A. DS二叉排序树之创建和插入
给出一个数据序列,建立二叉排序树,并实现插入功能
对二叉排序树进行中序遍历,可以得到有序的数据序列
输入
第一行输入t,表示有t个数据序列
第二行输入n,表示首个序列包含n个数据
第三行输入n个数据,都是自然数且互不相同,数据之间用空格隔开
第四行输入m,表示要插入m个数据
从第五行起,输入m行,每行一个要插入的数据,都是自然数且和前面的数据不等
以此类推输入下一个示例
1
6
22 33 55 66 11 44
3
77
50
10
输出
第一行输出有序的数据序列,对二叉排序树进行中序遍历可以得到
从第二行起,输出插入第m个数据后的有序序列,输出m行
以此类推输出下一个示例的结果
11 22 33 44 55 66
11 22 33 44 55 66 77
11 22 33 44 50 55 66 77
10 11 22 33 44 50 55 66 77 #include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
};
void inorder(node *root) {
if (root->lchild != NULL) inorder(root->lchild);
cout << root->data << " ";
if (root->rchild != NULL) inorder(root->rchild);
}
void insert(node* root, node* s) {
if (s->data < root->data) {
if (root->lchild != NULL) insert(root->lchild, s);
else {
root->lchild = s; return;
}
}
else {
if (root->rchild != NULL) insert(root->rchild, s);
else {
root->rchild = s; return;
}
}
}
int main() {
int t; cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int num; cin >> num;
int sum; cin >> sum;
node* root=new node{sum,NULL,NULL};
for (int i = 0; i < num - 1; i++) {
cin >> sum;
node* s = new node{ sum,NULL,NULL };
insert(root, s);
}
inorder(root); cout << endl;
cin >> num;
while (num--) {
cin >> sum;
node* s = new node{ sum,NULL,NULL };
insert(root, s);
inorder(root); cout << endl;
}
}
}B. DS二叉排序树之查找
给出一个数据序列,建立二叉排序树,并实现查找功能
对二叉排序树进行中序遍历,可以得到有序的数据序列
输入
第一行输入t,表示有t个数据序列
第二行输入n,表示首个序列包含n个数据
第三行输入n个数据,都是自然数且互不相同,数据之间用空格隔开
第四行输入m,表示要查找m个数据
从第五行起,输入m行,每行一个要查找的数据,都是自然数
以此类推输入下一个示例
1
6
22 33 55 66 11 44
7
11
22
33
44
55
66
77
输出
第一行输出有序的数据序列,对二叉排序树进行中序遍历可以得到
从第二行起,输出查找结果,如果查找成功输出查找次数,如果查找失败输出-1
以此类推输出下一个示例的结果
11 22 33 44 55 66
2
1
2
4
3
4
-1#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
};
class Tree {
public:
node* root;
int count=0;
Tree();
void inorder(node* root);
void insert(node* root, node* s);
void research(node* root, int num);
};
Tree::Tree() {
root = new node{0,NULL,NULL};
}
void Tree::inorder(node* root) {
if (root->lchild != NULL) inorder(root->lchild);
cout << root->data << " ";
if (root->rchild != NULL) inorder(root->rchild);
}
void Tree::insert(node* root, node* s) {
if (s->data < root->data) {
if (root->lchild != NULL) insert(root->lchild, s);
else {
root->lchild = s; return;
}
}
else {
if (root->rchild != NULL) insert(root->rchild, s);
else {
root->rchild = s; return;
}
}
}
void Tree::research(node *root,int num) {
count++;
node* next = new node;
if (root->data == num) return;
else {
if (root->data > num) next = root->lchild;
else next = root->rchild;
}
if (next) research(next, num);
else count = 0;
}
int main() {
int t; cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int sum,num;
cin >> sum >> num;
Tree* tree = new Tree;
tree->root->data = num;
for (int i = 0; i < sum - 1; i++) {
cin >> num;
node* s = new node{ num,NULL,NULL };
tree->insert(tree->root, s);
}
tree->inorder(tree->root); cout << endl;
cin >> sum;
while (sum--) {
tree->count = 0;
cin >> num;
tree->research(tree->root, num);
if (tree->count != 0) cout << tree->count << endl;
else cout << "-1" << endl;
}
}
}C. DS二叉排序树之删除
给出一个数据序列,建立二叉排序树,并实现删除功能
对二叉排序树进行中序遍历,可以得到有序的数据序列
输入
第一行输入t,表示有t个数据序列
第二行输入n,表示首个序列包含n个数据
第三行输入n个数据,都是自然数且互不相同,数据之间用空格隔开
第四行输入m,表示要删除m个数据
从第五行起,输入m行,每行一个要删除的数据,都是自然数
以此类推输入下一个示例
1
6
22 33 55 66 11 44
3
66
22
77
输出
第一行输出有序的数据序列,对二叉排序树进行中序遍历可以得到
从第二行起,输出删除第m个数据后的有序序列,输出m行
以此类推输出下一个示例的结果
11 22 33 44 55 66
11 22 33 44 55
11 33 44 55
11 33 44 55 提示
当删除数据不在序列中,那么删除操作等于不执行,所以输出序列不变化
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
};
class Tree {
public:
node* root;
node* temp;
node* pre;
int flag=0;
int count = 0;
Tree();
void inorder(node* root);
void insert(node* root, node* s);
node* search(node* root, int num);
void remove(node* root, int num);
int check(node* p, int num);
};
int Tree::check(node* root, int num) {
if (num > root->data)
{
if (root->rchild == NULL) { flag = 1; return -1; }
if (root->rchild->data == num)
{
if (root->rchild->lchild == NULL && root->rchild->rchild == NULL)pre = root;
}
check(root->rchild, num);
}
else if (num == root->data)
{
temp = root;
return 1;
}
else if (num < root->data)
{
if (root->lchild == NULL) { flag = 1; return -1;}
if (root->lchild->data == num)
{
if (root->lchild->lchild == NULL && root->lchild->rchild == NULL)pre = root;
}
check(root->lchild, num);
}
if (flag == 1) return -1;
else return 1;
}
void Tree::remove(node* p, int num) {
if (!p->rchild && p->lchild != NULL) {
node* q = new node();
q = p;
p = p->lchild;
delete p;
}
else if (!p->lchild && p->rchild != NULL)
{
node* q = new node();
q = p;
p = p->lchild;
delete q;
}
else if (p->lchild == NULL && p->rchild == NULL) {
if (pre->lchild->data == num) pre->lchild = NULL;
else pre->rchild = NULL;
node* q = new node();
q = p;
delete q;
}
else {
node* q = new node();
node* s = new node();
q = p;
s = p->lchild;
while (s->rchild) {
q = s;
s = s->rchild;
}
p->data = s->data;
if (q != p) q->rchild = s->lchild;
else q->lchild = s->lchild;
delete s;
}
}
Tree::Tree() {
root = new node{ -1,NULL,NULL };
}
void Tree::inorder(node* root) {
if (root->lchild) inorder(root->lchild);
cout << root->data << " ";
if (root->rchild) inorder(root->rchild);
}
void Tree::insert(node* root, node* s) {
if (s->data < root->data) {
if (root->lchild != NULL) insert(root->lchild, s);
else {
root->lchild = s; return;
}
}
else {
if (root->rchild != NULL) insert(root->rchild, s);
else {
root->rchild = s; return;
}
}
}
node* Tree::search(node* root, int num) {
if (root == NULL) return NULL;
count++;
node* next = new node;
if (root->data == num) return root;
else {
if (root->data > num) next = root->lchild;
else next = root->rchild;
}
if (next) return search(next, num);
else {
count = 0; return NULL;
}
}
int main() {
int t; cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int sum, num;
cin >> sum >> num;
Tree* tree = new Tree;
tree->root->data = num;
for (int i = 0; i < sum - 1; i++) {
cin >> num;
node* s = new node{ num,NULL,NULL };
tree->insert(tree->root, s);
}
tree->inorder(tree->root); cout << endl;
cin >> sum;
while (sum--) {
cin >> num;
int flag = tree->check(tree->root, num);
if(flag==1)tree->remove(tree->temp, num);
tree->inorder(tree->root); cout << endl;
}
}
}D. DS查找—二叉树平衡因子
二叉树用数组存储,将二叉树的结点数据依次自上而下,自左至右存储到数组中,一般二叉树与完全二叉树对比,比完全二叉树缺少的结点在数组中用0来表示。
计算二叉树每个结点的平衡因子,并按后序遍历的顺序输出结点的平衡因子。
--程序要求--
若使用C++只能include一个头文件iostream;若使用C语言只能include一个头文件stdio
程序中若include多过一个头文件,不看代码,作0分处理
不允许使用第三方对象或函数实现本题的要求
输入
测试次数t
每组测试数据一行,数组元素个数n,后跟n个字符,二叉树的数组存储。
2
6 ABC00D
24 ABCD0EF0000H00000000000I
输出
对每组测试数据,按后序遍历的顺序输出树中结点的平衡因子(测试数据没有空树)
B 0
D 0
C 1
A -1
D 0
B 1
I 0
H 1
E 2
F 0
C 2
A -2
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int height(char* tree, int i, int n) {
if (tree[i] == '0' || i >= n) return 0;
else {
int left = height(tree, 2 * i + 1, n) + 1;
int right = height(tree, 2 * i + 2, n) + 1;
return left > right ? left : right;
}
}
void func(char* tree, int i, int n) {
if (i < n) {
if (tree[i] != '0') {
func(tree, 2*i+1,n);
func(tree, 2 * i + 2, n);
int differrnt = height(tree, 2 * i + 1, n) - height(tree, 2 * i + 2, n);
cout << tree[i] << " " << differrnt << endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
int t; cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n; cin >> n;
char* tree = new char[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> tree[i];
func(tree, 0, n);
}
}E. DS哈希查找—二次探测再散列
定义哈希函数为H(key) = key%11。输入表长(大于、等于11),输入关键字集合,用二次探测再散列构建哈希表,并查找给定关键字。
输入
测试次数t
每组测试数据格式如下:
哈希表长m、关键字个数n
n个关键字
查找次数k
k个待查关键字
1
12 10
22 19 21 8 9 30 33 4 41 13
4
22
15
30
41
输出
对每组测试数据,输出以下信息:
构造的哈希表信息,数组中没有关键字的位置输出NULL
对k个待查关键字,分别输出:
0或1(0—不成功,1—成功)、比较次数、查找成功的位置(从1开始)
22 9 13 NULL 4 41 NULL 30 19 8 21 33
1 1 1
0 3
1 3 8
1 6 6
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int t; cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int m, n;
cin >> m >> n;
int* a = new int[m + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++)a[i] = -9999;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int num; cin >> num;
int power = 0,flag=0;
while (power <= m / 2) {
flag++;
int sign;
if (flag >= 2 && flag % 2 == 0) power++;
if (flag % 2 == 0) sign = 1;
else sign = -1;
int index = (num % 11 + sign * power * power) % m;
if (index < 0) index = m + index;
if (a[index] == -9999) {
a[index] = num; break;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (a[i] != -9999) cout << a[i];
else cout << "NULL";
if (i != m - 1) cout << " ";
else cout << endl;
}
int tt; cin >> tt;
while (tt--) {
int num; cin >> num;
int time = 0, power = 0, flag = 0;
while (1) {
time++; flag++;
int sign;
if (flag >= 2 && flag % 2 == 0) power++;
if (flag % 2 == 0) sign = 1;
else sign = -1;
int index = (num % 11 + sign * power * power) % m;
if (index < 0) index = m + index;
if (a[index] == -9999 || power > m / 2) {
cout << "0 " << time << endl;
break;
}
if (a[index] == num) {
cout << "1 " << time << " " << index + 1 << endl;
break;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}F. DS哈希查找--链地址法(表头插入)
给出一个数据序列,建立哈希表,采用求余法作为哈希函数,模数为11,哈希冲突用链地址法和表头插入
如果首次查找失败,就把数据插入到相应的位置中
实现哈希查找功能
输入
第一行输入n,表示有n个数据
第二行输入n个数据,都是自然数且互不相同,数据之间用空格隔开
第三行输入t,表示要查找t个数据
从第四行起,每行输入一个要查找的数据,都是正整数
6
11 23 39 48 75 62
6
39
52
52
63
63
52
输出
每行输出对应数据的查找结果
6 1
error
8 1
error
8 1
8 2
注意,当两次输入要相同的查找数据,如果第一次查找不成功就会执行插入,那么第二次查找必然成功,且查找次数为1次(因为做表头插入)
例如示例数据中输入两次52,第一次查找失败就把52插入到位置8,第二次查找就成功了,所以第一次输出error,第二次就输出8 1
为什么第三次输入52会输出8 2
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node* next;
};
class Hash {
public:
node* hash;
int n;
Hash(int n);
void insert(int index, int num);
void search(int num);
};
Hash::Hash(int n) {
this->n = n;
hash = new node[20];
}
void Hash::insert(int index, int num) {
node* p = new node();
p->next = hash[index].next;
p->data = hash[index].data;
hash[index].data = num;
hash[index].next = p;
}
void Hash::search(int num) {
int num1 = num % 11, count = 0,flag=0;
node* p = new node();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (hash[i].key == num1) {
flag = 1;
p = &hash[i];
while (p != NULL) {
count++;
if (p->data == num) {
cout << num1 << " " << count << endl;
break;
}
p = p->next;
}
if (p == NULL) {
cout << "error" << endl;
insert(i, num);
}
break;
}
}
if (flag == 0) {
cout << "error" << endl;
n += 1;
hash[n - 1].data = num;
hash[n - 1].key = num % 11;
hash[n - 1].next = NULL;
}
}
int main() {
int n,num; cin >> n;
Hash hs(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> num;
hs.hash[i].key = num % 11;
hs.hash[i].data = num;
hs.hash[i].next = NULL;
}
int t; cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> num;
hs.search(num);
}
return 0;
}G. DS哈希查找--Trie树
Trie树又称单词查找树,是一种树形结构,如下图所示。
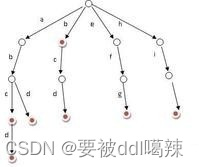
它是一种哈希树的变种。典型应用是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。它的优点是:利用字符串的公共前缀来节约存储空间,最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希表高。
输入的一组单词,创建Trie树。输入字符串,计算以该字符串为公共前缀的单词数。
(提示:树结点有26个指针,指向单词的下一字母结点。)
输入
测试数据有多组
每组测试数据格式为:
第一行:一行单词,单词全小写字母,且单词不会重复,单词的长度不超过10
第二行:测试公共前缀字符串数量t
后跟t行,每行一个字符串
abcd abd bcd efg hig
3
ab
bc
abcde输出
每组测试数据输出格式为:
第一行:创建的Trie树的层次遍历结果
第2~t+1行:对每行字符串,输出树中以该字符串为公共前缀的单词数。
abehbcficddggd
2
1
0#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct node {
char data;
struct node* next[26];
};
class Trie {
public:
struct node* trie;
Trie();
int getnum(node* t);
void print(node *t);
};
Trie::Trie() {
trie = new node[26];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
trie[i].data = '0';
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) trie[i].next[j] = NULL;
}
}
void Trie::print(node* t) {
queue<node*> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (t[i].data != '0') q.push(&t[i]);
}
while (!q.empty()) {
node* p = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << p->data;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (p->next[i] != NULL) q.push(p->next[i]);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int Trie::getnum(node* t) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (t->next[i] != NULL) count += getnum(t->next[i]);
}
if (count == 0) return 1;
else return count;
}
int main() {
char* s = new char[10000];
int n = 0;
while ((s[n] = getchar()) != '\n') n++;
Trie ti;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string s1;
while (s[i] != ' ' && i < n) {
s1 += s[i]; i++;
}
node* fa = &ti.trie[s1[0] - 'a'];
fa->data = s1[0];
for (int j = 1; j < (int)s1.length(); j++) {
if (fa->next[s1[j] - 'a'] != NULL) {
fa = fa->next[s1[j] - 'a'];
continue;
}
node* temp = new node;
temp->data = s1[j];
for (int k = 0; k < 26; k++) temp->next[k] = NULL;
fa->next[s1[j] - 'a'] = temp;
fa = fa->next[s1[j] - 'a'];
}
}
ti.print(ti.trie);
int t; cin >>t;
string ss;
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
cin >> ss;
node* fa = &ti.trie[ss[0] - 'a'];
for (int j = 1; j < (int)ss.length(); j++) {
fa = fa->next[ss[j] - 'a'];
if (fa == NULL) break;
}
if (fa == NULL) cout << "0" << endl;
else cout << ti.getnum(fa)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}H. 搜索树判断
对于二叉搜索树,我们规定任一结点的左子树仅包含严格小于该结点的键值,而其右子树包含大于或等于该结点的键值。如果我们交换每个节点的左子树和右子树,得到的树叫做镜像二叉搜索树。
现在我们给出一个整数键值序列,请编写程序判断该序列是否为某棵二叉搜索树或某镜像二叉搜索树的前序遍历序列,如果是,则输出对应二叉树的后序遍历序列。
输入
输入的第一行包含一个正整数N(≤1000),第二行包含N个整数,为给出的整数键值序列,数字间以空格分隔。
7
8 6 5 7 10 8 11输出
输出的第一行首先给出判断结果,如果输入的序列是某棵二叉搜索树或某镜像二叉搜索树的前序遍历序列,则输出YES,否侧输出NO。如果判断结果是YES,下一行输出对应二叉树的后序遍历序列。数字间以空格分隔,但行尾不能有多余的空格。
YES
5 7 6 8 11 10 8#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
};
class Tree {
node* root;
int* pre;
int* post;
int* a;
int n;
public:
Tree(int n);
void create(int *a);
void insert(node* root, node *s);
void postorder(node*root,int& count);
void preorder(node* root,int& count);
bool pre_dst();
bool post_dst();
void print();
};
void Tree::print() {
int count1 = 0, count2 = 0;
preorder(root, count1);
postorder(root, count2);
if (pre_dst() || post_dst()) {
cout << "YES" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) cout << post[i] << " ";
cout << post[n - 1];
}
else cout << "NO" << endl;
}
bool Tree::pre_dst() {//初始序列与先序序列或者初始序列的倒序与后序序列是否相等
bool flag=true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (a[i] != pre[i]) {
flag = false;
break;
}
return flag;
}
bool Tree::post_dst() {
bool flag = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (a[i] != post[n - i + 1]) {
flag = false;
break;
}
return flag;
}
void Tree::preorder(node* root,int& count) {
if (root == NULL) return;
pre[count++] = root->data;
preorder(root->lchild,count);
preorder(root->rchild, count);
}
void Tree::postorder(node* root, int& count) {
if (root == NULL) return;
postorder(root->lchild, count);
postorder(root->rchild, count);
post[count++] = root->data;
}
Tree::Tree(int n) {
this->n = n;
a = new int[n];
pre = new int[n];
post = new int[n];
}
void Tree::insert(node* root, node* s) {
if (s->data < root->data) {
if (root->lchild != NULL) insert(root->lchild, s);
else {
root->lchild = s; return;
}
}
else {
if (root->rchild != NULL) insert(root->rchild, s);
else {
root->rchild = s; return;
}
}
}
void Tree::create(int *a) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) this->a[i]= a[i];
root = new node{ a[0],NULL,NULL };
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
node* s = new node{ a[i],NULL,NULL};
insert(root,s);
}
}
int main() {
int n; cin >> n;
int* a = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i];
Tree *tree=new Tree(n);
tree->create(a);
tree->print();
}




![[论文解析]DREAMFUSION: TEXT-TO-3D USING 2D DIFFUSION](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c19ffe4f29a64662a723e7249b932607.png)