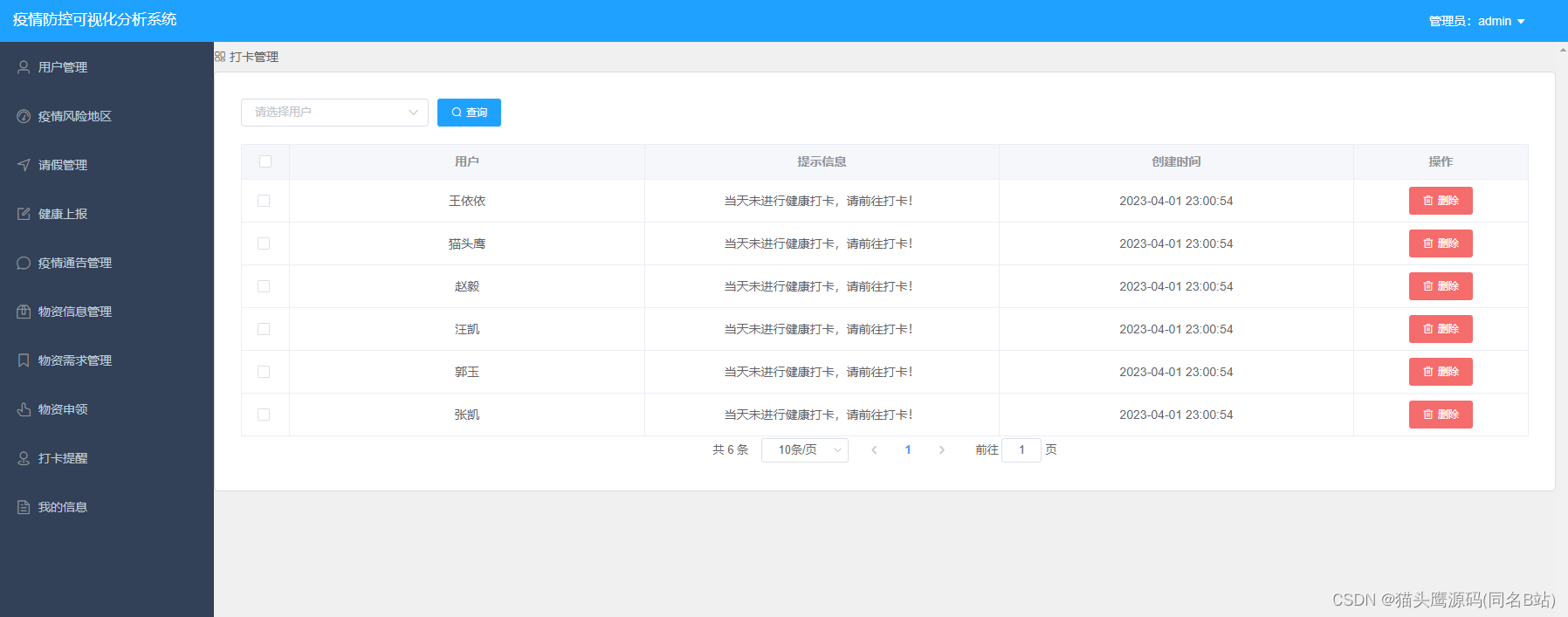
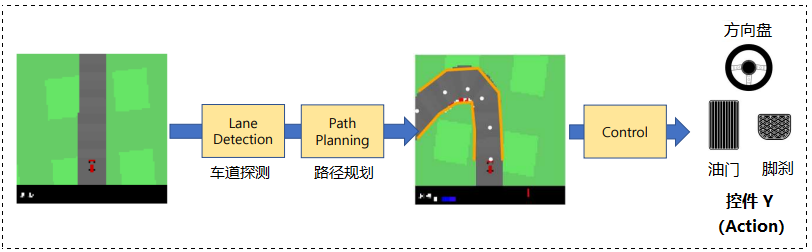
- 💭 写在前面:本篇是关于 OpenAI Gym-CarRacing 自动驾驶项目的博客,面向掌握 Python 并有一定的深度强化学习基础的读者。GYM-Box2D CarRacing 是一种在 OpenAI Gym 平台上开发和比较强化学习算法的模拟环境。它是流行的 Box2D 物理引擎的一个版本,经过修改以支持模拟汽车在赛道上行驶的物理过程。本篇是 CarRacing 系列博客的代码篇,提供 lane_dection 部分的完整代码。
📜 本章目录:
Ⅰ. 项目环境准备
0x00 实验说明
0x01 模板下载
Ⅱ. 代码:车道检测功能的实现
0x00 引入:lane_dection 部分的实现
0x01 完整代码
0x01 运行结果演示
0x02 转灰度图像:cur_gray
0x03 边缘检测:edge_detection
0x04 寻找边缘检测结果中的局部最大值:find_maxima_gradient_rowwise
🔗 OpenAI Gym-CarRacing 系列博客
Ⅰ. 项目环境准备
0x00 实验说明

🔗 Conda 安装:【Python】前置:Conda 安装教学
🔗 项目环境安装:Gym-CarRacing 环境安装
🚩 实践目标:实现一个模块化组件框架,落实简化版的模块化流水线。了解基本概念,并积累开发一个简单的自驱应用程序的经验。
🔨 环境选用:OpenAI GYM
- https://www.gymlibrary.ml/
- 我们将基于 Box2D CarRacing 实现,Box2D CarRacing 基本信息如下:
- Action:转向、加速、刹车
- Sensor input:96x96x3 屏幕(显示汽车的状态和路径信息)
0x01 模板下载
* 提供基础框架,只需要在 TODO 位置填写代码即可!
🔗 模板下载:CSDN资源:Box2D CarRacing lane-dection 项目模板
Ⅱ. 代码:车道检测功能的实现
0x00 引入:lane_dection 部分的实现
🚩 实践目标:
- 实现一个模块化组件框架,落实简化版的模块化流水线。
- 了解基本概念,并积累开发一个简单的自驱应用程序的经验。
📜 尝试:
- 为汽车上方的部分找到一个好的裁剪,一个好的方法来分配车道边界的边缘,一个好的梯度阈值和样条平滑度的参数选择。
- 尝试找到失败的案例。
0x01 完整代码
💬 参考代码:lane_detection.py
from turtle import distance
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import find_peaks
from scipy.interpolate import splprep, splev
from scipy.optimize import minimize
import time
class LaneDetection:
'''
Lane detection module using edge detection and b-spline fitting
args:
cut_size (cut_size=65) cut the image at the front of the car
spline_smoothness (default=10)
gradient_threshold (default=14)
distance_maxima_gradient (default=3)
使用边缘检测和b样条拟合的车道检测模块
参数:
cut_size(cut_size=65)在汽车前部剪切图像
spline_smoothness(默认值=10)
gradient_threshold(默认值=14)
distance_maxima_gradient(默认值=3)
'''
def __init__(self, cut_size=65, spline_smoothness=10, gradient_threshold=14, distance_maxima_gradient=3):
self.car_position = np.array([48,0])
self.spline_smoothness = spline_smoothness
self.cut_size = cut_size
self.gradient_threshold = gradient_threshold
self.distance_maxima_gradient = distance_maxima_gradient
self.lane_boundary1_old = 0
self.lane_boundary2_old = 0
## 将状态图像转化为灰度图像
def cut_gray(self, state_image_full):
'''
##### TODO #####
This function should cut the image at the front end of the car (e.g. pixel row 65)
and translate to gray scale
input:
state_image_full 96x96x3
output:
gray_state_image 65x96x1
此功能应在汽车前端切割图像(例如像素行65),并转换为灰度
输入:
状态图像完整96x96x3
输出:
灰度_状态_图像65x96x1
'''
copy_img = state_image_full[:self.cut_size, :]
red, green, blue = 0.2989, 0.5870, 0.1140
return np.dot(copy_img[...,:3], [red, green, blue])[::-1]
def edge_detection(self, gray_image):
'''
##### TODO #####
In order to find edges in the gray state image,
this function should derive the absolute gradients of the gray state image.
Derive the absolute gradients using numpy for each pixel.
To ignore small gradients, set all gradients below a threshold (self.gradient_threshold) to zero.
input:
gray_state_image 65x96x1
output:
gradient_sum 65x96x1
为了在灰度图像中找到边缘,
该函数应导出灰度图像的绝对梯度。
使用numpy为每个像素导出绝对梯度。
要忽略小渐变,请将阈值(self.gradient_threshold)以下的所有渐变设置为0。
'''
gradient = np.gradient(gray_image)
gradient_sum = abs(gradient[0]) + abs(gradient[1])
gradient = gradient_sum < self.gradient_threshold
gradient_sum[gradient] = 0
return gradient_sum
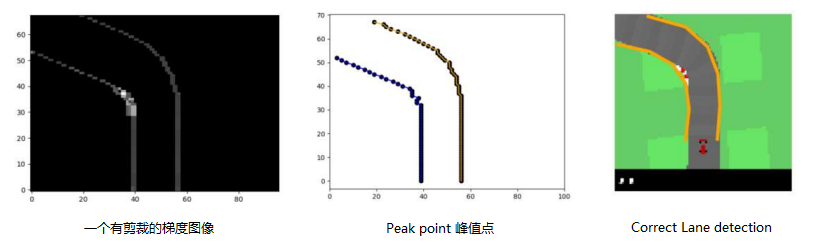
def find_maxima_gradient_rowwise(self, gradient_sum):
'''
##### TODO #####
This function should output arguments of local maxima for each row of the gradient image.
You can use scipy.signal.find_peaks to detect maxima.
Hint: Use distance argument for a better robustness.
input:
gradient_sum 65x96x1
output:
maxima (np.array) shape : (Number_maxima, 2)
这个函数应该为渐变图像的每一行输出局部最大值的参数。
您可以使用scipy.signal。查找峰值以检测最大值。
提示:使用距离参数可以获得更好的鲁棒性。
# 距离参数cuz车道应至少相隔3像素
# find_peaks返回`x`中满足所有给定条件的峰值指数。
'''
argmaxima = []
pixel = 3 # 相隔参数
i = 0
while (i < gradient_sum.shape[0]):
top, _ = find_peaks(gradient_sum[i], distance = pixel)
argmaxima.append(top)
i += 1
return argmaxima
def find_first_lane_point(self, gradient_sum):
'''
Find the first lane_boundaries points above the car.
Special cases like just detecting one lane_boundary or more than two are considered.
Even though there is space for improvement ;)
input:
gradient_sum 65x96x1
output:
lane_boundary1_startpoint
lane_boundary2_startpoint
lanes_found true if lane_boundaries were found
找到汽车上方的第一个车道边界点。
特殊情况下,如只检测一个或两个以上的车道边界。
尽管还有改进的空间;)
输入:
梯度_总和65x96x1
输出:
车道边界1_起点
车道边界2起点
如果找到车道边界,则lanes_found为true
'''
# Variable if lanes were found or not
lanes_found = False
row = 0
# loop through the rows
while not lanes_found:
# Find peaks with min distance of at least 3 pixel
argmaxima = find_peaks(gradient_sum[row],distance=3)[0]
# if one lane_boundary is found
if argmaxima.shape[0] == 1:
lane_boundary1_startpoint = np.array([[argmaxima[0], row]])
if argmaxima[0] < 48:
lane_boundary2_startpoint = np.array([[0, row]])
else:
lane_boundary2_startpoint = np.array([[96, row]])
lanes_found = True
# if 2 lane_boundaries are found
elif argmaxima.shape[0] == 2:
lane_boundary1_startpoint = np.array([[argmaxima[0], row]])
lane_boundary2_startpoint = np.array([[argmaxima[1], row]])
lanes_found = True
# if more than 2 lane_boundaries are found
elif argmaxima.shape[0] > 2:
# if more than two maxima then take the two lanes next to the car, regarding least square
A = np.argsort((argmaxima - self.car_position[0])**2)
lane_boundary1_startpoint = np.array([[argmaxima[A[0]], 0]])
lane_boundary2_startpoint = np.array([[argmaxima[A[1]], 0]])
lanes_found = True
row += 1
# if no lane_boundaries are found
if row == self.cut_size:
lane_boundary1_startpoint = np.array([[0, 0]])
lane_boundary2_startpoint = np.array([[0, 0]])
break
return lane_boundary1_startpoint, lane_boundary2_startpoint, lanes_found
def lane_detection(self, state_image_full):
'''
##### TODO #####
This function should perform the road detection
args:
state_image_full [96, 96, 3]
out:
lane_boundary1 spline
lane_boundary2 spline
此功能应执行道路检测
参数:
state_image_full [96, 96, 3]
输出:
lane_boundary1 spline
lane_boundary2 spline
'''
# to gray
gray_state = self.cut_gray(state_image_full)
# edge detection via gradient sum and thresholding
gradient_sum = self.edge_detection(gray_state)
maxima = self.find_maxima_gradient_rowwise(gradient_sum)
# first lane_boundary points
lane_boundary1_points, lane_boundary2_points, lane_found = self.find_first_lane_point(gradient_sum)
# if no lane was found,use lane_boundaries of the preceding step
# l1 = lane_boundary1_points
# l2 = lane_boundary2_points
if lane_found:
##### TODO #####
# in every iteration:
# 1- find maximum/edge with the lowest distance to the last lane boundary point
# 2- append maximum to lane_boundary1_points or lane_boundary2_points
# 3- delete maximum from maxima
# 4- stop loop if there is no maximum left
# or if the distance to the next one is too big (>=100)
'''
#在每次迭代中:
#1-查找到最后一个车道边界点的最小距离的最大/边缘
#2-将最大值附加到lane_boundary1_points或lane_boondary2_point斯
#3-从maxima中删除maximum
#4-如果没有最大剩余
# ,则停止循环
#或者如果到下一个的距离太大(>=100)
'''
l1 = lane_boundary1_points
l2 = lane_boundary2_points
row = 1
lim = 65
while (row < lim):
max_row = maxima[row]
if len(max_row) < 2:
break
#根据与先前车道预测的距离对点进行排序
#此外,argsort还返回可以按顺序迭代的索引
#因此,我们在排序后使用A[0]和B[0]
arrayA, arrayB = np.argsort(pow(max_row - l1[0][0], 2)), np.argsort(pow(max_row - l2[0][0], 2))
p1, p2 = np.array([[max_row[arrayA[0]], row]]), np.array([[max_row[arrayB[0]], row]])
lane_boundary1_points, lane_boundary2_points = np.append(lane_boundary1_points, p1, axis=0), np.append(lane_boundary2_points, p2, axis=0)
l1, l2 = p1, p2
row += 1
# lane_boundary 1
# lane_boundary 2
################
##### TODO #####
# spline fitting using scipy.interpolate.splprep
# and the arguments self.spline_smoothness
#
# if there are more lane_boundary points points than spline parameters
# else use perceding spline
'''
使用 scipy.interpolate.splprep 进行样条拟合
#以及自变量self.spline_splity
#如果车道边界点比样条曲线参数多
#否则使用perceding样条线
'''
if lane_boundary1_points.shape[0] > 4 and lane_boundary2_points.shape[0] > 4:
# Pay attention: the first lane_boundary point might occur twice
# lane_boundary 1
lane_boundary1, _ = splprep([lane_boundary1_points[1:,0], lane_boundary1_points[1:,1]], s=self.spline_smoothness, k=2)
# lane_boundary 2
lane_boundary2, _ = splprep([lane_boundary2_points[1:,0], lane_boundary2_points[1:,1]], s=self.spline_smoothness, k=2)
else:
lane_boundary1 = self.lane_boundary1_old
lane_boundary2 = self.lane_boundary2_old
################
else:
lane_boundary1 = self.lane_boundary1_old
lane_boundary2 = self.lane_boundary2_old
self.lane_boundary1_old = lane_boundary1
self.lane_boundary2_old = lane_boundary2
# output the spline
return lane_boundary1, lane_boundary2
def plot_state_lane(self, state_image_full, steps, fig, waypoints=[]):
'''
Plot lanes and way points
'''
# evaluate spline for 6 different spline parameters.
t = np.linspace(0, 1, 6)
lane_boundary1_points_points = np.array(splev(t, self.lane_boundary1_old))
lane_boundary2_points_points = np.array(splev(t, self.lane_boundary2_old))
plt.gcf().clear()
plt.imshow(state_image_full[::-1])
plt.plot(lane_boundary1_points_points[0], lane_boundary1_points_points[1]+96-self.cut_size, linewidth=5, color='orange')
plt.plot(lane_boundary2_points_points[0], lane_boundary2_points_points[1]+96-self.cut_size, linewidth=5, color='orange')
if len(waypoints):
plt.scatter(waypoints[0], waypoints[1]+96-self.cut_size, color='white')
plt.axis('off')
plt.xlim((-0.5,95.5))
plt.ylim((-0.5,95.5))
plt.gca().axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.gca().axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
fig.canvas.flush_events()
# t = np.linspace(0, 1, 5) # t = [0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1]
# Interpolated_lane_boundary_points = np.array(splev(t, self.lane_boundary))
0x01 运行结果演示
cd 到 skeleton 文件夹的路径下,输入 python test_lane_detection 运行代码:

🚩 运行结果:
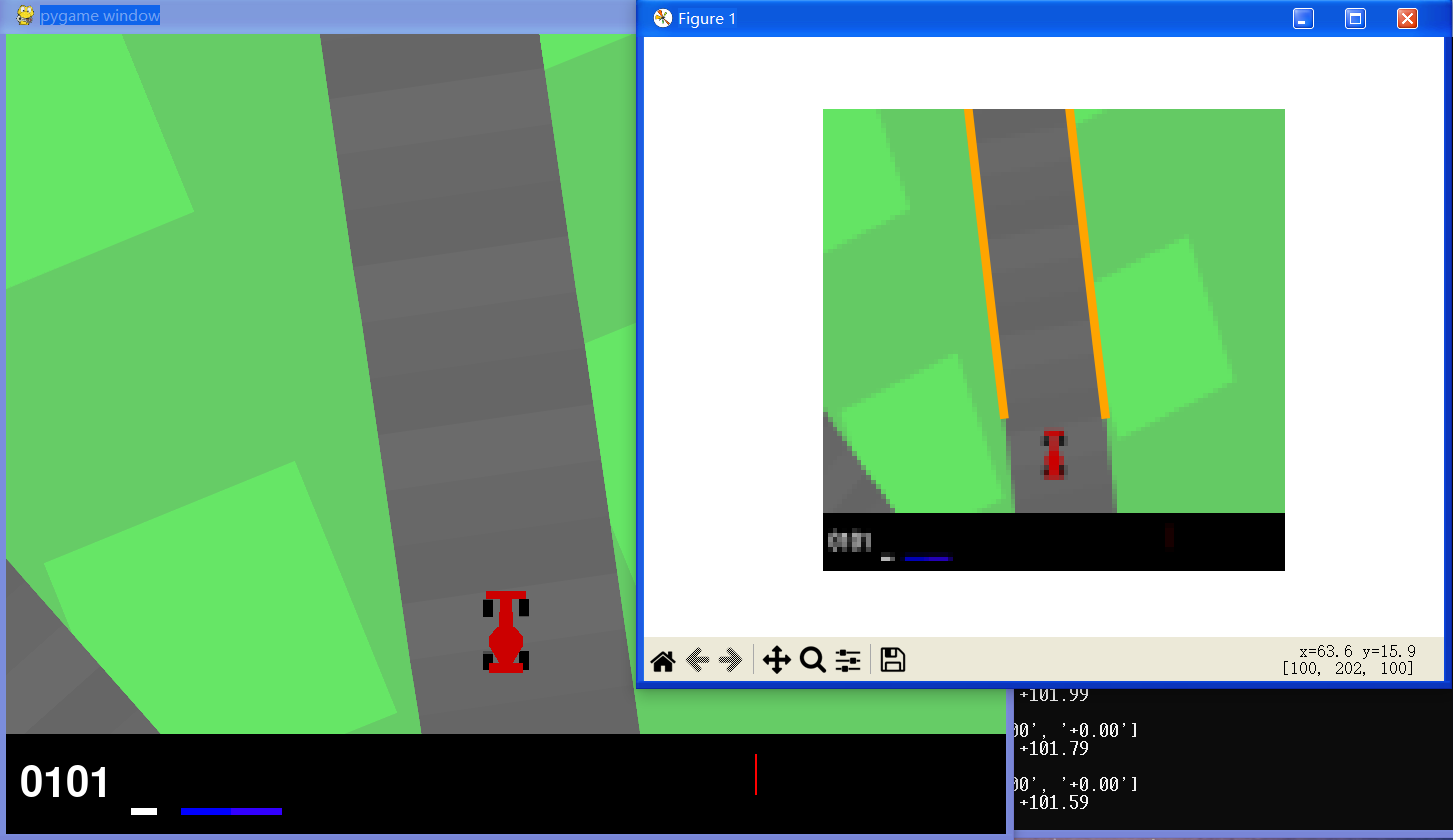
💻 GIF:
0x02 转灰度图像:cur_gray
cut_gray 函数需要我们实现将状态图像转化为灰度图像。
💬 参考代码:
def cut_gray(self, state_image_full):
copy_img = state_image_full[:self.cut_size, :]
red, green, blue = 0.2989, 0.5870, 0.1140
return np.dot(copy_img[...,:3], [red, green, blue])[::-1]0x03 边缘检测:edge_detection
💬 参考代码:
def edge_detection(self, gray_image):
'''
##### TODO #####
In order to find edges in the gray state image,
this function should derive the absolute gradients of the gray state image.
Derive the absolute gradients using numpy for each pixel.
To ignore small gradients, set all gradients below a threshold (self.gradient_threshold) to zero.
input:
gray_state_image 65x96x1
output:
gradient_sum 65x96x1
'''
gradient = np.gradient(gray_image)
gradient_sum = abs(gradient[0]) + abs(gradient[1])
gradient = gradient_sum < self.gradient_threshold
gradient_sum[gradient] = 0
return gradient_sum
0x04 寻找边缘检测结果中的局部最大值:find_maxima_gradient_rowwise
为渐变图像的每一行输出局部最大值的参数,可以使用 scipy.signal 查找峰值以检测最大值。
* 提示:使用距离参数(distance)可以获得更好的鲁棒性。
- 距离参数
cuz车道应至少相隔 3 像素 find_peaks返回 `x` 中满足所有给定条件的峰值指数。
💬 参考代码:
def find_maxima_gradient_rowwise(self, gradient_sum):
'''
##### TODO #####
This function should output arguments of local maxima for each row of the gradient image.
You can use scipy.signal.find_peaks to detect maxima.
Hint: Use distance argument for a better robustness.
input:
gradient_sum 65x96x1
output:
maxima (np.array) shape : (Number_maxima, 2)
'''
argmaxima = []
pixel = 3 # 相隔参数
i = 0
while (i < gradient_sum.shape[0]):
top, _ = find_peaks(gradient_sum[i], distance = pixel)
argmaxima.append(top)
i += 1
return argmaxima
🔗 OpenAI Gym-CarRacing 系列博客:
【OpenAI】Python:基于 Gym-CarRacing 的自动驾驶项目(1) | 前置知识介绍 | 项目环境准备 | 手把手带你一步步实现
【OpenAI】Python:基于 Gym-CarRacing 的自动驾驶项目(2)| 车道检测功能的实现 | 边缘检测与分配 | 样条拟合
【OpenAI】Python:基于 Gym-CarRacing 的自动驾驶项目(3) | 路径训练功能的实现 | 规划与决策 | 路径平滑 | 利用公式进行目标速度预测
【OpenAI】Python:基于 Gym-CarRacing 的自动驾驶项目(4) | 车辆控制功能的实现 | 开环控制 | 闭环控制 | 启停式控制 | PID 控制 | Stanley 控制器

📌 [ 笔者 ] foxny, Akam
📃 [ 更新 ] 2023.7.8(recently)
❌ [ 勘误 ] /* 暂无 */
📜 [ 声明 ] 由于作者水平有限,本文有错误和不准确之处在所难免,
本人也很想知道这些错误,恳望读者批评指正!| 📜 参考资料 [6] Montemerlo M, Becker J, Bhat S, et al. Junior: The Stanford entry in the Urban Challenge Slide Credit: Steven Waslander LaValle: Rapidly-exploring random trees: A new tool for path planning. Techical Report, 1998 Dolgov et al.: Practical Search Techniques in Path Planning for Autonomous Driving. STAIR, 2008. Microsoft. MSDN(Microsoft Developer Network)[EB/OL]. []. . 百度百科[EB/OL]. []. https://baike.baidu.com/. . [EB/OL]. []. https://blog.waymo.com/2021/10/the-waymo-driver-handbook-perception.html. |