本文基于Istio 1.18.0版本进行源码学习
1、Pilot-Discovery工作原理
Pilot-Discovery是Istio控制面的核心,负责服务网格中的流量管理以及控制面和数据面之间的配置下发
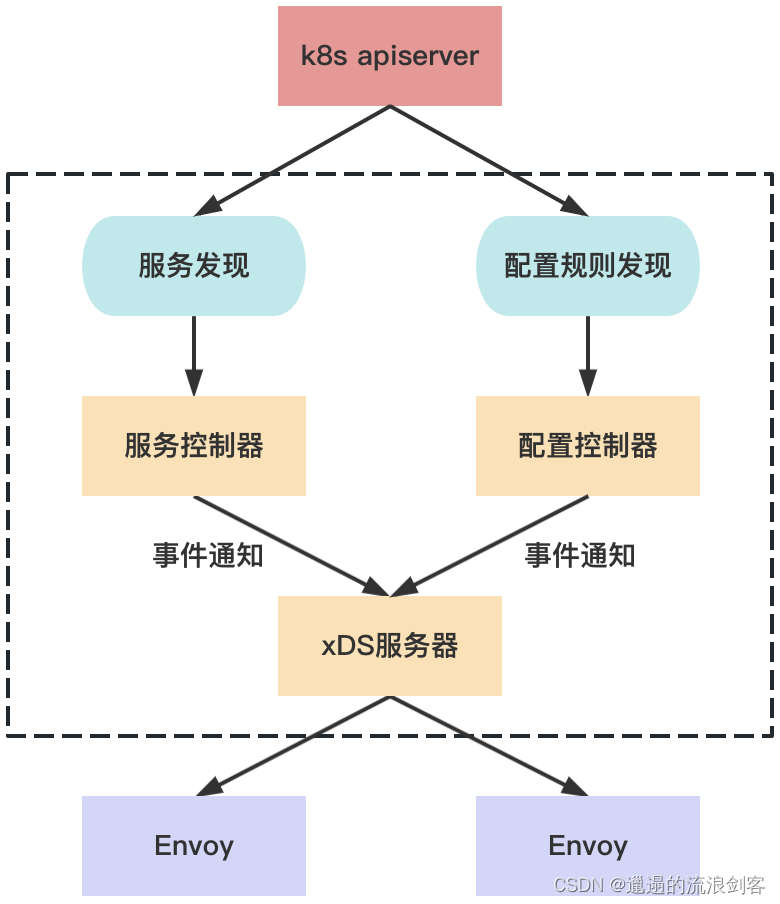
Pilot-Discovery从注册中心(如Kubernetes)获取服务信息并汇集,从Kubernetes API Server中获取配置规则,将服务信息和配置数据转换为xDS接口的标准数据结构,通过GRPC下发到数据面的Envoy
2、Pilot-Discovery代码结构

Pilot-Discovery的入口函数为:pilot/cmd/pilot-discovery/main.go中的main方法。main方法中创建了Pilot Server,Pilot Server中主要包含三部分逻辑:
- ConfigController:管理各种配置数据,包括用户创建的流量管理规则和策略
- ServiceController:获取Service Registry中的服务发现数据
- DiscoveryService:主要包含下述逻辑:
- 启动GRPC Server并接收来自Envoy端的连接请求
- 接收Envoy端的xDS请求,从ConfigController和ServiceController中获取配置和服务信息,生成响应消息发送给Envoy
- 监听来自ConfigController的配置变化消息和ServiceController的服务变化消息,并将配置和服务变化内容通过xDS接口推送到Envoy
3、Pilot-Discovery启动流程
创建Pilot Server代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/bootstrap/server.go
func NewServer(args *PilotArgs, initFuncs ...func(*Server)) (*Server, error) {
e := model.NewEnvironment()
e.DomainSuffix = args.RegistryOptions.KubeOptions.DomainSuffix
e.SetLedger(buildLedger(args.RegistryOptions))
ac := aggregate.NewController(aggregate.Options{
MeshHolder: e,
})
e.ServiceDiscovery = ac
s := &Server{
clusterID: getClusterID(args),
environment: e,
fileWatcher: filewatcher.NewWatcher(),
httpMux: http.NewServeMux(),
monitoringMux: http.NewServeMux(),
readinessProbes: make(map[string]readinessProbe),
readinessFlags: &readinessFlags{},
workloadTrustBundle: tb.NewTrustBundle(nil),
server: server.New(),
shutdownDuration: args.ShutdownDuration,
internalStop: make(chan struct{}),
istiodCertBundleWatcher: keycertbundle.NewWatcher(),
webhookInfo: &webhookInfo{},
}
// Apply custom initialization functions.
for _, fn := range initFuncs {
fn(s)
}
// Initialize workload Trust Bundle before XDS Server
e.TrustBundle = s.workloadTrustBundle
// 初始化discoveryServer
s.XDSServer = xds.NewDiscoveryServer(e, args.PodName, s.clusterID, args.RegistryOptions.KubeOptions.ClusterAliases)
prometheus.EnableHandlingTimeHistogram()
// make sure we have a readiness probe before serving HTTP to avoid marking ready too soon
s.initReadinessProbes()
// 初始化http和grpc server,向grpc server注册discoveryServer
s.initServers(args)
if err := s.initIstiodAdminServer(args, s.webhookInfo.GetTemplates); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error initializing debug server: %v", err)
}
if err := s.serveHTTP(); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error serving http: %v", err)
}
// Apply the arguments to the configuration.
if err := s.initKubeClient(args); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error initializing kube client: %v", err)
}
// used for both initKubeRegistry and initClusterRegistries
args.RegistryOptions.KubeOptions.EndpointMode = kubecontroller.DetectEndpointMode(s.kubeClient)
s.initMeshConfiguration(args, s.fileWatcher)
spiffe.SetTrustDomain(s.environment.Mesh().GetTrustDomain())
s.initMeshNetworks(args, s.fileWatcher)
s.initMeshHandlers()
s.environment.Init()
if err := s.environment.InitNetworksManager(s.XDSServer); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Options based on the current 'defaults' in istio.
caOpts := &caOptions{
TrustDomain: s.environment.Mesh().TrustDomain,
Namespace: args.Namespace,
DiscoveryFilter: args.RegistryOptions.KubeOptions.GetFilter(),
ExternalCAType: ra.CaExternalType(externalCaType),
CertSignerDomain: features.CertSignerDomain,
}
if caOpts.ExternalCAType == ra.ExtCAK8s {
// Older environment variable preserved for backward compatibility
caOpts.ExternalCASigner = k8sSigner
}
// CA signing certificate must be created first if needed.
if err := s.maybeCreateCA(caOpts); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 初始化configController和serviceController
if err := s.initControllers(args); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
s.XDSServer.InitGenerators(e, args.Namespace, s.internalDebugMux)
// Initialize workloadTrustBundle after CA has been initialized
if err := s.initWorkloadTrustBundle(args); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Parse and validate Istiod Address.
istiodHost, _, err := e.GetDiscoveryAddress()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Create Istiod certs and setup watches.
if err := s.initIstiodCerts(args, string(istiodHost)); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Secure gRPC Server must be initialized after CA is created as may use a Citadel generated cert.
if err := s.initSecureDiscoveryService(args); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error initializing secure gRPC Listener: %v", err)
}
// common https server for webhooks (e.g. injection, validation)
if s.kubeClient != nil {
s.initSecureWebhookServer(args)
wh, err := s.initSidecarInjector(args)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error initializing sidecar injector: %v", err)
}
s.webhookInfo.mu.Lock()
s.webhookInfo.wh = wh
s.webhookInfo.mu.Unlock()
if err := s.initConfigValidation(args); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error initializing config validator: %v", err)
}
}
// This should be called only after controllers are initialized.
// 向configController和serviceController注册事件回调函数
s.initRegistryEventHandlers()
// 设置discoveryServer启动函数
s.initDiscoveryService()
// Notice that the order of authenticators matters, since at runtime
// authenticators are activated sequentially and the first successful attempt
// is used as the authentication result.
authenticators := []security.Authenticator{
&authenticate.ClientCertAuthenticator{},
}
if args.JwtRule != "" {
jwtAuthn, err := initOIDC(args)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error initializing OIDC: %v", err)
}
if jwtAuthn == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("JWT authenticator is nil")
}
authenticators = append(authenticators, jwtAuthn)
}
// The k8s JWT authenticator requires the multicluster registry to be initialized,
// so we build it later.
if s.kubeClient != nil {
authenticators = append(authenticators,
kubeauth.NewKubeJWTAuthenticator(s.environment.Watcher, s.kubeClient.Kube(), s.clusterID, s.multiclusterController.GetRemoteKubeClient, features.JwtPolicy))
}
if len(features.TrustedGatewayCIDR) > 0 {
authenticators = append(authenticators, &authenticate.XfccAuthenticator{})
}
if features.XDSAuth {
s.XDSServer.Authenticators = authenticators
}
caOpts.Authenticators = authenticators
// Start CA or RA server. This should be called after CA and Istiod certs have been created.
s.startCA(caOpts)
// TODO: don't run this if galley is started, one ctlz is enough
if args.CtrlZOptions != nil {
_, _ = ctrlz.Run(args.CtrlZOptions, nil)
}
// This must be last, otherwise we will not know which informers to register
if s.kubeClient != nil {
s.addStartFunc(func(stop <-chan struct{}) error {
s.kubeClient.RunAndWait(stop)
return nil
})
}
return s, nil
}
NewServer()方法中核心逻辑如下:
- 初始化DiscoveryServer
- 初始化HTTP和GRPC Server,向GRPC Server注册DiscoveryServer
- 初始化ConfigController和ServiceController
- 向ConfigController和ServiceController注册事件回调函数,有配置和服务信息变更时会通知DiscoveryServer
- 设置DiscoveryServer启动函数
Pilot Server定义如下:
// pilot/pkg/bootstrap/server.go
type Server struct {
// discoveryServer
XDSServer *xds.DiscoveryServer
clusterID cluster.ID
// pilot环境所需的api集合
environment *model.Environment
// 处理kubernetes主集群的注册中心
kubeClient kubelib.Client
// 处理kubernetes多个集群的注册中心
multiclusterController *multicluster.Controller
// 统一处理配置规则的controller
configController model.ConfigStoreController
// 配置规则缓存
ConfigStores []model.ConfigStoreController
// 负责serviceEntry的服务发现
serviceEntryController *serviceentry.Controller
httpServer *http.Server // debug, monitoring and readiness Server.
httpAddr string
httpsServer *http.Server // webhooks HTTPS Server.
grpcServer *grpc.Server
grpcAddress string
secureGrpcServer *grpc.Server
secureGrpcAddress string
// monitoringMux listens on monitoringAddr(:15014).
// Currently runs prometheus monitoring and debug (if enabled).
monitoringMux *http.ServeMux
// internalDebugMux is a mux for *internal* calls to the debug interface. That is, authentication is disabled.
internalDebugMux *http.ServeMux
// httpMux listens on the httpAddr (8080).
// If a Gateway is used in front and https is off it is also multiplexing
// the rest of the features if their port is empty.
// Currently runs readiness and debug (if enabled)
httpMux *http.ServeMux
// httpsMux listens on the httpsAddr(15017), handling webhooks
// If the address os empty, the webhooks will be set on the default httpPort.
httpsMux *http.ServeMux // webhooks
// fileWatcher used to watch mesh config, networks and certificates.
fileWatcher filewatcher.FileWatcher
// certWatcher watches the certificates for changes and triggers a notification to Istiod.
cacertsWatcher *fsnotify.Watcher
dnsNames []string
CA *ca.IstioCA
RA ra.RegistrationAuthority
// TrustAnchors for workload to workload mTLS
workloadTrustBundle *tb.TrustBundle
certMu sync.RWMutex
istiodCert *tls.Certificate
istiodCertBundleWatcher *keycertbundle.Watcher
// pilot的所有组件都注册启动任务到此对象,便于在Start()方法中批量启动及管理
server server.Instance
readinessProbes map[string]readinessProbe
readinessFlags *readinessFlags
// duration used for graceful shutdown.
shutdownDuration time.Duration
// internalStop is closed when the server is shutdown. This should be avoided as much as possible, in
// favor of AddStartFunc. This is only required if we *must* start something outside of this process.
// For example, everything depends on mesh config, so we use it there rather than trying to sequence everything
// in AddStartFunc
internalStop chan struct{}
webhookInfo *webhookInfo
statusReporter *distribution.Reporter
statusManager *status.Manager
// RWConfigStore is the configstore which allows updates, particularly for status.
RWConfigStore model.ConfigStoreController
}
Pilot-Discovery启动流程如下图:

3、配置规则发现:ConfigController
Pilot的配置规则指网络路由规则及网络安全规则,包含Virtualservice、Destinationrule、Gateway、PeerAuthentication、RequestAuthentication等资源。目前支持三种类型的ConfigController:
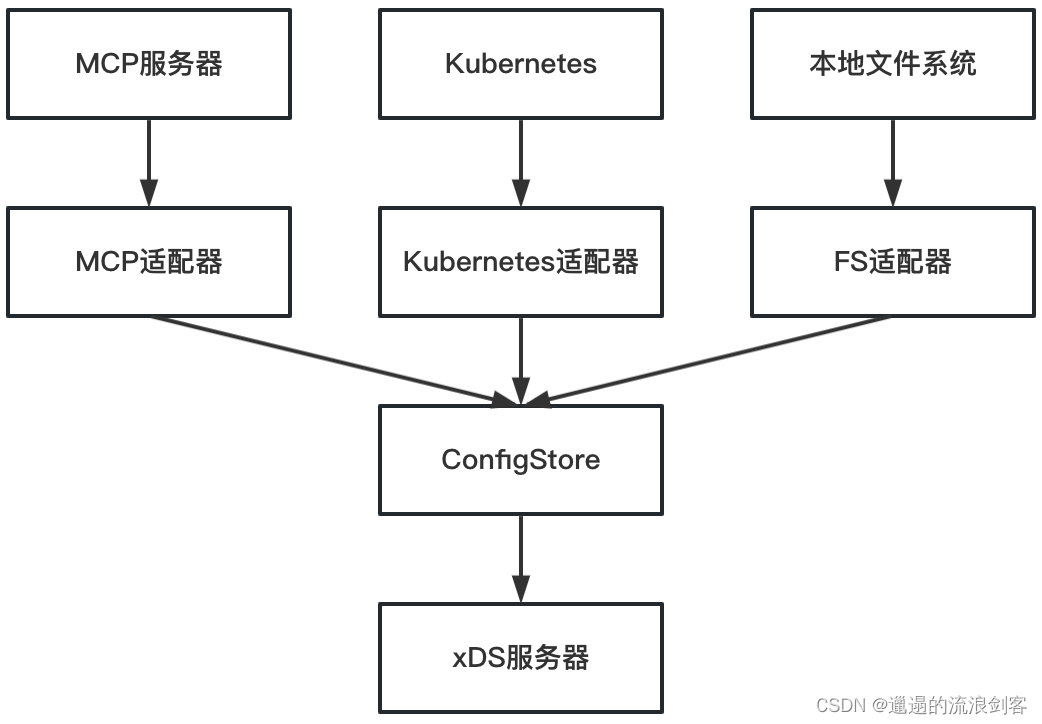
- MCP:是一种服务网格配置传输协议,用于隔离Pilot和底层平台(Kubernetes、文件系统或者其他注册中心),使得Pilot无需感知底层平台的差异,更专注于Envoy xDS配置的生成与分发
- Kubernetes:基于Kubernetes的Config发现利用了Kubernetes Informer的List-Watch能力。在Kubernetes集群中,Config以CustomResource的形式存在。Pilot通过配置控制器(CRD Controller)监听Kubernetes APIServer配置规则资源,维护所有资源的缓存,并触发事件处理回调函数
- File:通过文件监视器周期性地读取本地配置文件,将配置规则缓存在内存中,并维护配置的增加、更新、删除事件,当缓存有变化时,异步通知内存控制器执行事件回调函数
1)、ConfigController的核心接口
ConfigController实现了ConfigStoreController接口:
// pilot/pkg/model/config.go
type ConfigStoreController interface {
// 配置缓存接口
ConfigStore
// 注册事件处理函数
// RegisterEventHandler adds a handler to receive config update events for a
// configuration type
RegisterEventHandler(kind config.GroupVersionKind, handler EventHandler)
// 运行控制器
// Run until a signal is received.
// Run *should* block, so callers should typically call `go controller.Run(stop)`
Run(stop <-chan struct{})
// 配置缓存是否已同步
// HasSynced returns true after initial cache synchronization is complete
HasSynced() bool
}
ConfigStoreController继承ConfigStore接口,ConfigStore为控制器核心的资源缓存接口提供了对Config资源的增删改查功能:
// pilot/pkg/model/config.go
type ConfigStore interface {
// Schemas exposes the configuration type schema known by the config store.
// The type schema defines the bidirectional mapping between configuration
// types and the protobuf encoding schema.
Schemas() collection.Schemas
// Get retrieves a configuration element by a type and a key
Get(typ config.GroupVersionKind, name, namespace string) *config.Config
// List returns objects by type and namespace.
// Use "" for the namespace to list across namespaces.
List(typ config.GroupVersionKind, namespace string) []config.Config
// Create adds a new configuration object to the store. If an object with the
// same name and namespace for the type already exists, the operation fails
// with no side effects.
Create(config config.Config) (revision string, err error)
// Update modifies an existing configuration object in the store. Update
// requires that the object has been created. Resource version prevents
// overriding a value that has been changed between prior _Get_ and _Put_
// operation to achieve optimistic concurrency. This method returns a new
// revision if the operation succeeds.
Update(config config.Config) (newRevision string, err error)
UpdateStatus(config config.Config) (newRevision string, err error)
// Patch applies only the modifications made in the PatchFunc rather than doing a full replace. Useful to avoid
// read-modify-write conflicts when there are many concurrent-writers to the same resource.
Patch(orig config.Config, patchFn config.PatchFunc) (string, error)
// Delete removes an object from the store by key
// For k8s, resourceVersion must be fulfilled before a deletion is carried out.
// If not possible, a 409 Conflict status will be returned.
Delete(typ config.GroupVersionKind, name, namespace string, resourceVersion *string) error
}
2)、ConfigController的初始化
Kubernetes ConfigController实际上是一个CRD Operator,它从Kubernetes API Server监听所有的Istio API资源,其初始化过程如下:
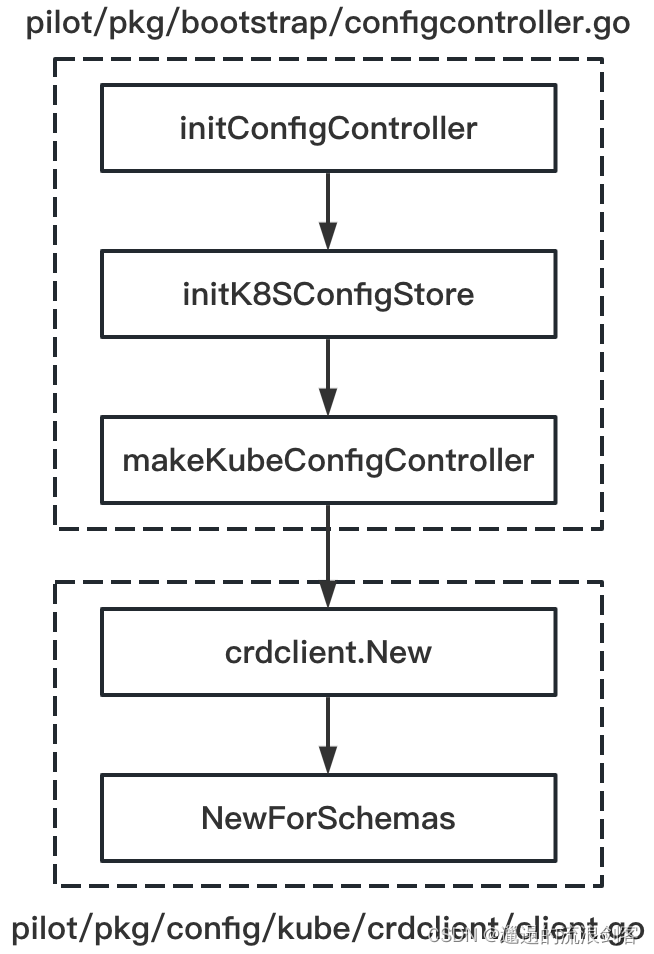
crdclient.New()方法代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/config/kube/crdclient/client.go
func New(client kube.Client, opts Option) (*Client, error) {
schemas := collections.Pilot
if features.EnableGatewayAPI {
schemas = collections.PilotGatewayAPI()
}
return NewForSchemas(client, opts, schemas)
}
collections.Pilot中定义了Istio所有的Config资源类型,代码如下:
// pkg/config/schema/collections/collections.gen.go
// Pilot contains only collections used by Pilot.
Pilot = collection.NewSchemasBuilder().
MustAdd(AuthorizationPolicy).
MustAdd(DestinationRule).
MustAdd(EnvoyFilter).
MustAdd(Gateway).
MustAdd(PeerAuthentication).
MustAdd(ProxyConfig).
MustAdd(RequestAuthentication).
MustAdd(ServiceEntry).
MustAdd(Sidecar).
MustAdd(Telemetry).
MustAdd(VirtualService).
MustAdd(WasmPlugin).
MustAdd(WorkloadEntry).
MustAdd(WorkloadGroup).
Build()
crdclient.New()方法中调用了NewForSchemas()方法:
// pilot/pkg/config/kube/crdclient/client.go
func NewForSchemas(client kube.Client, opts Option, schemas collection.Schemas) (*Client, error) {
schemasByCRDName := map[string]resource.Schema{}
for _, s := range schemas.All() {
// From the spec: "Its name MUST be in the format <.spec.name>.<.spec.group>."
name := fmt.Sprintf("%s.%s", s.Plural(), s.Group())
schemasByCRDName[name] = s
}
// 实例化crd client
out := &Client{
domainSuffix: opts.DomainSuffix,
schemas: schemas,
schemasByCRDName: schemasByCRDName,
revision: opts.Revision,
queue: queue.NewQueue(1 * time.Second),
kinds: map[config.GroupVersionKind]*cacheHandler{},
handlers: map[config.GroupVersionKind][]model.EventHandler{},
client: client,
// 创建crdWatcher,监听crd的创建
crdWatcher: crdwatcher.NewController(client),
logger: scope.WithLabels("controller", opts.Identifier),
namespacesFilter: opts.NamespacesFilter,
crdWatches: map[config.GroupVersionKind]*waiter{
gvk.KubernetesGateway: newWaiter(),
gvk.GatewayClass: newWaiter(),
},
}
// 添加回调函数,当crd创建时调用handleCRDAdd方法
out.crdWatcher.AddCallBack(func(name string) {
handleCRDAdd(out, name)
})
// 获取集群中当前所有的crd
known, err := knownCRDs(client.Ext())
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 遍历istio所有的config资源类型
for _, s := range schemas.All() {
// From the spec: "Its name MUST be in the format <.spec.name>.<.spec.group>."
name := fmt.Sprintf("%s.%s", s.Plural(), s.Group())
if s.IsBuiltin() {
handleCRDAdd(out, name)
} else {
// istio config资源类型对应crd已创建,调用handleCRDAdd方法
if _, f := known[name]; f {
handleCRDAdd(out, name)
} else {
out.logger.Warnf("Skipping CRD %v as it is not present", s.GroupVersionKind())
}
}
}
return out, nil
}
NewForSchemas()方法中实例化了CRD Client,CRD Client定义如下:
// pilot/pkg/config/kube/crdclient/client.go
type Client struct {
// schemas defines the set of schemas used by this client.
// Note: this must be a subset of the schemas defined in the codegen
schemas collection.Schemas
// domainSuffix for the config metadata
domainSuffix string
// revision for this control plane instance. We will only read configs that match this revision.
revision string
// kinds keeps track of all cache handlers for known types
// 记录所有资源类型对应的informer控制器
kinds map[config.GroupVersionKind]*cacheHandler
kindsMu sync.RWMutex
// 事件处理队列
queue queue.Instance
// handlers defines a list of event handlers per-type
// 资源类型及对应的事件处理回调函数
handlers map[config.GroupVersionKind][]model.EventHandler
// crd相关的schema
schemasByCRDName map[string]resource.Schema
// kubernetes客户端,包含istioClient操作istio api对象,istio informer监听istio api对象变更事件
client kube.Client
// 监听crd的创建
crdWatcher *crdwatcher.Controller
logger *log.Scope
// namespacesFilter is only used to initiate filtered informer.
namespacesFilter func(obj interface{}) bool
// crdWatches notifies consumers when a CRD is present
crdWatches map[config.GroupVersionKind]*waiter
stop <-chan struct{}
}
3)、ConfigController的工作机制
Kubernetes ConfigController为每种Config资源都创建了一个Informer,用于监听所有Config资源并注册EventHandler
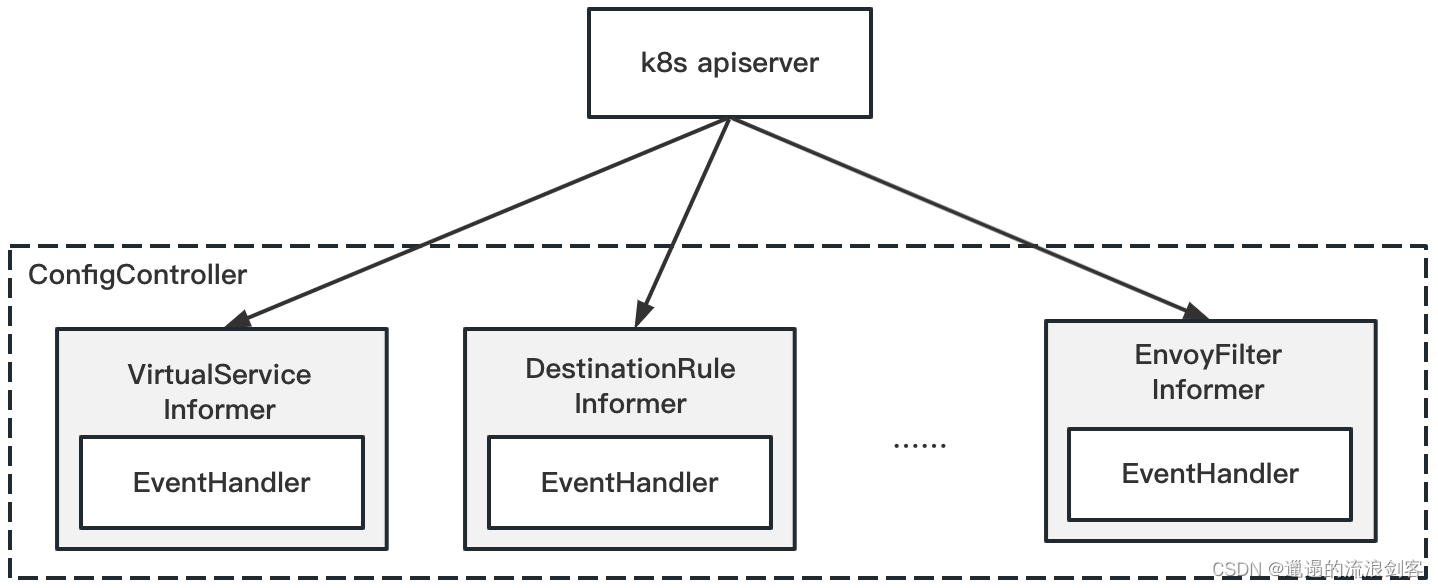
NewForSchemas()方法中,如果Istio Config资源类型对应CRD已创建或者crdWatcher监听CRD创建后,都会调用handleCRDAdd()方法:
// pilot/pkg/config/kube/crdclient/client.go
func handleCRDAdd(cl *Client, name string) {
cl.logger.Debugf("adding CRD %q", name)
s, f := cl.schemasByCRDName[name]
if !f {
cl.logger.Debugf("added resource that we are not watching: %v", name)
return
}
resourceGVK := s.GroupVersionKind()
gvr := s.GroupVersionResource()
cl.kindsMu.Lock()
defer cl.kindsMu.Unlock()
if _, f := cl.kinds[resourceGVK]; f {
cl.logger.Debugf("added resource that already exists: %v", resourceGVK)
return
}
var i informers.GenericInformer
var ifactory starter
var err error
// 根据api group添加到不同的sharedInformerFactory中
switch s.Group() {
case gvk.KubernetesGateway.Group:
ifactory = cl.client.GatewayAPIInformer()
i, err = cl.client.GatewayAPIInformer().ForResource(gvr)
case gvk.Pod.Group, gvk.Deployment.Group, gvk.MutatingWebhookConfiguration.Group:
ifactory = cl.client.KubeInformer()
i, err = cl.client.KubeInformer().ForResource(gvr)
case gvk.CustomResourceDefinition.Group:
ifactory = cl.client.ExtInformer()
i, err = cl.client.ExtInformer().ForResource(gvr)
default:
ifactory = cl.client.IstioInformer()
i, err = cl.client.IstioInformer().ForResource(gvr)
}
if err != nil {
// Shouldn't happen
cl.logger.Errorf("failed to create informer for %v: %v", resourceGVK, err)
return
}
_ = i.Informer().SetTransform(kube.StripUnusedFields)
// 调用createCacheHandler方法,为informer添加事件回调函数
cl.kinds[resourceGVK] = createCacheHandler(cl, s, i)
if w, f := cl.crdWatches[resourceGVK]; f {
cl.logger.Infof("notifying watchers %v was created", resourceGVK)
w.once.Do(func() {
close(w.stop)
})
}
// Start informer. In startup case, we will not start here as
// we will start all factories once we are ready to initialize.
// For dynamically added CRDs, we need to start immediately though
if cl.stop != nil {
// 启动informer
ifactory.Start(cl.stop)
}
}
每种Informer的事件回调函数均通过createCacheHandler()方法注册,代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/config/kube/crdclient/cache_handler.go
func createCacheHandler(cl *Client, schema resource.Schema, i informers.GenericInformer) *cacheHandler {
scope.Debugf("registered CRD %v", schema.GroupVersionKind())
h := &cacheHandler{
client: cl,
schema: schema,
// 创建informer,支持配置namespace级别隔离
informer: kclient.NewUntyped(cl.client, i.Informer(), kclient.Filter{ObjectFilter: cl.namespacesFilter}),
}
kind := schema.Kind()
// 添加事件回调函数
h.informer.AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(obj any) {
incrementEvent(kind, "add")
// 创建任务对象并将其发送到任务队列中
cl.queue.Push(func() error {
return h.onEvent(nil, obj, model.EventAdd)
})
},
UpdateFunc: func(old, cur any) {
incrementEvent(kind, "update")
cl.queue.Push(func() error {
return h.onEvent(old, cur, model.EventUpdate)
})
},
DeleteFunc: func(obj any) {
incrementEvent(kind, "delete")
cl.queue.Push(func() error {
return h.onEvent(nil, obj, model.EventDelete)
})
},
})
return h
}
当Config资源在Kubernetes中创建、更新和删除时,EventHandler会创建任务对象并将其发送到任务列中,然后由任务处理协程处理。处理资源变化的onEvent()方法代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/config/kube/crdclient/cache_handler.go
func (h *cacheHandler) onEvent(old any, curr any, event model.Event) error {
currItem := controllers.ExtractObject(curr)
if currItem == nil {
return nil
}
// 进行对象转换
currConfig := TranslateObject(currItem, h.schema.GroupVersionKind(), h.client.domainSuffix)
var oldConfig config.Config
if old != nil {
oldItem, ok := old.(runtime.Object)
if !ok {
log.Warnf("Old Object can not be converted to runtime Object %v, is type %T", old, old)
return nil
}
oldConfig = TranslateObject(oldItem, h.schema.GroupVersionKind(), h.client.domainSuffix)
}
if h.client.objectInRevision(&currConfig) {
// 执行事件处理回调函数
h.callHandlers(oldConfig, currConfig, event)
return nil
}
// Check if the object was in our revision, but has been moved to a different revision. If so,
// it has been effectively deleted from our revision, so process it as a delete event.
if event == model.EventUpdate && old != nil && h.client.objectInRevision(&oldConfig) {
log.Debugf("Object %s/%s has been moved to a different revision, deleting",
currConfig.Namespace, currConfig.Name)
// 执行事件处理回调函数
h.callHandlers(oldConfig, currConfig, model.EventDelete)
return nil
}
log.Debugf("Skipping event %s for object %s/%s from different revision",
event, currConfig.Namespace, currConfig.Name)
return nil
}
func (h *cacheHandler) callHandlers(old config.Config, curr config.Config, event model.Event) {
// TODO we may consider passing a pointer to handlers instead of the value. While spec is a pointer, the meta will be copied
// 执行该资源类型对应的事件处理回调函数
for _, f := range h.client.handlers[h.schema.GroupVersionKind()] {
f(old, curr, event)
}
}
onEvent()方法中通过TranslateObject()方法进行对象转换,然后执行该资源类型对应的事件处理回调函数
h.client.handlers是各种资源类型的处理函数集合,是通过ConfigController的RegisterEventHandler()注册的,注册代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/bootstrap/server.go
func (s *Server) initRegistryEventHandlers() {
...
if s.configController != nil {
configHandler := func(prev config.Config, curr config.Config, event model.Event) {
defer func() {
// 状态报告
if event != model.EventDelete {
s.statusReporter.AddInProgressResource(curr)
} else {
s.statusReporter.DeleteInProgressResource(curr)
}
}()
log.Debugf("Handle event %s for configuration %s", event, curr.Key())
// For update events, trigger push only if spec has changed.
// 对于更新事件,仅当对象的spec发生变化时才触发xds推送
if event == model.EventUpdate && !needsPush(prev, curr) {
log.Debugf("skipping push for %s as spec has not changed", prev.Key())
return
}
// 触发xds全量更新
pushReq := &model.PushRequest{
Full: true,
ConfigsUpdated: sets.New(model.ConfigKey{Kind: kind.MustFromGVK(curr.GroupVersionKind), Name: curr.Name, Namespace: curr.Namespace}),
Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.ConfigUpdate},
}
s.XDSServer.ConfigUpdate(pushReq)
}
schemas := collections.Pilot.All()
if features.EnableGatewayAPI {
schemas = collections.PilotGatewayAPI().All()
}
for _, schema := range schemas {
// This resource type was handled in external/servicediscovery.go, no need to rehandle here.
// 下面3种类型在serviceEntry controller中处理,这里不用为其注册事件处理函数
if schema.GroupVersionKind() == gvk.ServiceEntry {
continue
}
if schema.GroupVersionKind() == gvk.WorkloadEntry {
continue
}
if schema.GroupVersionKind() == gvk.WorkloadGroup {
continue
}
// 注册其他所有api对象的事件处理函数
s.configController.RegisterEventHandler(schema.GroupVersionKind(), configHandler)
}
...
}
完整的Config事件处理流程如下图所示:
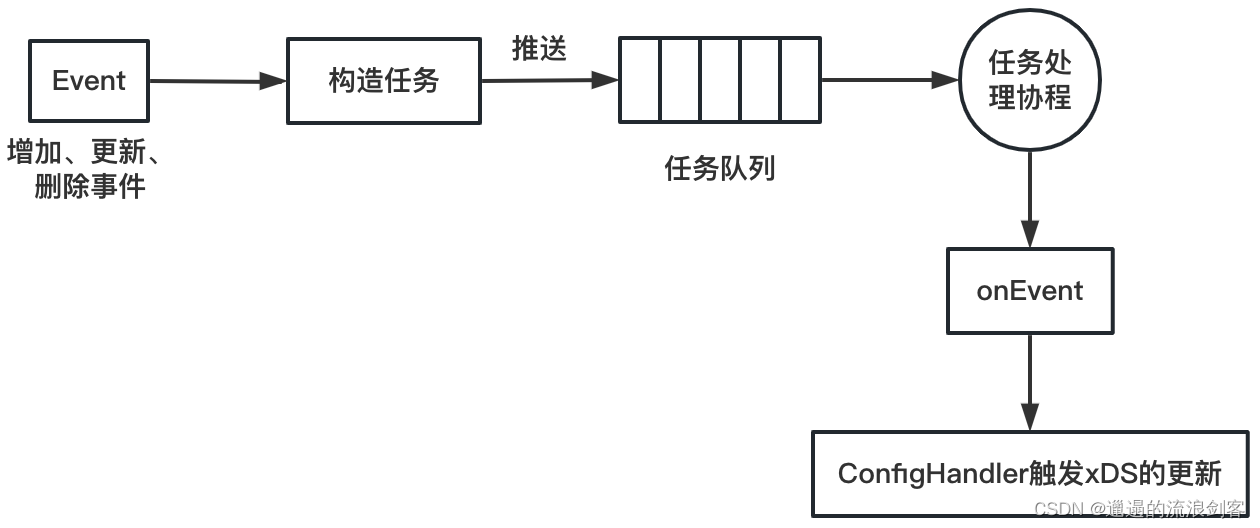
- EventHandler构造任务(Task),任务实际上是对onEvent函数的封装
- EventHandler将任务推送到任务队列中
- 任务处理协程阻塞式地读取任务队列,执行任务,通过onEvent方法处理事件,并通过ConfigHandler触发xDS的更新
参考:
《Istio权威指南 下》
3.深入Istio源码:Pilot配置规则ConfigController
Istio Pilot代码深度解析