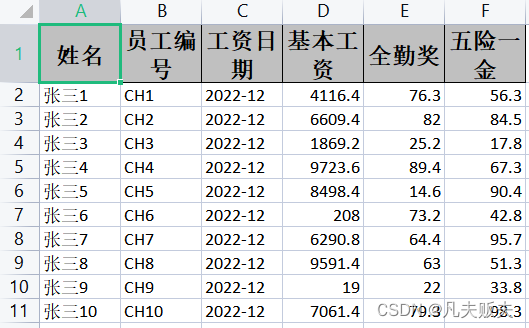
常规导出
常规导出excel有两种,个人比较推荐第一种:
1、新建一个导出数据的实体类,用@ExcelProperty()注解标明excel中列的中文名称;如果实体的类某些列不想导出,可以使用@ExcelIgnore进行忽略就可以了。
2、使用easyexcel的工厂类EasyExcel直接导出数据到excel表格中;
第一种
@Data
public class EmpSalary {
@ExcelProperty("姓名")
private String realName;
@ExcelProperty("员工编号")
private String empNo;
@ExcelProperty(value = "工资日期")
private String salaryDate;
@ExcelProperty("基本工资")
private Float baseAmount;
@ExcelProperty("全勤奖")
private Float fullAttendAmount;
@ExcelProperty("五险一金")
private Float insurance;
//特别资金
@ExcelIgnore
private Float specialAmount;
}@Test
public void write() {
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String exportPath = userDir + File.separator + "export";
File file = new File(exportPath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
String exportFile = exportPath + File.separator + "员工工资表-12月.xlsx";
EasyExcel.write(exportFile, EmpSalary.class).sheet("12月").doWrite(empSalaryData());
}
public List<EmpSalary> empSalaryData() {
List<EmpSalary> list = new ArrayList<>();
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
EmpSalary empSalary = new EmpSalary();
empSalary.setEmpNo("CH" + (i + 1));
empSalary.setRealName("张三" + (i + 1));
empSalary.setSalaryDate("2022-12");
empSalary.setBaseAmount(random.nextInt(100000) / 10.00f);
empSalary.setFullAttendAmount(random.nextInt(1000) / 10.00f);
empSalary.setInsurance(random.nextInt(1000) / 10.00f);
list.add(empSalary);
}
return list;
}
第二种:
通常情况这种不推荐。为啥都呢?表头的数据格式太奇怪(List>),比较麻烦。当然有些情况可以例外,如果表头比较复杂,或者表头需要动态生成。
public List<List<String>> headList(){
List<List<String>> headList=new ArrayList<>();
List<String> head1=new ArrayList<>();
head1.add("姓名");
headList.add(head1);
List<String> head2=new ArrayList<>();
head2.add("员工编号");
headList.add(head1);
List<String> head3=new ArrayList<>();
head3.add("工资日期");
headList.add(head3);
List<String> head4=new ArrayList<>();
head4.add("基本工资");
headList.add(head4);
List<String> head5=new ArrayList<>();
head5.add("全勤奖");
headList.add(head5);
List<String> head6=new ArrayList<>();
head6.add("保险");
headList.add(head6);
return headList;
}
@Test
public void write2(){
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String exportPath = userDir + File.separator + "export";
File file = new File(exportPath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
String exportFile = exportPath + File.separator + "员工工资表-12月_v2.xlsx";
EasyExcel.write(exportFile).head(headList()).sheet().doWrite(empSalaryData());
}
}大批量数据导出
有时候会遇到这样的的导出需求,比如上万、几十万,这种大批量数据的导出,如果还是使用常规的导出,在效能上不好,可以用下面的方法:
1、先通过easyexcel的工厂类(EasyExcel)构建出一个写入器(ExcelWriter);
2、构建出写出用的sheet页(WriteSheet);
3、把数据分批,使用第一步构建好的数据写入器(ExcelWriter)往第二步构建好的sheet页(ExcelSheet)里写入数据;
4、在全部数据写入完成后一定要关闭数据写入器(ExcelWriter);
注:示例里是把大批量的数据写入的同一个sheet页里面;如果想要把大量数据写入到不同的sheet页里,就需要把sheet页构建放到循环里面;
public String getExportPath() {
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String exportPath = userDir + File.separator + "export";
File file = new File(exportPath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
return exportPath;
}
public List<EmpSalary> empSalaryData(int rows) {
List<EmpSalary> list = new ArrayList<>();
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
EmpSalary empSalary = new EmpSalary();
empSalary.setEmpNo("CH" + (i + 1));
empSalary.setRealName("张三" + (i + 1));
empSalary.setSalaryDate("2022-12");
empSalary.setBaseAmount(random.nextInt(100000) / 10.00f);
empSalary.setFullAttendAmount(random.nextInt(1000) / 10.00f);
empSalary.setInsurance(random.nextInt(1000) / 10.00f);
list.add(empSalary);
}
return list;
}
@Test
public void writeBigData() {
String exportPath = this.getExportPath();
String exportFile = exportPath + File.separator + "超过10000万人的员工工资表.xlsx";
ExcelWriter excelWriter =null;
try {
excelWriter = EasyExcel.write(exportFile, EmpSalary.class).build();
WriteSheet writeSheet = EasyExcel.writerSheet(1).build();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
List<EmpSalary> empSalaries = this.empSalaryData(1000);
excelWriter.write(empSalaries, writeSheet);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (excelWriter != null) {
excelWriter.finish();
}
}
}复杂表头的导出
特别是一些财务类型的报表导出,表头往往是复合表头,比较复杂
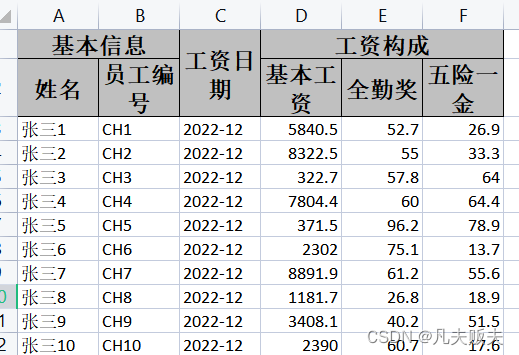
easyexcel对于这种场景提供了两种方法,一种是注解;另外一种是通过一种特殊的数据结构List<List<string>>;根据我的感受,我是推荐使用注解的;
第一种:
如果是所在列是复合表头,则使用@ExcelProperty()注解,从上到下标明表头组成;如果是普通表头,按普通的用法标明表头名称即可;是不是很简单?
@Data
public class EmpSalary {
@ExcelProperty({"基本信息","姓名"})
private String realName;
@ExcelProperty({"基本信息","员工编号"})
private String empNo;
//,converter = SalaryDateConverter.class
@ExcelProperty(value = "工资日期")
private String salaryDate;
@ExcelProperty({"工资构成","基本工资"})
private Float baseAmount;
@ExcelProperty({"工资构成","全勤奖"})
private Float fullAttendAmount;
@ExcelProperty({"工资构成","五险一金"})
private Float insurance;
//特别资金
@ExcelIgnore
private Float specialAmount;
}@Test
public void writeHead() {
String exportPath = this.getExportPath();
String exportFile = exportPath + File.separator + "员工工资表v3.xlsx";
EasyExcel.write(exportFile, EmpSalary.class).sheet().doWrite(this.empSalaryData(10));
}第二种:
使用List<List<string>>结构来组织表头数据,开始的时候还不是很理解表头的数据结构为什么这么奇怪,到这里是不是明白了。对于普通表头List<String>肯定就可以了,但是在一些复杂的场景就不行了。这么制定的话,什么场景都不在话下,关键还可以动态生成表头,这一点确实比注解的方式要灵活一些;所以具体使用哪种,要根据业务场景决定了。
@Test
public void writeHead() {
String exportPath = this.getExportPath();
String exportFile = exportPath + File.separator + "员工工资表v4.xlsx";
List<List<String>> headList = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> head1 = new ArrayList<>();
head1.add("基本信息");
head1.add("姓名");
headList.add(head1);
List<String> head2 = new ArrayList<>();
head2.add("基本信息");
head2.add("员工编号");
headList.add(head2);
List<String> head3 = new ArrayList<>();
head3.add("工资日期");
headList.add(head3);
List<String> head4 = new ArrayList<>();
head4.add("工资构成");
head4.add("基本工资");
headList.add(head4);
List<String> head5 = new ArrayList<>();
head5.add("工资构成");
head5.add("全勤奖");
headList.add(head5);
List<String> head6 = new ArrayList<>();
head6.add("工资构成");
head6.add("保险");
headList.add(head6);
EasyExcel.write(exportFile).head(headList).sheet().doWrite(this.empSalaryData(10));
}日期、数字、自定义格式转换后导出
自定义格式转换的后导出可以参考上一篇《Springboot+Easyexcel:导入excl》中的日期、数字及其他自定义格式的转换部分,SalaryDateConverter#convertToExcelData(),导出时候的数据格式转换逻辑可以写在这里面;SalaryDateConverter#convertToJavaData()导入时候的数据格式转换的实现逻辑可以写在这里;SalaryDateConverter实现了com.alibaba.excel.converters.Converter接口;
除了实现com.alibaba.excel.converters.Converterr接口,easyexcel也预置了一些常用的注解来实现格式转换,导入导出的时候都能用,如@DateTimeFormat、@NumberFormat;
这里特别注意别导错类了:
com.alibaba.excel.annotation.format.DateTimeFormat;
com.alibaba.excel.annotation.format.NumberFormat;
@Data
public class EmpSalary {
@ExcelProperty({"基本信息","姓名"})
private String realName;
@ExcelProperty({"基本信息","员工编号"})
private String empNo;
@DateTimeFormat("yyyy年MM月")
@ExcelProperty(value = "工资日期")
private Date salaryDate;
@ExcelProperty({"工资构成","基本工资"})
private Float baseAmount;
@ExcelProperty({"工资构成","全勤奖"})
private Float fullAttendAmount;
@ExcelProperty({"工资构成","五险一金"})
private Float insurance;
//特别资金
@ExcelIgnore
@NumberFormat
private Float specialAmount;
@NumberFormat("#.##%")
@ExcelProperty("绩效完成百分比")
private Double jixiao;
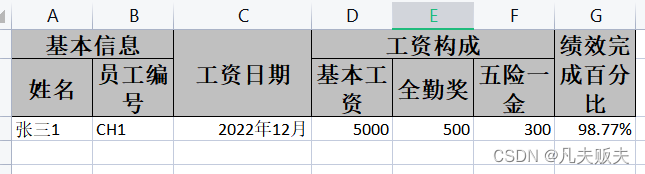
}@Test
public void writeByConverter(){
String exportPath = this.getExportPath();
String exportFile = exportPath + File.separator + "员工工资表v5.xlsx";
List<EmpSalary> list=new ArrayList<>();
EmpSalary empSalary = new EmpSalary();
empSalary.setEmpNo("CH" + ( 1));
empSalary.setRealName("张三" + ( 1));
empSalary.setSalaryDate(new Date());
empSalary.setBaseAmount(5000f);
empSalary.setFullAttendAmount(500f);
empSalary.setInsurance(300f);
empSalary.setJixiao(0.9877);
list.add(empSalary);
EasyExcel.write(exportFile, EmpSalary.class).sheet("12月").doWrite(list);
}


![[附源码]计算机毕业设计的高校车辆租赁管理系统Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8446bc8eadeb4699a046129b32333c53.png)