实例讲解
一、准备工作
1、问题实体
问题实体包含编号、类型(类型即题型,分为五种:单选,多选,判断,填空,问答, 分别用1、2、3、4、5表示)、分数、难度系数、知识点。一道题至少有一个知识点,为简单易懂,知识点用List 表示(知识点编号集合)。
代码如下:
public class Problem
{
public Problem()
{
ID = 0;
Type = 0;
Score = 0;
Difficulty = 0.00;
Points = new List<int>();
}
public Problem(Problem p)
{
this.ID = p.ID;
this.Type = p.Type;
this.Score = p.Score;
this.Difficulty = p.Difficulty;
this.Points = p.Points;
}
/// <summary>
/// 编号
/// </summary>
public int ID { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 题型(1、2、3、4、5对应单选,多选,判断,填空,问答)
/// </summary>
public int Type { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 分数
/// </summary>
public int Score { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 难度系数
/// </summary>
public double Difficulty { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 知识点
/// </summary>
public List<int> Points { get; set; }
}
2、题库
为了简单,这里没有用数据库,题目信息临时创建,保存在内存中。因为对不同层次的考生一道题目在不同试卷中的分数可能不一样,因此题目分数一般是老师出卷时定的,不保存在题库中。且单选,多选,判断题每题分数应该相同,填空题一般根据空数来定分数,而问答题一般根据题目难度来定的,因此这里的单选、多选、判断分数相同,填空空数取1-4间的随机数,填空题分数即为空数,问答题即为该题难度系数*10取整。这里各种题型均为1000题,具体应用时改为数据库即可。
代码如下:
public class DB
{
/// <summary>
/// 题库
/// </summary>
public List<Problem> ProblemDB;
public DB()
{
ProblemDB = new List<Problem>();
Problem model;
Random rand = new Random();
List<int> Points;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5000; i++)
{
model = new Problem();
model.ID = i;
//试题难度系数取0.3到1之间的随机值
model.Difficulty = rand.Next(30, 100) * 0.01;
//单选题1分
if (i < 1001)
{
model.Type = 1;
model.Score = 1;
}
//单选题2分
if (i > 1000 && i < 2001)
{
model.Type = 2;
model.Score = 2;
}
//判断题2分
if (i > 2000 && i < 3001)
{
model.Type = 3;
model.Score = 2;
}
//填空题1—4分
if (i > 3000 && i < 4001)
{
model.Type = 4;
model.Score = rand.Next(1, 5);
}
//问答题分数为难度系数*10
if (i > 4000 && i < 5001)
{
model.Type = 5;
model.Score = model.Difficulty > 0.3 ? (int)(double.Parse(model.Difficulty.ToString("f1")) * 10) : 3;
}
Points = new List<int>();
//每题1到4个知识点
int count = rand.Next(1, 5);
for (int j = 0; j < count; j++)
{
Points.Add(rand.Next(1, 100));
}
model.Points = Points;
ProblemDB.Add(model);
}
}
}
3、 试卷实体
试卷一般包含试卷编号,试卷名称,考试时间,难度系数,知识点分布,总题数, 总分数,各种题型所占比率等属性,这里为简单去掉了试卷名称跟考试时间。其中的知识点分布即老师出卷时选定本试卷要考查的知识点,这里用List(知识点编号集合)表示。
代码如下:
public class Paper
{
/// <summary>
/// 编号
/// </summary>
public int ID { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 总分
/// </summary>
public int TotalScore { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 难度系数
/// </summary>
public double Difficulty { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 知识点
/// </summary>
public List<int> Points { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 各种题型题数
/// </summary>
public int[] EachTypeCount { get; set; }
}
二、开始遗传算法组卷之旅
准备工作已经OK,下面就按上一篇介绍的流程进行操作啦!
1、产生初始种群
这里保证题数跟总分达到出卷要求即可,但为操作方便,这里再定义一个种群个体实体类Unit,包含编号、适应度、题数、总分、难度系数、知识点分布、包含的题目等信息(也可以修改一下试卷实体,用试卷实体表示):
public class Unit
{
public Unit()
{
ID = 0;
AdaptationDegree = 0.00;
KPCoverage = 0.00;
ProblemList = new List<Problem>();
}
/// <summary>
/// 编号
/// </summary>
public int ID { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 适应度
/// </summary>
public double AdaptationDegree { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 难度系数(本试卷所有题目分数*难度系数/总分)
/// </summary>
public double Difficulty
{
get
{
double diff = 0.00;
ProblemList.ForEach(delegate(Problem p)
{
diff += p.Difficulty * p.Score;
});
return diff / SumScore;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 题目数量
/// </summary>
public int ProblemCount
{
get
{
return ProblemList.Count;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 总分
/// </summary>
public int SumScore
{
get
{
int sum = 0;
ProblemList.ForEach(delegate(Problem p)
{
sum += p.Score;
});
return sum;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 知识点分布
/// </summary>
public double KPCoverage { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 题目
/// </summary>
public List<Problem> ProblemList { get; set; }
}
下面即来产生初始种群,按个体数量,期望试卷知识点分布,各类型题目数等限制产生初始种群:
/// <summary>
/// 初始种群
/// </summary>
/// <param name="count">个体数量</param>
/// <param name="paper">期望试卷</param>
/// <param name="problemList">题库</param>
/// <returns>初始种群</returns>
public List<Unit> CSZQ(int count, Paper paper, List<Problem> problemList)
{
List<Unit> unitList = new List<Unit>();
int[] eachTypeCount = paper.EachTypeCount;
Unit unit;
Random rand = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
unit = new Unit();
unit.ID = i + 1;
unit.AdaptationDegree = 0.00;
//总分限制
while (paper.TotalScore != unit.SumScore)
{
unit.ProblemList.Clear();
//各题型题目数量限制
for (int j = 0; j < eachTypeCount.Length; j++)
{
List<Problem> oneTypeProblem = problemList
.Where(o => o.Type == (j + 1))
.Where(p => IsContain(paper, p))
.ToList();
Problem temp = new Problem();
for (int k = 0; k < eachTypeCount[j]; k++)
{
//选择不重复的题目
int index = rand.Next(0, oneTypeProblem.Count - k);
unit.ProblemList.Add(oneTypeProblem[index]);
temp = oneTypeProblem[oneTypeProblem.Count - 1 - k];
oneTypeProblem[oneTypeProblem.Count - 1 - k] = oneTypeProblem[index];
oneTypeProblem[index] = temp;
}
}
}
unitList.Add(unit);
}
//计算知识点覆盖率及适应度
unitList = GetKPCoverage(unitList, paper);
unitList = GetAdaptationDegree(unitList, paper, kpcoverage, difficulty);
return unitList;
}
2、计算种群个体的适应度
在上面的代码中最后调用了两个方法,GetKPCoverage跟GetAdaptationDegree,这两个方法分别是计算种群中个体的知识点覆盖率跟适应度。
关于种群个体的知识点覆盖率在上一篇文章中已经说过了(知识点分布用一个个体知识点的覆盖率来衡量,例如期望本试卷包含N个知识点,而一个个体中所有题目知识点的并集中包含M个(M<=N),则知识点的覆盖率为M/N。),具体算法如下:
/// <summary>
/// 计算知识点覆盖率
/// </summary>
/// <param name="unitList">种群</param>
/// <param name="paper">期望试卷</param>
/// <returns>List</returns>
public List<Unit> GetKPCoverage(List<Unit> unitList, Paper paper)
{
List<int> kp;
for (int i = 0; i < unitList.Count; i++)
{
kp = new List<int>();
unitList[i].ProblemList.ForEach(delegate(Problem p)
{
kp.AddRange(p.Points);
});
//个体所有题目知识点并集跟期望试卷知识点交集
var common = kp.Intersect(paper.Points);
unitList[i].KPCoverage = common.Count() * 1.00 / paper.Points.Count;
}
return unitList;
}
适应度方法的确定上一篇文章里已经说过,即:
f=1-(1-M/N)*f1-|EP-P|*f2
其中M/N为知识点覆盖率,EP为期望难度系数,P为种群个体难度系数,f1为知识点分布的权重,f2为难度系数所占权重。当f1=0时退化为只限制试题难度系数,当f2=0时退化为只限制知识点分布。 实现代码如下:
/// <summary>
/// 计算种群适应度
/// </summary>
/// <param name="unitList">种群</param>
/// <param name="paper">期望试卷</param>
/// <param name="KPCoverage">知识点分布在适应度计算中所占权重</param>
/// <param name="Difficulty">试卷难度系数在适应度计算中所占权重</param>
/// <returns>List</returns>
public List<Unit> GetAdaptationDegree(List<Unit> unitList, Paper paper, double KPCoverage, double Difficulty)
{
unitList = GetKPCoverage(unitList, paper);
for (int i = 0; i < unitList.Count; i++)
{
unitList[i].AdaptationDegree = 1 - (1 - unitList[i].KPCoverage) * KPCoverage - Math.Abs(unitList[i].Difficulty - paper.Difficulty) * Difficulty;
}
return unitList;
}
3、选择算子
这里选择算子采用轮盘赌选择法,即适应度越大的被选择到的概率越大。比如说种群中有20个个体,那么每个个体的适应度除以20个个体适应度的和得到的就是该个体的被选择的概率。轮盘赌选择时,每个个体类似于轮盘中的一小块扇形,扇形的大小与该个体被选择的概率成正比。那么,扇形越大的个体被选择的概率越大。这就是轮盘赌选择法。 算法实现代码如下:
/// <summary>
/// 选择算子(轮盘赌选择)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="unitList">种群</param>
/// <param name="count">选择次数</param>
/// <returns>进入下一代的种群</returns>
public List<Unit> Select(List<Unit> unitList, int count)
{
List<Unit> selectedUnitList = new List<Unit>();
//种群个体适应度和
double AllAdaptationDegree = 0;
unitList.ForEach(delegate(Unit u)
{
AllAdaptationDegree += u.AdaptationDegree;
});
Random rand = new Random();
while (selectedUnitList.Count != count)
{
//选择一个0—1的随机数字
double degree = 0.00;
double randDegree = rand.Next(1, 100) * 0.01 * AllAdaptationDegree;
//选择符合要求的个体
for (int j = 0; j < unitList.Count; j++)
{
degree += unitList[j].AdaptationDegree;
if (degree >= randDegree)
{
//不重复选择
if (!selectedUnitList.Contains(unitList[j]))
{
selectedUnitList.Add(unitList[j]);
}
break;
}
}
}
return selectedUnitList;
}
4、交叉算子
交叉算子在上一篇也做了说明,写程序时为方便略做了一点更改,即把多点交叉改为单点交叉。在交叉过程在有几个地方需要注意,一是要保正总分不变,二是保证交叉后没有重复个体,算法实现如下:
/// <summary>
/// 交叉算子
/// </summary>
/// <param name="unitList">种群</param>
/// <param name="count">交叉后产生的新种群个体数量</param>
/// <param name="paper">期望试卷</param>
/// <returns>List</returns>
public List<Unit> Cross(List<Unit> unitList, int count, Paper paper)
{
List<Unit> crossedUnitList = new List<Unit>();
Random rand = new Random();
while (crossedUnitList.Count != count)
{
//随机选择两个个体
int indexOne = rand.Next(0, unitList.Count);
int indexTwo = rand.Next(0, unitList.Count);
Unit unitOne;
Unit unitTwo;
if (indexOne != indexTwo)
{
unitOne = unitList[indexOne];
unitTwo = unitList[indexTwo];
//随机选择一个交叉位置
int crossPosition = rand.Next(0, unitOne.ProblemCount - 2);
//保证交叉的题目分数合相同
double scoreOne = unitOne.ProblemList[crossPosition].Score + unitOne.ProblemList[crossPosition + 1].Score;
double scoreTwo = unitTwo.ProblemList[crossPosition].Score + unitTwo.ProblemList[crossPosition + 1].Score;
if (scoreOne == scoreTwo)
{
//两个新个体
Unit unitNewOne = new Unit();
unitNewOne.ProblemList.AddRange(unitOne.ProblemList);
Unit unitNewTwo = new Unit();
unitNewTwo.ProblemList.AddRange(unitTwo.ProblemList);
//交换交叉位置后面两道题
for (int i = crossPosition; i < crossPosition + 2; i++)
{
unitNewOne.ProblemList[i] = new Problem(unitTwo.ProblemList[i]);
unitNewTwo.ProblemList[i] = new Problem(unitOne.ProblemList[i]);
}
//添加到新种群集合中
unitNewOne.ID = crossedUnitList.Count;
unitNewTwo.ID = unitNewOne.ID + 1;
if (crossedUnitList.Count < count)
{
crossedUnitList.Add(unitNewOne);
}
if (crossedUnitList.Count < count)
{
crossedUnitList.Add(unitNewTwo);
}
}
}
//过滤重复个体
crossedUnitList = crossedUnitList.Distinct(new ProblemComparer()).ToList();
}
//计算知识点覆盖率及适应度
crossedUnitList = GetKPCoverage(crossedUnitList, paper);
crossedUnitList = GetAdaptationDegree(crossedUnitList, paper, kpcoverage, difficulty);
return crossedUnitList;
}
上面过滤重复个体中用到了ProblemComparer类,这是一个自定义的比较类,代码如下:
public class ProblemComparer : IEqualityComparer<Unit>
{
public bool Equals(Unit x, Unit y)
{
bool result = true;
for (int i = 0; i < x.ProblemList.Count; i++)
{
if (x.ProblemList[i].ID != y.ProblemList[i].ID)
{
result = false;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
public int GetHashCode(Unit obj)
{
return obj.ToString().GetHashCode();
}
}
5、 变异算子
在变异过程中主要是要保证替换题目至少包含一个被替换题的有效知识点(期望试卷中也包含此知识点),并要类型相同,分数相同而题号不同。 算法实现代码如下:
/// <summary>
/// 变异算子
/// </summary>
/// <param name="unitList">种群</param>
/// <param name="problemList">题库</param>
/// <param name="paper">期望试卷</param>
/// <returns>List</returns>
public List<Unit> Change(List<Unit> unitList, List<Problem> problemList, Paper paper)
{
Random rand = new Random();
int index = 0;
unitList.ForEach(delegate(Unit u)
{
//随机选择一道题
index = rand.Next(0, u.ProblemList.Count);
Problem temp = u.ProblemList[index];
//得到这道题的知识点
Problem problem = new Problem();
for (int i = 0; i < temp.Points.Count; i++)
{
if (paper.Points.Contains(temp.Points[i]))
{
problem.Points.Add(temp.Points[i]);
}
}
//从数据库中选择包含此题有效知识点的同类型同分数不同题号试题
var otherDB = from a in problemList
where a.Points.Intersect(problem.Points).Count() > 0
select a;
List<Problem> smallDB = otherDB.Where(p => IsContain(paper, p)).Where(o => o.Score == temp.Score && o.Type == temp.Type && o.ID != temp.ID).ToList();
//从符合要求的试题中随机选一题替换
if (smallDB.Count > 0)
{
int changeIndex = rand.Next(0, smallDB.Count);
u.ProblemList[index] = smallDB[changeIndex];
}
});
//计算知识点覆盖率跟适应度
unitList = GetKPCoverage(unitList, paper);
unitList = GetAdaptationDegree(unitList, paper, kpcoverage, difficulty);
return unitList;
}
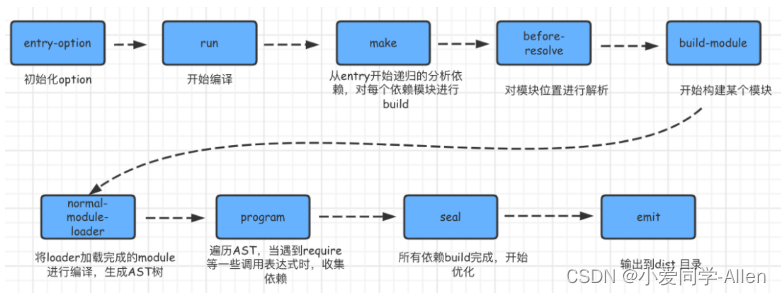
遗传算法主要算法上面都已实现,现在就是调用了。调用过程按如下流程图进行:
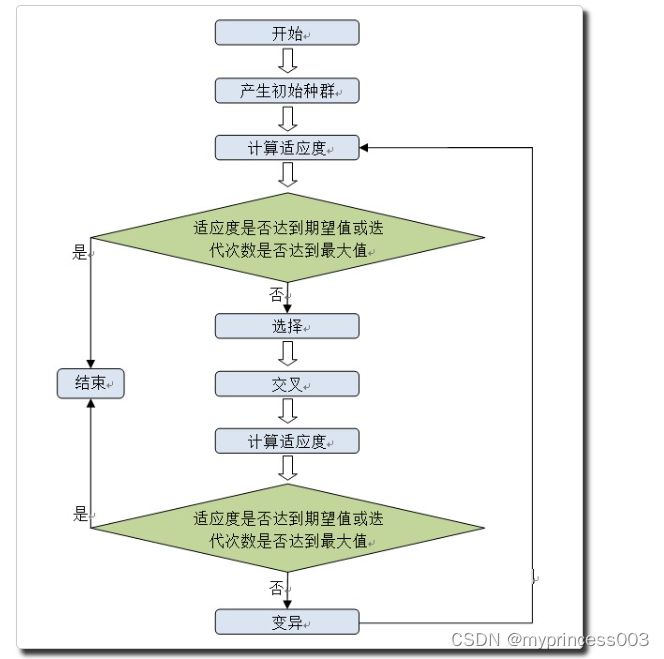
这里初始种群大小设定为20,最大迭代次数为500,适应度为0.98,选择算子选择次数为10次,交叉算子产生的个体数量为20,期望试卷难度系数为0.72,总分为100分,各种题型题数为:20(单选), 5(多选), 10(判断), 7(填空), 5(问答),包含的知识点为:1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39, 41, 43, 45, 47, 49, 51, 53, 55, 57, 59, 61, 63, 65, 67, 69, 71, 73, 75, 77, 79, 81。代码如下:
/// <summary>
/// 调用示例
/// </summary>
public void Show()
{
//题库
DB db = new DB();
//期望试卷
Paper paper = new Paper()
{
ID = 1,
TotalScore = 100,
Difficulty = 0.72,
Points = new List<int>() { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39, 41, 43, 45, 47, 49, 51, 53, 55, 57, 59, 61, 63, 65, 67, 69, 71, 73, 75, 77, 79, 81 },
EachTypeCount = new[] { 20, 5, 10, 7, 5 }
};
//迭代次数计数器
int count = 1;
//适应度期望值
double expand = 0.98;
//最大迭代次数
int runCount = 500;
//初始化种群
List<Unit> unitList = CSZQ(20, paper, db.ProblemDB);
Console.WriteLine("\n\n -------遗传算法组卷系统(http://www.cnblogs.com/durongjian/)---------\n\n");
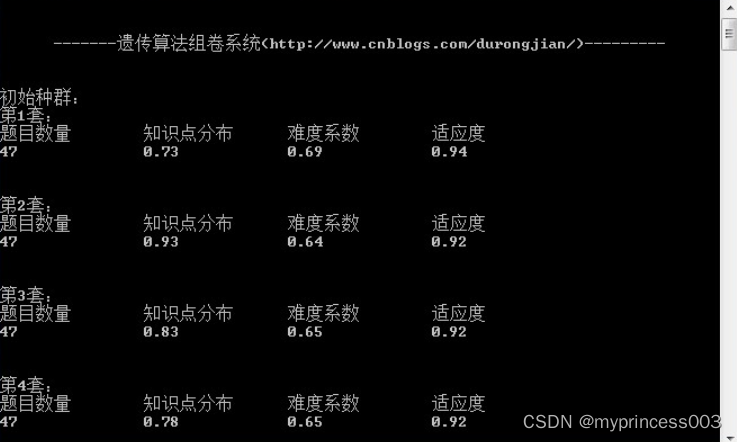
Console.WriteLine("初始种群:");
ShowUnit(unitList);
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------迭代开始------------------------");
//开始迭代
while (!IsEnd(unitList, expand))
{
Console.WriteLine("在第 " + (count++) + " 代未得到结果");
if (count > runCount)
{
Console.WriteLine("计算 " + runCount + " 代仍没有结果,请重新设计条件!");
break;
}
//选择
unitList = Select(unitList, 10);
//交叉
unitList = Cross(unitList, 20, paper);
//是否可以结束(有符合要求试卷即可结束)
if (IsEnd(unitList, expand))
{
break;
}
//变异
unitList = Change(unitList, db.ProblemDB, paper);
}
if (count <= runCount)
{
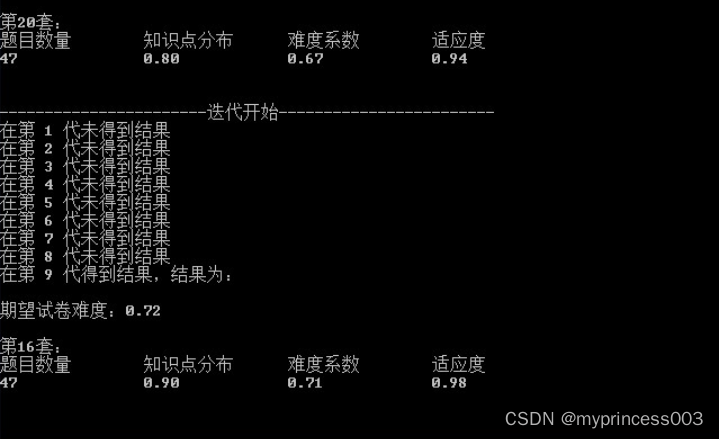
Console.WriteLine("在第 " + count + " 代得到结果,结果为:\n");
Console.WriteLine("期望试卷难度:" + paper.Difficulty + "\n");
ShowResult(unitList, expand);
}
}
最后在控制台中调用此方法即可。
7、其他辅助方法
在上面的代码中还调用了几个辅助方法,下面一并给出:
#region 是否达到目标
/// <summary>
/// 是否达到目标
/// </summary>
/// <param name="unitList">种群</param>
/// <param name="endcondition">结束条件(适应度要求)</param>
/// <returns>bool</returns>
public bool IsEnd(List<Unit> unitList, double endcondition)
{
if (unitList.Count > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < unitList.Count; i++)
{
if (unitList[i].AdaptationDegree >= endcondition)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
#endregion
#region 显示结果
/// <summary>
/// 显示结果
/// </summary>
/// <param name="unitList">种群</param>
/// <param name="expand">期望适应度</param>
public void ShowResult(List<Unit> unitList, double expand)
{
unitList.OrderBy(o => o.ID).ToList().ForEach(delegate(Unit u)
{
if (u.AdaptationDegree >= expand)
{
Console.WriteLine("第" + u.ID + "套:");
Console.WriteLine("题目数量\t知识点分布\t难度系数\t适应度");
Console.WriteLine(u.ProblemCount + "\t\t" + u.KPCoverage.ToString("f2") + "\t\t" + u.Difficulty.ToString("f2") + "\t\t" + u.AdaptationDegree.ToString("f2")+"\n\n");
}
});
}
#endregion
#region 显示种群个体题目编号
/// <summary>
/// 显示种群个体题目编号
/// </summary>
/// <param name="u">种群个体</param>
public void ShowUnit(Unit u)
{
Console.WriteLine("编号\t知识点分布\t难度系数");
Console.WriteLine(u.ID + "\t" + u.KPCoverage.ToString("f2") + "\t\t" + u.Difficulty.ToString("f2"));
u.ProblemList.ForEach(delegate(Problem p)
{
Console.Write(p.ID + "\t");
});
Console.WriteLine();
}
#endregion
#region 题目知识点是否符合试卷要求
/// <summary>
/// 题目知识点是否符合试卷要求
/// </summary>
/// <param name="paper">期望试卷</param>
/// <param name="problem">一首试题</param>
/// <returns>bool</returns>
private bool IsContain(Paper paper, Problem problem)
{
for (int i = 0; i < problem.Points.Count; i++)
{
if (paper.Points.Contains(problem.Points[i]))
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
#endregion






![[C++项目] Boost文档 站内搜索引擎(3): 建立文档及其关键字的正排 倒排索引、jieba库的安装与使用...](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/fc0e861d01e0270ee1e9a3ad197899cc.png)