- CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue: 异步构建ConsumerQueue。
- CommitLogDispatcherBuildIndex: 异步构建IndexFile。
文章目录
- 1.CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue构建ConsumeQueue
- 1.1 putMessagePositionInfo写入消息位置信息
- 1.2 findConsumeQueue查找ConsumeQueue
- 1.2.1 创建ConsumeQueue
- 1.3 putMessagePositionInfoWrapper追加消息索引
- 1.3.1 putMessagePositionInfo写入消息位置信息
- 1.3.2 MappedFile#appendMessage追加消息
- 2.CommitLogDispatcherBuildIndex构建IndexFile
- 2.1 buildIndex构建Index索引
- 2.1.1 retryGetAndCreateIndexFile获取IndexFile
- 2.1.2 getAndCreateLastIndexFile获取最新索引文件
- 2.1.3 创建IndexFile
- 2.1.4 buildKey构建Key
- 2.1.5 putKey构建Index索引
- 3.总结
1.CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue构建ConsumeQueue
CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue用于接收分发请求并构建ConsumeQueue。
对于非事务消息或者是事务commit消息, 调用DefaultMessageStore#putMessagePositionInfo方法写入消息位置信息到consumeQueue, 如果是事务prepared消息和事务rollback消息, 则不出理。
class CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue implements CommitLogDispatcher {
/**
* DefaultMessageStore的方法
*
* @param request 分派消息请求
*/
@Override
public void dispatch(DispatchRequest request) {
//从该消息的消息系统flag中获取事务状态
final int tranType = MessageSysFlag.getTransactionValue(request.getSysFlag());
switch (tranType) {
//如果不是事务消息或者是事务commit消息,则进行处理
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_NOT_TYPE:
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_COMMIT_TYPE:
//写入消息位置信息到consumeQueue
DefaultMessageStore.this.putMessagePositionInfo(request);
break;
//如果是事务prepared消息或者是事务rollback消息,则不进行处理
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_PREPARED_TYPE:
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_ROLLBACK_TYPE:
break;
}
}
}
1.1 putMessagePositionInfo写入消息位置信息
- 首先调用findConsumeQueue方法根据topic和队列id确定需要写入的ConsumeQueue。
- 然后调用ConsumeQueue#putMessagePositionInfoWrapper方法将消息信息追加到ConsumeQueue索引文件中。
/**
* DefaultMessageStore的方法
* 写入消息位置信息
*
* @param dispatchRequest 分派消息请求
*/
public void putMessagePositionInfo(DispatchRequest dispatchRequest) {
/*
* 根据topic和队列id确定ConsumeQueue
*/
ConsumeQueue cq = this.findConsumeQueue(dispatchRequest.getTopic(), dispatchRequest.getQueueId());
/*
* 将消息信息追加到ConsumeQueue索引文件中
*/
cq.putMessagePositionInfoWrapper(dispatchRequest, checkMultiDispatchQueue(dispatchRequest));
}
1.2 findConsumeQueue查找ConsumeQueue
根据topic和队列id确定需要写入的ConsumeQueue, 查找的目标是consumeQueueTable缓存集合。ConsumerQueue文件是延迟加载的。需要到该ConsumeQueue的时候才会新建。
/**
* DefaultMessageStore
* <p>
* 根据topic和队列id查找ConsumeQueue
*/
public ConsumeQueue findConsumeQueue(String topic, int queueId) {
//从consumeQueueTable中获取该topic所有的队列
ConcurrentMap<Integer, ConsumeQueue> map = consumeQueueTable.get(topic);
//如果没有保存该topic的喜喜,那么存入一个空的map
if (null == map) {
ConcurrentMap<Integer, ConsumeQueue> newMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, ConsumeQueue>(128);
ConcurrentMap<Integer, ConsumeQueue> oldMap = consumeQueueTable.putIfAbsent(topic, newMap);
if (oldMap != null) {
map = oldMap;
} else {
map = newMap;
}
}
// 从map中根据queueId 获取对应的 消费队列
ConsumeQueue logic = map.get(queueId);
//如果ConsumeQueue为null,那么新建,所以说ConsumeQueue是延迟创建的
if (null == logic) {
//新建ConsumeQueue
ConsumeQueue newLogic = new ConsumeQueue(
topic,
queueId,
StorePathConfigHelper.getStorePathConsumeQueue(this.messageStoreConfig.getStorePathRootDir()),
//单个文件大小,默认为可存储30W数据的大小,每条数据20Byte
this.getMessageStoreConfig().getMappedFileSizeConsumeQueue(),
this);
//存入map中,如果已存在则取旧的
ConsumeQueue oldLogic = map.putIfAbsent(queueId, newLogic);
if (oldLogic != null) {
logic = oldLogic;
} else {
// light message queue(LMQ)
if (MixAll.isLmq(topic)) {
lmqConsumeQueueNum.getAndIncrement();
}
logic = newLogic;
}
}
return logic;
}
1.2.1 创建ConsumeQueue
创建ConsumerQueue, 初始化各种属性, 会初始化20个字节的堆外内存, 用于临时存储单个索引, 可以重复使用。
public ConsumeQueue(
final String topic,
final int queueId,
final String storePath,
final int mappedFileSize,
final DefaultMessageStore defaultMessageStore) {
//各种属性
this.storePath = storePath;
//单个文件大小,默认为可存储30W数据的大小,每条数据20Byte
this.mappedFileSize = mappedFileSize;
this.defaultMessageStore = defaultMessageStore;
this.topic = topic;
this.queueId = queueId;
//queue的路径 $HOME/store/consumequeue/{topic}/{queueId}/{fileName}
String queueDir = this.storePath
+ File.separator + topic
+ File.separator + queueId;
//创建mappedFileQueue,内部保存在该queueId下面的所有的consumeQueue文件集合mappedFiles相当于一个文件夹
this.mappedFileQueue = new MappedFileQueue(queueDir, mappedFileSize, null);
//分配20个字节的堆外内存,用于临时存储单个索引,这段内存可循环使用
this.byteBufferIndex = ByteBuffer.allocate(CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE);
//是否启用消息队列的扩展存储,默认false
if (defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isEnableConsumeQueueExt()) {
this.consumeQueueExt = new ConsumeQueueExt(
topic,
queueId,
StorePathConfigHelper.getStorePathConsumeQueueExt(defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getStorePathRootDir()),
defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getMappedFileSizeConsumeQueueExt(),
defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getBitMapLengthConsumeQueueExt()
);
}
}
ConsumeQueue文件可以看成是基于topic的commitlog索引文件, ConsumeQueue文件的组织方式: topic/queue/file三层组织结构, $HOME/store/consumequeue/{topic}/{queueId}/{fileName}。
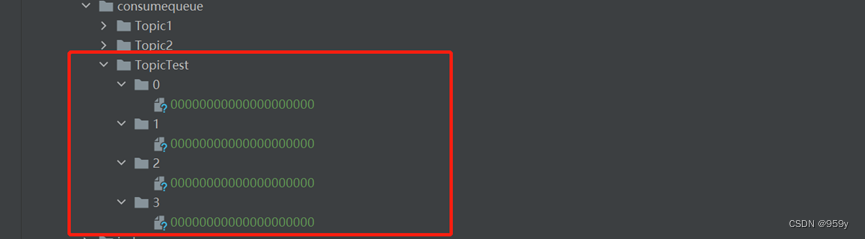
1.3 putMessagePositionInfoWrapper追加消息索引
构建消息索引信息并且存入找到的ConsumeQueue文件中。支持重试, 最多30次。
/**
* ConsumeQueue的方法
* <p>
* 将消息信息追加到ConsumeQueue索引文件中
*/
public void putMessagePositionInfoWrapper(DispatchRequest request, boolean multiQueue) {
//最大重试次数30
final int maxRetries = 30;
//检查ConsumeQueue文件是否可写
boolean canWrite = this.defaultMessageStore.getRunningFlags().isCQWriteable();
//如果文件可写,并且重试次数小于30次,那么写入ConsumeQueue索引
for (int i = 0; i < maxRetries && canWrite; i++) {
//获取tagCode
long tagsCode = request.getTagsCode();
//如果支持扩展信息写入,默认false
if (isExtWriteEnable()) {
ConsumeQueueExt.CqExtUnit cqExtUnit = new ConsumeQueueExt.CqExtUnit();
cqExtUnit.setFilterBitMap(request.getBitMap());
cqExtUnit.setMsgStoreTime(request.getStoreTimestamp());
cqExtUnit.setTagsCode(request.getTagsCode());
long extAddr = this.consumeQueueExt.put(cqExtUnit);
if (isExtAddr(extAddr)) {
tagsCode = extAddr;
} else {
log.warn("Save consume queue extend fail, So just save tagsCode! {}, topic:{}, queueId:{}, offset:{}", cqExtUnit,
topic, queueId, request.getCommitLogOffset());
}
}
/*
* 写入消息位置信息到ConsumeQueue中
*/
boolean result = this.putMessagePositionInfo(request.getCommitLogOffset(),
request.getMsgSize(), tagsCode, request.getConsumeQueueOffset());
if (result) {
if (this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getBrokerRole() == BrokerRole.SLAVE ||
this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isEnableDLegerCommitLog()) {
//修改StoreCheckpoint中的physicMsgTimestamp:最新commitlog文件的刷盘时间戳,单位毫秒
this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(request.getStoreTimestamp());
}
this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setLogicsMsgTimestamp(request.getStoreTimestamp());
if (multiQueue) {
multiDispatchLmqQueue(request, maxRetries);
}
return;
} else {
// XXX: warn and notify me
log.warn("[BUG]put commit log position info to " + topic + ":" + queueId + " " + request.getCommitLogOffset()
+ " failed, retry " + i + " times");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn("", e);
}
}
}
// XXX: warn and notify me
log.error("[BUG]consume queue can not write, {} {}", this.topic, this.queueId);
this.defaultMessageStore.getRunningFlags().makeLogicsQueueError();
}
1.3.1 putMessagePositionInfo写入消息位置信息
将消息位置信息写入到ConsumeQueue文件中:
- 如果消息偏移量+消息大小小于等于ConsumeQueue已处理的最大物理偏移量, 说明该消息已经被写过了, 返回true。
- 将消息信息offset、size、tagsCode按照顺序存入临时缓冲区byteBufferIndex中。
- 调用getLastMappedFile方法, 根据偏移量获取将要写入的最新ConsumeQueue文件的MappedFile。
- 进行一系列校验, 例如是否需要重设索引信息, 是否存在写入错误等等。
- 更新消息最大物理偏移量maxPhysicOffset = 消息在CommitLog中的物理偏移量 + 消息的大小。
- 调用MappedFile#appendMessage方法将临时缓冲区中的索引信息追加到mappedFile的mappedByteBuffer中, 并且更新wrotePosition的位置信息。
8B的offset+4B的size+8BtagsCode, offset: 消息在CommitLog中的物理偏移量。size: 消息大小。tagsCode: 延迟消息就是消息投递时间, 其他消息就是消息的tags的hashCode。
/**
* 写入消息位置信息到ConsumeQueue中
*
* @param offset 消息在CommitLog中的物理偏移量
* @param size 消息大小
* @param tagsCode 消息tagsCode,延迟消息就是消息投递时间,其他消息就是消息的tags的hashCode
* @param cqOffset 消息在消息消费队列的偏移量
*/
private boolean putMessagePositionInfo(final long offset, final int size, final long tagsCode,
final long cqOffset) {
//如果消息偏移量+消息大小 小于等于ConsumeQueue已处理的最大物理偏移量
//说明该消息已经被写过了,直接返回true
if (offset + size <= this.maxPhysicOffset) {
log.warn("Maybe try to build consume queue repeatedly maxPhysicOffset={} phyOffset={}", maxPhysicOffset, offset);
return true;
}
/*
* 将消息信息offset、size、tagsCode按照顺序存入临时缓冲区byteBufferIndex中
*/
//position指针移到缓冲区头部
this.byteBufferIndex.flip();
//缓冲区的限制20B
this.byteBufferIndex.limit(CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE);
//存入8个字节长度的offset,消息在CommitLog中的物理偏移量
this.byteBufferIndex.putLong(offset);
//存入4个字节长度的size,消息大小
this.byteBufferIndex.putInt(size);
//存入8个字节长度的tagsCode,延迟消息就是消息投递时间,其他消息就是消息的tags的hashCode
this.byteBufferIndex.putLong(tagsCode);
//已存在索引数据的最大预计偏移量
final long expectLogicOffset = cqOffset * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
/*
* 根据偏移量获取将要写入的最新ConsumeQueue文件的MappedFile,可能会新建ConsumeQueue文件
*/
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile(expectLogicOffset);
if (mappedFile != null) {
//如果mappedFile是第一个创建的消费队列,并且消息在消费队列的偏移量不为0,并且消费队列写入指针为0
//那么表示消费索引数据错误,需要重设索引信息
if (mappedFile.isFirstCreateInQueue() && cqOffset != 0 && mappedFile.getWrotePosition() == 0) {
//设置最小偏移量为预计偏移量
this.minLogicOffset = expectLogicOffset;
//设置刷盘最新位置,提交的最新位置
this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(expectLogicOffset);
this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(expectLogicOffset);
//对该ConsumeQueue文件expectLogicOffset之前的位置填充前导0
this.fillPreBlank(mappedFile, expectLogicOffset);
log.info("fill pre blank space " + mappedFile.getFileName() + " " + expectLogicOffset + " "
+ mappedFile.getWrotePosition());
}
//如果消息在消费队列的偏移量不为0,即此前有数据
if (cqOffset != 0) {
//获取当前ConsumeQueue文件最新已写入物理偏移量
long currentLogicOffset = mappedFile.getWrotePosition() + mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
//最新已写入物理偏移量大于预期偏移量,那么表示重复构建消费队列
if (expectLogicOffset < currentLogicOffset) {
log.warn("Build consume queue repeatedly, expectLogicOffset: {} currentLogicOffset: {} Topic: {} QID: {} Diff: {}",
expectLogicOffset, currentLogicOffset, this.topic, this.queueId, expectLogicOffset - currentLogicOffset);
return true;
}
//如果不相等,表示存在写入错误,正常情况下,两个值应该相等,因为一个索引条目固定大小20B
if (expectLogicOffset != currentLogicOffset) {
LOG_ERROR.warn(
"[BUG]logic queue order maybe wrong, expectLogicOffset: {} currentLogicOffset: {} Topic: {} QID: {} Diff: {}",
expectLogicOffset,
currentLogicOffset,
this.topic,
this.queueId,
expectLogicOffset - currentLogicOffset
);
}
}
//更新消息最大物理偏移量 = 消息在CommitLog中的物理偏移量 + 消息的大小
this.maxPhysicOffset = offset + size;
/*
* 将临时缓冲区中的索引信息追加到mappedFile的mappedByteBuffer中,并且更新wrotePosition的位置信息,到此构建ComsumeQueue完毕
*/
return mappedFile.appendMessage(this.byteBufferIndex.array());
}
return false;
}
1.3.2 MappedFile#appendMessage追加消息
该方法用于将数据追加到MappedFile, 追加到对应的mappedByteBuffer中, 基于mmap技术仅仅是将数据写入pageCache中, 没有立即刷盘, 依靠操作系统判断刷盘, 保证写入的高可用。
/**
* MappedFile的方法
* <p>
* 追加消息
*
* @param data 追加的数据
*/
public boolean appendMessage(final byte[] data) {
//获取写入位置
int currentPos = this.wrotePosition.get();
//如果当前位置加上消息大小小于等于文件大小,那么将消息写入mappedByteBuffer
if ((currentPos + data.length) <= this.fileSize) {
try {
//消息写入mappedByteBuffer即可,并没有执行刷盘
ByteBuffer buf = this.mappedByteBuffer.slice();
buf.position(currentPos);
buf.put(data);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Error occurred when append message to mappedFile.", e);
}
//更新写入位置
this.wrotePosition.addAndGet(data.length);
return true;
}
return false;
}
2.CommitLogDispatcherBuildIndex构建IndexFile
接收分发请求并构建IndexFile。判断是否支持消息Index, 调用IndexService#buildIndex方法构建, 不存在则不构建, Index文件是否存在都不影响RocketMQ的正常运行, 提高根据keys或者时间范围查询消息的效率。
/**
* DefaultMessageStore的方法
* 写入消息位置信息到IndexFile
*
* @param request 分派消息请求
*/
@Override
public void dispatch(DispatchRequest request) {
//是否支持IndexFile,默认true
if (DefaultMessageStore.this.messageStoreConfig.isMessageIndexEnable()) {
//构建Index
DefaultMessageStore.this.indexService.buildIndex(request);
}
}
2.1 buildIndex构建Index索引
- 通过retryGetAndCreateIndexFile方法获取或创建最新索引文件IndexFile, 最多重试3次。
- 判断当前消息在commitlog中的偏移量小于该文件的结束索引在commitlog中的偏移量, 表示已为该消息构建Index索引, 直接返回。如果该消息是事务回滚消息, 同样直接返回, 不创建索引。
- 获取客户端生成的uniqId, 也叫msgId, 代表客户端生成的唯一一条消息, 如果uniqId不为null的话, 调用putKey()为uniqId创建索引。
- 获取客户端传递的keys, 如果keys不是空, 那么调用putKey方法为keys中的每一个key构建索引。
/**
* IndexService的方法
* <p>
* 构建Index索引
*/
public void buildIndex(DispatchRequest req) {
/*
* 获取或创建最新索引文件,支持重试最多3次
*/
IndexFile indexFile = retryGetAndCreateIndexFile();
if (indexFile != null) {
//获取结束物理索引
long endPhyOffset = indexFile.getEndPhyOffset();
DispatchRequest msg = req;
//获取topic和keys
String topic = msg.getTopic();
String keys = msg.getKeys();
//如果消息在commitlog中的偏移量小于该文件的结束索引在commitlog中的偏移量,那么表示已为该消息之后的消息构建Index索引
//此时直接返回,不需要创建索引
if (msg.getCommitLogOffset() < endPhyOffset) {
return;
}
//获取该消息的事务类型
final int tranType = MessageSysFlag.getTransactionValue(msg.getSysFlag());
switch (tranType) {
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_NOT_TYPE:
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_PREPARED_TYPE:
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_COMMIT_TYPE:
break;
//如果是事务回滚消息,则直接返回,不需要创建索引
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_ROLLBACK_TYPE:
return;
}
//获取客户端生成的uniqId,也被称为msgId,从逻辑上代表客户端生成的唯一一条消息
//如果uniqId不为null,那么为uniqId构建索引
if (req.getUniqKey() != null) {
indexFile = putKey(indexFile, msg, buildKey(topic, req.getUniqKey()));
if (indexFile == null) {
log.error("putKey error commitlog {} uniqkey {}", req.getCommitLogOffset(), req.getUniqKey());
return;
}
}
//获取客户端传递的keys
//如果keys不为空,那么为keys中的每一个key构建索引
if (keys != null && keys.length() > 0) {
//按照空格拆分key
String[] keyset = keys.split(MessageConst.KEY_SEPARATOR);
//为keys中的每一个key构建索引
for (int i = 0; i < keyset.length; i++) {
String key = keyset[i];
if (key.length() > 0) {
indexFile = putKey(indexFile, msg, buildKey(topic, key));
if (indexFile == null) {
log.error("putKey error commitlog {} uniqkey {}", req.getCommitLogOffset(), req.getUniqKey());
return;
}
}
}
}
} else {
log.error("build index error, stop building index");
}
}
2.1.1 retryGetAndCreateIndexFile获取IndexFile
该方法用于获取或创建索引文件, 支持重试, 最多循环3次, 循环中调用getAndCreateLastIndexFile方法获取最新索引文件, 如果文件写满了或者没有文件, 则自动创建文件。
/**
* IndexService的方法
* <p>
* 获取或创建索引文件,支持重试
*/
public IndexFile retryGetAndCreateIndexFile() {
IndexFile indexFile = null;
//循环尝试,尝试创建索引文件的最大次数为3
for (int times = 0; null == indexFile && times < MAX_TRY_IDX_CREATE; times++) {
//获取最新的索引文件,如果文件写满了或者还没有文件则会自动创建新的索引文件
indexFile = this.getAndCreateLastIndexFile();
//如果获取的indexFile不为null,那么退出循环
if (null != indexFile)
break;
try {
log.info("Tried to create index file " + times + " times");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("Interrupted", e);
}
}
//标记indexFile异常
if (null == indexFile) {
this.defaultMessageStore.getAccessRights().makeIndexFileError();
log.error("Mark index file cannot build flag");
}
return indexFile;
}
2.1.2 getAndCreateLastIndexFile获取最新索引文件
获取最新IndexFile, 如果文件写满了或者还没有文件则会自动创建新的索引文件。
- 获取读锁。
- 如果indexFileList不为空, 重试获取最后的indexFile, 否则创建一个新的。
- 如果最后一个indexFile没写满, 赋值给indexFile。
- 如果最后一个IndexFile写满了, 创建新文件, 获取目前最后一个文件的endPhyOffset, endTimestamp等信息。
- 如果上一步没有获取到indexFile, 创建新的IndexFile。
- 获取完整文件名
$HOME/store/index${fileName}。fileName是以创建时的时间戳命名的。 - 调用IndexFile的构造器创建新的IndexFile。
- 获取写锁, 将新建的IndexFile加入indexFileList, 释放写锁。
- 创建新文件后, 尝试将上一个文件刷盘。
- 获取完整文件名
- 返回获取的indexFile。
/**
* IndexService的方法
* <p>
* 获取最新的索引文件,如果文件写满了或者还没有文件则会自动创建新的索引文件
*/
public IndexFile getAndCreateLastIndexFile() {
IndexFile indexFile = null;
IndexFile prevIndexFile = null;
long lastUpdateEndPhyOffset = 0;
long lastUpdateIndexTimestamp = 0;
/*
* 尝试获取最新IndexFile
*/
{
//尝试获取读锁
this.readWriteLock.readLock().lock();
//如果indexFileList不为空
if (!this.indexFileList.isEmpty()) {
//尝试获取最后一个IndexFile
IndexFile tmp = this.indexFileList.get(this.indexFileList.size() - 1);
if (!tmp.isWriteFull()) {
//如果最后一个IndexFile没写满,则赋值给indexFile
indexFile = tmp;
} else {
//如果最后一个IndexFile写满了,则创建新文件
//获取目前最后一个文件的endPhyOffset
lastUpdateEndPhyOffset = tmp.getEndPhyOffset();
//获取目前最后一个文件的endTimestamp
lastUpdateIndexTimestamp = tmp.getEndTimestamp();
//赋值给prevIndexFile
prevIndexFile = tmp;
}
}
this.readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();
}
/*
* 尝试创建一个新的IndexFile
*/
if (indexFile == null) {
try {
//获取完整文件名$HOME/store/index${fileName},fileName是以创建时的时间戳命名的,精确到毫秒
String fileName =
this.storePath + File.separator
+ UtilAll.timeMillisToHumanString(System.currentTimeMillis());
//创建IndexFile
indexFile =
new IndexFile(fileName, this.hashSlotNum, this.indexNum, lastUpdateEndPhyOffset,
lastUpdateIndexTimestamp);
//获取写锁
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
//加入到indexFileList集合中
this.indexFileList.add(indexFile);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("getLastIndexFile exception ", e);
} finally {
//释放写锁
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
/*
* 创建了新的文件之后,尝试将上一个文件刷盘
*/
if (indexFile != null) {
final IndexFile flushThisFile = prevIndexFile;
/*
* 新开一个线程,异步的对上一个IndexFile文件刷盘
*/
Thread flushThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
IndexService.this.flush(flushThisFile);
}
}, "FlushIndexFileThread");
flushThread.setDaemon(true);
flushThread.start();
}
}
return indexFile;
}
2.1.3 创建IndexFile
第一次构建Index或者之前的IndexFile写满了的时候, 创建新的IndexFile。IndexFile文件大小约为
40B 头数据indexHeader + 500w * 4B hashslot + 2000w * 20B index = 420000040B: 400M大小。
/**
* 创建IndexFile
*
* @param fileName 文件名
* @param hashSlotNum 哈希槽数量,默认5000000
* @param indexNum 索引数量默认,默认5000000 * 4
* @param endPhyOffset 上一个文件的endPhyOffset
* @param endTimestamp 上一个文件的endTimestamp
* @throws IOException
*/
public IndexFile(final String fileName, final int hashSlotNum, final int indexNum,
final long endPhyOffset, final long endTimestamp) throws IOException {
//文件大小,默认约400M左右
//40B 头数据 + 500w * 4B hashslot + 2000w * 20B index
int fileTotalSize =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + (hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize) + (indexNum * indexSize);
//构建mappedFile
this.mappedFile = new MappedFile(fileName, fileTotalSize);
this.fileChannel = this.mappedFile.getFileChannel();
this.mappedByteBuffer = this.mappedFile.getMappedByteBuffer();
this.hashSlotNum = hashSlotNum;
this.indexNum = indexNum;
//生成DirectByteBuffer,对该buffer写操作会被反映到文件里面
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = this.mappedByteBuffer.slice();
//获取indexHeader
this.indexHeader = new IndexHeader(byteBuffer);
//设置新文件的起始物理索引和结束物理索引都为上一个文件的结束物理索引
if (endPhyOffset > 0) {
this.indexHeader.setBeginPhyOffset(endPhyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setEndPhyOffset(endPhyOffset);
}
//设置新文件的起始时间戳和结束时间戳都为上一个文件的结束时间戳
if (endTimestamp > 0) {
this.indexHeader.setBeginTimestamp(endTimestamp);
this.indexHeader.setEndTimestamp(endTimestamp);
}
}
2.1.4 buildKey构建Key
构建Index索引的key, RocketMQ将会为uniqId和keys中的每个key构建索引。
UniqKey将会转换为topic#UniqKey, 而keys则会先通过空格拆分, 然后将每个key转换为topic#key。
/**
* IndexService的方法
* 构建key
*/
private String buildKey(final String topic, final String key) {
//拼接
return topic + "#" + key;
}
2.1.5 putKey构建Index索引
IndexFile文件大约400M, 一个IndexFile文件可以保存2000W个索引, IndexFile底层是HashMap结构, 故RocketMQ的索引文件底层实现为hash索引。
putKey方法循环调用indexFile#putKey方法构建Index索引, 每次构建失败都将调用retryGetAndCreateIndexFile方法尝试获取或创建最新索引文件然后再尝试构建。
- 判断如果当前文件的index索引数量小于2000w, 则表明当前文件还可以继续构建索引。
- 计算Key的哈希值keyHash, 通过 哈希值keyHash & hash槽数量hashSlotNum获取key对应的hash槽的下标slotPos, 计算该消息的绝对hash槽偏移量 absSlotPos = 40B + slotPos * 4B。
- 计算当前消息在commitlog中的消息存储时间与该Index文件起始时间差timeDiff, 计算该消息的索引存放位置的绝对偏移量absIndexPos = 40B + 500w * 4B + indexCount * 20B。
- 在absIndexPos位置顺序存放Index索引数据, 大小为20B, 存入4B的当前消息的Key的哈希值, 存入8B的当前消息在commitlog中的物理偏移量, 存入4B的当前消息在commitlog中的消息存储时间与该Index文件起始时间差, 存入4B的slotValue, 可更新当前hash槽的值为最新的IndexFile的索引条目计数的编号。
- 在absSlotPos位置更新当前hash槽的值为最新的IndexFile的索引条目计数的编号, 为当前索引存入的编号。
- 判断如果索引数量小于等于1, 说明时该文件第一次存入索引, 初始化beginPhyOffset和beginTimestamp。
- 判断如果slotValue为0, 则为一个新槽, hashSlotCount + 1。
- 索引条目计数indexCount自增1, 设置新的endPhyOffset和endTimestamp。
/**
* IndexService的方法
* <p>
* 构建Index索引
*
* @param indexFile indexFile
* @param msg 消息
* @param idxKey key
*/
private IndexFile putKey(IndexFile indexFile, DispatchRequest msg, String idxKey) {
//循环尝试构建Index索引
for (boolean ok = indexFile.putKey(idxKey, msg.getCommitLogOffset(), msg.getStoreTimestamp()); !ok; ) {
log.warn("Index file [" + indexFile.getFileName() + "] is full, trying to create another one");
//构建失败,则尝试获取或创建最新索引文件,支持重试
indexFile = retryGetAndCreateIndexFile();
if (null == indexFile) {
return null;
}
//再次尝试构建Index索引
ok = indexFile.putKey(idxKey, msg.getCommitLogOffset(), msg.getStoreTimestamp());
}
return indexFile;
}
/**
* IndexFile的方法
* <p>
* 构建Index索引
*
* @param key key
* @param phyOffset 当前消息在commitlog中的物理偏移量
* @param storeTimestamp 当前消息在commitlog中的消息存储时间
* @return
*/
public boolean putKey(final String key, final long phyOffset, final long storeTimestamp) {
//如果当前文件的index索引数量小于2000w,则表明当前文件还可以继续构建索引
if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() < this.indexNum) {
//计算Key的哈希值
int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key);
//通过 哈希值 & hash槽数量 的方式获取当前key对应的hash槽下标位置,hashSlotNum默认为5000w
int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum;
//计算该消息的绝对hash槽偏移量 absSlotPos = 40B + slotPos * 4B
int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + slotPos * hashSlotSize;
FileLock fileLock = null;
try {
// fileLock = this.fileChannel.lock(absSlotPos, hashSlotSize,
// false);
//获取当前hash槽的值,一个hash槽大小为4B
int slotValue = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absSlotPos);
//如果值不为0说明这个hash key已经存在,即存在hash冲突
if (slotValue <= invalidIndex || slotValue > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()) {
slotValue = invalidIndex;
}
//当前消息在commitlog中的消息存储时间与该Index文件起始时间差
long timeDiff = storeTimestamp - this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp();
timeDiff = timeDiff / 1000;
if (this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() <= 0) {
timeDiff = 0;
} else if (timeDiff > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
timeDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
} else if (timeDiff < 0) {
timeDiff = 0;
}
//获取该消息的索引存放位置的绝对偏移量 absIndexPos = 40B + 500w * 4B + indexCount * 20B
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() * indexSize;
//存入4B的当前消息的Key的哈希值
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos, keyHash);
//存入8B的当前消息在commitlog中的物理偏移量
this.mappedByteBuffer.putLong(absIndexPos + 4, phyOffset);
//存入4B的当前消息在commitlog中的消息存储时间与该Index文件起始时间差
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8, (int) timeDiff);
//存入4B的slotValue,即前面读出来的 slotValue,可能是0,也可能不是0,而是上一个发生hash冲突的索引条目的编号
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4, slotValue);
//更新当前hash槽的值为最新的IndexFile的索引条目计数的编号,也就是当前索引存入的编号
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absSlotPos, this.indexHeader.getIndexCount());
/*
* 从存入的数据可以看出来:
* IndexFile采用用slotValue字段将所有冲突的索引用链表的方式串起来了,而哈希槽SlotTable并不保存真正的索引数据,
* 而是保存每个槽位对应的单向链表的头,即可以看作是头插法插入数据
*/
//如果索引数量小于等于1,说明时该文件第一次存入索引,那么初始化beginPhyOffset和beginTimestamp
if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() <= 1) {
this.indexHeader.setBeginPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setBeginTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
//如果slotValue为0,那么表示采用了一个新的哈希槽,此时hashSlotCount自增1
if (invalidIndex == slotValue) {
this.indexHeader.incHashSlotCount();
}
//因为存入了新的索引,那么索引条目计数indexCount自增1
this.indexHeader.incIndexCount();
//设置endPhyOffset和endTimestamp
this.indexHeader.setEndPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setEndTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("putKey exception, Key: " + key + " KeyHashCode: " + key.hashCode(), e);
} finally {
if (fileLock != null) {
try {
fileLock.release();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Failed to release the lock", e);
}
}
}
} else {
log.warn("Over index file capacity: index count = " + this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
+ "; index max num = " + this.indexNum);
}
return false;
}
3.总结
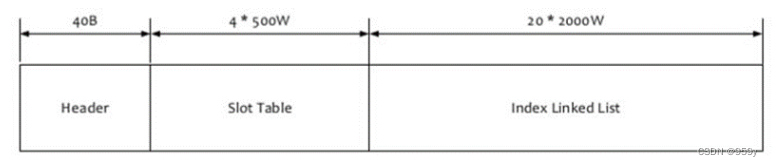
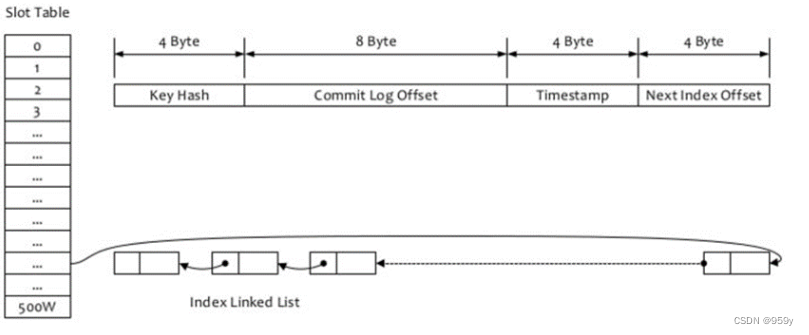
IndexFile的构成包括40B的Header头信息, 4 x 500wB的Slot信息, 20 x 2000wB的Index信息
-
Header: java为IndexHeader, 8B的的beginTimestamp, 8B的endTimestamp, 8B的beginPhyOffset, 8B的endPhyOffset, 4B的hashSlotCount 哈希槽计数, 4B的indexCount 索引条目计数。
-
slot Table并不保存真正的索引数据, 存储的是每个槽位对应的单向链表的头。即最新消息的索引条目计数的编号indexCount。
-
索引信息: 4B的Key Hash, Key的哈希值。8B的CommitLog Offset, 当前消息在commitlog中的物理偏移量。4B的Timestamp, 当前消息在commitlog中的消息存储时间与该Index文件起始时间差。4B的NextIndex offset, 链表的下一个索引的Index位置。