【LetMeFly】2050.并行课程 III:DFS
力扣题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/parallel-courses-iii/
给你一个整数 n ,表示有 n 节课,课程编号从 1 到 n 。同时给你一个二维整数数组 relations ,其中 relations[j] = [prevCoursej, nextCoursej] ,表示课程 prevCoursej 必须在课程 nextCoursej 之前 完成(先修课的关系)。同时给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 time ,其中 time[i] 表示完成第 (i+1) 门课程需要花费的 月份 数。
请你根据以下规则算出完成所有课程所需要的 最少 月份数:
- 如果一门课的所有先修课都已经完成,你可以在 任意 时间开始这门课程。
- 你可以 同时 上 任意门课程 。
请你返回完成所有课程所需要的 最少 月份数。
注意:测试数据保证一定可以完成所有课程(也就是先修课的关系构成一个有向无环图)。
示例 1:

输入:n = 3, relations = [[1,3],[2,3]], time = [3,2,5] 输出:8 解释:上图展示了输入数据所表示的先修关系图,以及完成每门课程需要花费的时间。 你可以在月份 0 同时开始课程 1 和 2 。 课程 1 花费 3 个月,课程 2 花费 2 个月。 所以,最早开始课程 3 的时间是月份 3 ,完成所有课程所需时间为 3 + 5 = 8 个月。
示例 2:
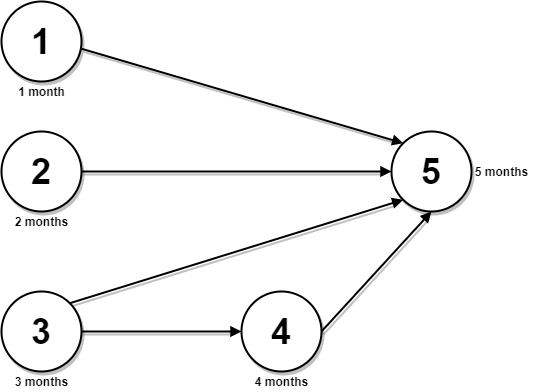
输入:n = 5, relations = [[1,5],[2,5],[3,5],[3,4],[4,5]], time = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:12 解释:上图展示了输入数据所表示的先修关系图,以及完成每门课程需要花费的时间。 你可以在月份 0 同时开始课程 1 ,2 和 3 。 在月份 1,2 和 3 分别完成这三门课程。 课程 4 需在课程 3 之后开始,也就是 3 个月后。课程 4 在 3 + 4 = 7 月完成。 课程 5 需在课程 1,2,3 和 4 之后开始,也就是在 max(1,2,3,7) = 7 月开始。 所以完成所有课程所需的最少时间为 7 + 5 = 12 个月。
提示:
1 <= n <= 5 * 1040 <= relations.length <= min(n * (n - 1) / 2, 5 * 104)relations[j].length == 21 <= prevCoursej, nextCoursej <= nprevCoursej != nextCoursej- 所有的先修课程对
[prevCoursej, nextCoursej]都是 互不相同 的。 time.length == n1 <= time[i] <= 104- 先修课程图是一个有向无环图。
方法一:深度优先搜索(DFS)
这道题其实不难,无脑记忆化搜索就可以了。
首先建立一个邻接表pre,pre[i]记录课程i的所有先修课程,接着写一个函数dfs(n),用来求课程n最早修完的日期。
公式: 课程 i 的最早完成时 = m a x ( 其先修课的最早完成时 ) + 课程 i 耗时 课程i的最早完成时 = max(其先修课的最早完成时) + 课程i耗时 课程i的最早完成时=max(其先修课的最早完成时)+课程i耗时
int dfs(n) {
若已计算过n则直接返回
int ans = 0;
for (int thisPre : pre[n]) {
ans = max(ans, dfs(thisPre));
}
ans += time[n];
return ans; // 返回并“记忆之”
}
- 时间复杂度 O ( n + l e n ( r e l a t i o n s ) ) O(n + len(relations)) O(n+len(relations))
- 空间复杂度 O ( n + l e n ( r e l a t i o n s ) ) O(n + len(relations)) O(n+len(relations))
AC代码
Python
# from typing import List
# from functools import cache
class Solution:
@cache
def dfs(self, n):
if self.dp[n]:
return self.dp[n]
for thisPre in self.pre[n]:
self.dp[n] = max(self.dp[n], self.dfs(thisPre))
self.dp[n] += self.time[n]
return self.dp[n]
def minimumTime(self, n: int, relations: List[List[int]], time: List[int]) -> int:
self.time = time
self.dp = [0] * n
self.pre = [[] for _ in range(n)] # 这里不能写成[[]] * n!!!
for thisPre, thisNext in relations:
self.pre[thisNext - 1].append(thisPre - 1)
return max(self.dfs(i) for i in range(n))
C++
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> pre;
vector<int> dp;
vector<int> time;
int dfs(int n) { // n从0开始
if (dp[n]) {
return dp[n];
}
for (int thisPre : pre[n]) {
// printf("n = %d, thisPre = %d, max(%d", n, thisPre, dp[n]); //******
dp[n] = max(dp[n], dfs(thisPre));
// printf(", %d) = %d\n", dfs(thisPre), dp[n]); //*********
}
return (dp[n] += time[n]);
}
public:
int minimumTime(int n, vector<vector<int>>& relations, vector<int>& time) {
this->time = time;
pre.resize(n);
dp.resize(n);
for (vector<int>& relation : relations) {
pre[relation[1] - 1].push_back(relation[0] - 1);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ans = max(ans, dfs(i));
}
return ans;
}
};
因Py代码较为简洁,故今日将Py代码置于了C艹前。
同步发文于CSDN,原创不易,转载请附上原文链接哦~
Tisfy:https://letmefly.blog.csdn.net/article/details/131973511