- OS提供的轻量级进程接口
- POSIX线程库
- 线程使用
- 1.如何创建一堆线程
- 2.线程如何终止
- 3.线程如何取消
- 线程等待
- 线程退出返回值
- C++11的多线程
- 线程ID及地址空间布局
- 线程地址空间布局
- 线程局部存储
- 分离线程
OS提供的轻量级进程接口
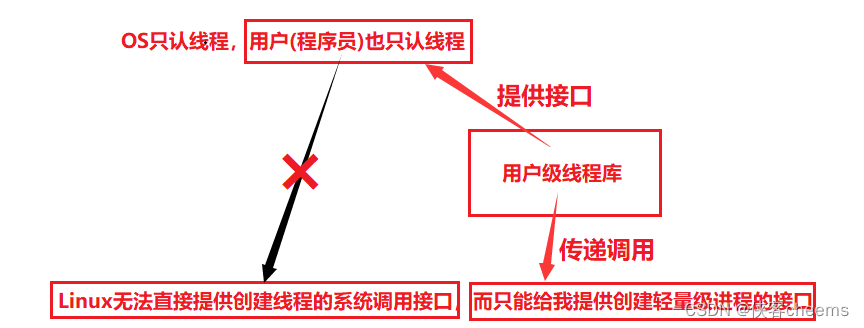
(关于 用户 → 库 → OS :具体可看下面线程地址空间布局)
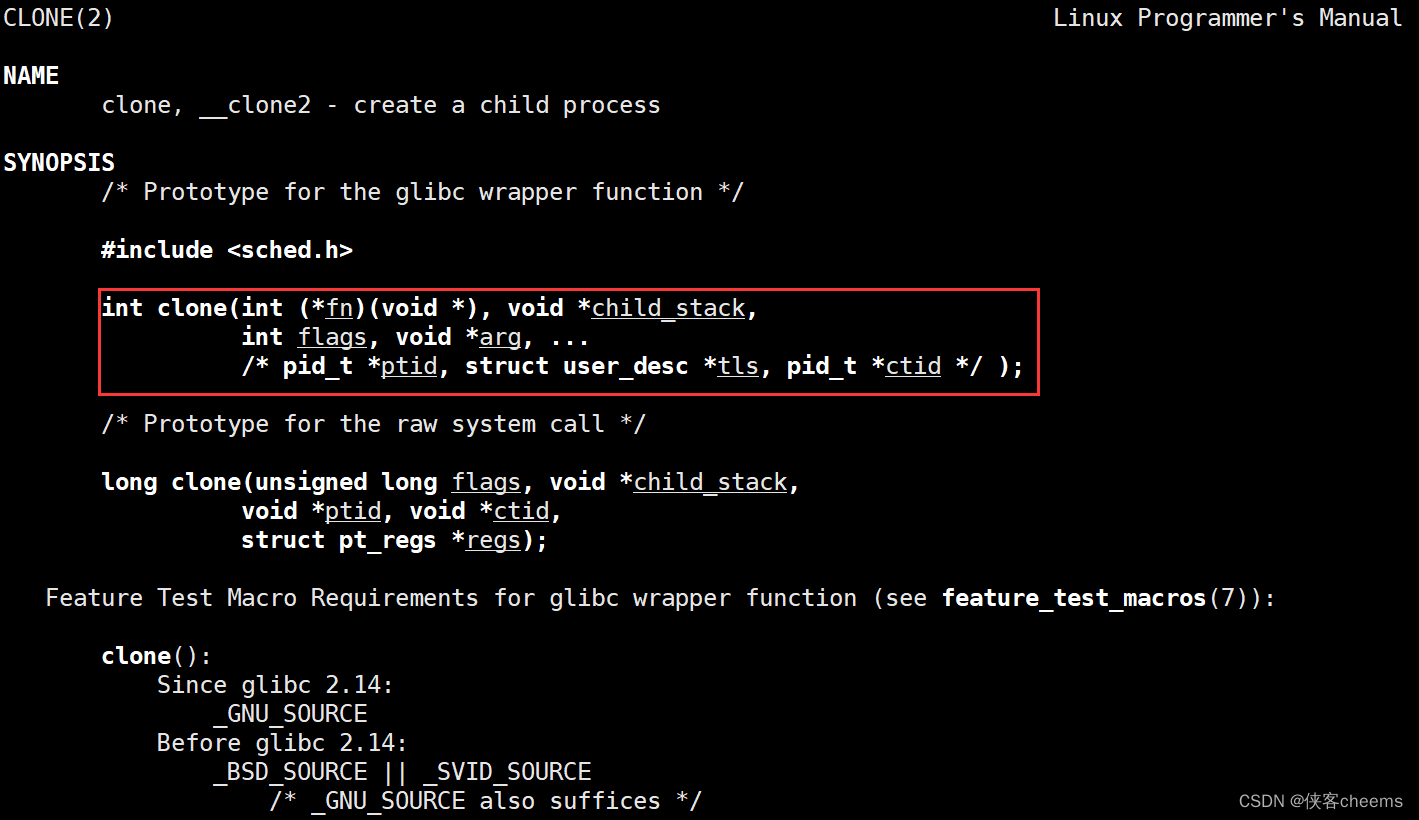
这个
clone我们不用,这是OS提供给第三方库所用的接口
POSIX线程库
与线程有关的函数构成了一个完整的系列,绝大多数函数的名字都是以“
pthread_”开头的,要使用这些函数库,要通过引入头文<pthread.h>,链接这些线程函数库时要使用编译器命令的“-lpthread”选项
创建线程:
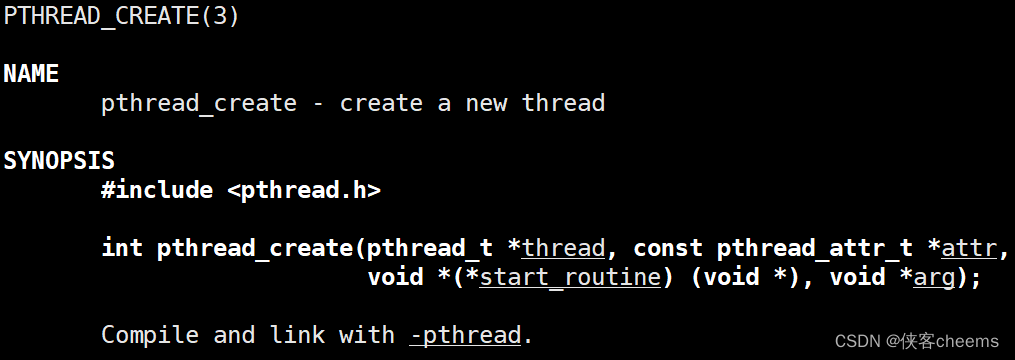
函数原型:
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
参数
thread:返回线程IDattr:设置线程的属性,attr为NULL表示使用默认属性start_routine:是个函数地址,线程启动后要执行的函数arg:传给线程启动函数的参数
返回值:成功返回0;失败返回错误码
错误检查:
- 传统的一些函数是,成功返回0,失败返回-1,并且对全局变量errno赋值以指示错误。
pthreads函数出错时不会设置全局变量errno(而大部分其他POSIX函数会这样做)。而是将错误代码通过返回值返回pthreads同样也提供了线程内的errno变量,以支持其它使用errno的代码。对于pthreads函数的错误,
建议通过返回值业判定,因为读取返回值要比读取线程内的errno变量的开销更小
线程使用
1.如何创建一堆线程
试验:创建一批线程:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
void *start_routine(void *args)
{
string name = static_cast<const char *>(args);
while (true)
{
cout << "new thread create success , name: " << name << endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
vector<pthread_t> tids;
#define NUM 10
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++)
{
pthread_t tid;
char namebuffer[64];
snprintf(namebuffer, sizeof(namebuffer), "%s:%d", "thread", i);
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, start_routine, namebuffer);
// sleep(1);
}
while (true)
{
cout << "new thread create success , name: main thread" << endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
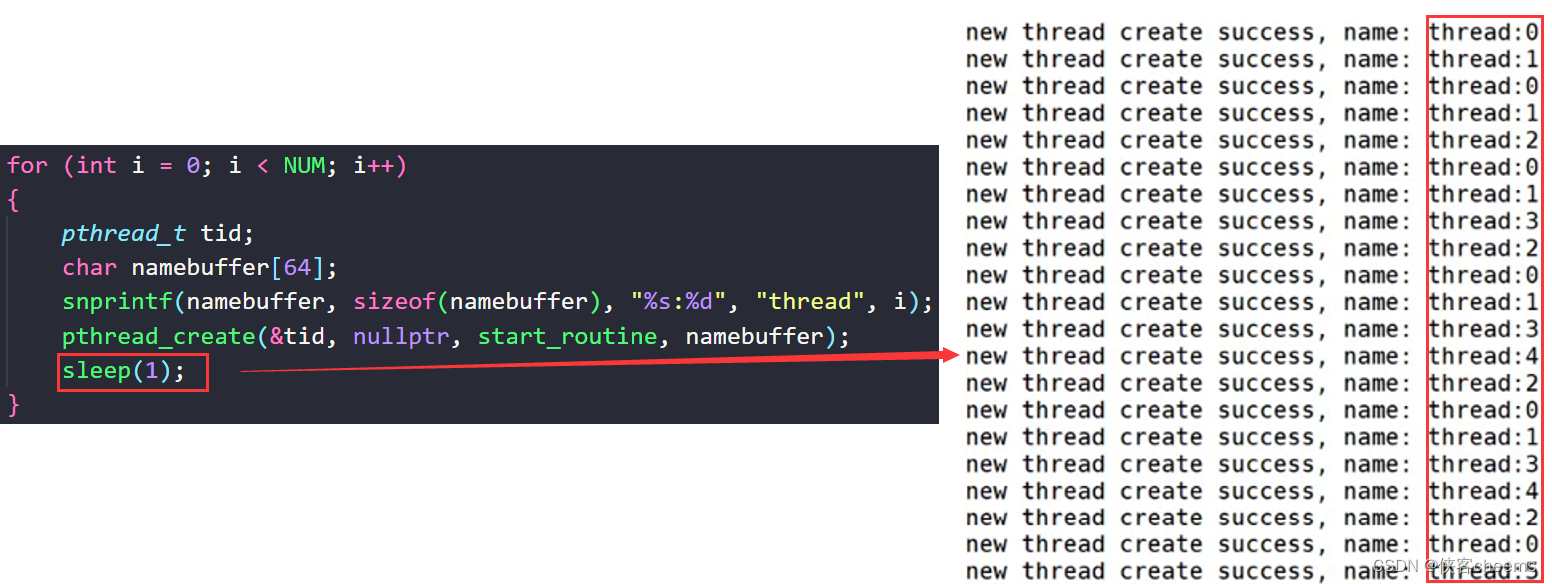
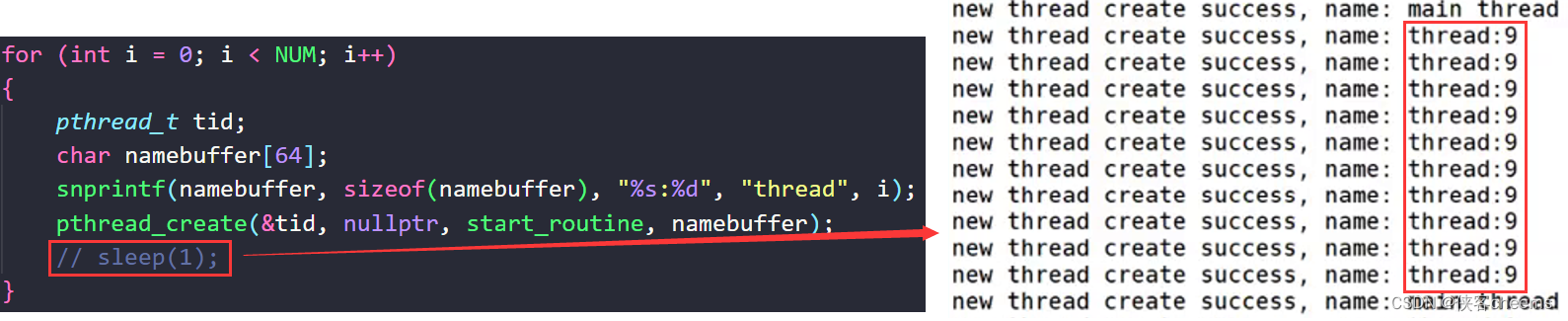
为什么这里连续输出9呢?

我们这样的写法是有问题的,我们可以对其进行更改:
class ThreadData
{
public:
int number;
pthread_t tid;
char namebuffer[64];
};
void *start_routine(void *args)
{
ThreadData *td = static_cast<ThreadData *>(args); // 安全的进行强制类型转化
int cnt = 10;
while (cnt)
{
cout << "new thread create success, name: " << td->namebuffer << " cnt: " << cnt-- << endl;
}
delete td;
return nullptr;
}
int main()
{
vector<ThreadData *> threads;
#define NUM 10
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++)
{
ThreadData *td = new ThreadData();
td->number = i + 1;
snprintf(td->namebuffer, sizeof(td->namebuffer), "%s:%d", "thread", i + 1);
pthread_create(&td->tid, nullptr, start_routine, td);
threads.push_back(td);
}
for (auto &iter : threads)
{
cout << "create thread: " << iter->namebuffer << " : " << iter->tid << " suceesss" << endl;
}
while (true)
{
cout << "new thread create success , name: main thread" << endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
将其创建成结构体,每次创建都new一个ThreadData对象,然后将结构体对象的地址传递给start_routine,每一个结构体对象都有自己独立的缓冲区,这样就能避免缓冲区被刷新了的问题。
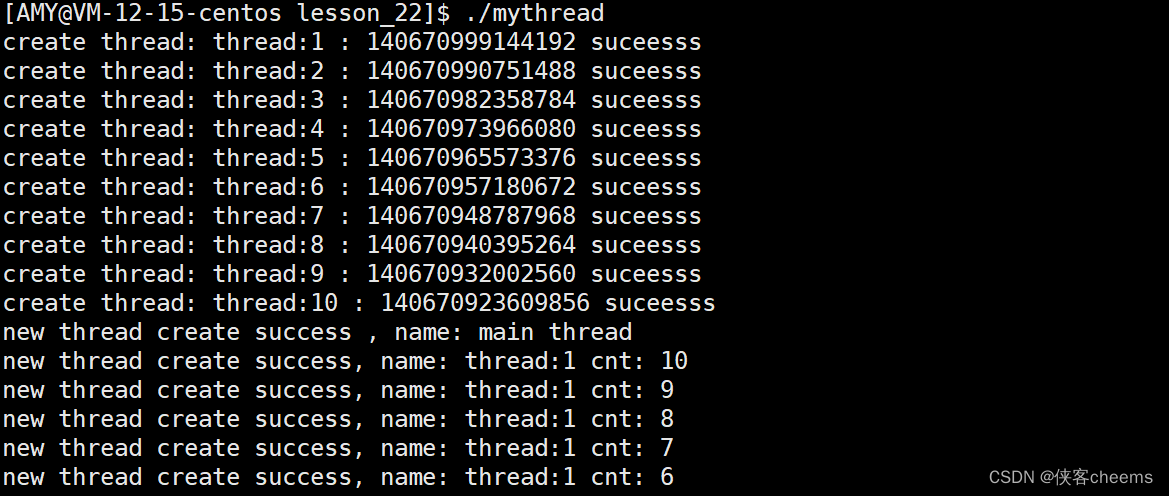
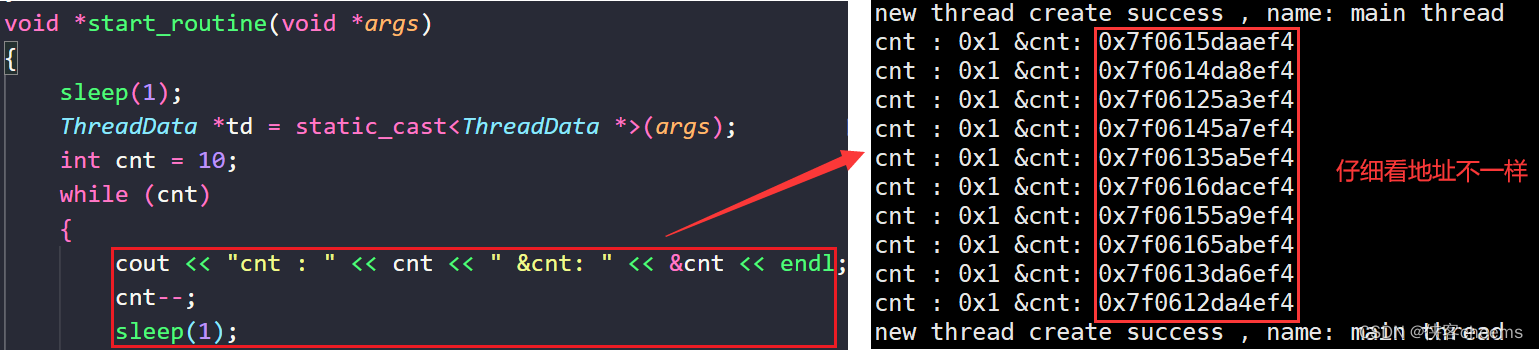
思考:start_routine这个函数被10个线程同时运行,它是什么状态?函数里面定义的td与cnt在变化会影响别的线程吗?
start_routine这个函数现在是重入状态,该函数是可重入函数,虽然cnt在变化,但是在函数内定义的变量,都叫做局部变量,具有临时性,现在依旧适用在多线程情况下,也没有问题。其实每一个线程都有自己独立的栈结构!(打印输出现在不解释,这个输出是往文件输出,当然只能执行一个)
2.线程如何终止
return nullptr;线程函数结束,return的时候,线程就算终止了pthread_exit(nullptr);我们在start_routine函数while循环中终止:
void *start_routine(void *args)
{
sleep(1);
ThreadData *td = static_cast<ThreadData *>(args); // 安全的进行强制类型转化
int cnt = 10;
while (cnt)
{
cout << "cnt : " << cnt << " &cnt: " << &cnt << endl;
cnt--;
pthread_exit(nullptr);//终止线程
sleep(1);
}
delete td;
return nullptr;
}
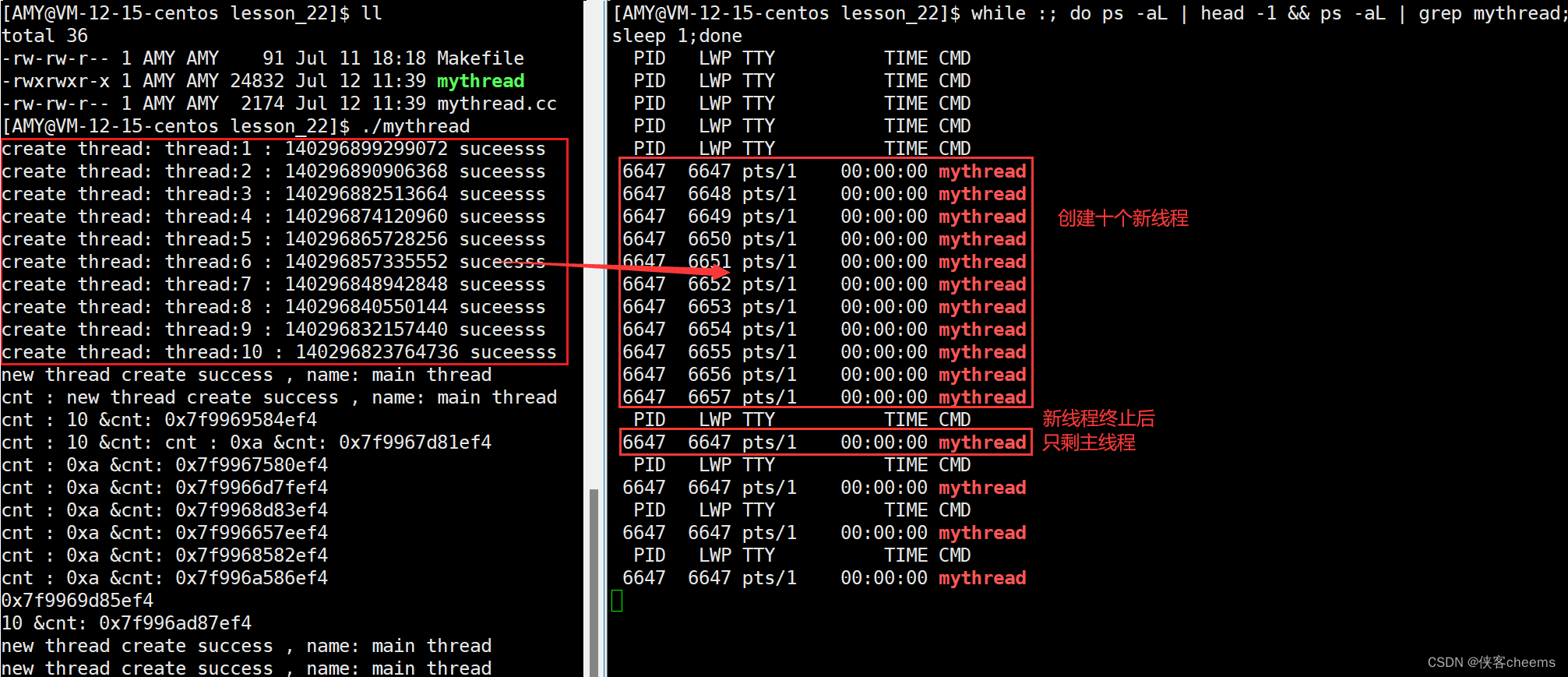
循环打印线程脚本:
while :; do ps -aL | head -1 && ps -aL | grep mythread;sleep 1;done
我们不能之间在线程中使用exit(),因为这是直接终止进程的,如果有线程调用这个函数,那么整个线程都会终止,pthread_exit(nullptr);可以终止新线程而不影响主线程。
3.线程如何取消
线程是可以被取消的但是注意:线程要被取消,前提是这个线程已经跑起来了
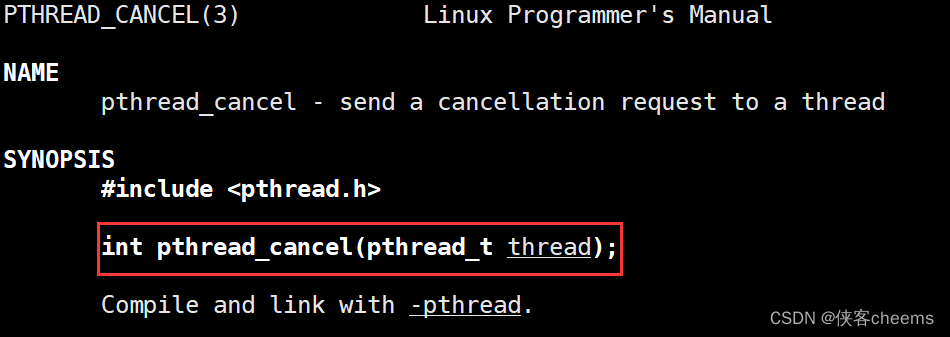
函数原型:
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
实操代码:
//新线程部分代码
void* start_routine(void *args)
{
//....
return (void*)123;
}
//主线程部分代码
for(int i = 0; i < threads.size()/2; i++)
{
pthread_cancel(threads[i]->tid);
cout << "pthread_cancel : " << threads[i]->namebuffer << " success" << endl;
}
for (auto &iter : threads)
{
void* tmp=nullptr;
int n = pthread_join(iter->tid, &tmp);
assert(n == 0);
cout << "join thread : " << iter->namebuffer <<"exit : "<< (long long)tmp << endl;
delete iter;
}
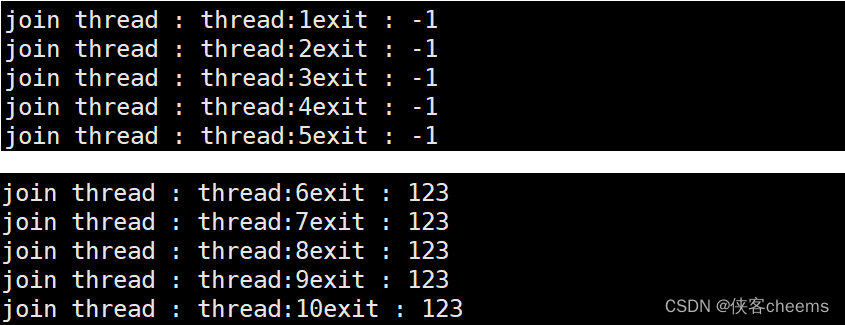
线程如果是被取消的,退出码:-1(PTHREAD_CANCELED)
线程等待
线程也是要被等待的,如果不等待,会造成类似僵尸进程的问题–内存泄漏
线程必须也要被等待:
- 获取新线程的退出信息→可以不关心退出信息吗?可以
- 回收新线程对应的PCB等内核资源,防止内存泄漏 – 暂时无法查看!
线程等待函数pthread_join:
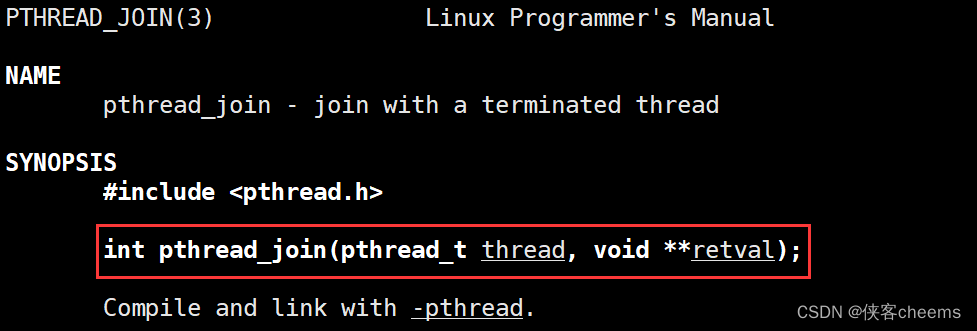
函数原型:
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
在主线程中等待并释放:
for (auto &iter : threads)
{
int n = pthread_join(iter->tid,nullptr);
assert(n ==0);
cout << "join thread : " << iter->namebuffer << " success" << endl;
delete iter;
}

线程退出返回值
我们的start_routine函数返回值是void*类型,这个类型有什么说法吗?

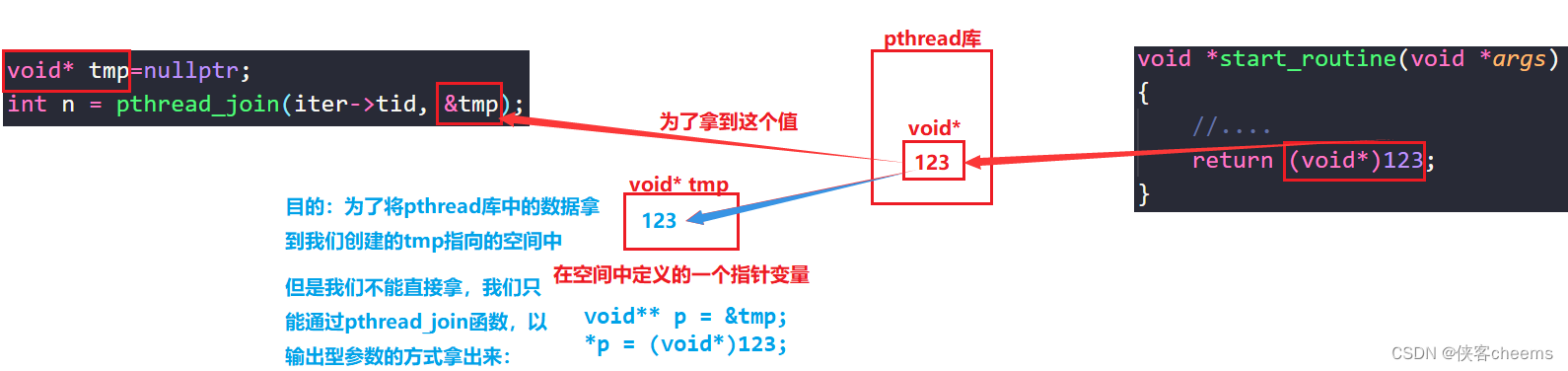
//新线程部分代码
void *start_routine(void *args)
{
//....
return (void*)123;
}
//主线程部分代码:
for (auto &iter : threads)
{
void* tmp=nullptr;
int n = pthread_join(iter->tid, &tmp);
assert(n == 0);
cout << "join thread : " << iter->namebuffer <<"exit : " << (long long)tmp<< " success" << endl;//(long long)类型是因为我使用的Linux版本是64位的
delete iter;
}
//其余代码跟之前一样,这里只是增加的或更改了一点
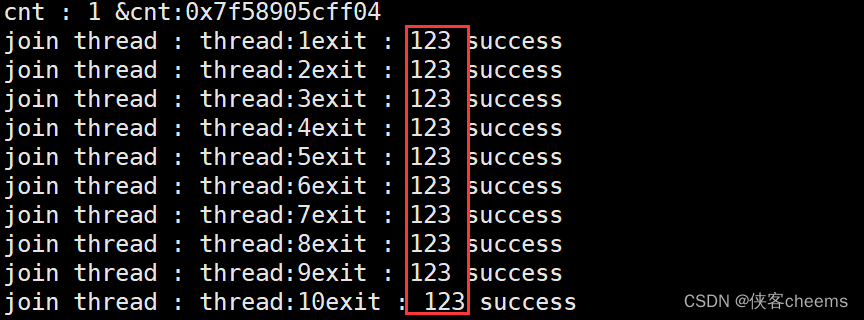
这个的返回值也跟上述return是一样的
pthread_exit((void*)123);
既然假的地址,整数都能被外部拿到,那么如何返回的是,堆空间的地址呢?对象的地址呢?
返回一个对象指针:
class ThreadReturn
{
public:
int exit_code;
int exit_result;
};
//新线程部分代码
void* start_routine(void *args)
{
//.....
ThreadReturn * tr = new ThreadReturn();
tr->exit_code = 1;
tr->exit_result = 123;
return (void*)tr;
}
//主线程部分代码
for (auto &iter : threads)
{
ThreadReturn* tmp=nullptr;
int n = pthread_join(iter->tid, (void**)&tmp);
assert(n == 0);
cout << "join thread : " << iter->namebuffer <<"exit_code : " << tmp->exit_code<< " exit_result : "<<tmp->exit_result << endl;
delete iter;
}
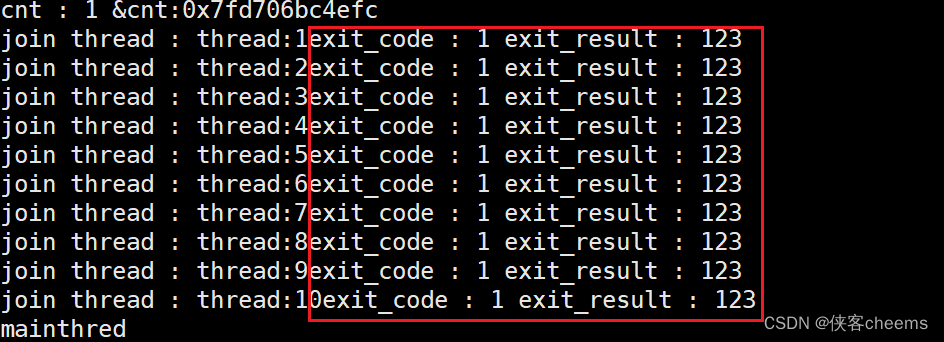
为什么没有见到,线程退出的时候,对应的退出信号???
线程出异常,收到信号,整个进程都会退出!pthread_join:默认就认为函数会调用成功!不考虑异常问题,异常问题是进程该考虑的问题!
C++11的多线程
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thread>
void thread_run()
{
while (true)
{
std::cout << "我是新线程..." << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
std::thread t1(thread_run);
while (true)
{
std::cout << "我是主线程..." << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
t1.join();
return 0;
}
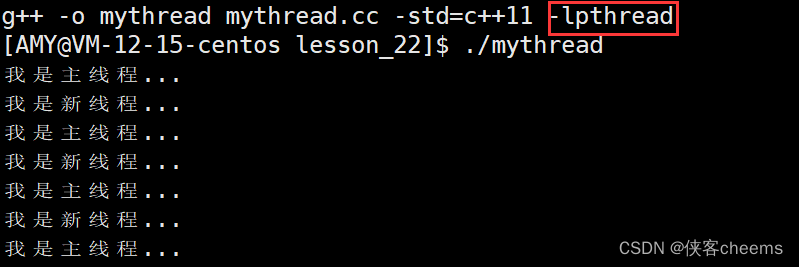
任何语言,在linux中如果要实现多线程,必定要是用pthread库
如何看待C++11中的多线程呢?
C++11 的多线程,在Linux环境中,本质是对pthread库的封装!(使用原生线程库还是C++11的线程库都可以,只是C++11的线程库在windows下也能运行,Linux与windows底层的线程库的接口不一样)
线程ID及地址空间布局
pthread_create函数会产生一个线程ID,存放在第一个参数指向的地址中。该线程ID和前面说的线程ID不是一回事。- 前面讲的线程
ID属于进程调度的范畴。因为线程是轻量级进程,是操作系统调度器的最小单位,所以需要一个数值来唯一表示该线程。 pthread_create函数第一个参数指向一个虚拟内存单元,该内存单元的地址即为新创建线程的线程ID,属于NPTL线程库的范畴。线程库的后续操作,就是根据该线程ID来操作线程的。- 线程库
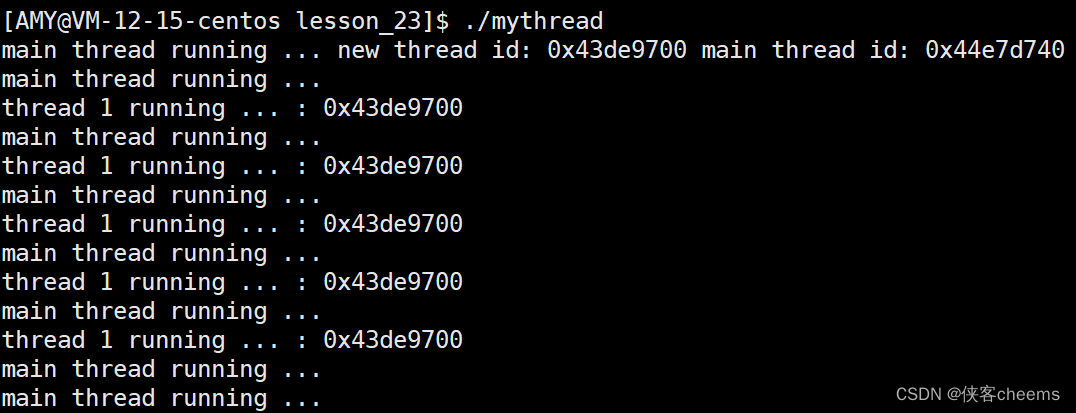
NPTL提供了pthread_self函数,可以获得线程自身的ID:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
std::string changeId(const pthread_t &thread_id)
{
char tid[128];
snprintf(tid, sizeof(tid), "0x%x", thread_id);
return tid;
}
void *start_routine(void *args)
{
std::string threadname = static_cast<const char *>(args);
while (true)
{
std::cout << threadname << " running ... : " << changeId(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, start_routine, (void *)"thread 1");
std::string main_id = changeId(pthread_self());
std::cout << "main thread running ... new thread id: " << changeId(tid) <<" main thread id: " << main_id << std::endl;
pthread_join(tid,nullptr);
return 0;
}
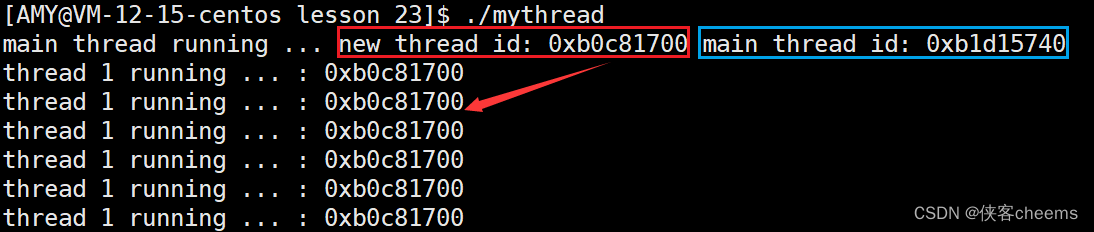
线程地址空间布局
pthread_t 到底是什么类型呢?取决于实现。对于Linux目前实现的NPTL实现而言,pthread_t类型的线程ID,本质就是一个进程地址空间上的一个地址。
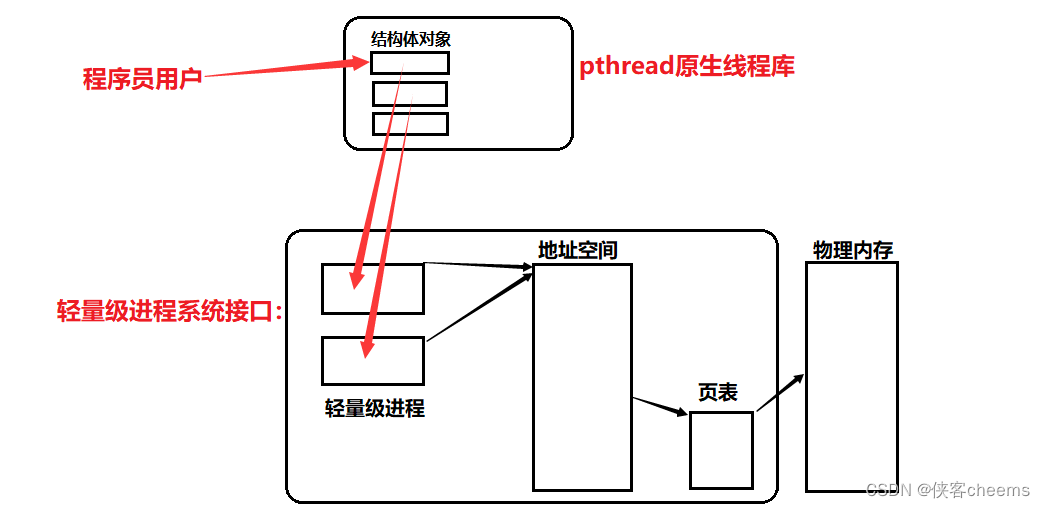
原生线程库可能存在多个线程,我们同样也要对线程进行管理(先描述再组织),每一个轻量级进程对应原生库中的一个结构体对象(TCB),这是Linux的方案 – 用户级线程,用户关心的线程属性在库中,而内核里面提供执行流的调度。Linux用户级线程对比内核轻量级进程是1:1。
线程布局图:
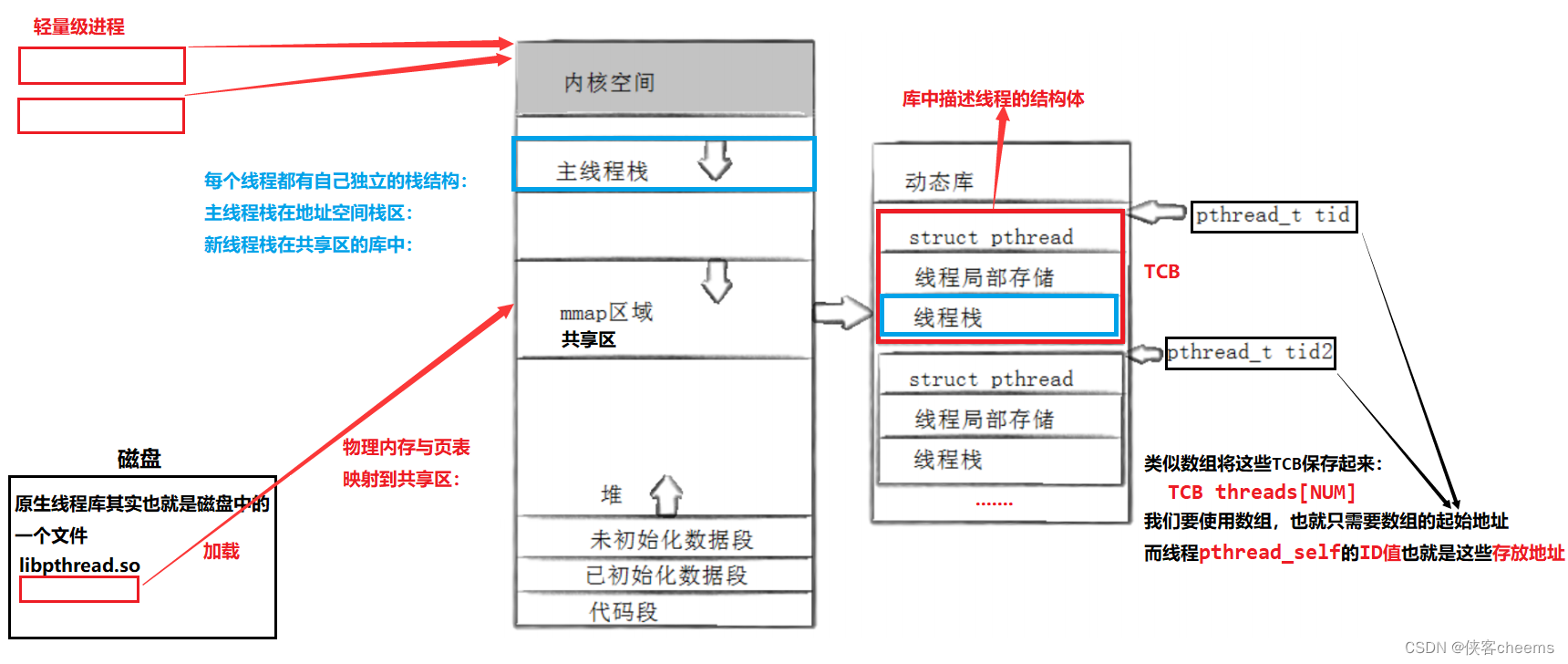
用户级线程:线程ID值就是库中结构体(TCB)对象的地址
线程局部存储
我们在之前的“什么是线程?”一文已经了解到了:线程一旦被创建,几乎所有资源都是被线程所共享的
//定义一个全局变量
int g_val= 100;
//新线程:
std::cout << threadname << " running ... : " << changeId(pthread_self())
<<" g_val: "<< g_val++ << " &g_val: " << &g_val << std::endl;
//主线程:
std::cout << "main thread running ... new thread id: " <<changeId(tid)
<<" main thread id: " << main_id << " g_val: "<< g_val << " &g_val: " << &g_val << std::endl;
我们在主线程与新线程都打印输出g_val的值与地址:
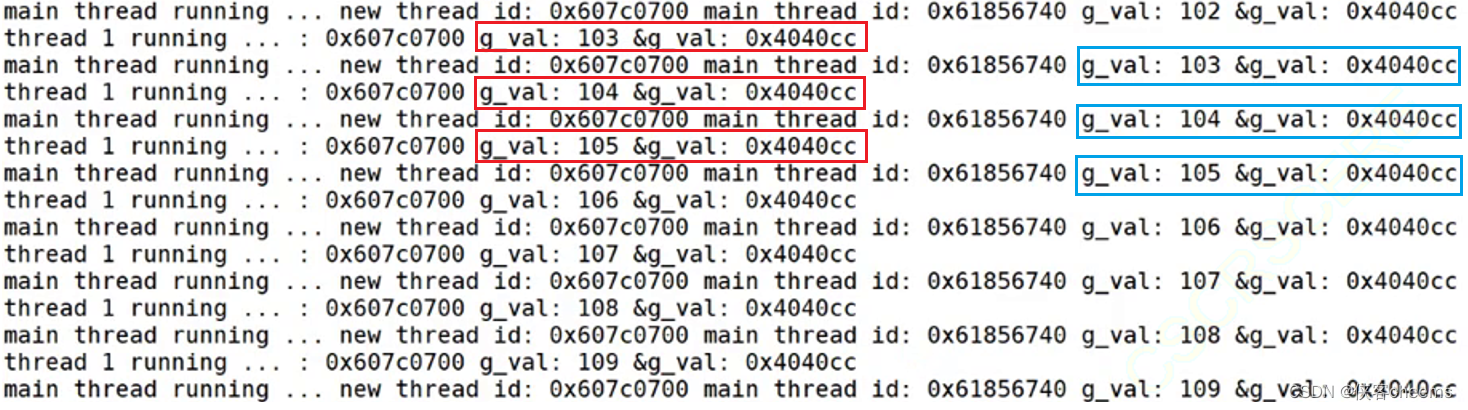
我们可以发现,主线程与新线程都是输出同一个g_val值与地址,且这个地址非常小
添加__thread,可以将一个内置类型设置为线程局部存储
__thread int g_val = 100;
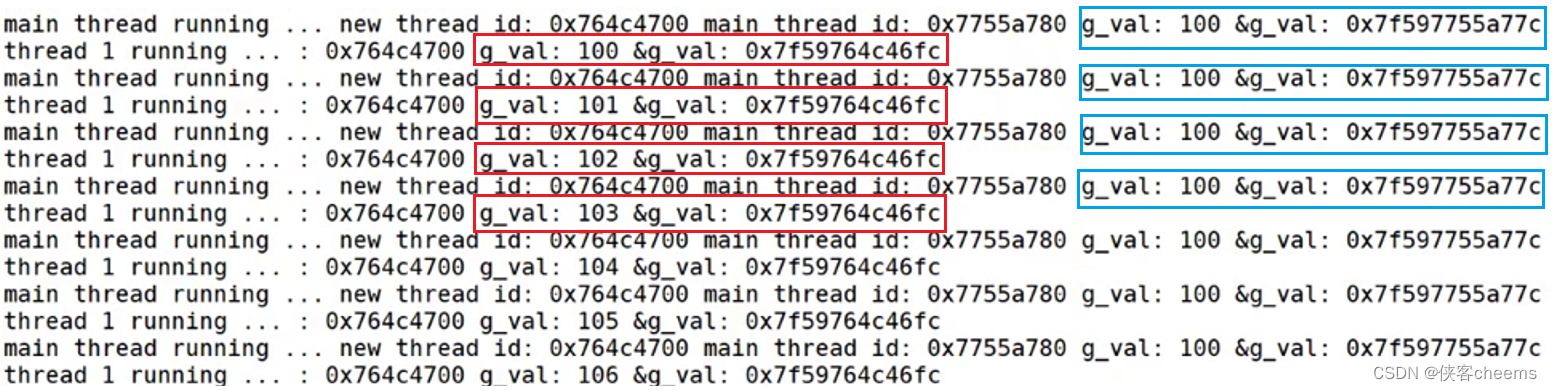
我们可以发现,给g_val添加__thread后,主线程与新线程打印输出的地址不一样了,新线程对g_val的值进行修改,主线程打印的值没有变化。
原因图:
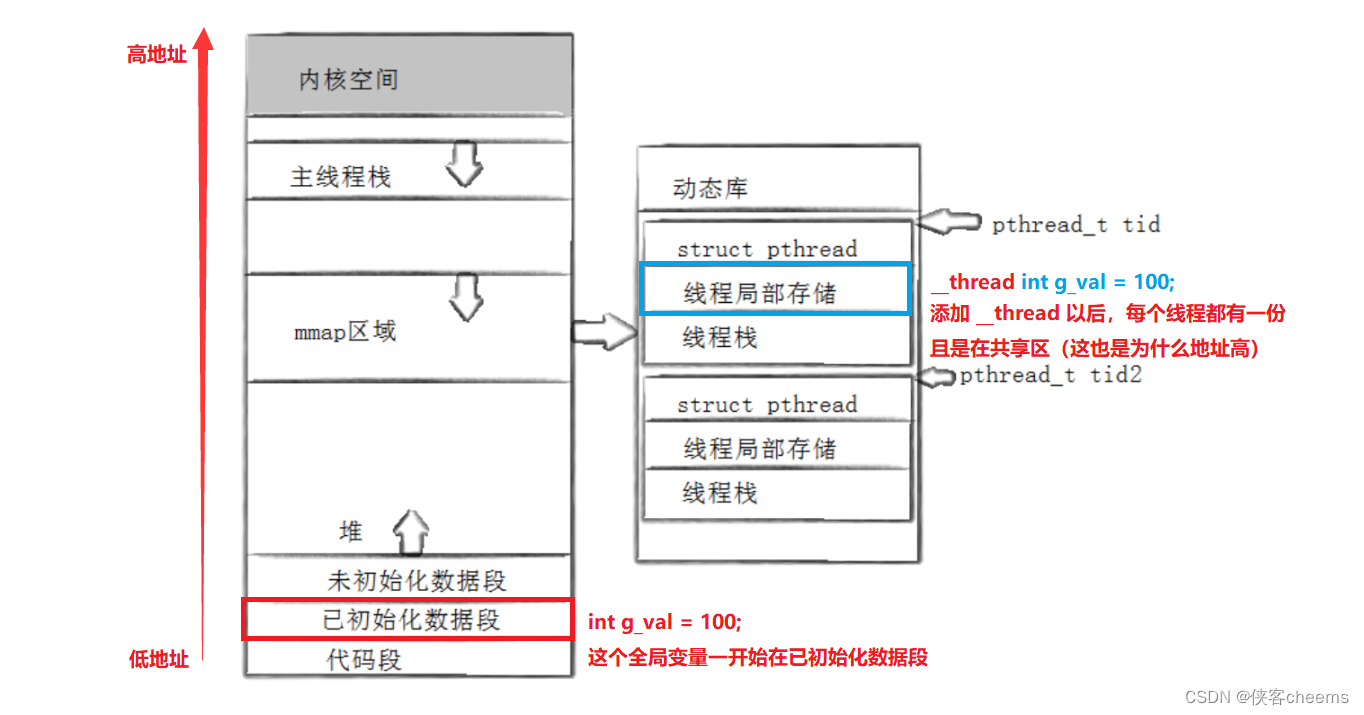
一开始g_val在已初始化数据段,添加__thread以后,使其设置为线程局部存储,每个线程都有一份且是在共享区,已初始化数据段→共享区(地址由低到高),且它们访问不会互相影响。
分离线程
- 默认情况下,新创建的线程是
joinable的,线程退出后,需要对其进行pthread_join操作,否则无法释放资源,从而造成系统泄漏。 - 如果不关心线程的返回值,
join是一种负担,这个时候,我们可以告诉系统,当线程退出时,自动释放线程资源。 - 如果线程设置了分离状态,那么就不能
join等待了。
分离一个线程:
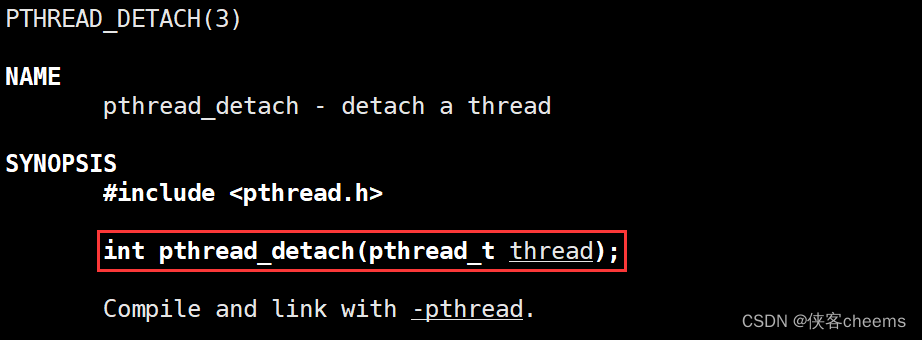
函数原型:
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);
可以是线程组内其他线程对目标线程进行分离,也可以是线程自己分离
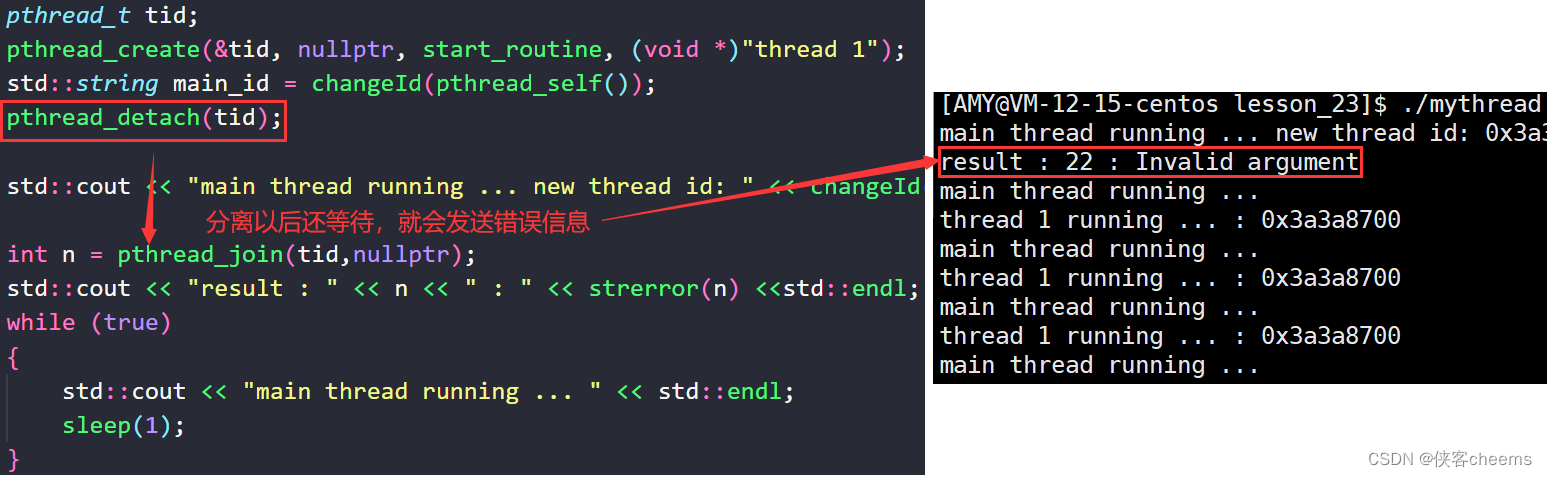
验证分离以后不能join(里面有小bug,请思考):
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <unistd.h>
std::string changeId(const pthread_t &thread_id)
{
char tid[128];
snprintf(tid, sizeof(tid), "0x%x", thread_id);
return tid;
}
void *start_routine(void *args)
{
std::string threadname = static_cast<const char *>(args);
// pthread_detach(pthread_self());
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
std::cout << threadname << " running ... : " << changeId(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, start_routine, (void *)"thread 1");
std::string main_id = changeId(pthread_self());
std::cout << "main thread running ... new thread id: " << changeId(tid) <<" main thread id: " << main_id << std::endl;
int n = pthread_join(tid,nullptr);
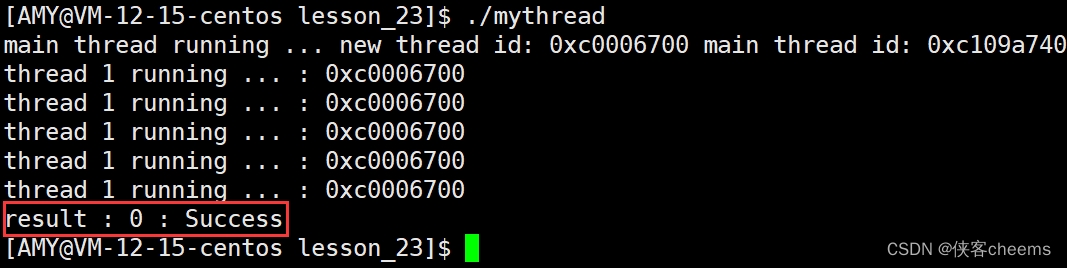
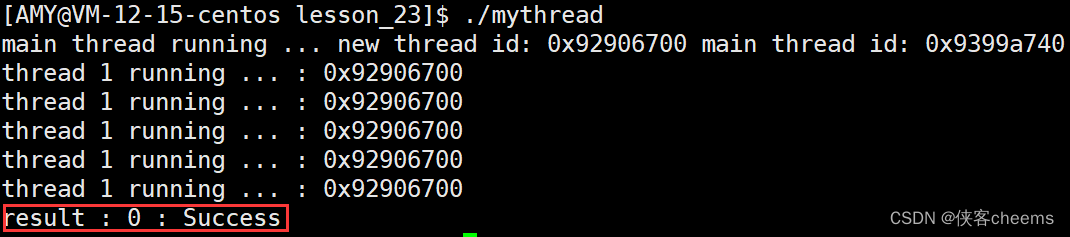
std::cout << "result : " << n << " : " << strerror(n) <<std::endl;
return 0;
}
1.我们在start_routine里面没有使用线程分离:
2.我们在start_routine里面使用线程分离pthread_detach:
思考:为什么我在start_routine里面使用线程分离pthread_detach然后pthread_join还是成功了?
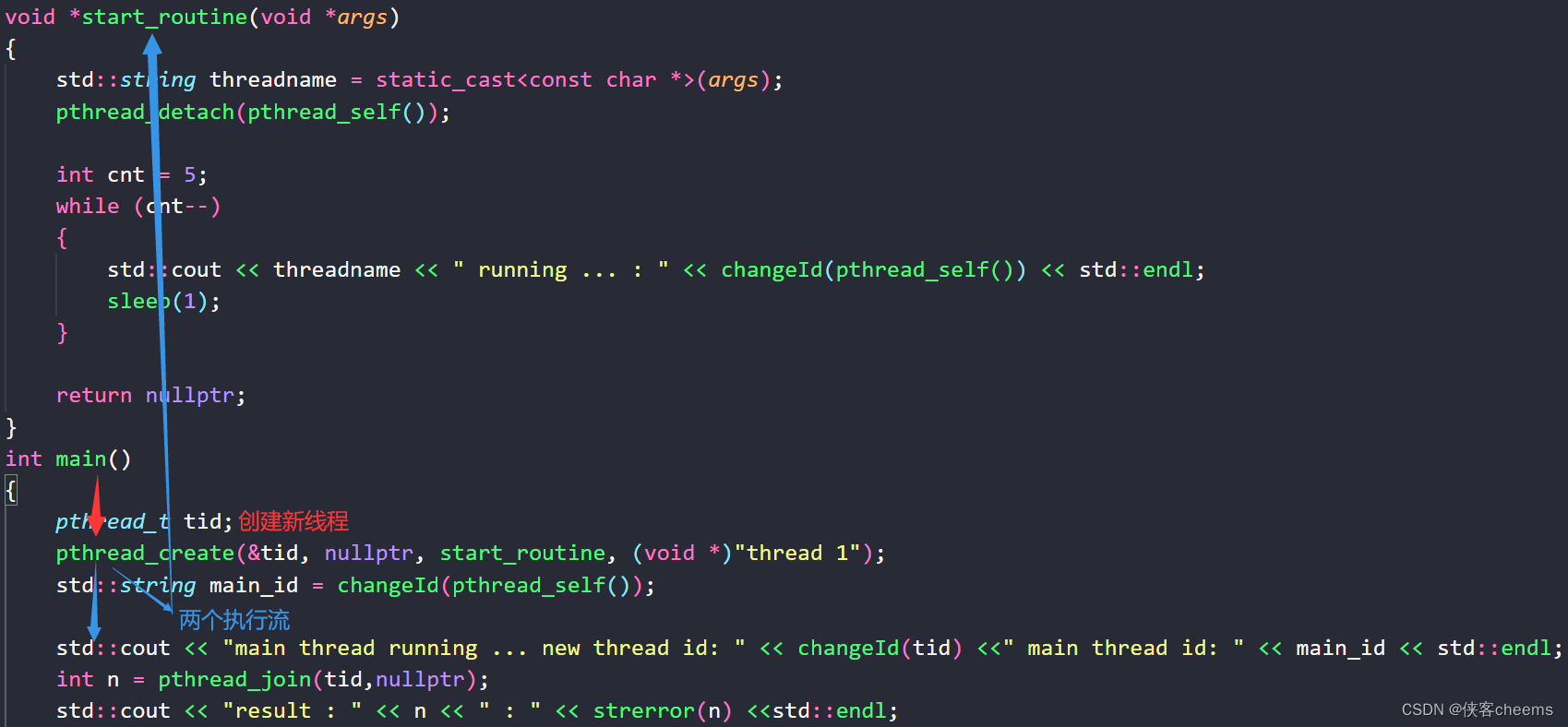
原因:由于主线程创建新线程以后,到底是主线程先运行还是新线程先运行是随机的,如果主线程先运行了pthread_join使得其已经阻塞式等待了,然后新线程才pthread_detach分离,这个时候已经晚了。
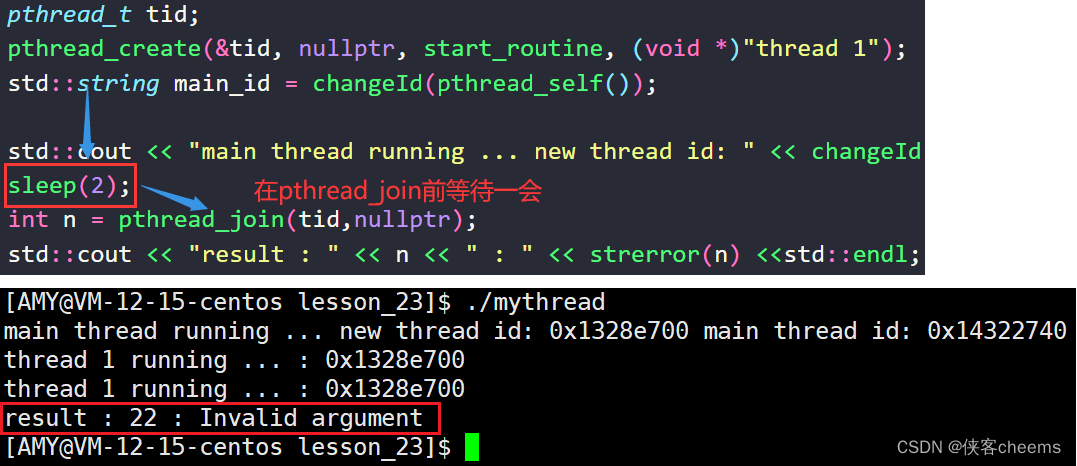
当然这种分离方式我们不赞成,我们一般这样使用线程分离:
std::string changeId(const pthread_t &thread_id)
{
char tid[128];
snprintf(tid, sizeof(tid), "0x%x", thread_id);
return tid;
}
void *start_routine(void *args)
{
std::string threadname = static_cast<const char *>(args);
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
std::cout << threadname << " running ... : " << changeId(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, start_routine, (void *)"thread 1");
std::string main_id = changeId(pthread_self());
pthread_detach(tid);//线程分离
std::cout << "main thread running ... new thread id: " << changeId(tid) << " main thread id: " << main_id << std::endl;
// int n = pthread_join(tid,nullptr);
// std::cout << "result : " << n << " : " << strerror(n) <<std::endl;
while (true)
{
std::cout << "main thread running ... " << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
如有错误或者不清楚的地方欢迎私信或者评论指出🚀🚀







![[C++] C++入门第一篇 -- 命名空间,输入输出,缺省函数,函数重载底层原理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/fd87802f510b5c3cf790cd01cf140dce.png)