JDBCTemplate
是Spring对JDBC的封装,使用JDBCTemplate方便实现对数据的操作。
<!-- orm:Object relationship mapping m对象 关系 映射-->
引入依赖
<!-- 基于Maven依赖的传递性,导入spring-content依赖即可导入当前所需的所有jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Mybatis核心-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.18</version>
</dependency>
<!-- LomBok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.10</version>
</dependency>
<!-- log4j日志-->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.12</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring持久层jar包-->
<!-- orm:Object relationship mapping m对象 关系 映射-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 德鲁伊数据库连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.21</version>
</dependency>
创建实体类
User
package com.lobo.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.ToString;
/**
* className: User<br/>
* author: MacieSerenity <br/>
* date: 2022-08-14 14:24
**/
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
准备DataSource
jdbc-config.properties
#jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=li1473606768
Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd">
<!-- 引入jdbc-config.properties文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc-config.properties"/>
<bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" id="druidDataSource" >
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource" ></property>
</bean>
</beans>
注意,Druid数据库连接池配置的property的name=“driverClassName”,不要打错了
测试
package com.lobo;
import com.lobo.entity.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.util.List;
/**
* className: test<br/>
* author: MacieSerenity <br/>
* date: 2022-08-14 10:28
**/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring-jdbc.xml")
public class test {
//@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//指定当前测试类在spring的测试环境中执行,此时就可以通过依赖注入的方式直接获取IOC容器中的bean
//@ContextConfiguration
//设置Spring测试环境的配置文件
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplateInsert(){
String preparedSql="insert into t_user(username,password,age,gender,email) values (?,?,?,?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.update(preparedSql,"admin","123",30,"男","hello@123.com");
}
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplateQuery(){
String sql = "select * from t_user where id = ?";
User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class), 1);
System.out.println(user);
}
@Test
public void getAllUser(){
String sql = "select * from t_user";
List<User> query = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class));
query.forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Test
public void testGetCount(){
String sql = "select count(*) from t_user";
Integer integer = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class);
System.out.println(integer);
}
}
声明式事务
编程式事务
Connection conn=null;
try{
//开启事务
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//核心操作
//提交事务
conn.commit()
}catch(Exception e){
//回滚事务
conn.rollBack();
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//释放数据库连接
conn.close()
}
以上方式存在的缺陷:
操作繁琐、复用性不高
声明式事务
由于事务的代码相对固定,所以框架就可以将固定模式的代码抽取出来,进行相关的封装。
封装之后:提高开发效率,消除冗余代码、可以对健壮性、性能等方面优化。
编程式事务:程序员自己写代码实现功能
声明式事务:通过配置让框架自动实现功能
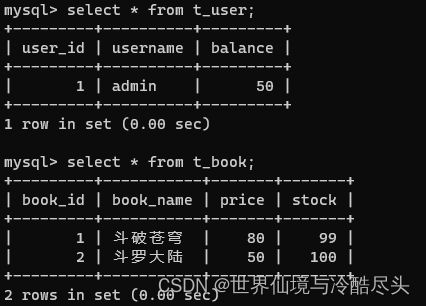
创建测试表:t_book和t_user
drop table if exists t_book;
CREATE TABLE t_book(
book_id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
book_name varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '图书名称',
price int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '价格',
stock int(10) unsigned DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '库存(无符号)',
PRIMARY KEY (book_id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into t_book(book_id,book_name,price,stock) values (1,'斗破苍穹' ,80,100),(2,'斗罗大陆',50,100);
drop table if exists t_user;
CREATE TABLE t_user(
user_id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
username varchar (20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户名',
balance int(10) unsigned DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' 余额(无符号) ',
PRIMARY KEY (user_id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into t_user(user_id,username,balance) values (1,'admin',50);
创建Controller、Service、Dao层
package com.lobo.controller;
@Controller
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
public void buyBook(Integer userId,Integer bookId){
bookService.buyBook(userId,bookId);
}
}
-----service接口
package com.lobo.service;
public interface BookService {
/**
* 买书
* @param userId 用户ID
* @param bookId 图书ID
*/
void buyBook(Integer userId, Integer bookId);
}
-----service实现类
package com.lobo.service.impl;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Override
public void buyBook(Integer userId, Integer bookId) {
//1、查询图书价格
Integer price =bookDao.getPriceByBookId(bookId);
//2、更新图书库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
//3、更新用户余额
bookDao.updateBalance(userId,price);
}
}
-------Dao接口
package com.lobo.dao;
public interface BookDao {
/**
* 根据图书ID获取价格
* @param bookId 图书ID
* @return 图书的价格
*/
Integer getPriceByBookId(Integer bookId);
/**
* 更新图书库存
* @param bookId 图书ID
*/
void updateStock(Integer bookId);
/**
* 更新用户余额
* @param userId 用户ID
* @param price 价格
*/
void updateBalance(Integer userId, Integer price);
}
-------Dao层实现
package com.lobo.dao.impl;
import com.lobo.dao.BookDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* className: BookDaoImpl<br/>
* author: MacieSerenity <br/>
* date: 2022-08-14 15:30
**/
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public Integer getPriceByBookId(Integer bookId) {
String sql = "select price from t_book where book_id =?";
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,Integer.class,bookId);
}
@Override
public void updateStock(Integer bookId) {
String sql = "update t_book set stock = stock - 1 where book_id= ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,bookId);
}
@Override
public void updateBalance(Integer userId, Integer price) {
String sql="update t_user set balance = balance - ? where user_id =?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,price,userId);
}
}
创建配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd">
<!-- 包扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lobo"/>
<!-- 引入jdbc-config.properties文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc-config.properties"/>
<bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" id="druidDataSource" >
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" id="jdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
创建测试类
package com.lobo;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:tx-annotation.xml")
public class testBuyBook {
@Autowired
private BookController bookController;
@Test
public void buyBook(){
bookController.buyBook(1,1);
}
}
错误:
org.springframework.dao.DataIntegrityViolationException: PreparedStatementCallback; SQL [update t_user set balance = balance - ? where user_id =?]; Data truncation: BIGINT UNSIGNED value is out of range in '(`mybatisstudy`.`t_user`.`balance` - 80)'; nested exception is com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.MysqlDataTruncation: Data truncation: BIGINT UNSIGNED value is out of range in '(`mybatisstudy`.`t_user`.`balance` - 80)'
因为图书价格为80,而用户ID为1的用户只有80,50-80之后就会变为-30,而我们使用的是无符号的数来表示,这样变成负数之后,就会超出范围。
此时,由于没有开启事务,第一个方法update了图书的库存,而第二个方法扣除用户余额时失败。
我们应该将这几个方法封装在一个事务当中,一旦有某一个程序执行错误,我们都需要将整个事务回滚。
开启事务
需要在配置文件中开启事务,以及开启@Transactional注解
在tx-annotation.xml的spring配置类中添加以下内容
<!-- 配置事务管理器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="dataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource" />
</bean>
<!-- 开启事务的注解驱动,注意是使用的tx-->
<!-- 将事务管理器中的通知作用到切面中-->
<!-- 将@Transaction注解所表示的方法或者类中的所有方法使用事务进行管理-->
<!-- 若事务管理器bean的id默认为transactionManager,则该属性可以不用填写-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="dataSourceTransactionManager" />
记住要选择tx:annotation-driven中tx结尾的标签
然后在需要进行事务管理的方法或者类中,使用@Transactional进行标记(一般事务标记在Service层中)
package com.lobo.service.impl;
...
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Override
@Transactional
public void buyBook(Integer userId, Integer bookId) {
//1、查询图书价格
Integer price =bookDao.getPriceByBookId(bookId);
//2、更新图书库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
//3、更新用户余额
bookDao.updateBalance(userId,price);
}
}
* 声明式事务的配置步骤:
* 1、在Spring的配置文件中配置事务管理器
* 2、开启事务的注解驱动
* 只需要在需要被事务管理的方法上,添加@Transactional注解,该方法就会被事务管理器管理
声明式事务的属性
只读
告诉数据库,我们当前的操作没有任何修改或者写的操作,这样数据库就可以针对查询操作来进行优化:
@Transactional(readOnly=true)
若在声明了只读的方法或者类中,使用了增删改操作,会抛出以下异常:
SQLException:Connection is read-only,Queries leading to data modification are not allowd;
不光可以防止脏读,开启高隔离后,多个读操作成一个事务还可以防止不可重复读
超时
事务执行的过程中,有可能会因为某些问题导致程序卡主,从而长时间占用数据库资源,而长时间占用资源大概率是因为程序运行出现了问题(程序、数据库、网络等)
此时这个出现问题的程序就应该回滚,释放资源。
@Transactional(timeout = 3)
3表示3秒,以秒为单位
默认是-1,也就是永久等待
可以使用TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);来测试
若超时,会抛出以下异常:
TransactionTimeOutException:Transaction time out:deadline was ...
抛出异常后,强制回滚
回滚策略
声明式事务默认只对所有的运行时异常进行回滚,编译时异常不进行回滚。
因为什么进行回滚:
rollbackForClassName
rollbackFor
(一般不使用前两个)
不因为什么进行回滚:
noRollBackFor
noRollbackForClassName
如果在事务运行中,出现了计算错误的异常(举例),我们不希望对计算错误的异常进行回滚,则可以使用
这里的noRollBackFor的参数是一个数组对象,当数组内的对象只有一个时,可以不使用{}包裹,而数组内有多个时,需要使用{}进行包裹,且用逗号分割
@Transaction(noRollBackFor = ArithmeticException.class)
或者
@Transaction(noRollBackFor = java.lang.ArithmeticException ) 全类名
隔离级别
事务的隔离级别
读未提交 read uncommited
只存在理论上,允许事务A读取事务B未提交的修改
读已提交 read commited
事务A只能读取事务B已经提交的修改,可能会产生脏读
可重复读 repeatable read
事务A可以多次读取一个字段中相同的值,事务A执行期间,禁止其它事务对这个字段进行更新,也就是当前事务只会读取到同一个值。可能会产生幻读
序列化 serializable
确保事务A可以多次从一个表中读取到相同的行,在事务A执行期间,禁止其他事务对这个表进行添加、更新、删除操作。可以避免任何并发问题,但是性能低下。
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 读未提交read uncommited | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 读已提交read commited | 否 | 是 | 是 |
| 可重复读repeatable read | 否 | 否 | 是 |
| 序列化serializable | 否 | 否 | 否 |
各个数据库产品对事务隔离级别的支持
| 隔离级别 | Oracle | MySQL |
|---|---|---|
| read uncommited | x | v |
| read commited | v | v |
| repeatable read | x | v |
| serializable | v | v |
使用方式:
@Transactional(isolation= Isolation.DEFAULT)//使用数据默认的隔离级别
@Transactional(isolation= Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITED)//读未提交
@Transactional(isolation= Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)//读已提交
@Transactional(isolation= Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ)//可重复读
@Transactional(isolation= Isolation.SERIALIZABLE)//序列化
事务的传播性
停止事务的传播
新建CheckoutService接口
package com.lobo.service;
...
public interface CheckoutService {
/**
* 为多本书结账
* @param userId 用户ID
* @param bookIds 图书ID
*/
void checkOut(Integer userId, Integer[] bookIds);
}
CheckoutServiceImpl
package com.lobo.service.impl;
...
@Service
public class CheckoutServiceImpl implements CheckoutService {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@Override
@Transactional
public void checkOut(Integer userId, Integer[] bookIds) {
for(Integer bookId:bookIds){
bookService.buyBook(userId,bookId);
}
}
}
我们在这个新的类中添加了一个事务,这个方法的功能是调用Service中的其它事务
package com.lobo.service.impl;
...
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Override
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void buyBook(Integer userId, Integer bookId) {
//1、查询图书价格
Integer price =bookDao.getPriceByBookId(bookId);
//2、更新图书库存
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
//3、更新用户余额
bookDao.updateBalance(userId,price);
}
}
可以看出我们的循环是一个事务,而循环内调用的buyBook又是另外一个事务。
测试:
@Test
public void buyBook(){
bookController.checkOut(1,new Integer[]{1,2});
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) //默认值
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIERS_NEW) //开启新事务(使用自己的事务)
当设置为默认时,买两本书的任何一本买不起,都会直接触发事务的回滚,回滚到一开始还没有买书的位置;
而设置为第二种开启新的事务时,其中每一次执行BuyBook都是一次新的事务,无法购买第二本书不会影响第一本书的购买,即便是回滚,也是回滚到买第二本书之前。
mysql> select * from t_user;
+---------+----------+---------+
| user_id | username | balance |
+---------+----------+---------+
| 1 | admin | 20 |
+---------+----------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t_book;
+---------+-----------+-------+-------+
| book_id | book_name | price | stock |
+---------+-----------+-------+-------+
| 1 | 斗破苍穹 | 80 | 98 |
| 2 | 斗罗大陆 | 50 | 100 |
+---------+-----------+-------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
当设置为默认时,会使用所有的事务,也就是事务的嵌套,将多个事务视作一个事务,被嵌套的任何一个事务失败或者超时,都会使最外面的事务失效回滚。
而设置为 Propagation.REQUIERS_NEW 时,在遇见@Transactional注解时,会自动创建一个新的事务,这个事务独立于其它被嵌套的事务,独立执行。
两个属性中,回滚的地方才是区别(大回滚和小回滚)
基于xml配置文件的声明式事务
想要基于XML配置文件配置声明式事务的话,必须引入aspect的依赖
<!-- spring 切面-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
然后需要在XML文件中写入:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 包扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lobo"/>
<!-- 引入jdbc-config.properties文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc-config.properties"/>
<bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" id="druidDataSource" >
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" id="jdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="dataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource" />
</bean>
<!-- 开启事务的注解驱动,注意是使用的tx-->
<!-- 将事务管理器中的通知作用到切面中-->
<!-- 将@Transaction注解所表示的方法或者类中的所有方法使用事务进行管理-->
<!-- 若事务管理器bean的id默认为transactionManager,则该属性可以不用填写-->
<!-- <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="dataSourceTransactionManager" />-->
<!-- 基于xml的配置事务管理需要注释上面这句-->
<!-- 配置事务通知,id为唯一标识,transaction-manager指定使用的事务管理器-->
<tx:advice id="interceptor" transaction-manager="dataSourceTransactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- tx:method指配置具体的事务方法-->
<!-- name属性:指定方法名,可以使用星号代表多个字符-->
<!-- <tx:method name="buyBook" />-->
<!-- 将查询方法的read-only指定为true,为读取做优化-->
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="query*" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true" />
<!-- read-only:设置只读-->
<!-- rollback-for:设置回滚的异常-->
<!-- no-rollback-for:设置不回滚的异常-->
<!-- isolation设置事务的隔离级别-->
<!-- timeout设置事务的超时属性-->
<!-- propagation设置事物的传播级别-->
<tx:method name="save*" read-only="false" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW" />
<tx:method name="update*" read-only="false" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW" />
<tx:method name="delete*" read-only="false" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="interceptor" pointcut="execution(* com.lobo.service.impl.*.*(..))" />
</aop:config>
</beans>