
}
Mapper映射文件
<select id="selectByID" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where
id = #{id};
</select>
参数占位符
- #{}
会将其替换为?防止了sql注入 - $ {}
会将sql拼进去,存在sql注入问题
- 使用时机
1.参数传递时:#{}
2.表名或者列名不固定的情况下:${}会存在SQL注入问题
细节:
- 参数类型:parameterType:可以省略
- 特殊字符处理
1.转义字符
2.CDATA区
输入CD会出现提示
语法:
<![CDATA[
内容
]]>
可以将字符直接写入,由于xml语句中许多符号无法直接打入 例如:<
4.4、条件查询
4.4.1、多条件查询
- 编写接口方法: Mapper接口
参数:所有查询条件
结果:List<Brand> - 编写SQL语句:SQL映射文件
- 执行方法,测试
测试:
public void testselectByCondition() throws IOException {
//接收参数
int status = 1;
String companyName = "华为";
String brandName = "华为";
//处理参数
companyName = "%" + companyName +"%";
brandName = "%" + brandName +"%";
//使用brand对象进行查询
/*Brand brand = new Brand();
brand.setStatus(status);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setBrandName(brandName);*/
//使用Map集合处理
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("status",status);
map.put("companyName",companyName);
map.put("brandName",brandName);
//1.获取sqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SQLsession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4.执行方法
// 4.1 使用散装参数进行查询
//List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(status, companyName, brandName);
//4.2 使用brand对象进行查询
//List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(brand);
//4.3 使用Map集合处理
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(map);
//打印结果
System.out.println(brands);
sqlSession.close();
}
接口:
/*
* 条件查询
* 参数:
* 1. 散装参数:如果方法中有多个参数,需要使用@Param("SQL参数占位符名称")
* 2. brand对象参数: 对象的属性名称要和参数占位符名称一致
* 3. Map集合参数
*
* */
List<Brand> selectByCondition(@Param("status")int status,
@Param("companyName")String companyName,
@Param("brandName")String brandName);
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Brand brand);
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Map map);
}
Mapper映射文件:
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
<where>
<if test="status !=null ">
status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="companyName !=null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="brandName !=null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</if>
</where>
</select>
- 散装参数
如果方法中有多个参数,需要使用@Param(“SQL参数占位符名称”)
- 实体类对象参数:
对象的属性名称要和参数占位符名称一致
- Map集合参数:
只需要保证SQL中的参数名 和 map集合的键的名称对应上,即可设置成功
4.4.2、动态条件查询
SQL语句会随着用户的输入或外部条件的变化而变化,我们称为动态SQL
MyBatis 对动态SQL有很强大的支撑:
- if
test:逻辑表达式 - choose (when, otherwise)
- foreach
问题:
当第一个条件判断不满足要求,后面的条件判断满足要求,会导致后面语句的and出现在第一个条件判断中,使得报错
解决方案:
写恒等式
<where>替换 where关键字
public void testselectByCondition() throws IOException {
//接收参数
int status = 1;
String companyName = "华为";
String brandName = "华为";
//处理参数
companyName = "%" + companyName +"%";
brandName = "%" + brandName +"%";
//使用brand对象进行查询
/*Brand brand = new Brand();
brand.setStatus(status);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setBrandName(brandName);*/
//使用Map集合处理
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("status",status);
map.put("companyName",companyName);
//map.put("brandName",brandName);
//1.获取sqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SQLsession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4.执行方法
// 4.1 使用散装参数进行查询
//List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(status, companyName, brandName);
//4.2 使用brand对象进行查询
//List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(brand);
//4.3 使用Map集合处理
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(map);
//打印结果
System.out.println(brands);
sqlSession.close();
}
接口文件没有变化
Mapper映射文件
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
<!--
当第一个条件判断不满足要求,后面的条件判断满足要求,会导致后面语句的and出现在第一个条件判断中,使得报错
解决方案:
1. 写恒等式
2. `<where>`替换 `where`关键字
-->
<!--where
//第一种解决方案
1=1
-->
<!--第二种解决方案-->
<where>
<if test="status !=null ">
status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="companyName !=null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="brandName !=null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</if>
</where>
</select>
4.4.3、单条件动态条件查询
从多个条件中选择一个:
choose (when, otherwise):选择,类似于Java 中的switch语句
测试文件:
@Test
public void testselectByConditionSingle() throws IOException {
//接收参数
int status = 1;
String companyName = "华为";
String brandName = "华为";
//处理参数
companyName = "%" + companyName +"%";
brandName = "%" + brandName +"%";
//使用brand对象进行查询
Brand brand = new Brand();
brand.setStatus(status);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setBrandName(brandName);
//1.获取sqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SQLsession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4.执行方法
//使用brand对象进行查询
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByConditionSingle(brand);
//打印结果
System.out.println(brands);
sqlSession.close();
}
接口文件:
List<Brand> selectByConditionSingle(Brand brand);
}
Mapper映射文件:
<select id="selectByConditionSingle" resultType="com.Smulll.pojo.Brand">
select *
from tb_brand
where
<choose>
<when test="status !=null">
status = #{status}
</when>
<when test="companyName !=null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</when>
<when test="brandName !=null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</when>
<otherwise>
1=1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
<!-- ----------------------- -------------------------------------------------- ------>
<select id="selectByConditionSingle" resultType="com.Smulll.pojo.Brand">
select *
from tb_brand
<where>
<choose><!--类似于switch-->
<when test="status !=null"><!--类似于case-->
status = #{status}
</when>
<when test="companyName !=null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</when>
<when test="brandName !=null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</when>
<otherwise><!--类似于default-->
1=1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
4.5、添加
- 编写接口方法: Mapper接口>
参数:除了id之外的所有数据
结果:void - 编写SQL语句:SQL映射文件
<insert id="add">
insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status)
values (#{brandName},#{companyName},#{ordered},#{description},#{status});
</insert>
- 进行测试
MyBatis事务:
- openSession():默认开启事务,进行增删改操作后需要使
sqlSession.commit();手动提交事务 - openSession(true):可以设置为自动提交事务(关闭事务)
/*
* 添加字段
* */
@Test
public void testAdd() throws IOException {
//接收参数
int status = 1;
String companyName = "阿里粑粑有限公司";
String brandName = "阿里嘎多汽车";
int order = 100;
String description = "华华华华短视的";
//使用brand对象进行查询
Brand brand = new Brand();
brand.setStatus(status);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setBrandName(brandName);
brand.setOrdered(order);
brand.setDescription(description);
//1.获取sqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SQLsession 在里面传参数可以控制是否自动提交
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4.执行方法
brandMapper.add(brand);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
-
添加-主键返回
在数据添加成功后,需要获取插入数据库数据的主键的值 -
比如:添加订单和订单项
-
添加订单
添加订单项,订单项中需要设置所属订单的id
<insert id="agdOrder" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into tb_order (payment, payment_type, status)
values (#{payment},#{paymentType},#{status});
<linsert>
<insert id="addOrderltem">
insert into tb_order_item (goods_name, goods_price,count,order_id)
values (#{goodsName},#{goodsPrice},#{count},#{orderld});
</insert>
4.6、修改功能
4.6.1、修改全部字段
- 编写接口u方法:Mapper接口
参数:所有数据
结果:void - 编写SQL语句:SQL映射文件
- 执行方法,测试
/*
* 更新字段
* */
@Test
public void testUpdateAll() throws IOException {
//接收参数
int status = 1;
String companyName = "阿里粑粑有限公司";
String brandName = "阿里嘎多汽车";
int order = 100;
String description = "华华华华短视的";
int id = 5;
//使用brand对象进行查询
Brand brand = new Brand();
brand.setStatus(status);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
brand.setBrandName(brandName);
brand.setOrdered(order);
brand.setDescription(description);
brand.setId(id);
//1.获取sqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SQLsession 在里面传参数可以控制是否自动提交
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4.执行方法
brandMapper.update(brand);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
Mapper映射文件
<update id="updateAll">
update tb_brand
set brand_name = #{brandName},
company_name=#{companyName},
ordered=#{ordered},
description=#{description},
status=#{status}
where id=#{id};
</update>
接口文件:
void updateAll(Brand brand);
4.6.2、修改动态字段
- 编写接口方法: Mapper接口
参数:部分数据,封装到对象中
结果: void - 编写SQL语句:SQL映射文件
- 执行方法测试
public void testUpdate() throws IOException {
//接收参数
int status = 1;
String companyName = "阿里粑粑有限公司";
String brandName = "阿里嘎多汽车";
int order = 100;
String description = "华华华华短视的";
int id = 5;
//使用brand对象进行查询
Brand brand = new Brand();
//brand.setStatus(status);
//brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
//brand.setBrandName(brandName);
brand.setOrdered(order);
//brand.setDescription(description);
brand.setId(id);
//1.获取sqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SQLsession 在里面传参数可以控制是否自动提交
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4.执行方法
brandMapper.update(brand);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
接口文件
void update(Brand brand);
Mapper映射文件
<update id="update">
update tb_brand
<set>
<if test="brandName !=null and brandName != '' ">
brand_name = #{brandName},
</if>
<if test="companyName !=null and companyName != '' ">
company_name=#{companyName},
</if>
<if test="ordered= !null ">
ordered=#{ordered},
</if>
<if test="description !=null and description != '' ">
description=#{description},
</if>
<if test="status !=null ">
status=#{status},
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id};
</update>
4.7、删除功能
4.7.1、删除单个字段
- 编写接口方法: Mapper接口>
参数: id
结果:void - 编写SQL语句: SQL映射文件
- 执行方法,测试
/*
* 删除字段
* */
@Test
public void testDelete() throws IOException {
int id = 6;
//设置对象
Brand brand = new Brand();
brand.setId(id);
//1.获取sqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SQLsession 在里面传参数可以控制是否自动提交
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4.执行方法
brandMapper.deleteById(brand);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
接口文件:
void deleteById(Brand brand);
Mapper映射文件:
<delete id="deleteById">
delete from tb_brand
where id = #{id}
</delete>
4.7.2、批量删除
- 编写接口方法: Mapper接口>
参数:id数组
结果: void - 编写SQL语句: SQL映射文件
- 执行方法,测试
/*
* 批量删除字段
* */
@Test
public void testDeleteIds() throws IOException {
int[] ids = {7,8};
//1.获取sqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SQLsession 在里面传参数可以控制是否自动提交
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
//4.执行方法
brandMapper.deleteByIds(ids);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
接口
mybatis会将数组参数,封装为一个Map集合
- 默认:array = 数组
- 使用@Param注解改变map集合的默认key的名称
void deleteByIds(@Param("Ids")int[] ids);
Mapper映射文件
<delete id="deleteByIds">
delete from tb_brand
where id in
(<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open= "(" close= ")" >
#{id}
</foreach>)
</delete>
4.8、参数传递
MyBatis 接口方法中可以接收各种各样的参数,MyBatis底层对于这些参数进行不同的封装处理方式
- 单个参数:
- POJO类型:直接使用,属性名 和 参数占位符名称一致
- Map集合:直接使用,键名 和 参数占位符名称一致
- Collection:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
map.put("arg0",Collection集合)
map.put("collection",Collection集合)
- List:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
map.put("arg0",List集合)
map.put("collection",List集合)
map.put("List",List集合)
- Array:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
map.put("arg0",数组)
map.put("array",数组)
- 其他类型:直接使用
- 多个参数:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
map.put("arg0",参数1)
map.put("param1",参数1)
map.put("arg1",参数2)
map.put("param2",参数2)
-------------@Param("username")
map.put("username",参数1)
map.put("param1",参数1)
map.put("arg1",参数2)
map.put("param2",参数2)
MyBatis提供了ParamNameResolver类来进行参数封装
建议:将来都使用@Param注解来修改Map集合中默认的键名,并使用修改后的名称来获取值,这样可读性更高
4.9、注解开发
使用注解开发会比配置文件开发更加方便
@Select("select * from tb_user where id = #{id}")
public User selectByld(int id);
- 查询:
@Select - 添加:
@Insert - 修改:
@Update - 删除:
@Delete
提示:
- 注解完成简单功能
- 配置文件完成复杂功能
使用注解来映射简单语句会使代码显得更加简洁,但对于稍微复杂一点的语句,Java注解不仅力不从心,还会址你本就复杂的SQL语句更加期乱不堪。因此。如果你需要的一些很亮杂的涯作,最好用XML来映射语句。
选择何种方式来配置映射,以及认为是否应该要统一映射语句定义的形式,完全取决于你和你的团队。换句话说,永远不要拘泥于一种方式,你可以很轻松的在基于注解和XML的语句映射方式间自由移植和切换。