ArkTS是HamronyOS优选的主力语言,但官方文档指南中对于Native应用开发并没有详细的描述,只有一篇Codelab可以学习(简易Native C++ 示例(ArkTS) (huawei.com)),本文将在Native应用中使用C/C++的system方法创建一个文件。
【具体实现】
Step1.
首先在DevEco Studio中选择创建native应用程序
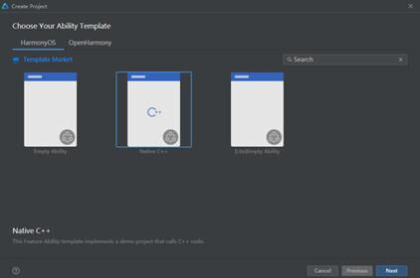
Step2.
工程创建后整体目录如下,
首先src目录下有两个文件夹cpp和ets,cpp目录主要是用来定义对外的接口实现(index.d.ts),C++代码功能实现(hello.cpp)和编译的工具链(CMakeLists.txt)。
ets目录即为我们主要工程目录,实现应用的主体逻辑和UI界面。
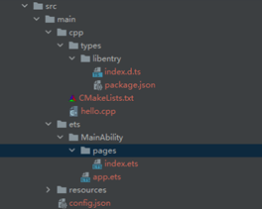
默认工程目录cpp/types/libentry中有一个示例的接口add,它在index.d.ts中定义为两个数相加返回相加后的结果:
export const add: (a: number, b: number) => number;package.json中定义了对外调用的静态库名称和接口文件
{
"name": "libentry.so",
"types": "./index.d.ts"
}然后在ets目录下index.ets中就可以导入这个libentry.so的静态库文件,使用定义的方法了
import hilog from '@ohos.hilog';
import testNapi from 'libentry.so'//导入静态库
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'Hello World'
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.onClick(() => {
hilog.isLoggable(0x0000, 'testTag', hilog.LogLevel.INFO);
hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', 'Test NAPI 2 + 3 = %{public}d', testNapi.add(2, 3));//调用定义的native方法
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}Step3.
下面就是我们C++层代码逻辑的实现了:
首先在hello.cpp添加创建文件的函数实现,使用了strcpy和system函数,所以需要导入对应的库文件
#include <cstdlib>
#include <string.h>这边有一个需要注意的地方是创建的文件目录路径必须是应用的私有文件目录下(/data/data/包名/文件名),否则文件不能创建成功。
static napi_value CreateFile(napi_env env, napi_callback_info info){
napi_value ret;
char command[50];
strcpy( command, "touch /data/data/com.example.nativets/1.txt" );
int result=system(command);
napi_create_double(env,result, &ret);
return ret;
}然后我们需要在Init方法的desc[]中注册模块,“createFile”为定义接口,CreateFile是我们上面C++的方法名。
{ "createFile", nullptr, CreateFile, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr },模块注册后需要在接口文件index.d.ts中添加这个接口的定义
export const createFile:()=>number;CMakeList文件不需要修改,直接编译工程就可以在ets的index.ets中使用这个新的接口 createFile()了。
Step4.
运行程序并执行方法,验证文件是否创建成功可以通过adb命令查看系统”/data/data/包名/文件名”是否存在。
欲了解更多更全技术文章,欢迎访问https://developer.huawei.com/consumer/cn/forum/?ha_source=zzh