目录
- 数据集介绍
- VOC 格式转换为 YOLO 格式
- YOLO 格式转换为 VOC 格式
数据集介绍
本文使用的数据集是自制的安全帽数据集,共含有 6696 张图片,部分图片如下:

以及对应的 6696 个 VOC 格式的 xml 标注文件,部分文件如下:
首先,按照 VOC2007 的数据集格式要求,分别创建文件夹 VOCdevkit、VOC2007、Annotations、ImageSets、和 JPEGImages,它们的层级结构如下所示:
VOCdevkit
└───VOC2007
├───Annotations
├───ImageSets 【空】
└───JEPGImages
其中,Annotations 文件夹用来存放标签数据 xml 文件,JEPGImages 文件夹用来存放图片文件,ImageSets用来存放划分后的数据集。

- 其中 VOC 格式与 YOLO 格式相互转换的
Voc2Yolo.py以及Yolo2Voc.py我在下面的内容里均已提供; - 按照
8:2以及7:2:1划分数据集的split82.py以及split721.py我也在 YOLO 划分数据集(训练集、验证集、测试集)这篇博客提供 - 免费 下载本文数据集 请移步
以下代码亲测可以直接复制运行(以下所有的路径修改成自己对应的路径) {\color{Red} \mathbf{以下代码亲测可以直接复制运行 (以下所有的路径修改成自己对应的路径)}} 以下代码亲测可以直接复制运行(以下所有的路径修改成自己对应的路径)
VOC 格式转换为 YOLO 格式
在做目标检测时候,都会通过一些方法获得大量的数据集,或是网上下载,或是自己用软件比如 IabelImg,手动地一个一个打标签。
在日常生活中,我们也通常会打 VOC 格式的标签(xml 文件),因为它所包含的数据最多,使人一目了然,如:
<annotation>
<folder>hat01</folder>
<filename>000000.jpg</filename>
<path>D:\dataset\000000.jpg</path>
<source>
<database>Unknown</database>
</source>
<size>
<width>947</width>
<height>1421</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>hat</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>60</xmin>
<ymin>66</ymin>
<xmax>910</xmax>
<ymax>1108</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
而 YOLO 格式的数据就很抽象,如:
0 0.512143611404435 0.4130893736805067 0.8975712777191129 0.733286418015482
当我们使用 YOLO算法进行我们的项目实战时,将标签数据的 VOC 格式(xml文件)转换为 YOLO 格式(txt文件)就显得格外重要 ——
VOC 格式转换为 YOLO 格式的代码 Voc2Yolo.py内容如下:
import os
import shutil
import cv2
from lxml import etree
def VOC2Yolo(class_num, voc_img_path, voc_xml_path, yolo_txt_save_path, yolo_img_save_path=None):
xmls = os.listdir(voc_xml_path)
xmls = [x for x in xmls if x.endswith('.xml')]
if yolo_img_save_path is not None:
if not os.path.exists(yolo_img_save_path):
os.mkdir(yolo_img_save_path)
if not os.path.exists(yolo_txt_save_path):
os.mkdir(yolo_txt_save_path)
all_xmls = len(xmls)
for idx, one_xml in enumerate(xmls):
xl = etree.parse(os.path.join(voc_xml_path, one_xml)) # os.path.join(a,b)会自动在ab之间加/
root = xl.getroot()
objects = root.findall('object')
img_size = root.find('size')
img_w = 0
img_h = 0
if img_size:
img_width = img_size.find('width')
if img_width is not None:
img_w = int(img_width.text)
img_height = img_size.find('height')
if img_height is not None:
img_h = int(img_height.text)
label_lines = []
for ob in objects:
one_annotation = {}
label = ob.find('name').text
one_annotation['tag'] = label
one_annotation['flag'] = False
bbox = ob.find('bndbox')
xmin = int(bbox.find('xmin').text)
ymin = int(bbox.find('ymin').text)
xmax = int(bbox.find('xmax').text)
ymax = int(bbox.find('ymax').text)
if img_w == 0 or img_h == 0:
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(voc_img_path, one_xml.replace('.xml', '.jpg')))
img_h, img_w = img.shape[:2]
bbox_w = (xmax - xmin) / img_w
bbox_h = (ymax - ymin) / img_h
bbox_cx = (xmin + xmax) / 2 / img_w
bbox_cy = (ymin + ymax) / 2 / img_h
try:
bbox_label = class_num[label]
label_lines.append(f'{bbox_label} {bbox_cx} {bbox_cy} {bbox_w} {bbox_h}' + '\n')
except Exception as e:
print("not find number label in class_num ", e, one_xml)
label_lines = []
break
if len(label_lines):
with open(os.path.join(yolo_txt_save_path, one_xml.replace('.xml', '.txt')), 'w') as fp:
fp.writelines(label_lines)
if yolo_img_save_path is not None:
shutil.copy(os.path.join(voc_img_path, one_xml.replace('.xml', '.jpg')),
os.path.join(yolo_img_save_path))
print(f"processing: {idx+1}/{all_xmls}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
VOC2Yolo(
class_num={'hat': 0, 'person': 1}, # 标签种类
voc_img_path='./VOCdevkit/VOC2007/JPEGImages', # 数据集图片文件夹存储路径
voc_xml_path='./VOCdevkit/VOC2007/Annotations', # 标签xml文件夹存储路径
yolo_txt_save_path='./YoloLabels' # 将要生成的txt文件夹存储路径
)
转换完成!
YOLO 格式转换为 VOC 格式
什么情况下我们需要将 YOLO 格式转换为 VOC 格式?
这个问题还真困惑了我一段时间,当我们使用 YOLO 算法跑代码的时候,不就是需要YOLO格式的标注文件吗,这不现成的 YOLO 格式吗,为什么还要转换回 VOC 格式呢?
目前初学的我也不知道,呜呜呜~ 知道有知道的友友可以评论或私信我哦
YOLO 格式转换为 VOC 格式的代码 Yolo2Voc.py 内容如下:
from xml.dom.minidom import Document
import os
import cv2
def makexml(picPath, txtPath, xmlPath): # txt所在文件夹路径,xml文件保存路径,图片所在文件夹路径
"""此函数用于将yolo格式txt标注文件转换为voc格式xml标注文件
"""
dic = {'0': "hat", # 创建字典用来对类型进行转换
'1': "person", # 此处的字典要与自己的classes.txt文件中的类对应,且顺序要一致
}
files = os.listdir(txtPath)
all_txts = len(files)
if not os.path.exists(xmlPath):
os.mkdir(xmlPath)
for i, name in enumerate(files):
xmlBuilder = Document()
annotation = xmlBuilder.createElement("annotation") # 创建annotation标签
xmlBuilder.appendChild(annotation)
txtFile = open(txtPath + name)
# txtFile = open(os.path.join(txtPath, name))
txtList = txtFile.readlines()
img = cv2.imread(picPath + name[0:-4] + ".jpg")
Pheight, Pwidth, Pdepth = img.shape
folder = xmlBuilder.createElement("folder") # folder标签
foldercontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("driving_annotation_dataset")
folder.appendChild(foldercontent)
annotation.appendChild(folder) # folder标签结束
filename = xmlBuilder.createElement("filename") # filename标签
filenamecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(name[0:-4] + ".jpg")
filename.appendChild(filenamecontent)
annotation.appendChild(filename) # filename标签结束
size = xmlBuilder.createElement("size") # size标签
width = xmlBuilder.createElement("width") # size子标签width
widthcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pwidth))
width.appendChild(widthcontent)
size.appendChild(width) # size子标签width结束
height = xmlBuilder.createElement("height") # size子标签height
heightcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pheight))
height.appendChild(heightcontent)
size.appendChild(height) # size子标签height结束
depth = xmlBuilder.createElement("depth") # size子标签depth
depthcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pdepth))
depth.appendChild(depthcontent)
size.appendChild(depth) # size子标签depth结束
annotation.appendChild(size) # size标签结束
for j in txtList:
oneline = j.strip().split(" ")
object = xmlBuilder.createElement("object") # object 标签
picname = xmlBuilder.createElement("name") # name标签
namecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(dic[oneline[0]])
picname.appendChild(namecontent)
object.appendChild(picname) # name标签结束
pose = xmlBuilder.createElement("pose") # pose标签
posecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("Unspecified")
pose.appendChild(posecontent)
object.appendChild(pose) # pose标签结束
truncated = xmlBuilder.createElement("truncated") # truncated标签
truncatedContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
truncated.appendChild(truncatedContent)
object.appendChild(truncated) # truncated标签结束
difficult = xmlBuilder.createElement("difficult") # difficult标签
difficultcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
difficult.appendChild(difficultcontent)
object.appendChild(difficult) # difficult标签结束
bndbox = xmlBuilder.createElement("bndbox") # bndbox标签
xmin = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmin") # xmin标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[1])) * Pwidth + 1) - (float(oneline[3])) * 0.5 * Pwidth)
xminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
xmin.appendChild(xminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmin) # xmin标签结束
ymin = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymin") # ymin标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[2])) * Pheight + 1) - (float(oneline[4])) * 0.5 * Pheight)
yminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
ymin.appendChild(yminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymin) # ymin标签结束
xmax = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmax") # xmax标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[1])) * Pwidth + 1) + (float(oneline[3])) * 0.5 * Pwidth)
xmaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
xmax.appendChild(xmaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmax) # xmax标签结束
ymax = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymax") # ymax标签
mathData = int(((float(oneline[2])) * Pheight + 1) + (float(oneline[4])) * 0.5 * Pheight)
ymaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
ymax.appendChild(ymaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymax) # ymax标签结束
object.appendChild(bndbox) # bndbox标签结束
annotation.appendChild(object) # object标签结束
print(f"processing: {i+1}/{all_txts}")
f = open(xmlPath + name[0:-4] + ".xml", 'w')
xmlBuilder.writexml(f, indent='\t', newl='\n', addindent='\t', encoding='utf-8')
f.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
picPath = "./VOCdevkit/VOC2007/JPEGImages/" # 图片所在文件夹路径,后面的/一定要带上
txtPath = "./YoloLabels/" # txt所在文件夹路径,后面的/一定要带上
xmlPath = "./VocLabels/" # xml文件保存路径,后面的/一定要带上
makexml(picPath, txtPath, xmlPath)
转换完成!
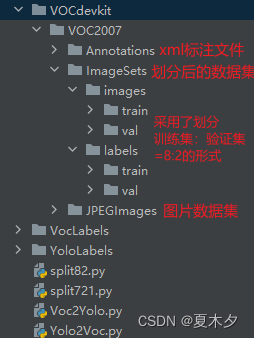
完成本文 VOC 格式与 YOLO 格式的相互转换以及我的另一篇博客YOLO 划分数据集(训练集、验证集、测试集)之后,我的整个项目结构如下图所示:
![[Linux]进程间通信](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/e6fe24a78706bc605f79d5dcc4e6ef9e.png)