目录
Object类的equals方法
Student类
测试类
第一步:使用==比较
第二步:使用equals比较
第三步:在子类-Student类中重写equals方法
代码逐句分析
运行
Object类的equals方法
首先写一个类Student,属性有name和age,然后创建两个Student对象,并分别给赋值,然后比较两个对象
Student类
package com.hspedu.equalsheima;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
测试类
package com.hspedu.equalsheima;
public class ObjectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setName("林青霞");
s1.setAge(65);
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.setName("林青霞");
s2.setAge(65);
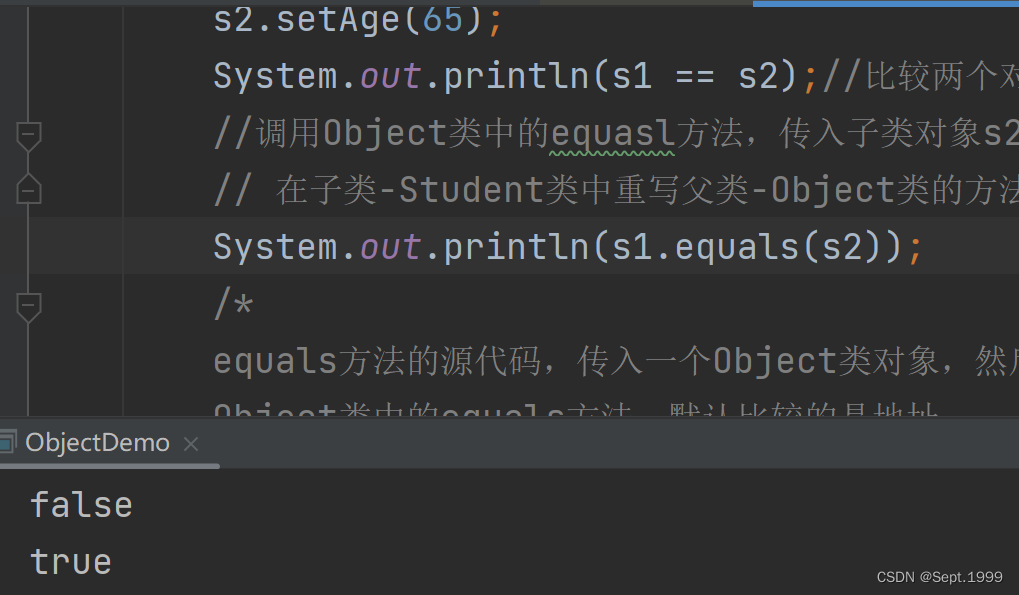
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//比较两个对象的地址
}
}
第一步:使用==比较
因为==在比较引用类型数据的时候,是比较两个对象的地址是否相同,s1和s2指向不同的地址空间,所以结果为false
第二步:使用equals比较

此时使用的是Object类中的equals方法,此时比较的还是两个对象的地址,结果还是false
源代码:用ctrl+B调出
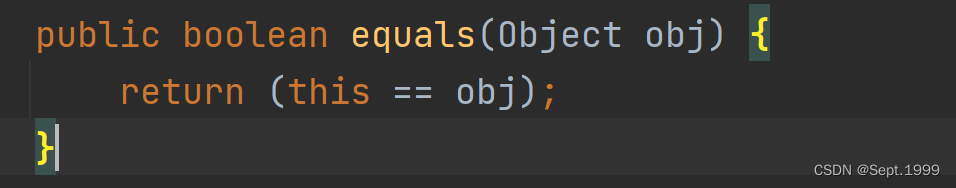
对源代码的分析:1)传入一个Object类对象,然后比较 2) Object类中的equals方法,默认比较的是地址
在这个案例中 this就是指调用方法的对象,即s1;obj就是s2
//this------->s1 //obj ------->s2
第三步:在子类-Student类中重写equals方法
使用Alt + Insert快捷键在Student类中重写父类-Object类的equals方法
public boolean equals(Object o) {
/*
this --- s1
o ---s2
*/
//比较地址是否相同,如果相同,直接返回true
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;// student = s2;
if (age != student.age) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
}
代码逐句分析
if (this == o) return true;//比较地址是否相同
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
1)o == null :首先判断传入的参数s2是否为null;如果为null,返回false
2)getClass() != o.getClass():判断s1和s2是否来自同一个类
3)如果判断结果为true,表示不是同一个类,那么内容肯定不会相等,返回false
4)||短路或,有真为真,只要满足上述任一条件,就返回false
Student student = (Student) o;//在传参的时候完成了向上转型,此时再向下转型
if (age != student.age) return false;//判断s1和s2的age,如果不相同,返回false
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
上述语句是一个三元运算符:规则一真大师
1) name != null?如果结果为true,则返回name.equals(student.name)的比较结果
2)name.equals(student.name):比较字符串的内容是否相同;
3)String类是Object类的子类,重写了Object类的equals方法,所以可以比较内容(韩顺平equals方法)
4)如果name != null的结果为false,说明s1=null,此时接收student.name == null的返回结果
运行
在重写过后就可以比较内容,此时的结果就是true而非false




![[附源码]计算机毕业设计基于Vue的社区拼购商城Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/005011ba90164b02a28520def08818da.png)