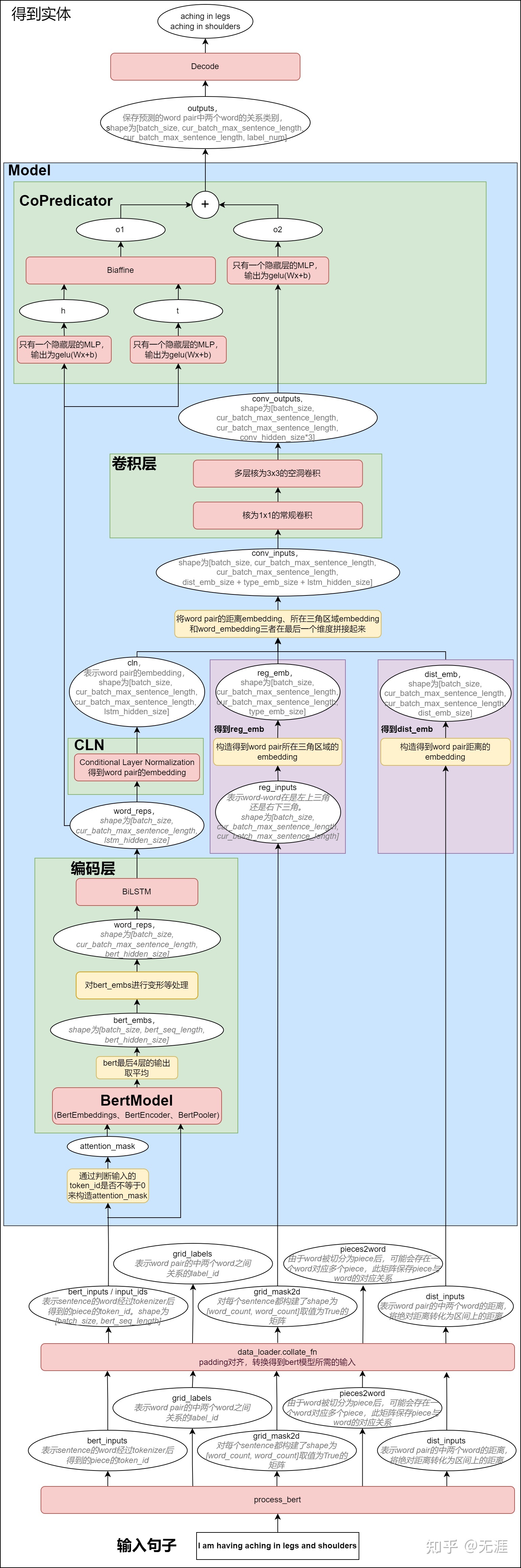
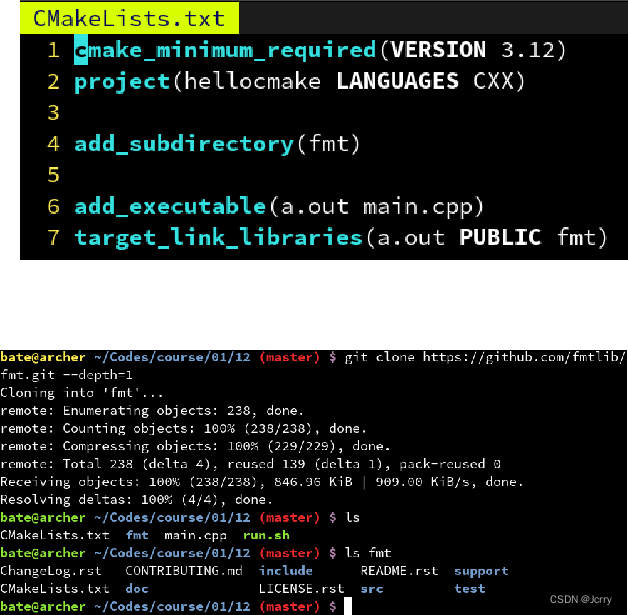
CAS作为一款企业级中央认证服务系统,其票据的生成是非常重要的一环,在票据的生成中,有一个比较重要的点就是为票据生成唯一ID,本文将深入解析CAS系统中的TGT和ST的唯一ID是怎样生成的。
文章重点分析源码的过程,不想看分析过程可以直接跳到总结处看结论!!!
文章目录
- A.涉及源码位置介绍
- B.源码深入解析
- 1.调用入口
- 2.TGT默认唯一ID生成器分析
- 3.默认NumericGenerator分析
- 4.默认RandomStringGenerator分析
- 5.总结:ID组装逻辑
- C.总结
A.涉及源码位置介绍
1.票据生成相关factory位于cas-server-core-tickets-api模块下的factory包下(该处的factory是调用ID生成器的入口):
2.ID生成器位于cas-server-core-tickets-api模块下的util包下(这里是支持的各种ID生成器):
3.ID生成器涉及的一些工具类位于cas-server-core-util-api模块下的gen包下(包括数字生成、字符串生成等等):
B.源码深入解析
ID生成器会被所有票据所用到,这里先分析TGT使用的默认ID生成器,ST类似。本节将分别从调用入口,几个部分详细的介绍CAS中ID生成器的设计思路。
1.调用入口
ID生成器会在创建票据前调用,唯一ID是创建票据的必须参数。
1.在创建票据时,会进入到org.apereo.cas.ticket.factory.DefaultTicketGrantingTicketFactory的create方法。
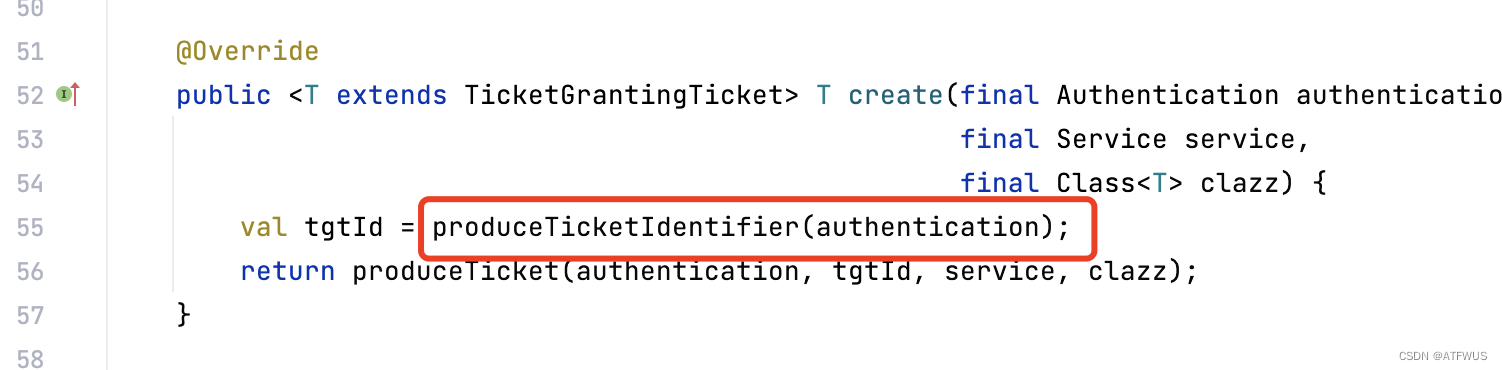
2.进入produceTicketIdentifier方法即可看到对ID生成器的调用:
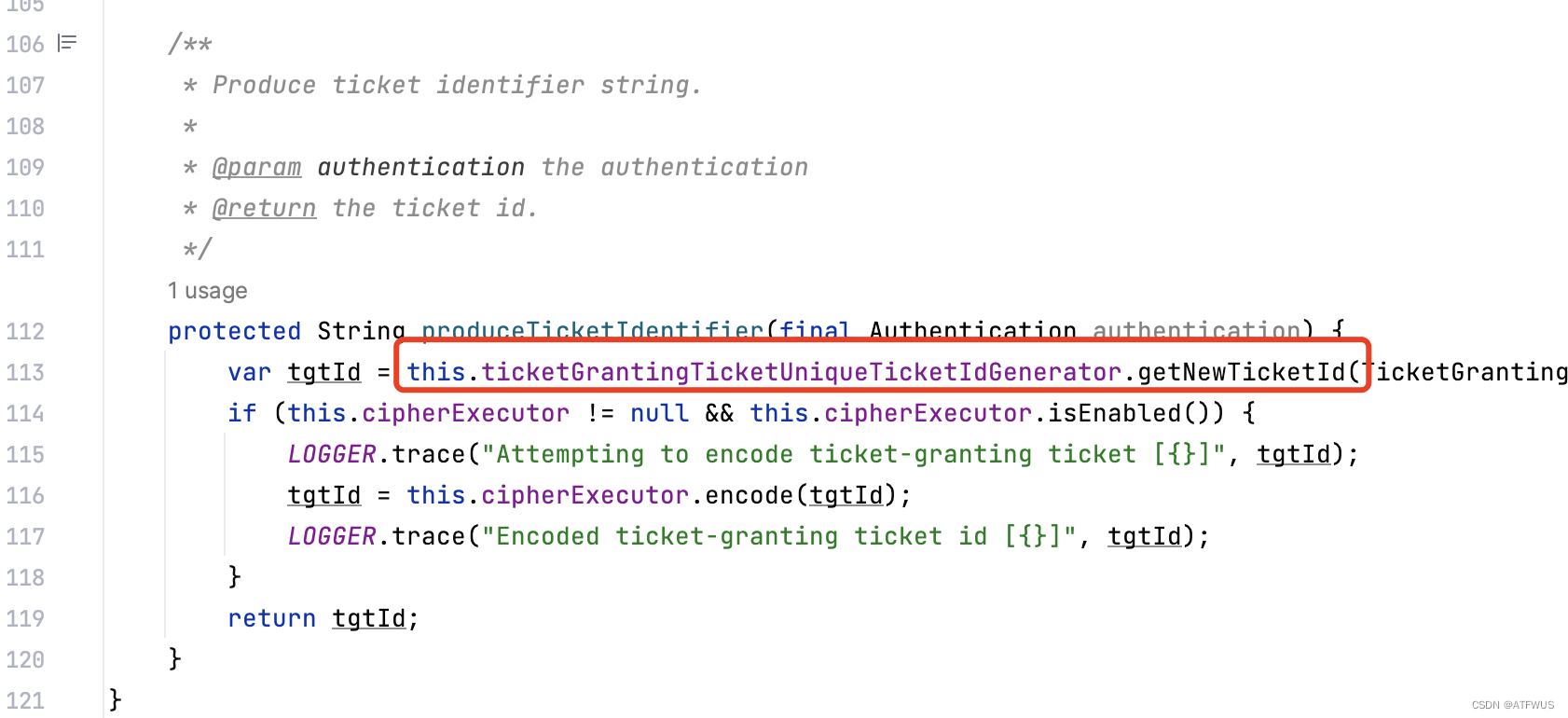
3.去DefaultTicketGrantingTicketFactory中寻找默认注入的ticketGrantingTicketUniqueTicketIdGenerator是哪个实现类。源码位置:org.apereo.cas.config.CasCoreTicketsConfiguration。
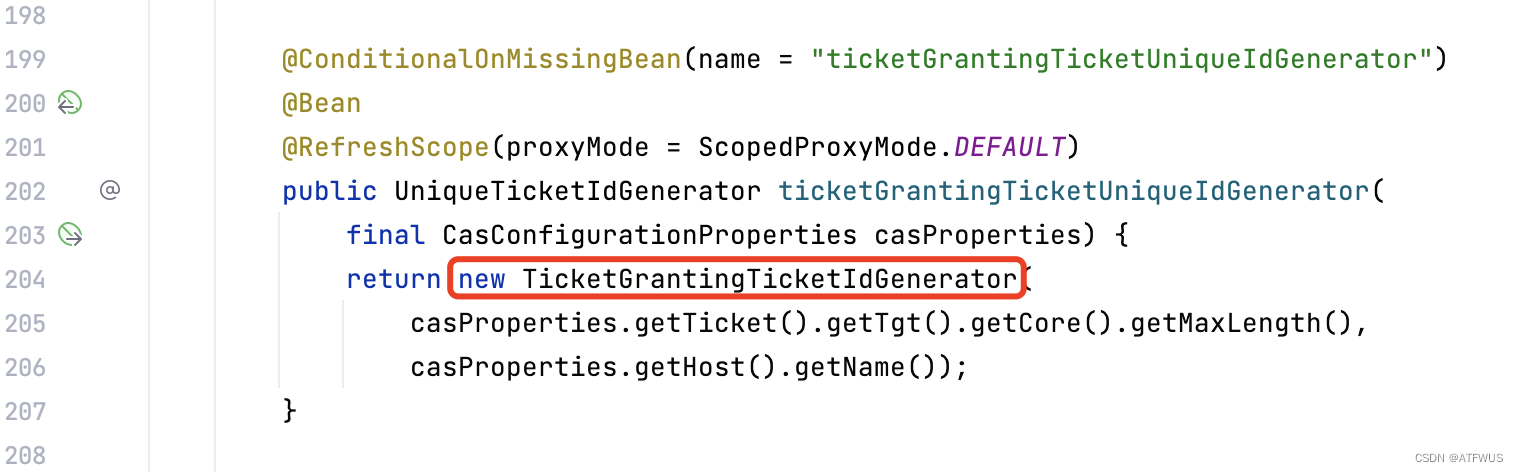
可以发现默认使用的是TicketGrantingTicketIdGenerator的实体,并且长度和后缀都是从配置文件中取的。查看配置类,可以看到默认的长度和后缀分别是(50和空):
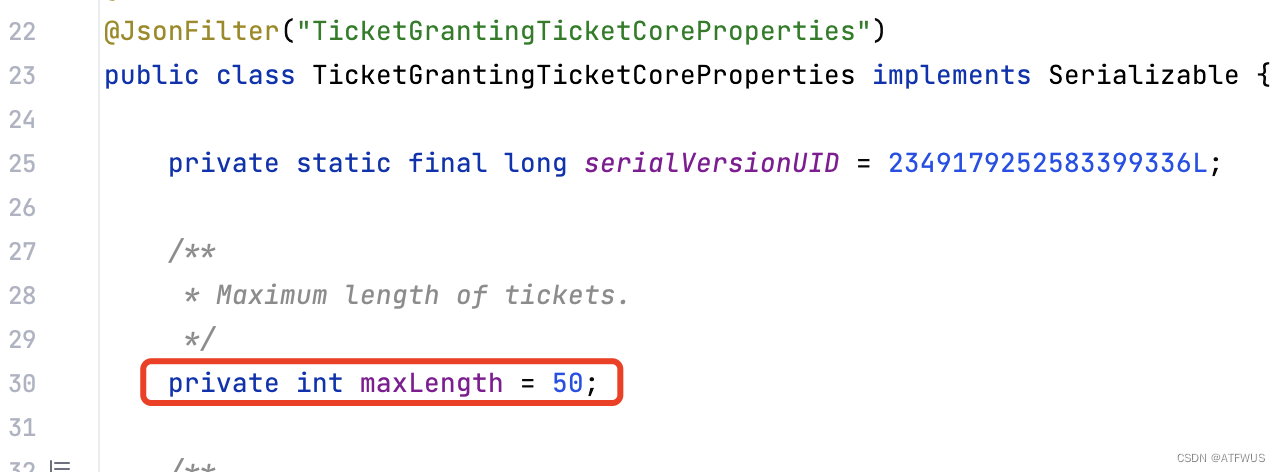
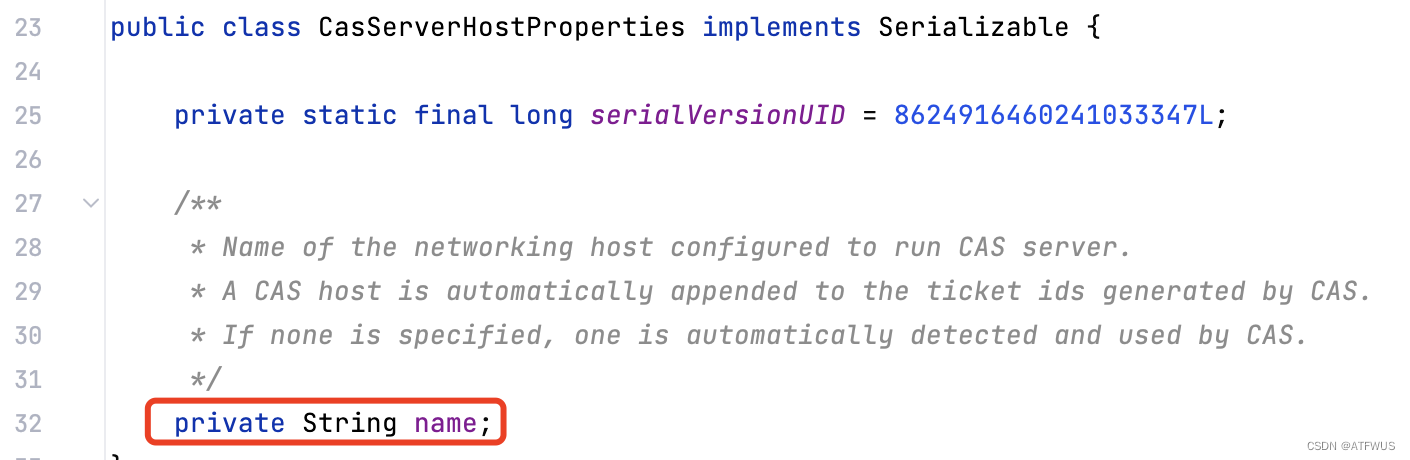
总结上述四个过程,可以确定,从创建票据的入口处,最终会调到TicketGrantingTicketIdGenerator的getNewTicketId方法。
2.TGT默认唯一ID生成器分析
1.先来看一下TicketGrantingTicketIdGenerator的类关系图:
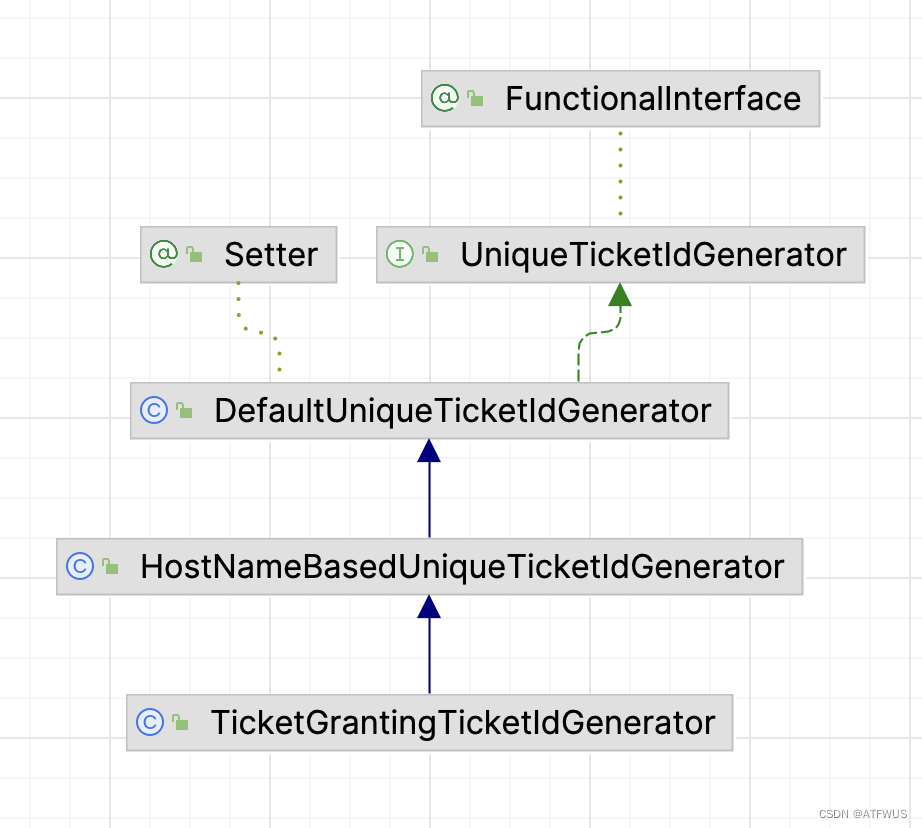 从上图可以发现,TGT的ID生成器实现了
从上图可以发现,TGT的ID生成器实现了UniqueTicketIdGenerator接口,继承自HostNameBasedUniqueTicketIdGenerator。
3.接下来看一下TicketGrantingTicketIdGenerator的源码:
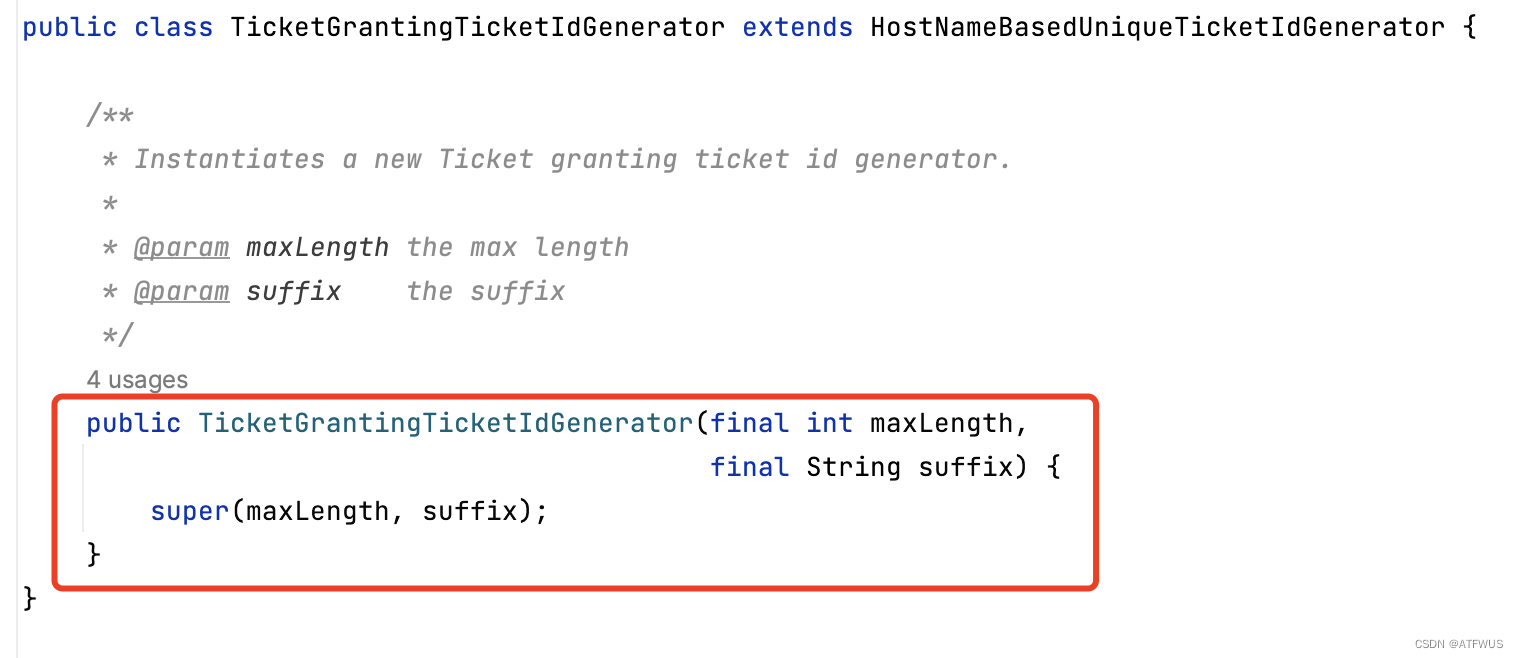
很简单,只是表示用的是HostNameBasedUniqueTicketIdGenerator的类。
4.接下来看一下HostNameBasedUniqueTicketIdGenerator的源码:(省去注释)
public class HostNameBasedUniqueTicketIdGenerator extends DefaultUniqueTicketIdGenerator {
public HostNameBasedUniqueTicketIdGenerator(final long maxLength, final String suffix) {
super(maxLength, determineTicketSuffixByHostName(suffix));
}
private static String determineTicketSuffixByHostName(final String suffix) {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(suffix)) {
return suffix;
}
return InetAddressUtils.getCasServerHostName();
}
}
可以发现,也很简单,就做了一件事情:是否配置了ID的后缀,没有则使用主机名作为ID的后缀。
5.上面两个类都很简单,所以重点在DefaultUniqueTicketIdGenerator中。直接上源码:
@Setter
public class DefaultUniqueTicketIdGenerator implements UniqueTicketIdGenerator {
/**
* The numeric generator to generate the static part of the id.
*/
private NumericGenerator numericGenerator;
/**
* The RandomStringGenerator to generate the secure random part of the id.
*/
private RandomStringGenerator randomStringGenerator;
/**
* Optional suffix to ensure uniqueness across JVMs by specifying unique
* values.
*/
private String suffix;
/**
* Creates an instance of DefaultUniqueTicketIdGenerator with default values
* including a {@link DefaultLongNumericGenerator} with a starting value of
* 1.
*/
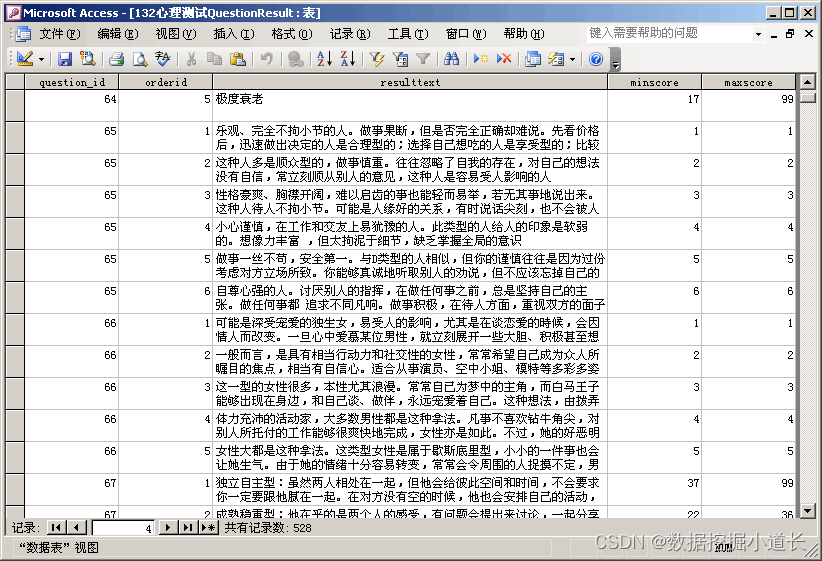
public DefaultUniqueTicketIdGenerator() {
this(TICKET_SIZE);
}
/**
* Creates an instance of DefaultUniqueTicketIdGenerator with a specified
* maximum length for the random portion.
*
* @param maxLength the maximum length of the random string used to generate
* the id.
*/
public DefaultUniqueTicketIdGenerator(final long maxLength) {
this(maxLength, null);
}
/**
* Creates an instance of DefaultUniqueTicketIdGenerator with a specified
* maximum length for the random portion.
*
* @param maxLength the maximum length of the random string used to generate
* the id.
* @param suffix the value to append at the end of the unique id to ensure
* uniqueness across JVMs.
*/
public DefaultUniqueTicketIdGenerator(final long maxLength, final String suffix) {
setMaxLength(maxLength);
setSuffix(suffix);
}
/**
* Creates an instance of DefaultUniqueTicketIdGenerator with a specified
* maximum length for the random portion.
*
* @param numericGenerator the numeric generator
* @param randomStringGenerator the random string generator
* @param suffix the value to append at the end of the unique id to ensure
* uniqueness across JVMs.
* @since 4.1.0
*/
public DefaultUniqueTicketIdGenerator(final NumericGenerator numericGenerator,
final RandomStringGenerator randomStringGenerator,
final String suffix) {
this.randomStringGenerator = randomStringGenerator;
this.numericGenerator = numericGenerator;
setSuffix(suffix);
}
/**
* Due to a bug in mod-auth-cas and possibly other clients in the way tickets are parsed,
* the ticket id body is sanitized to remove the character "_", replacing it with "-" instead.
* This might be revisited in the future and removed, once at least mod-auth-cas fixes
* the issue.
*
* @param prefix The prefix we want attached to the ticket.
* @return the ticket id
*/
@Override
public String getNewTicketId(final String prefix) {
val number = this.numericGenerator.getNextNumberAsString();
val ticketBody = this.randomStringGenerator.getNewString().replace('_', SEPARATOR);
val origSuffix = StringUtils.defaultString(this.suffix);
val finalizedSuffix = StringUtils.isEmpty(origSuffix) ? origSuffix : SEPARATOR + origSuffix;
return prefix + SEPARATOR + number + SEPARATOR + ticketBody + finalizedSuffix;
}
/**
* Sets max length of id generation.
*
* @param maxLength the max length
*/
public void setMaxLength(final long maxLength) {
this.randomStringGenerator = new Base64RandomStringGenerator(maxLength);
this.numericGenerator = new DefaultLongNumericGenerator(1);
}
}
其中有两个重要属性numericGenerator和randomStringGenerator。可以看到这两个对象的都是在setMaxLength方法中进行的初始化,getNewTicketId方法其实只是对这两个生成器的内容做一次简单的组装。
这里对两个对象初始化的时候,给randomStringGenerator传入的参数是票据最大长度,给numericGenerator传入的是1。
3.默认NumericGenerator分析
首先来看第一个对象,DefaultLongNumericGenerator是怎样生成数字的。
1.类关系图如下:
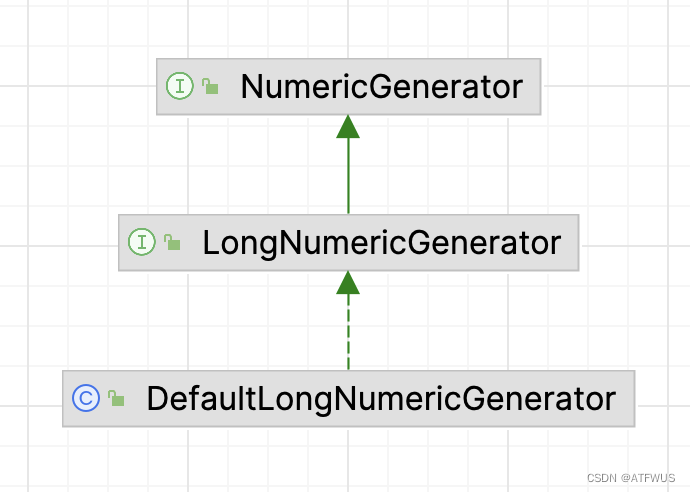
主要实现了两个接口。源码如下:
public class DefaultLongNumericGenerator implements LongNumericGenerator {
/**
* The maximum length the string can be.
*/
private static final int MAX_STRING_LENGTH = Long.toString(Long.MAX_VALUE).length();
/**
* The minimum length the String can be.
*/
private static final int MIN_STRING_LENGTH = 1;
private final AtomicLong count;
/**
* Instantiates a new default long numeric generator.
*/
public DefaultLongNumericGenerator() {
this(0);
}
/**
* Instantiates a new default long numeric generator.
*
* @param initialValue the initial value
*/
public DefaultLongNumericGenerator(final long initialValue) {
this.count = new AtomicLong(initialValue);
}
@Override
public long getNextLong() {
return this.getNextValue();
}
@Override
public String getNextNumberAsString() {
return Long.toString(this.getNextValue());
}
@Override
public int maxLength() {
return DefaultLongNumericGenerator.MAX_STRING_LENGTH;
}
@Override
public int minLength() {
return DefaultLongNumericGenerator.MIN_STRING_LENGTH;
}
/**
* Gets the next value.
*
* @return the next value. If the count has reached {@link Long#MAX_VALUE},
* then {@link Long#MAX_VALUE} is returned. Otherwise, the next increment.
*/
protected long getNextValue() {
if (this.count.compareAndSet(Long.MAX_VALUE, 0)) {
return Long.MAX_VALUE;
}
return this.count.getAndIncrement();
}
}
2.初始化时,首先初始化了一个原子变量,值为0。并且定义了最小字符串长度为1,最大字符串长度为Long最大值转为字符串的长度。在使用的时候,传入的初始值位1。
3.核心方法getNextNumberAsString实际上就是产生一个自增后的数字,其中,这个数字的自增操作采用原子变量及CAS的方式保证了线程安全。并且当达到Long的最大值后,又会从0开始循环使用。
总结:DefaultLongNumericGenerator实际上就是在保证线程安全的前提下生成一个自增的数字。
4.默认RandomStringGenerator分析
再来看是如何生成随机字符串的。
1.Base64RandomStringGenerator的类关系如下:
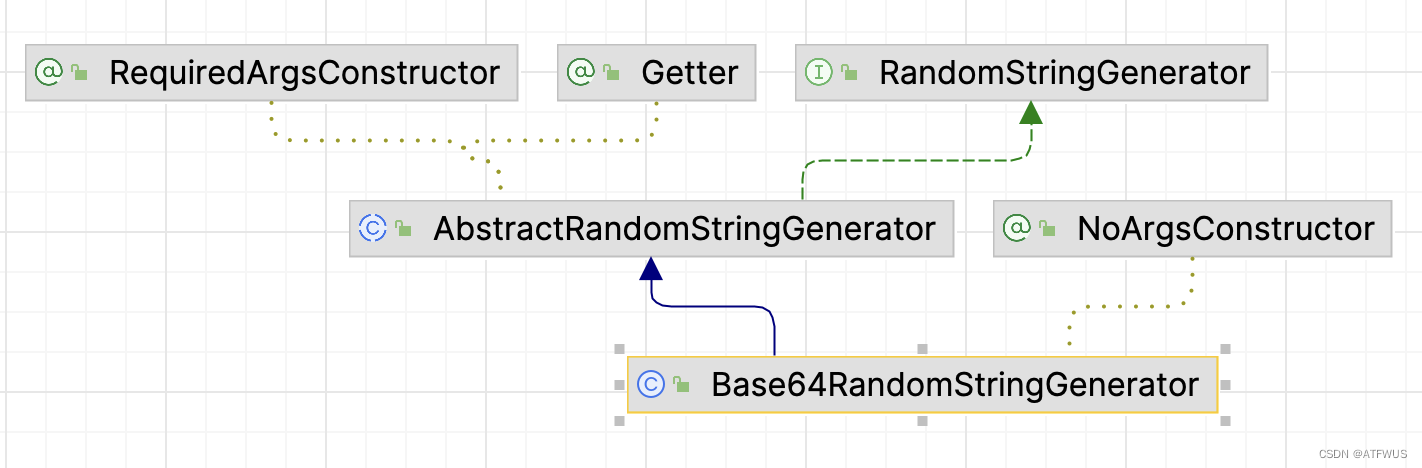
源码如下:
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Base64RandomStringGenerator extends AbstractRandomStringGenerator {
public Base64RandomStringGenerator(final long defaultLength) {
super(defaultLength);
}
/**
* Converts byte[] to String by Base64 encoding.
*
* @param random raw bytes
* @return a converted String
*/
@Override
protected String convertBytesToString(final byte[] random) {
return EncodingUtils.encodeUrlSafeBase64(random);
}
}
可以发现主要是将父类生成的随机字节转换成了Base64.
2.查看父类AbstractRandomStringGenerator。
@Getter
@RequiredArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
public abstract class AbstractRandomStringGenerator implements RandomStringGenerator {
/**
* An instance of secure random to ensure randomness is secure.
*/
protected final SecureRandom randomizer = RandomUtils.getNativeInstance();
/**
* Default string length before encoding.
*/
protected final long defaultLength;
/**
* Instantiates a new default random string generator
* with length set to {@link RandomStringGenerator#DEFAULT_LENGTH}.
*/
protected AbstractRandomStringGenerator() {
this(DEFAULT_LENGTH);
}
@Override
public String getAlgorithm() {
return randomizer.getAlgorithm();
}
/**
* Converts byte[] to String by simple cast. Subclasses should override.
*
* @param random raw bytes
* @return a converted String
*/
protected String convertBytesToString(final byte[] random) {
return new String(random, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
@Override
public String getNewString(final int size) {
val random = getNewStringAsBytes(size);
return convertBytesToString(random);
}
@Override
public String getNewString() {
return getNewString(Long.valueOf(getDefaultLength()).intValue());
}
@Override
public byte[] getNewStringAsBytes(final int size) {
val random = new byte[size];
this.randomizer.nextBytes(random);
return random;
}
}
核心是通过this.randomizer.nextBytes(random);生成随机字节。其中randomizer来自java.security包下的SecureRandom类。
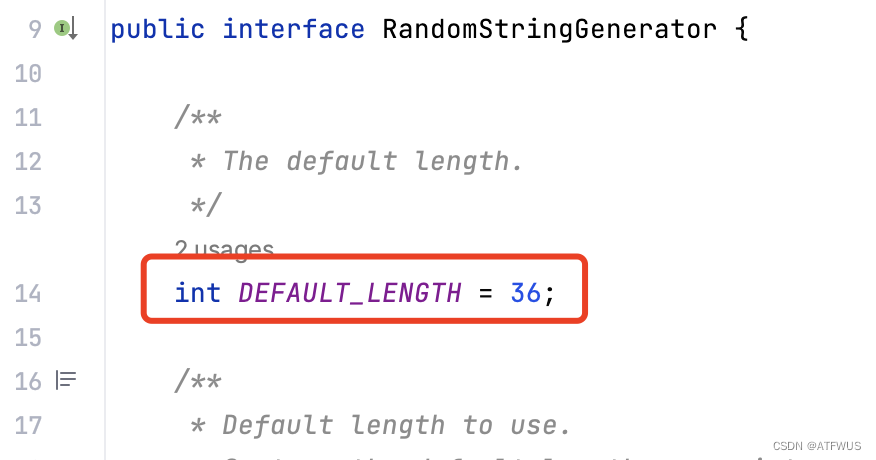
可以在顶级接口RandomStringGenerator中看到,默认的随机字节大小为36,但是默认ID生成器在调用的时候,传入的最大长度是50。所以最终产生了长度为50的字节数组。

5.总结:ID组装逻辑
核心组装逻辑如下:

其中:
- 前缀是在调用的时候传入的,是票据的类型:TGT或者ST。
- 数字是全局自增的数字。
- 字符串是随机50字节按BASE64进行编码,其中所有下划线会被替换成横杠。
- 后缀是配置定义,若配置未定义则是主机名。
- 每一个部分中间用横杠连接。
所以,默认的TGT ID是采用如下的规则生成的:
前缀(TGT或ST)-全局自增数字-随机50字节转成的BASE64-主机名或自定义后缀
一个TGT的样例如下:
TGT-1-OTGAU1o-LI-R-F-B1S3g8svY5kBDsQSeZ3sahJaZyP0k-GzFiywCjGRfYNc-FIdt84w-myMacBook-Pro
ST票据的默认ID生成除了前缀不同外,其余与TGT一致。
C.总结
从保障唯一性上来看:
- 从TGT唯一ID的结构可以看出唯一性,是由一个全局自增的数字和随机的50字节保证的,后缀可以由用户自定义,不是用来保证唯一性的。
- 注意,这个全局自增的数字是保存在内存中的,一旦CAS重启,这个数字将又会从0开始。随机的50个字节400位,产生冲突的概率极小。
从结构设计上来看:
- 可拓展性极强,基本上ID生成的所有过程都可以拓展,比如数字生成过程、随机字符串生成过程,ID组装过程,、后缀等等。
- 整个的ID生成器设计,将业务流程划分很明确,接口设计非常精细,可以多个类分离拓展完成的,绝不写在一个类里面。写在一个类里面意味着部分逻辑丧失拓展性。
- 上述所有分析都只是针对CAS的默认配置而言,对于不同的业务,可以通过新增
UniqueTicketIdGenerator接口的实现类,并注入容器中,实现自定义。或者采用overlay的方式重写某个实现类。
中肯评价:代码优美、拓展性极强
ATFWUS 2023-07-31