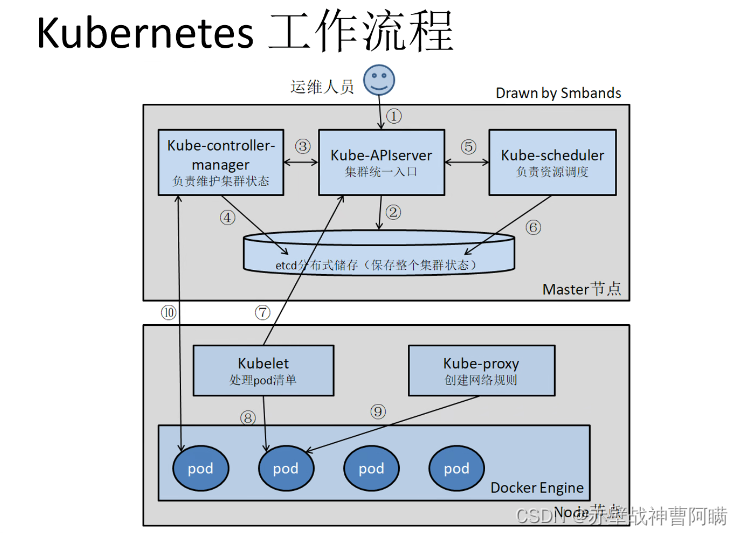
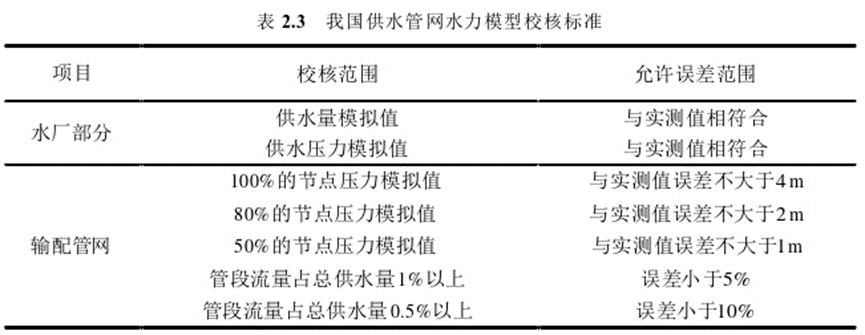
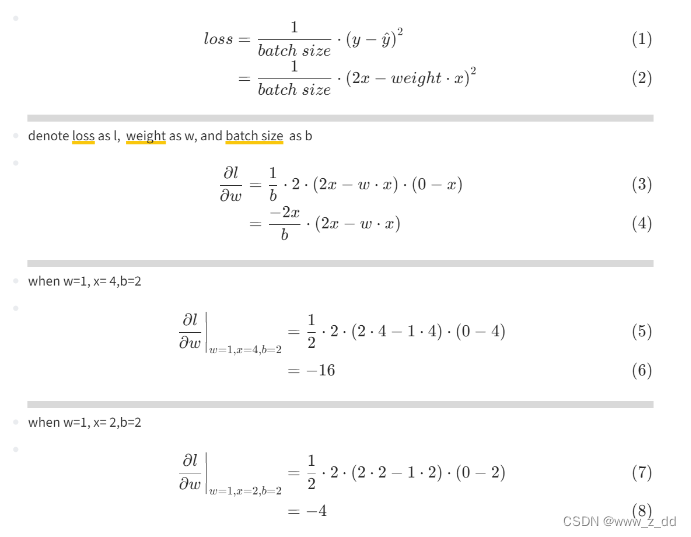
1. C# 调用 Python 常见的方法有4种
参考链接
1.1 Pythonnet (推荐)
可以很好的支持第三方库。
推荐这个,经本人验证这个很好用。
后文 2. 详细使用。
1.2 IronPython
如果使用第三方库就放弃这个吧,真的用不了,使用时报各种错。
如果只是标准库,可以用这个。
只需要在 nuget 里装上 IronPython 和 IronPython.StdLib 即可。

使用参考链接
1.3 利用C#的 process 方式
弊端:
1.当传入参数过长时,此方式是用不了的。会报错,没有解决办法。
2.需要安装python环境,并在程序中指定 pyython.exe 位置,及 脚本.py的位置。
1.3.1 示例演示
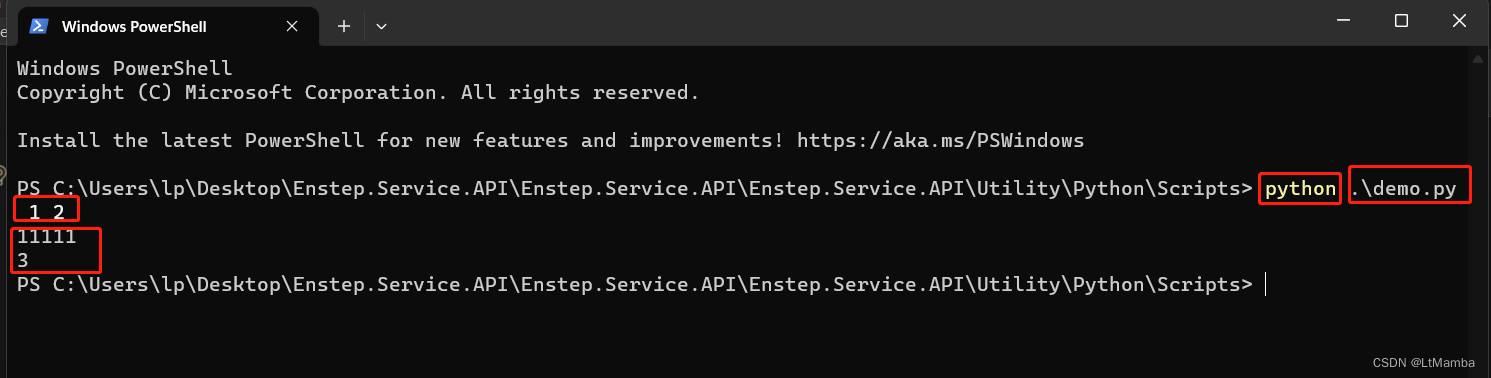
此方式类似执行命令加参数,如:
#demo.py
import sys
def str_add(str1, str2):
print("11111")
return int(str1) + int(str2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(str_add(sys.argv[1],sys.argv[2]))
1.4 使用C++调用Python,然后将C++程序做成动态链接库
这个实现很复杂,不了解C++的就很难搞了,也不推荐。
2.Pythonnet 详细使用
gitee repositroy
3. 利用C#的 process 方式 详细使用
实现其实就一个方法,套用即可。
private string RunPythonByexe(string scriptName, params string[] args)
{
string result= null;
try
{
using (var p = new Process())
{
string path = System.AppDomain.CurrentDomain.SetupInformation.ApplicationBase;
p.StartInfo.FileName = _pyexeLocation;//指定 python.exe 位置
p.StartInfo.Arguments = _pyLocation + scriptName; //指定脚本位置及名字,也就是上面例子的 .\demo.py
foreach (var item in args)
{
p.StartInfo.Arguments += " \"" + item.ToString() +"\""; //指定参数 若参数无空格可以不加双引号扩住,参数全部都加双引号是最好的
}
p.StartInfo.UseShellExecute = false;
p.StartInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true;
p.StartInfo.RedirectStandardInput = true;
p.StartInfo.RedirectStandardError = true;
p.StartInfo.CreateNoWindow = true;
p.Start();
while (!p.StandardOutput.EndOfStream)
{
result += p.StandardOutput.ReadLine();
}
p.WaitForExit();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ex;
}
return result;
}