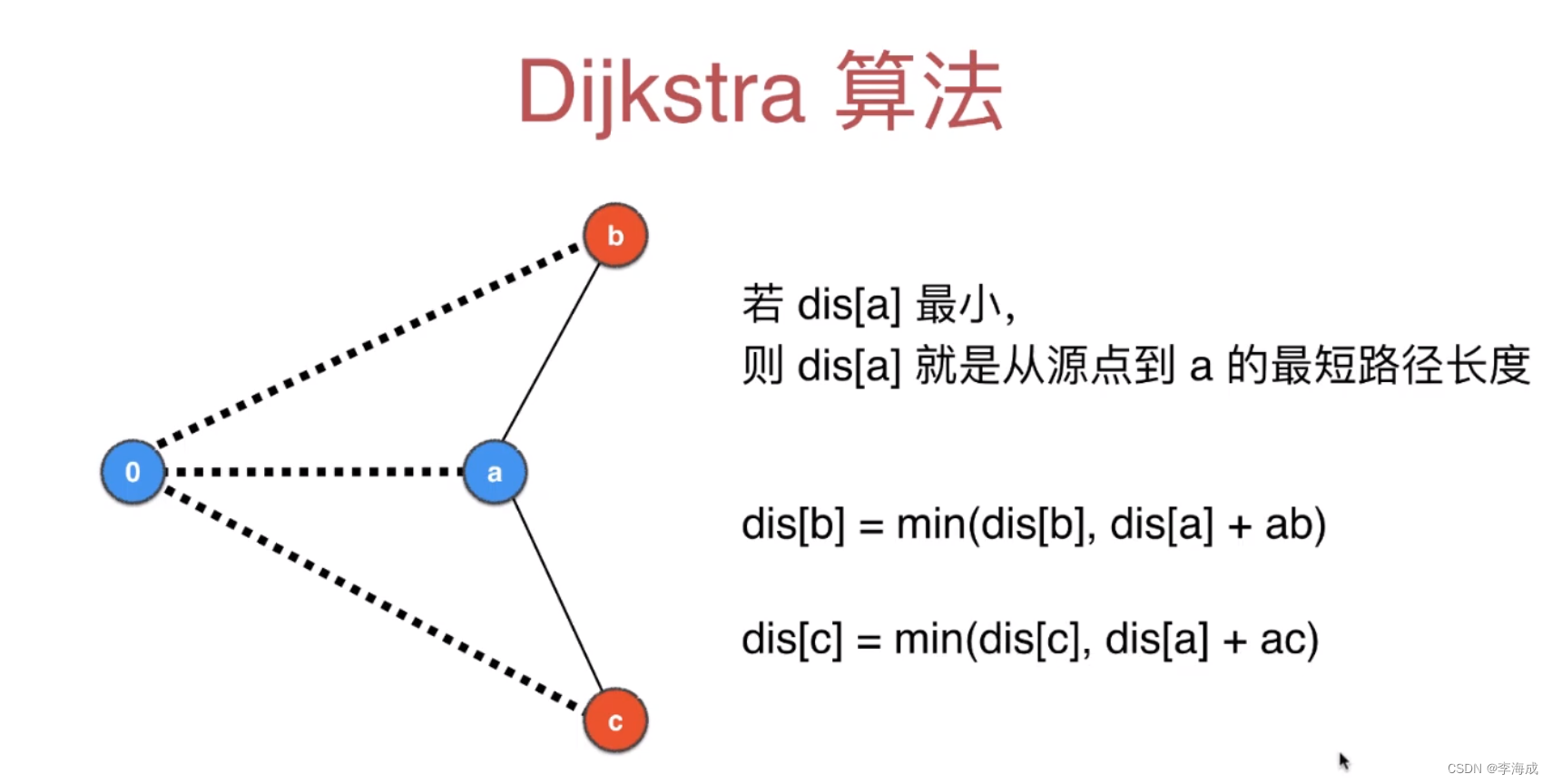
springboot启动流程参考。Springboot总结。本内容主要解析里面的配置文件的加载过程。
springboot资源加载
入口。SpringApplication#run
我们知道,run方法是构建容器的过程。里面有一个方法:prepareEnvironment。用于构建环境组件Environment,发布环境准备事件,有相关监听器完成资源的加载。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 看这里看这里。
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
prepareEnvironment的源码如下:
1. 根据webApplicationType,实例化对应的environment对象。environment的父类AbstractEnvironment实例化会调用customizePropertySources方法完成一些资源文件的加载。customizePropertySources的落地实现在对应environment的实现类中。
2. main函数入参配置。增加一个name为configurationProperties的PropertySources。这个包含上面加载的所有propertySource。
3. springApplicationRunListener发布environmentPrepared事件。处理事件的监听器有以下几种。
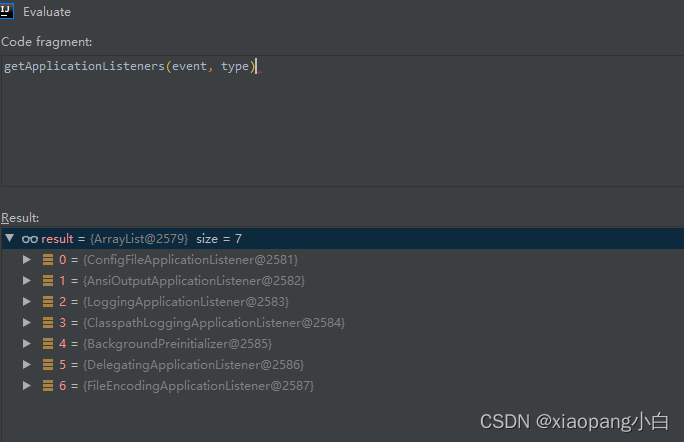
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment 创建一个Environment对象。
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
ConfigFileApplicationListener监听器对资源的加载
ConfigFileApplicationListener主要完成对application相关的资源加载。我们重点看这个监听器。对其他几个感兴趣的,可以自己debug看看代码。
// ConfigFileApplicationListener#onApplicationEvent
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> loadPostProcessors() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(EnvironmentPostProcessor.class, getClass().getClassLoader());
}
由源码我们可以看出,对事件的处理是调用的onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent方法。其中loadPostProcessors方法是通过spi机制加载spring.factories文件获取key为:EnvironmentPostProcessor.class的对象集合。这些对象都实现了EnvironmentPostProcessor接口的postProcessEnvironment接口。ConfigFileApplicationListener这个类本身也实现了EnvironmentPostProcessor接口。我们接着看ConfigFileApplicationListener#EnvironmentPostProcessor。
跟进ConfigFileApplicationListener#EnvironmentPostProcessor。主要逻辑来着load()方法的执行。
void load() {
FilteredPropertySource.apply(this.environment, DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, LOAD_FILTERED_PROPERTY,
(defaultProperties) -> {
this.profiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.activatedProfiles = false;
this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>();
initializeProfiles();
while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
Profile profile = this.profiles.poll();
if (isDefaultProfile(profile)) {
addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName());
}
// 看这里看这里
load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter,
addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false));
this.processedProfiles.add(profile);
}
// 看这里看这里
load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true));
addLoadedPropertySources();
applyActiveProfiles(defaultProperties);
});
}
private void load(Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
// getSearchLocations方法获取扫描文件的目录地址。getSearchNames获取查询文件的名称。
getSearchLocations().forEach((location) -> {
boolean isDirectory = location.endsWith("/");
Set<String> names = isDirectory ? getSearchNames() : NO_SEARCH_NAMES;
names.forEach((name) -> load(location, name, profile, filterFactory, consumer));
});
}
我们重点看getSearchLocations方法和getSearchNames方法。
1. getSearchLocations方法主要获取查询资源文件的目录信息。这也是我们配置文件加载的先后顺序。
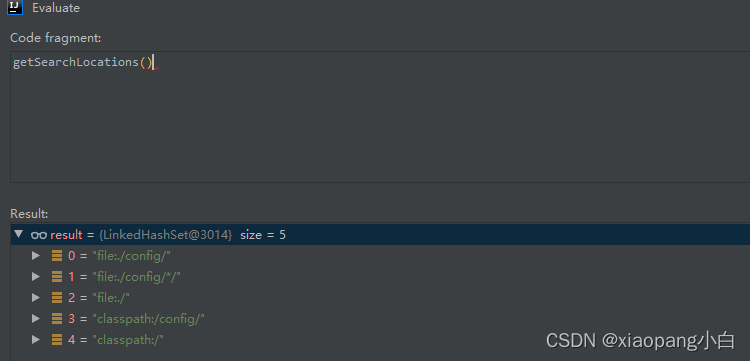
2. getSearchNames获取需要加载的文件名称。当environment中不存在key:spring.config.name时,获取默认name的名称:application。如果environment中存在key:spring.config.name时,获取的name为对应的value。当前获取到的name为appplicaition。
private Set<String> getSearchNames() {
// CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY: spring.config.name
if (this.environment.containsProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY)) {
String property = this.environment.getProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY);
Set<String> names = asResolvedSet(property, null);
names.forEach(this::assertValidConfigName);
return names;
}
// DEFAULT_NAMES: application
return asResolvedSet(ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.names, DEFAULT_NAMES);
}
接着遍历propertySourceLoader,拼接文件名称,在扫描的目录下加载对应的文件。propertySourceLoader也是通过spi机制加载spring.factories文件获取key为:PropertySourceLoader.class的对象集合,我们可以看到有两个加载类。这个集合是一个List集合,所以根据顺序会先执行PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,然后执行YamlPropertySourceLoader。
1. PropertiesPropertySourceLoader处理后缀名为"properties", “xml"的文件。
2. YamlPropertySourceLoader处理后缀名为"yml”, "yaml"的文件。
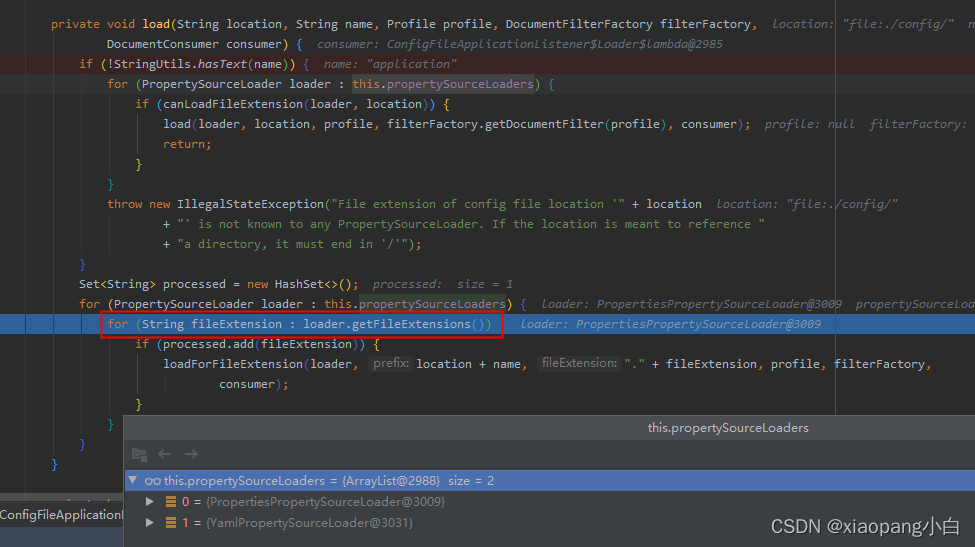
跟进debug,我们可以发现,加载对应的资源名称封装为:“applicationConfig: [” + getLocationName(location, resource) + “]”;
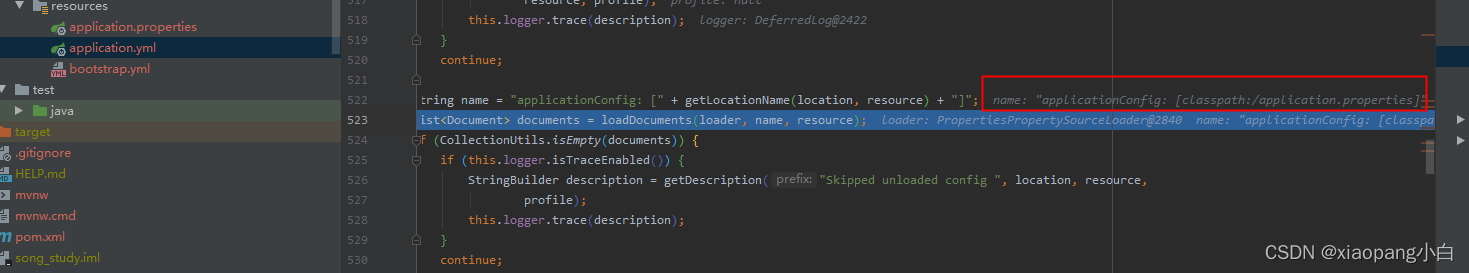
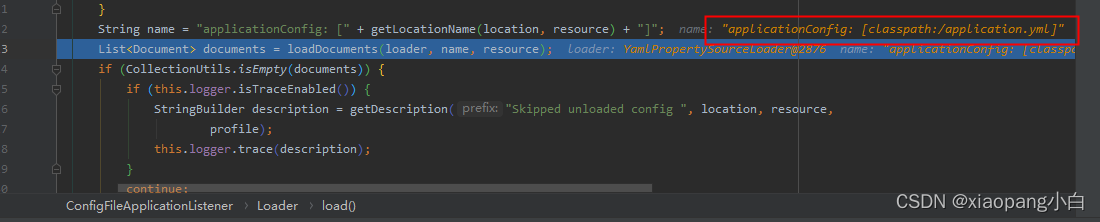
加载到资源封装为document后,会调用consume函数接口处理。主要做的就是将解析获取到的资源文件封装为OriginTrackedMapPropertySource并放入到environment中。
private DocumentConsumer addToLoaded(BiConsumer<MutablePropertySources, PropertySource<?>> addMethod,
boolean checkForExisting) {
return (profile, document) -> {
if (checkForExisting) {
for (MutablePropertySources merged : this.loaded.values()) {
if (merged.contains(document.getPropertySource().getName())) {
return;
}
}
}
MutablePropertySources merged = this.loaded.computeIfAbsent(profile,
(k) -> new MutablePropertySources());
addMethod.accept(merged, document.getPropertySource());
};
}
/**
* Add the given property source object with lowest precedence.
* 这个是addMethod对应的处理。addMethod也是consume函数接口
*/
public void addLast(PropertySource<?> propertySource) {
synchronized (this.propertySourceList) {
removeIfPresent(propertySource);
// 加入到environment中。
this.propertySourceList.add(propertySource);
}
}
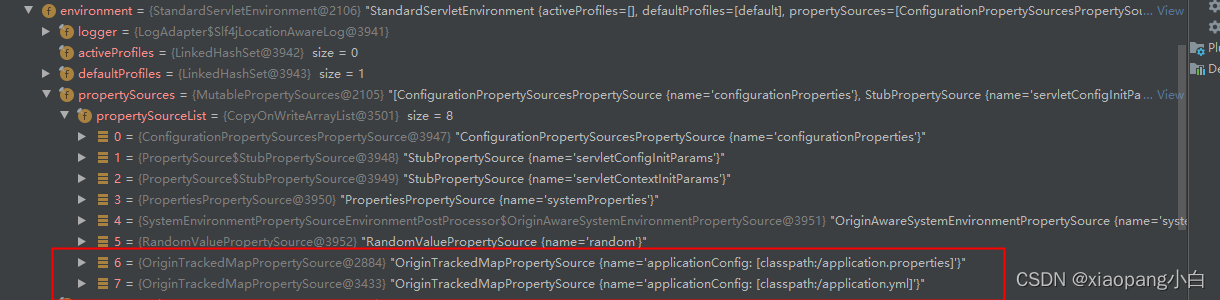
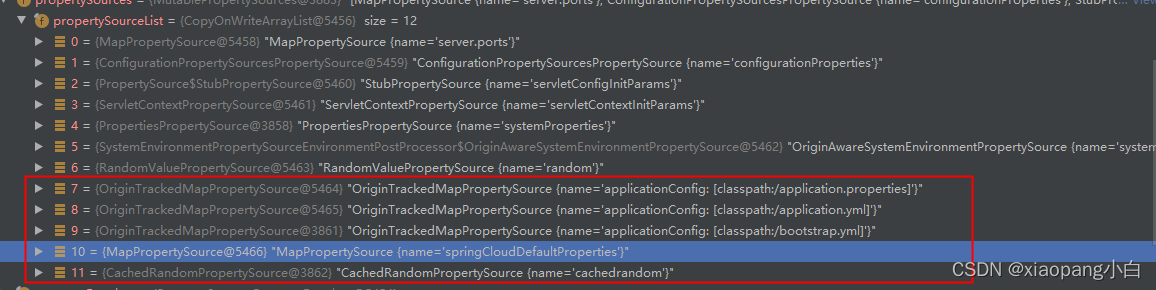
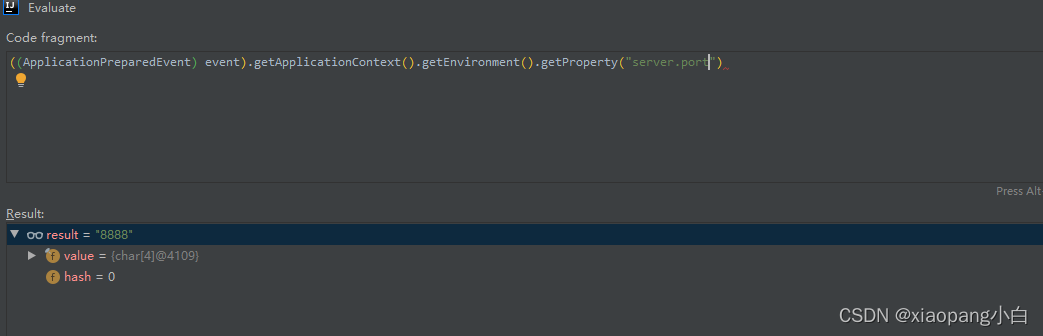
两个配置文件中都有server.port配置。解析完的时候我们通过debug执行看看获取的配置是哪个。结果很明显,是获取到的applicaiton.properties的配置。getProperties查询是遍历propertySources。查询到返回。按照这个逻辑的话。配置文件优先级应该是(未验证):.properties > xml > yml > yaml。

基于springboot的springcloud资源加载
基于springboot的springcloud服务,在处理environmentPrepared事件(这个是方法名,事件名称为ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent)增加了两个监听器在spring-cloud-context包中。我们重点看看第一个BootstrapApplicationListener。
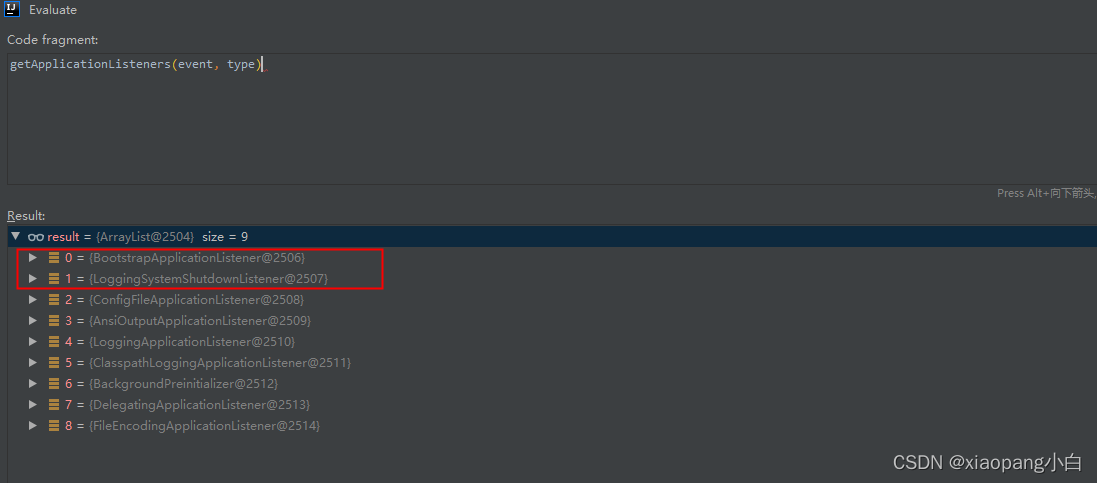
BootstrapApplicationListener
首先,BootstrapApplicationListener在处理ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件的时候,首先从环境中判断key:spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled对应的value是否为true,不配置的话默认值为true。其次,从环境中获取key:spring.cloud.bootstrap.name对应的value,不配置的话默认为bootstrap。
构建一个bootstrapServiceContext对象。这个一个容器对象AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
对当前应用中增加监听器CloseContextOnFailureApplicationListener。
对当前应用springapplication进行相关配置。增加一些容器初始化类。
// BootstrapApplicationListener#onApplicationEvent
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
// 校验是否开启bootstrap的引导类
if (!environment.getProperty("spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled", Boolean.class,
true)) {
return;
}
// don't listen to events in a bootstrap context
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) {
return;
}
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
String configName = environment
.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.name:bootstrap}");
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : event.getSpringApplication()
.getInitializers()) {
if (initializer instanceof ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) {
context = findBootstrapContext(
(ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) initializer,
configName);
}
}
if (context == null) {
// 构建容器对象AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。里面逻辑复杂,见下文分析。
context = bootstrapServiceContext(environment, event.getSpringApplication(),
configName);
// 对当前应用中增加监听器CloseContextOnFailureApplicationListener。
event.getSpringApplication()
.addListeners(new CloseContextOnFailureApplicationListener(context));
}
// 根据新创建的容器对当前应用springapplication进行相关配置。增加一些容器初始化类。
apply(context, event.getSpringApplication(), environment);
}
构建bootstrapServiceContext对象(容器对象AnnotationConfigApplicationContext)
构建容器对象就是创建一个新的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
1. 构建一个空的environment。类型是StandardEnvironment
2. 获取当前应用中key为:spring.cloud.bootstrap.location,spring.cloud.bootstrap.additional-location的路径。如果存在,下面代码会根据这个地址去加载文件。我们没有配置,默认是""。
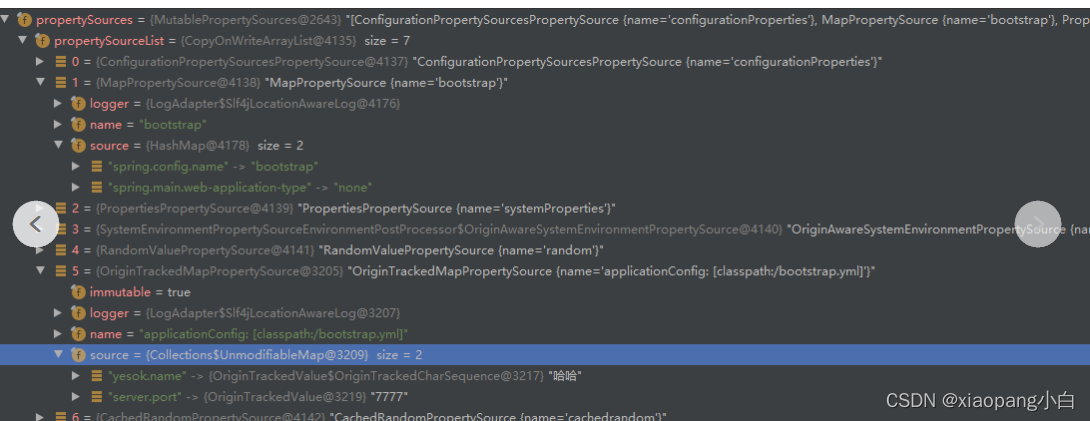
3. 构建Map对象,里面有spring.config.name的配置。上文讲解springboot解析的内容中,在遍历资源目录的时候,获取文件名,取得就是这个key的值。相当于这里配置了,那么就不会取applicaiton了,取的是bootstrap。将Map对象封装成MapPropertySource对象,添加到bootstrapServiceContext的环境对象中。
4. 将当前环境对象中的propertySource对象,筛选添加到bootstrapServiceContext的环境对象中。这种类型StubPropertySource的不添加。StubPropertySource对应的是servlet相关的资源文件。
5. 通过SpringApplicationBuild构建器构造SpringApplicaiton对象。webApplicaitonType为none。
6. 设置BootstrapServiceContext容器id为bootstrap。给当前应用的SpringApplciaiton中添加容器初始化处理类AncestorInitializer。AncestorInitializer里面包含了bootstrap容器。会在后续当前应用的容器初始化的时候,设置容器的父容器为boootstrap容器。
7. bootstrap容器中的环境中移除name为bootsratp的propertySource。里面存储的就是spring.config.name配置,还有其他配置的MapPropertySource。移除后,后面的资源加载获取的文件名默认就是application了。
8. 合并bootstrap容器中的Environment的propertySource到当前应用的Environment中。name为:springCloudDefaultProperties。sources为bootstrap容器中Environment的propertySource集合。
private ConfigurableApplicationContext bootstrapServiceContext(
// 构建一个空的environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, final SpringApplication application,
String configName) {
StandardEnvironment bootstrapEnvironment = new StandardEnvironment();
MutablePropertySources bootstrapProperties = bootstrapEnvironment
.getPropertySources();
for (PropertySource<?> source : bootstrapProperties) {
bootstrapProperties.remove(source.getName());
}
String configLocation = environment
.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.location:}");
String configAdditionalLocation = environment
.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.additional-location:}");
// 构建Map对象,后面会放入到Envrionment中。传进来的configName为bootstrap。
Map<String, Object> bootstrapMap = new HashMap<>();
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.name", configName);
// if an app (or test) uses spring.main.web-application-type=reactive, bootstrap
// will fail
// force the environment to use none, because if though it is set below in the
// builder
// the environment overrides it
bootstrapMap.put("spring.main.web-application-type", "none");
if (StringUtils.hasText(configLocation)) {
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.location", configLocation);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(configAdditionalLocation)) {
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.additional-location",
configAdditionalLocation);
}
bootstrapProperties.addFirst(
new MapPropertySource(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, bootstrapMap));
// 将当前环境对象中的propertySource对象,筛选添加到bootstrapServiceContext的环境对象中。
for (PropertySource<?> source : environment.getPropertySources()) {
if (source instanceof StubPropertySource) {
continue;
}
bootstrapProperties.addLast(source);
}
// TODO: is it possible or sensible to share a ResourceLoader?
// 构建SpringApplication对象
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder()
.profiles(environment.getActiveProfiles()).bannerMode(Mode.OFF)
.environment(bootstrapEnvironment)
// Don't use the default properties in this builder
.registerShutdownHook(false).logStartupInfo(false)
.web(WebApplicationType.NONE);
final SpringApplication builderApplication = builder.application();
if (builderApplication.getMainApplicationClass() == null) {
// gh_425:
// SpringApplication cannot deduce the MainApplicationClass here
// if it is booted from SpringBootServletInitializer due to the
// absense of the "main" method in stackTraces.
// But luckily this method's second parameter "application" here
// carries the real MainApplicationClass which has been explicitly
// set by SpringBootServletInitializer itself already.
builder.main(application.getMainApplicationClass());
}
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains("refreshArgs")) {
// If we are doing a context refresh, really we only want to refresh the
// Environment, and there are some toxic listeners (like the
// LoggingApplicationListener) that affect global static state, so we need a
// way to switch those off.
builderApplication
.setListeners(filterListeners(builderApplication.getListeners()));
}
builder.sources(BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration.class);
final ConfigurableApplicationContext context = builder.run();
// gh-214 using spring.application.name=bootstrap to set the context id via
// `ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer` prevents apps from getting the actual
// spring.application.name
// during the bootstrap phase.
// 设置容器的id为bootstrap
context.setId("bootstrap");
// Make the bootstrap context a parent of the app context
// 给当前应用的SpringApplication中添加ApplicationContextInitializer监听器。AncestorInitializer
addAncestorInitializer(application, context);
// It only has properties in it now that we don't want in the parent so remove
// it (and it will be added back later)
// bootstrap容器中的环境中移除name为bootsratp的propertySource。里面存储的就是spring.config.name配置,还有其他配置的MapPropertySource。
bootstrapProperties.remove(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
// 合并bootstrap容器中的Environment的propertySource到当前应用的Environment中。name为:springCloudDefaultProperties。sources为bootstrap容器中Environment的propertySource集合。
mergeDefaultProperties(environment.getPropertySources(), bootstrapProperties);
return context;
}
以下是bootstrap容器解析后的环境。
当前应用继续解析
后续监听器继续解析。再记载文件的时候,当前的配置文件名称就是applicaiton了。
再初始化当前应用的容器的时候,会设置父容器为bootstrap的容器。新的环境内容为。里面顺序调整应该是容器初始化处理类里面做的操作(暂时没看)。