简介:Elasticsearch 是一个分布式、高扩展、高实时的搜索与数据分析引擎。它能很方便的使大量数据具有搜索、分析和探索的能力。充分利用Elasticsearch的水平伸缩性,能使数据在生产环境变得更有价值。Elasticsearch 的实现原理主要分为以下几个步骤,首先用户将数据提交到Elasticsearch 数据库中,再通过分词控制器去将对应的语句分词,将其权重和分词结果一并存入数据,当用户搜索数据时候,再根据权重将结果排名,打分,再将返回结果呈现给用户。Elasticsearch是与名为Logstash的数据收集和日志解析引擎以及名为Kibana的分析和可视化平台一起开发的。这三个产品被设计成一个集成解决方案,称为“Elastic Stack”(以前称为“ELK stack”)。
历史攻略:
centos7:docker安装Elasticsearch
运行Elasticsearch:
docker run -d --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.13.1
安装:
pip install elasticsearch
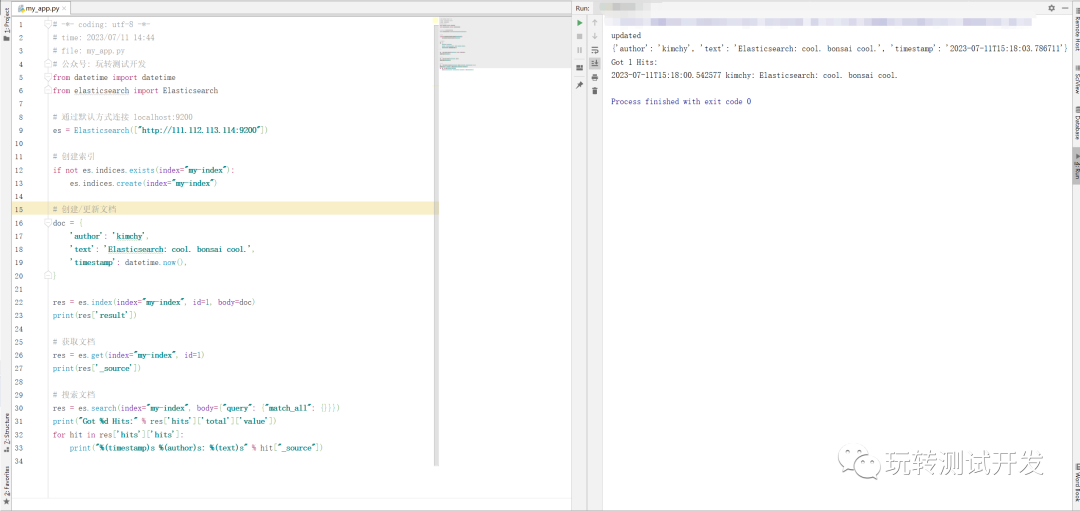
案例源码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# time: 2023/07/11 14:44
# file: my_app.py
# 公众号: 玩转测试开发
from datetime import datetime
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
# 通过默认方式连接 localhost:9200
es = Elasticsearch(["http://111.112.113.114:9200"])
# 创建索引
if not es.indices.exists(index="my-index"):
es.indices.create(index="my-index")
# 创建/更新文档
doc = {
'author': 'kimchy',
'text': 'Elasticsearch: cool. bonsai cool.',
'timestamp': datetime.now(),
}
res = es.index(index="my-index", id=1, body=doc)
print(res['result'])
# 获取文档
res = es.get(index="my-index", id=1)
print(res['_source'])
# 搜索文档
res = es.search(index="my-index", body={"query": {"match_all": {}}})
print("Got %d Hits:" % res['hits']['total']['value'])
for hit in res['hits']['hits']:
print("%(timestamp)s %(author)s: %(text)s" % hit["_source"])
浏览器访问客户端结果:http://:9200/
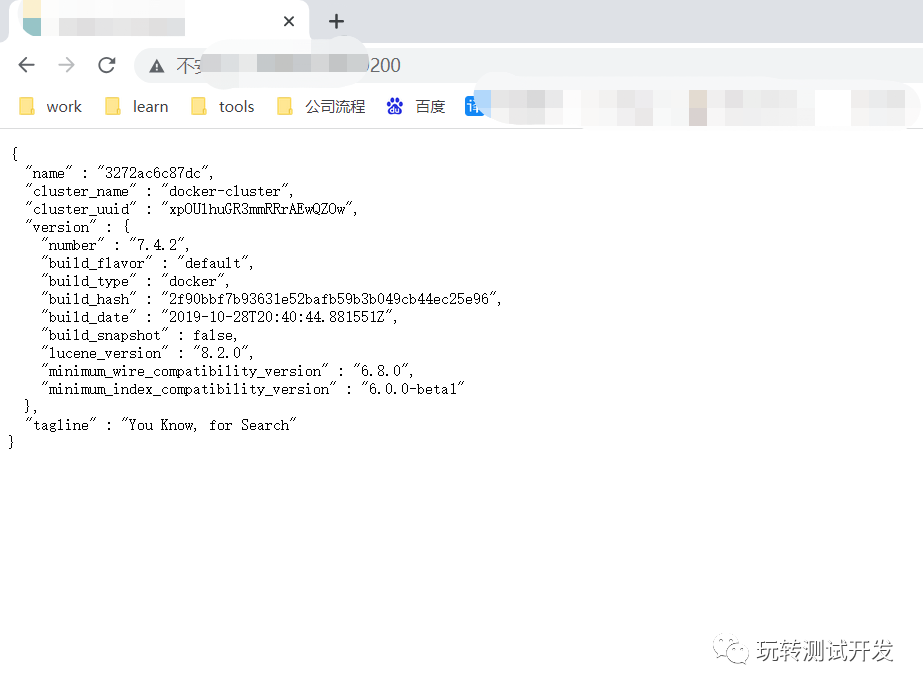
python运行结果: