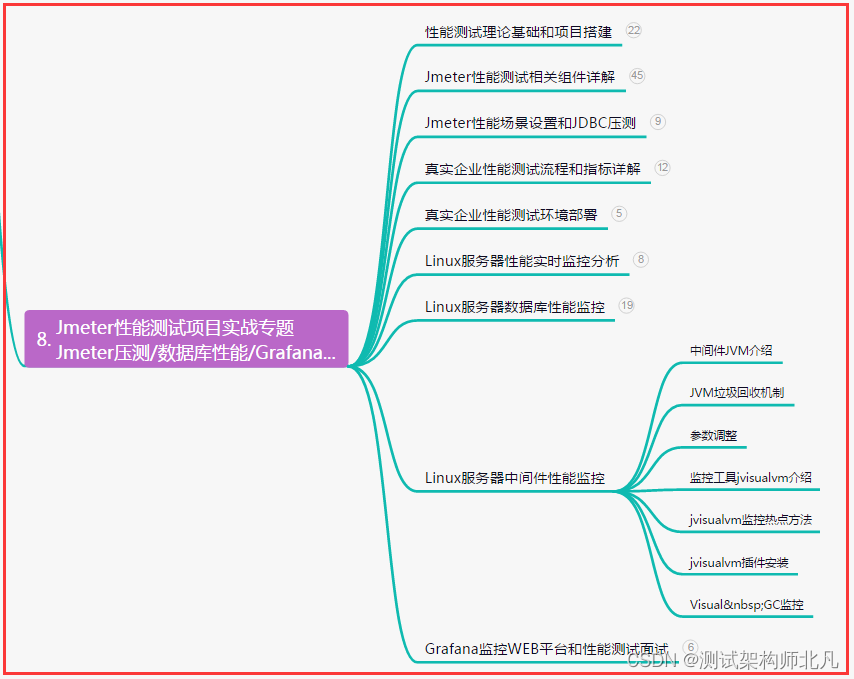
如何克隆一个引用所指的对象呢?首先一个前提,他是可克隆的,我们要实现一个Clonable 接口。我们来看一个这个接口:

可以发现里面是空的,我们把这种空接口叫做标记接口,作用就是表示当前对象是可以被克隆的。
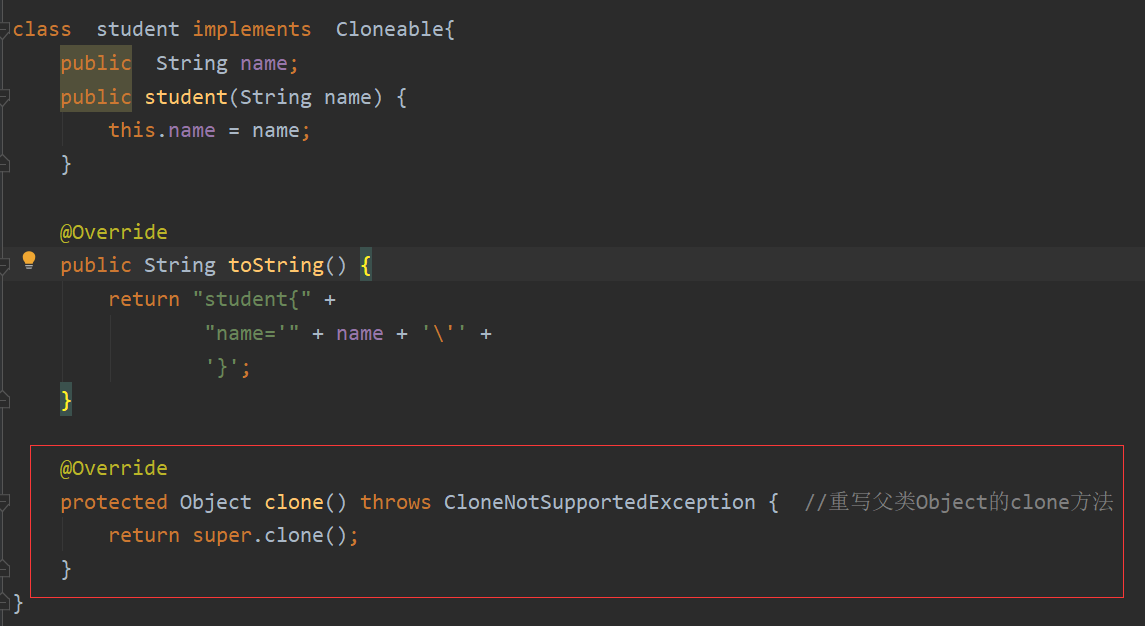
我们要实现克隆,首先要在类中重写Object的clone方法:

package csdn;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
class student implements Cloneable{
public String name;
public student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { //重写父类Object的clone方法
return super.clone();
}
}
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{
student student1=new student("张三");
student student2= (student)student1.clone(); //实现克隆,然后向下转型
System.out.println(student1);
System.out.println(student2);
}
}

这样就实现了简单的克隆。
那我们再考虑另一种情况,我们来看这一段代码:
package csdn;
import com.sun.scenario.effect.impl.sw.sse.SSEBlend_SRC_OUTPeer;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
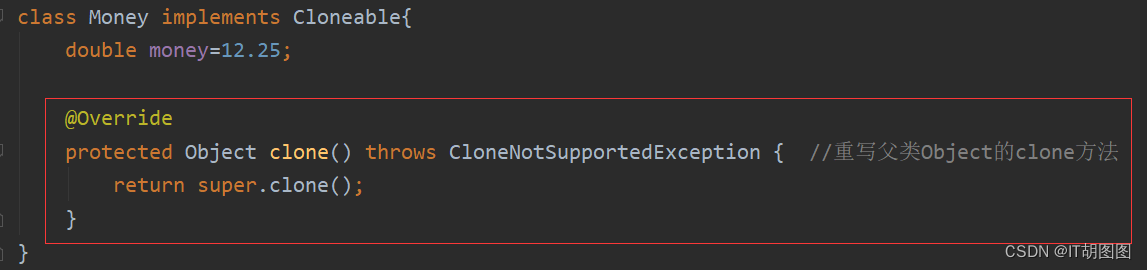
class Money{
double money=12.25;
}
class student implements Cloneable{
public String name;
public Money m=new Money();
public student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { //重写父类Object的clone方法
return super.clone();
}
}
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{
student student1=new student("张三");
student student2= (student)student1.clone(); //实现克隆,然后向下转型
System.out.println(student1.m.money);
System.out.println(student2.m.money);
student2.m.money=99;
System.out.println("==============");
System.out.println(student1.m.money);
System.out.println(student2.m.money);
}
}
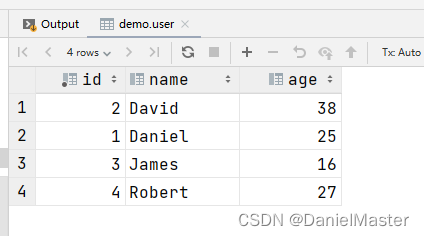
理论上来说,给克隆的对象改了值应该不会影响原对象的money值,我们这都是克隆出去的,但是当我们运行的时候却发现原来对象的money值也被修改了(这种拷贝方式叫做浅拷贝):

这跟我们的需求就不一样,这是什么原因呢?这是因为我们在克隆的时候没有克隆Money对象。

(糟糕的画图技术,希望大家能看明白)
我们解决方法是把Money也克隆出来就可以了,Money也必须支持克隆,也就是实现Clonable 接口。
然后我们再来修改一下student类里面的克隆方法:

此时我们再来看一下运行结果,就跟之前不一样了:
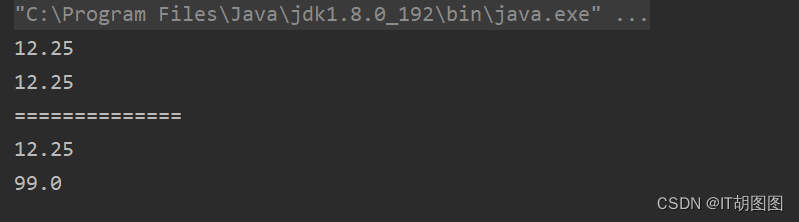
此时就达到了我们的深拷贝。所以如果要实现深拷贝,你当前对象里面的每一个对象都得克隆。
代码:
package csdn;
import com.sun.scenario.effect.impl.sw.sse.SSEBlend_SRC_OUTPeer;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
class Money implements Cloneable{
double money=12.25;
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { //重写父类Object的clone方法
return super.clone();
}
}
class student implements Cloneable{
public String name;
public Money m=new Money();
public student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { //重写父类Object的clone方法
student student=(student)super.clone(); //只是克隆了student对象
student.m=(Money)this.m.clone(); //克隆了student对象里面的Money对象
return student;
}
}
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{
student student1=new student("张三");
student student2= (student)student1.clone(); //实现克隆,然后向下转型
System.out.println(student1.m.money);
System.out.println(student2.m.money);
student2.m.money=99;
System.out.println("==============");
System.out.println(student1.m.money);
System.out.println(student2.m.money);
}
}