手写promise之前需要知道
- 宏任务 & 微任务
我们都知道 Js 是单线程的,但是一些高耗时操作就带来了进程阻塞问题。为了解决这个问题,Js 有两种任务的执行模式:同步模式(Synchronous)和异步模式(Asynchronous)。
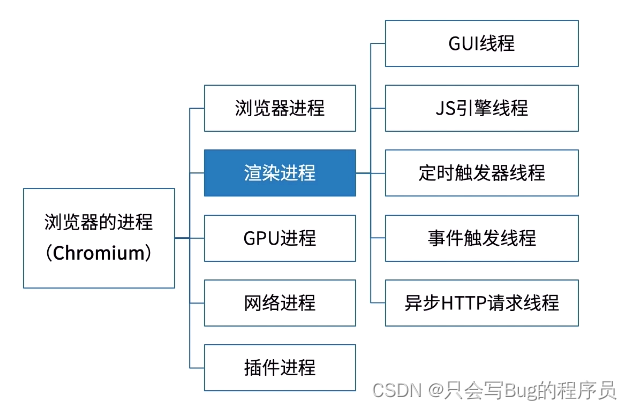
JS异步的实现靠的就是浏览器的多线程,当他遇到异步API时,就将这个任务交给对应的线程,当这个异步API满足回调条件时,对应的线程又通过事件触发线程将这个事件放入任务队列,然后主线程从任务队列取出事件继续执行。以浏览器为例,有以下几个常见的进程和线程:
在异步模式下,创建异步任务主要分为宏任务与微任务两种。ES6 规范中,宏任务(Macrotask) 称为 Task, 微任务(Microtask) 称为 Jobs。宏任务是由宿主(浏览器、Node)发起的,而微任务由 JS 自身发起。
宏任务与微任务的几种创建方式 👇
| 宏任务(Macrotask) | 微任务(Microtask) |
|---|---|
| setTimeout | requestAnimationFrame(有争议) |
| setInterval | MutationObserver(浏览器环境) |
| MessageChannel | Promise.[ then/catch/finally ] |
| I/O,事件队列 | process.nextTick(Node环境) |
| setImmediate(Node环境) | queueMicrotask |
| script(整体代码块) |
来道面试题:
async function async1 () {
console.log('async1 start');
await async2();
console.log('async end')
}
async function async2 () {
console.log('async2')
}
console.log('script start')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('serTimeout')
}, 0)
async1()
new Promise((function (resolve) {
console.log('promise1')
resolve()
})).then(function () {
console.log('promise2')
}).then(function () {
console.log('promise3')
}).then(function () {
console.log('promise4')
})
console.log('script end')
queueMicrotask的用法
console.log('script start');
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('pr start');
resolve();
}).then(res => {
console.log('pr then');
}) .then(res => {
console.log('pr end');
})
queueMicrotask(() => {
console.log('queueMicrotask');
})
console.log('script end');
- 什么是Promise A+规范
当别人问起来什么是Promise/A+规范,可能会觉得有点懵,你可能用过Promise,但很可能不了解什么是Promise规范。
其实Promise 规范有很多,如Promise/A,Promise/B,Promise/D 以及 Promise/A 的升级版 Promise/A+。ES6中采用了 Promise/A+ 规范。 - Promise标准解读
- 一个promise的当前状态只能是pending、fulfilled和rejected三种之一。状态改变只能是pending到fulfilled或者pending到rejected。状态改变不可逆。
- promise的then方法接收两个可选参数,表示该promise状态改变时的回调(promise.then(onFulfilled, onRejected))。then方法返回一个promise,then 方法可以被同一个 promise 调用多次。
- Promise/A+并未规范race、all、catch方法,这些是ES6自己规范的。
正式开始
- 确定一个异步方法
| 微任务(Microtask) |
|---|
| requestAnimationFrame(有争议) |
| MutationObserver(浏览器环境) |
| Promise.[ then/catch/finally ] |
| process.nextTick(Node环境) |
| queueMicrotask |
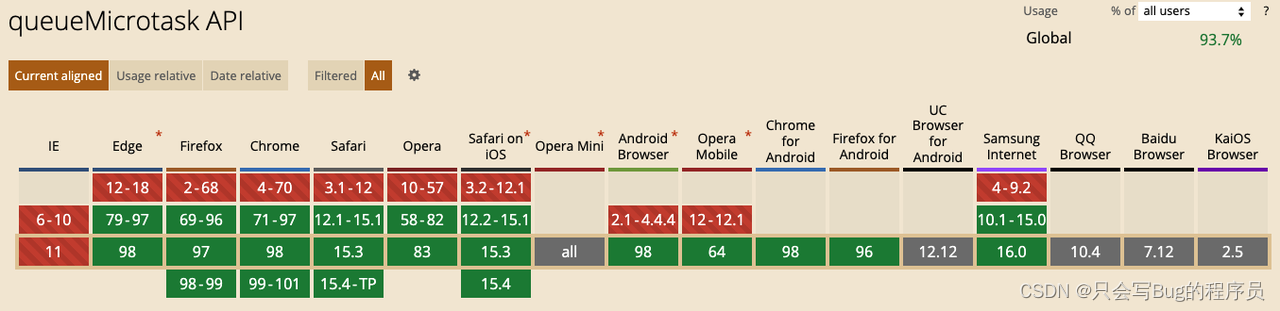
其中不需要判断环境的,也就queueMicrotask了,但是queueMicrotask的兼容性不是很好,所以写一个兼容方法:
const asyncFn = function () {
if (typeof queueMicrotask === 'function') {
return queueMicrotask;
}
if (typeof process === 'object' && process !== null && typeof (process.nextTick) === 'function') {
return process.nextTick;
}
if (typeof (setImmediate) === 'function') {
return setImmediate
}
return setTimeout
}()
- 写一个基础的Promise
const pr = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const number = Math.random();
if (number > 0.5) {
resolve(number);
} else {
reject(new Error(number));
}
});
const STATUS_PADDING = Symbol('PADDING');
const STATUS_FULFILLED = Symbol('FULFILLED');
const STATUS_REJECTED = Symbol('REJECTED');
class MiniPromise {
constructor(callback){
try {
callback(this.onFulfilled.bind(this), this.onRejected.bind(this));
} catch (error) {
this.onRejected(error);
}
}
value = null;
status = STATUS_PADDING;
onFulfilled(value) {
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
}
onRejected(error) {
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.value = error;
}
}
- 实现then
pr.then(res => {
console.log('success::', res);
}, err => {
console.error('error:::', err);
});
// 调用then中的方法时,需要判断当前promise的状态
// 如果是padding状态,需要等待promise的状态更新为fulfilled/rejected时才能调用
// 所以需要保存一下callback,等更新后再调用这个方法。
then(resolve, reject) {
// 平常使用的时候,一般只传递了第一个参数,没有传reject方法,所以给他们加上默认值
resolve = typeof resolve === 'function' ? resolve : value => value;
reject = typeof reject === 'function' ? reject : value => value;
const newPromise = new MiniPromise(() => {});
switch(this.status) {
case STATUS_PADDING:
this.resolveCallback = resolve;
this.rejectCallback = reject;
this.thenPromise = newPromise;
break;
case STATUS_FULFILLED:
try {
newPromise.onFulfilled(resolve(this.value));
} catch(err) {
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
newPromise.onRejected(reject(err));
}
break;
case STATUS_REJCETED:
try {
newPromise.onRejected(reject(this.value));
} catch(err) {
newPromise.onRejected(reject(err));
}
break;
}
return newPromise;
}
- 多个then调用
const pr2 = pr.then(res => {
console.log('success:222:', res);
}, err => {
console.error('error:222:', err);
});
const pr3 = pr.then(res => {
console.log('success:333:', res);
}, err => {
console.error('error:333:', err);
});
想想改咋改?
// 将this.rejectCallback改为数组就好了
onFulfilled(value) {
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
let index = 0;
while(this.resolveCallback.length) {
const item = this. resolveCallback.shift();
try {
const result = item(this.value);
this.thenPromiseList[index]. onFulfilled(result);
} catch(err) {
console.log('xxx resolve:::::', err);
this.thenPromiseList[index].onRejected(err);
}
index ++;
}
}
onRejected(error) {
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.value = error;
let index = 0;
while(this.rejectCallback.length) {
const item = this.rejectCallback.shift();
try {
const result = item(this.value);
this.thenPromiseList[index].onRejected(result);
} catch(err) {
console.log('xxx resolve:::', err);
this.thenPromiseList[index].onRejected(err);
}
index ++;
}
}
then(resolve, reject) {
// ......
switch(this.status) {
case STATUS_PADDING:
this.resolveCallback = resolve;
this.rejectCallback = reject;
this.resolveCallback.push(resolve);
this.rejectCallback.push(reject);
this.thenPromiseList.push(newPromise)
break;
// .....
}
}
- 实现错误catch
catch(onRejected) {
if (typeof onRejected !== 'function') {
onRejected = reason => reason;
}
const newPromise = new MiniPromise(() => {});
switch(this.status) {
case STATUS_REJECTED:
newPromise.status = this.status;
newPromise.value = onRejected(this.value);
break;
case STATUS_PADDING:
this.rejectCallbackList.push(onRejected);
this.thenPromiseList.push(newPromise);
break;
}
return newPromise;
}
- 实现直接调用resolve和reject
// 一般来说,写在class中只有属性和方法.都可以被实例化的对象进行调用,比如:
class Animal {
type = '动物'
name = 'animal'
}
const dog = new Animal();
dog.type // 动物
dog.name // animal
// 假如想要在外部直接使用class内部的方法,或属性,比如这样:
class Person {
name = "shen"
}
console.log(Person.name); // 这样会打印Person1【类的名称】,并取不到shen
// 这时就需要使用static关键字
class Person {
static name = 'shen';
}
console.log(Person.name); // 这样就可以得到 shen 了
// 静态的方法中也可以使用同一个类下的其他静态属性或方法
class Person2 {
static hhha = "aaa"
static sayHi() {
console.log(this.hhha + ' hi~');
}
}
Person2.sayHi() // aaa hi~
// 如果hhha 不是static的,那么sayHi会打印出 undefined hi~
// react中的getDerivedStateFromProps,也是一个静态方法
回归正题,想要实现直接调用resolve,和reject方法,也需要使用static关键字
// 先看看使用方法
const resPr = Promise.resolve(123);
class MiniPromise {
// ...
static resolve(value) {
const newPr = new MiniPromise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
resolve(value);
} catch(err) {
reject(err);
}
})
return newPr;
}
static reject(value) {
const newPr = new MiniPromise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
reject(value);
} catch(err) {
reject(err);
}
})
return newPr;
}
// ...
}
整体看一下代码
class MiniPromise {
constructor(callback) {
try {
callback(this.handleFulfilled.bind(this), this.handleRejected.bind(this));
} catch(err) {
this.handleRejected(err);
}
}
status = STATUS_PADDING;
value = undefined;
rejectCallbackList = [];
fulfillCallbackList = [];
thenPromiseList = [];
static resolve(value) {
const newPromise = new MiniPromise((resolve, rejcet) => {
try {
console.log(value);
resolve(value);
} catch(err) {
rejcet(err);
}
});
return newPromise;
}
static reject(value) {
const newPromise = new MiniPromise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
reject(value);
} catch(err) {
reject(err);
}
});
return newPromise;
}
handleFulfilled(value) {
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
console.log('resolve', value, this.fulfillCallbackList);
let index = 0;
while(this.fulfillCallbackList.length) {
const item = this.fulfillCallbackList.shift();
try {
const result = item(this.value);
if (result === this.thenPromiseList[index]) {
this.thenPromiseList[index].handleRejected(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>'));
continue
};
this.thenPromiseList[index].handleFulfilled(result);
} catch(err) {
console.log('xxx resolve:::::', err);
this.thenPromiseList[index].handleRejected(err);
}
index ++;
}
}
handleRejected(reason) {
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.value = reason;
console.log('rejcet', reason);
let index = 0
while(this.rejectCallbackList.length) {
const item = this.rejectCallbackList.shift();
try {
const result = item(this.value);
if (result === this.thenPromiseList[index]) {
this.thenPromiseList[index].handleRejected(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>'))
continue
};
this.thenPromiseList[index].handleRejected(result);
} catch(err) {
this.thenPromiseList[index].handleRejected(err);
}
index ++;
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === 'function' ? onFulfilled : value => value;
onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : reason => reason;
const newPromise = new MiniPromise(() => {});
switch(this.status) {
case STATUS_FULFILLED:
try {
newPromise.status = this.status;
newPromise.value = onFulfilled(this.value);
} catch(err) {
console.log('errr', err);
newPromise.value = onRejected(err);
}
break;
case STATUS_REJECTED:
newPromise.status = this.status;
try {
newPromise.value = onRejected(this.value);
} catch(err) {
newPromise.value = onRejected(err);
}
break;
case STATUS_PADDING:
this.rejectCallbackList.push(onRejected);
this.fulfillCallbackList.push(onFulfilled);
this.thenPromiseList.push(newPromise);
break;
}
return newPromise;
}
catch(onRejected) {
if (typeof onRejected !== 'function') {
onRejected = reason => reason;
}
const newPromise = new MiniPromise(() => {});
switch(this.status) {
case STATUS_REJECTED:
newPromise.status = this.status;
newPromise.value = onRejected(this.value);
break;
case STATUS_PADDING:
this.rejectCallbackList.push(onRejected);
this.thenPromiseList.push(newPromise);
break;
}
return newPromise;
}
}