一、基础项目搭建:
开发工具推荐 VS Code 开发,配合插件如下:
| 插件名 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| TypeScript Vue Plugin (Volar) | 用于 TypeScript 的 Vue 插件 |
| Vue Language Features (Volar) | Vue3.0 语法支持 |
1. 创建项目
可以通过附加的命令行选项直接指定项目名称和你想要使用的模板。例如:
# npm 6.x
npm create vite@latest my-vue-app --template vue
# npm 7+, extra double-dash is needed:
npm create vite@latest my-vue-app -- --template vue
# yarn
yarn create vite my-vue-app --template vue
# pnpm
pnpm create vite my-vue-app --template vue
2. 启动项目
npx degit user/project my-project
cd my-project
npm install
npm run dev
过多vite相关知识点不多陈述,附上vite官方链接:
Vite 官方中文文档
二、使用 Element Plus 组件库
1. 安装
# 选择一个你喜欢的包管理器
# NPM
$ npm install element-plus --save
# Yarn
$ yarn add element-plus
# pnpm
$ pnpm install element-plus
2. 用法
2.1 完整引入
如果你对打包后的文件大小不是很在乎,那么使用完整导入会更方便。
// main.ts
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import ElementPlus from 'element-plus'
import 'element-plus/dist/index.css'
import App from './App.vue'
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(ElementPlus)
app.mount('#app')
2.2 按需导入
您需要使用额外的插件来导入要使用的组件。
2.3 自动导入
首先你需要安装unplugin-vue-components 和 unplugin-auto-import这两款插件
npm install -D unplugin-vue-components unplugin-auto-import
然后把下列代码插入到你的 Vite 的配置文件中:
// vite.config.ts
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import AutoImport from 'unplugin-auto-import/vite'
import Components from 'unplugin-vue-components/vite'
import { ElementPlusResolver } from 'unplugin-vue-components/resolvers'
export default defineConfig({
// ...
plugins: [
// ...
AutoImport({
resolvers: [ElementPlusResolver()],
}),
Components({
resolvers: [ElementPlusResolver()],
}),
],
})
2.4 手动导入
Element Plus 提供了基于 ES Module 的开箱即用的 Tree Shaking 功能。
但你需要安装 unplugin-element-plus 来导入样式。 配置文档参考 docs
App.vue
<template>
<el-button>我是 ElButton</el-button>
</template>
<script>
import { ElButton } from 'element-plus'
export default {
components: { ElButton },
}
</script>
// vite.config.ts
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import ElementPlus from 'unplugin-element-plus/vite'
export default defineConfig({
// ...
plugins: [ElementPlus()],
})
三、使用全局状态管理工具 pinia
1. pinia 介绍
Pinia 是 Vue 的专属状态管理库,它允许你跨组件或页面共享状态。
pinia优点:
- 支持Vue2和Vue3,也就是老项目也可以使用Pinia。
- 足够轻量,压缩后的体积只有1kb左右。
- 完整的TypeScript支持,Vue3版本的一大优势就是对TypeScript的支持,所以Pinia也做到了完整的支持。如果你对Vuex很熟悉的化,一定知道Vuex对TS的语法支持不是完整的。
- 代码更加简洁,可以实现很好的代码自动分割。Vue2的时代,写代码需要来回翻滚屏幕屏幕找变量,非常的麻烦,Vue3的Composition api完美了解决这个问题。 可以实现代码自动分割,pinia也同样继承了这个优点。
- 去除 mutations,只有 state,getters,actions;actions 支持同步和异步。
- 不需要嵌套模块,让代码更加扁平化,只有 store 的概念,store 之间可以自由使用,每一个store都是独立的,符合Vue3的Composition api 。
- 无需手动添加 store,store 一旦创建便会自动添加。
1.1 安装
yarn add pinia
# 或者使用 npm
npm install pinia
1.2 引入
创建一个 pinia 实例 (根 store) 并将其传递给应用:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import App from './App.vue'
const pinia = createPinia()
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(pinia)
app.mount('#app')
1.3 使用
在 src 文件夹下创建 store 文件夹,并添加 counter.js 文件。
2. Pinia中的Store
2.1 定义store
Store(如 Pinia)是一个保存状态和业务逻辑的实体,它并不与你的组件树绑定。换句话说,它承载着全局状态。它有点像一个永远存在的组件,每个组件都可以读取和写入它。它有三个概念,state、getter和action,我们可以假设这些概念相当于组件中的data、computed和methods。store是用defineStore(name, function | options)定义的,建议其函数返回的值命名为use…Store方便理解
- 参数
name:必填值且唯一,简单点说就可以理解成是一个命名空间。 - 参数
function | options:可以是对象或函数形式。 -
- 对象形式【选项模式】,其中配置
state、getters和actions选项。
- 对象形式【选项模式】,其中配置
-
- 函数形式【组合模式,类似组件组合式 API 的书写方式】,定义响应式变量和方法,并且 return 对应的变量和方法;ref() 相当于 state,computed() 相当于 getters,function() 相当于 actions。
2.2 使用store读取和写入 state
下面案例以选项模式为例:
在 store 文件夹下创建 counter.js 文件,这个文件就是存有关 counter 的一些相关的数据。
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
/*defineStore 是需要传参数的,其中第一个参数是id,就是一个唯一的值,
简单点说就可以理解成是一个命名空间.
第二个参数就是一个对象,里面有三个模块需要处理,第一个是 state,
第二个是 getters,第三个是 actions。
*/
const useCounter = defineStore("counter",{
state:() => ({
count:88,
}),
getters: {
},
actions: {
}
})
//暴露useCounter这个模块
export default useCounter
在页面中使用:
<template>
<div>
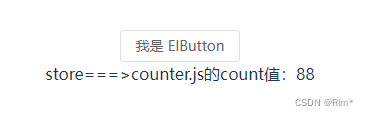
<el-button>我是 ElButton</el-button>
<div>store===>counter.js的count值:{{ counterStore.count }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
// 引入创建的store
import useCounter from "./store/counter";
// 调用store里的方法
const counterStore = useCounter();
console.log("counterStore", counterStore.count);
</script>
<style scoped></style>
**注意:**在使用时 ,取值时不用和 vuex 一样还要.state,直接.state里面的count值就行了,写法:counterStore.count。
案例需求,点击按钮加一:
我们分别用两种方法取count值,一个解构,一个不解构
<template>
<div>
<h2>Home Word</h2>
<h2>展示pinia的counter的count值: {{ counterStore.count }}</h2>
<h2>展示解构出来的pinia的counter的count值: {{ count }}</h2>
<el-button @click="addCount">function count+1</el-button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
// 引入创建的store
import useCounter from "./store/counter";
// 调用store里的方法
const counterStore = useCounter();
// 结构count值
const { count } = counterStore;
function addCount() {
//这里可以直接操作count,修改(写入)store,在vuex还要commit在mutaitions修改数据
counterStore.count++;
}
</script>

我们发现解构出来的值 失去响应式了。
解决方案:
为了从 store 中提取属性时保持其响应性,你需要使用 storeToRefs() 。它将为每一个响应式属性创建引用。当你只使用 store 的状态而不调用任何 action 时,它会非常有用。
<template>
<div>
<h2>Home Word</h2>
<!-- 2.使用useCounter的实例获取state中的值 -->
<h2>展示pinia的counter的count值: {{ counterStore.count }}</h2>
<h2>展示解构出来的pinia的counter的count值: {{ count }}</h2>
<el-button @click="addCount">function count+1</el-button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { storeToRefs } from "pinia";
// 引入创建的store
import useCounter from "./store/counter";
// 调用store里的方法
const counterStore = useCounter();
// 结构count值
const { count } = storeToRefs(counterStore);
function addCount() {
//这里可以直接操作count,修改(写入)store,在vuex还要commit在mutaitions修改数据
counterStore.count++;
}
</script>

2.3 修改state数据
- 定义一个关于user的Store
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
const useUser = defineStore("user", {
state: () => ({
name: "why",
age: 18,
level: 100
})
})
export default useUser
- 三种修改state的方法
<template>
<div>
<h2>Home Word</h2>
<h2>姓名: {{ name }}</h2>
<h2>年龄: {{ age }}</h2>
<h2>等级: {{ level }}</h2>
<el-button @click="updateStore">修改user信息</el-button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import useUser from "./store/user";
import { storeToRefs } from "pinia";
const userStore = useUser();
const { name, age, level } = storeToRefs(userStore);
function updateStore() {
// 方法一:一个个的修改状态
// userStore.name = "zimo";
// userStore.age = 20;
// 方法二 :一次性修改多个状态
// userStore.$patch({
// name: "zimo",
// age: 20,
// });
// 方法三:替换state为新的对象
const oldState = userStore.$state;
userStore.$state = {
name: "curry",
level: 200,
};
// 下面会返回true
console.log(oldState === userStore.$state);
}
</script>


2.4 重置state数据
新增一个重置按钮:
<el-button @click="resetStore">重置user信息</el-button>
新增一个重置方法:
function resetStore() {
userStore.$reset();
}

3. Pinia中的getters
getters 类似于 vue 里面的计算属性,可以对已有的数据进行修饰。getters中可以定义接受一个state作为参数的函数,不管调用多少次,getters中的函数只会执行一次,且都会缓存。
3.1 定义getters
- 基本使用
- 一个getter引入另外一个getter
- getters也支持返回一个函数
- getters中用到别的store中的数据
// 定义关于counter的store
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
const useCounter = defineStore("counter", {
state: () => ({
count: 99
}),
getters: {
// 1.基本使用
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2
},
// 2.一个getter引入另外一个getter
doubleCountAddOne() {
// this是store实例,可以直接使用另一个getter
return this.doubleCount + 1
},
// 3.getters也支持返回一个函数
getFriendById(state) {
return function(id) {
return id
}
},
// 4.getters中用到别的store中的数据
showMessage(state) {
//获取user信息,拿到useUser模块
const userStore = useUser()
//拼接信息
return `name:${userStore.name}-count:${state.count}`
}
},
})
export default useCounter
3.2 访问getters
<template>
<div>
<!-- 在模板中使用 -->
<h2>基本使用:doubleCount: {{ counterStore.doubleCount }}</h2>
<h2>
一个getter引入另外一个getter:doubleCountAddOne:
{{ counterStore.doubleCountAddOne }}
</h2>
<h2>函数id-99: {{ counterStore.getFriendById(99) }}</h2>
<h2>
getters中获取另一个store中的state/getters数据==>showMessage:{{
counterStore.showMessage
}}
</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import useCounter from "./store/counter";
const counterStore = useCounter();
// 在js文件中使用
const doubleCount = counterStore.doubleCount;
const doubleCountAddOne = counterStore.doubleCountAddOne;
const frend = counterStore.getFriendById(99);
</script>

**注意:**getters中用别的store中的数据 ,在counter模块中拿user模块的store数据,要引入user模块。