JUC并发编程第九篇,原子操作类分类解析,LongAdder为什么这么快原理分析?
- 一、基本类型原子类
- 二、数组类型原子类
- 三、引用类型原子类
- 四、对象的属性修改原子类
- 五、原子操作增强类
- 六、原理分析,LongAdder 为什么这么快?
- 位于 java.base 模块, java.util.concurrent.atomic 工具包,它支持对单个变量进行无锁线程安全编程。
一、基本类型原子类
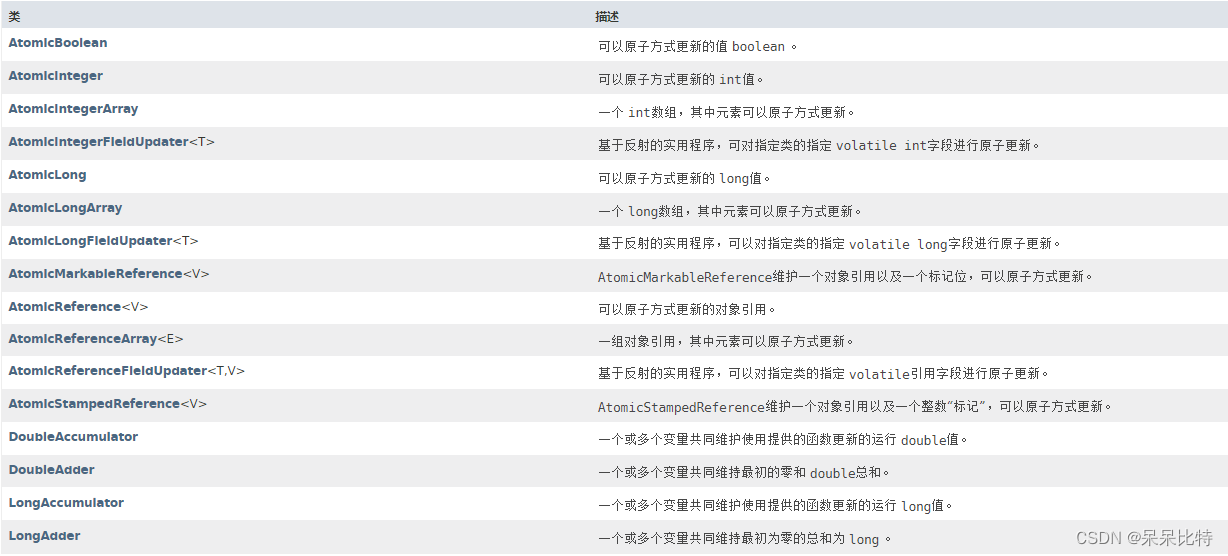
可以原子方式更新的 int,boolean,long值,基本类型原子类包括三个:AtomicInteger、AtomicBoolean、AtomicLong
常用API如下:
- public final int get(); 获取当前的值
- public final int getAndSet(int newValue); 获取当前的值,并设置新的值
- public final int getAndIncrement(); 获取当前的值,并自增
- public final int getAndDecrement(); 获取当前的值,并自减
- public final int getAndAdd(int delta); 获取当前的值,并加上预期的值
- boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update); 如果输入的数值等于预期值,则以原子方式将该值设置为输入值(update)
举例:AtomicInteger
class MyNumber{
private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
public void addPlus(){
atomicInteger.incrementAndGet();
}
public AtomicInteger getAtomicInteger() {
return atomicInteger;
}
}
public class AtomicIntegerDemo {
//100个线程,每个线程加5000次,CountDownLatch 等待上一个线程执行完毕
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyNumber myNumber = new MyNumber();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(100);
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 5000; j++) {
myNumber.addPlus();
}
}finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println(myNumber.getAtomicInteger().get());
}
}
二、数组类型原子类
一个数组,其中元素可以原子方式更新,数组类型原子类包括三个:AtomicIntegerArray、AtomicLongArray、AtomicReferenceArray
常用API如下:
- accumulateAndGet(int i, int x, IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction); 原子更新索引 i处的元素以及将给定函数应用于当前值和给定值的结果,返回更新的值。
- addAndGet(int i, int delta); 原子地将给定值添加到索引 i 处的元素。
- compareAndExchange(int i, int expectedValue, int newValue); 如果元素的当前值等于期望值,原子方式将 i 索引处的元素设置为 newValue。
- getAndIncrement(int i); 原子地增加索引 i处元素的值。
- getAndSet(int i, int newValue); 以原子方式设置索引 i 处值为 newValue ,并返回原来的值。
举例:AtomicIntegerArray
public class AtomicIntegerArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//三种初始化方式
AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[5]);
//AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(5);
//AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[]{1,2,3,4,5});
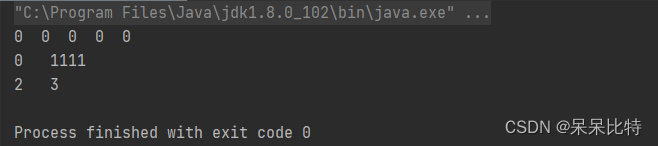
for (int i = 0; i < atomicIntegerArray.length(); i++) {
System.out.print(atomicIntegerArray.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
int tmpInt = 0;
tmpInt = atomicIntegerArray.getAndSet(0, 1111);
System.out.println(tmpInt+"\t"+atomicIntegerArray.get(0));
atomicIntegerArray.getAndIncrement(1);
atomicIntegerArray.getAndIncrement(1);
tmpInt = atomicIntegerArray.getAndIncrement(1);
System.out.println(tmpInt+"\t"+atomicIntegerArray.get(1));
}
}
三、引用类型原子类
AtomicReference : 可以原子方式更新的对象引用。
class User{
String userName;
int age;
public User(String userName, int age) {
this.userName = userName;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"userName='" + userName + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
public class AtomicReferenceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User z3 = new User("shangsan", 24);
User l4 = new User("lisi", 28);
AtomicReference<User> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();
atomicReference.set(z3);
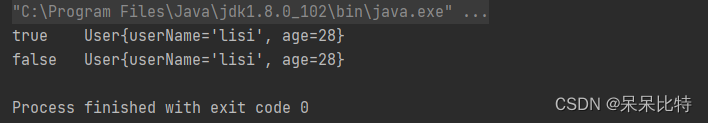
System.out.println(atomicReference.compareAndSet(z3,l4)+"\t"+atomicReference.get().toString());
System.out.println(atomicReference.compareAndSet(z3,l4)+"\t"+atomicReference.get().toString());
}
}
AtomicStampedReference : 维护一个对象引用以及一个整数“标记”,可以原子方式更新。
携带版本号的引用类型原子类,可以解决ABA问题,可以记录修改过几次
public class ABADemo {
static AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(100);
//初始标记1
static AtomicStampedReference atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference(100,1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
abaProblem();
abaResolve();
}
public static void abaResolve() {
//过程:t3打印初始标记 -》 t4打印初始标记 -》 t3 ABA -》 t4 compareAndSet 失败 (代码里边的sleep为了保证代码执行顺序)
new Thread(() -> {
int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println("t3 ----第1次stamp "+stamp);
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(100,101,stamp,stamp+1);
System.out.println("t3 ----第2次stamp "+atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(101,100,atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),atomicStampedReference.getStamp()+1);
System.out.println("t3 ----第3次stamp "+atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
},"t3").start();
new Thread(() -> {
int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println("t4 ----第1次stamp "+stamp);
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
boolean result = atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(100, 222222, stamp, stamp + 1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+result+"\t"+atomicStampedReference.getReference());
},"t4").start();
}
public static void abaProblem() {
//t1线程:A -> B -> A
new Thread(() -> {
atomicInteger.compareAndSet(100,101);
atomicInteger.compareAndSet(101,100);
},"t1").start();
try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
//t2线程:不知道
new Thread(() -> {
atomicInteger.compareAndSet(100,22222222);
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
},"t2").start();
}
}
AtomicMarkableReference : 维护一个对象引用以及一个标记位,可以原子方式更新。
一次性的,只能记录是否修改过,因为它将状态标记简化为了Boolean 的 true/false
public class MarkableReferenceDemo {
static AtomicMarkableReference<Integer> markableReference = new AtomicMarkableReference<>(100,false);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//AtomicMarkableReference不关心引用变量更改过几次,只关心是否更改过
new Thread(() -> {
boolean marked = markableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 1次版本号"+marked);
try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
markableReference.compareAndSet(100,101,marked,!marked);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 2次版本号"+markableReference.isMarked());
markableReference.compareAndSet(101,100,markableReference.isMarked(),!markableReference.isMarked());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 3次版本号"+markableReference.isMarked());
},"t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
boolean marked = markableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 1次版本号"+marked);
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
markableReference.compareAndSet(100,2020,marked,!marked);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+markableReference.getReference()+"\t"+markableReference.isMarked());
},"t2").start();
}
}
四、对象的属性修改原子类
- 使用目的:以一种线程安全的方式操作非线程安全对象内的某些字段。
- 使用要求:1、更新的对象属性必须使用 public volatile 修饰符。 2、因为对象的属性修改类型原子类都是抽象类,所以每次使用都必须使用静态方法newUpdater()创建一个更新器,并且需要设置想要更新的类和属性。
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater 原子更新对象中int类型字段的值
AtomicLongFieldUpdater 原子更新对象中Long类型字段的值
class BankAccount {
String bankName = "CCB";
//以一种线程安全的方式操作非线程安全对象内的某些字段
//1 更新的对象属性必须使用 public volatile 修饰符。
public volatile int money = 0;
//2 因为对象的属性修改类型原子类都是抽象类,所以每次使用都必须使用静态方法newUpdater()创建一个更新器,并且需要设置想要更新的类和属性。
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater FieldUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(BankAccount.class,"money");
public void transfer(BankAccount bankAccount) {
FieldUpdater.incrementAndGet(bankAccount);
}
}
public class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BankAccount bankAccount = new BankAccount();
for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
bankAccount.transfer(bankAccount);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"---bankAccount: "+bankAccount.money);
}
}
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater 原子更新引用类型字段的值
/**
* 多线程并发调用一个类的初始化方法,如果未被初始化过,将执行初始化工作,要求只能初始化一次
*/
class MyVar {
public volatile Boolean isInit = Boolean.FALSE;
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<MyVar,Boolean> FieldUpdater = AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(MyVar.class,Boolean.class,"isInit");
public void init(MyVar myVar) {
if(FieldUpdater.compareAndSet(myVar,Boolean.FALSE,Boolean.TRUE)) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"---start init");
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"---end init");
}else{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"---抢夺失败,已经有线程在修改中");
}
}
}
public class AtomicReferenceFieldUpdaterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyVar myVar = new MyVar();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
myVar.init(myVar);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
五、原子操作增强类
包括:DoubleAccumulator、DoubleAdder、LongAccumulator、LongAdder
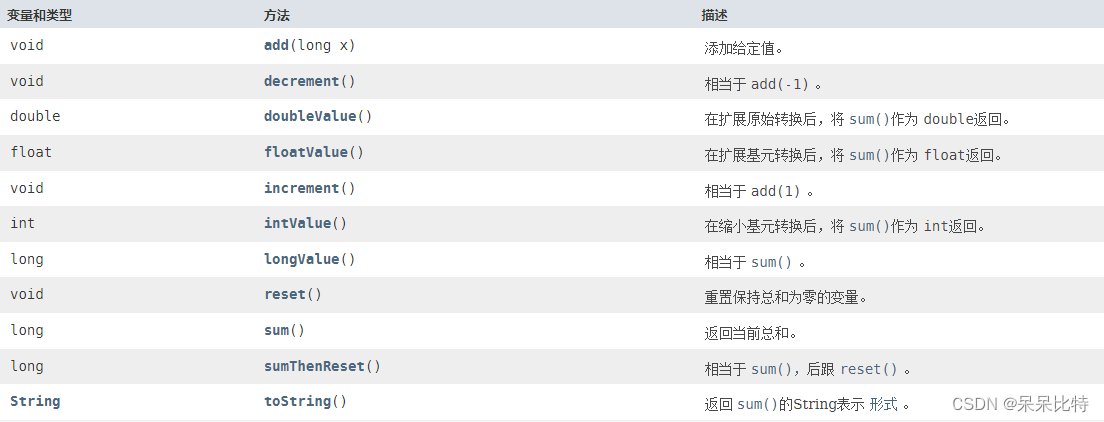
演示(LongAccumulator,LongAdder)
- LongAdder只能用来计算加法,且从零开始计算,LongAccumulator提供了自定义的函数操作
public class LongAdderAPIDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
System.out.println(longAdder.longValue());
//=======================================
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x,y) -> x * y ,2);
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);
longAccumulator.accumulate(2);
longAccumulator.accumulate(3);
System.out.println(longAccumulator.longValue());
}
}
- 性能对比:
class ClickNumberNet {
int number = 0;
public synchronized void clickBySync(){
number++;
}
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0);
public void clickByAtomicLong(){
atomicLong.incrementAndGet();
}
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x,y) -> x + y,0);
public void clickByLongAccumulator(){
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);
}
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
public void clickByLongAdder(){
longAdder.increment();
}
}
public class LongAdderDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ClickNumberNet clickNumberNet = new ClickNumberNet();
long startTime;
long endTime;
CountDownLatch countDownLatch1 = new CountDownLatch(50);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch2 = new CountDownLatch(50);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch3 = new CountDownLatch(50);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch4= new CountDownLatch(50);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= 50 ; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * 10000; j++) {
clickNumberNet.clickBySync();
}
}finally {
countDownLatch1.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch1.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒"+"\t clickBySync result: "+clickNumberNet.number);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <=50; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <=100 * 10000; j++) {
clickNumberNet.clickByAtomicLong();
}
}finally {
countDownLatch2.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch2.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒"+"\t clickByAtomicLong result: "+clickNumberNet.atomicLong);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <=50; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <=100 * 10000; j++) {
clickNumberNet.clickByLongAccumulator();
}
}finally {
countDownLatch3.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch3.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒"+"\t clickByLongAccumulator result: "+clickNumberNet.longAccumulator.longValue());
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <=50; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <=100 * 10000; j++) {
clickNumberNet.clickByLongAdder();
}
}finally {
countDownLatch4.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch4.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒"+"\t clickByLongAdder result: "+clickNumberNet.longAdder.sum());
}
}
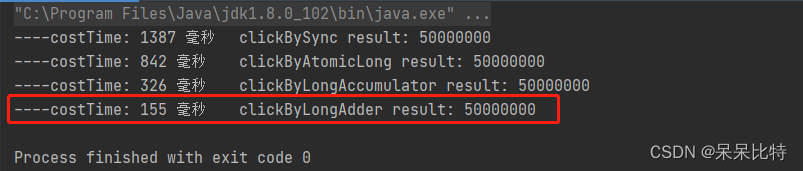
六、原理分析,LongAdder 为什么这么快?
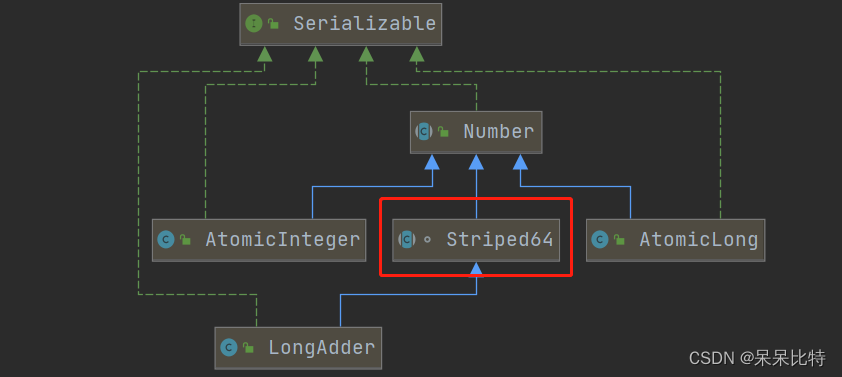
和其他不同的是,LongAdder是Striped64的子类,Striped64有两个重要的属性:
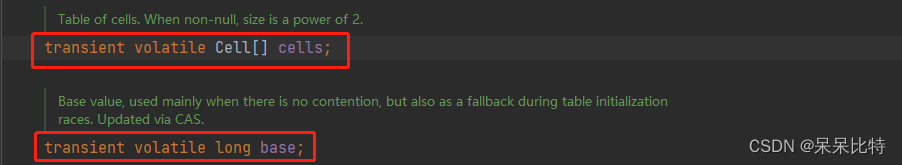
LongAdder的基本思路就是分散热点,将value值分散到一个Cell数组中,不同线程会命中到数组的不同槽中,各个线程只对自己槽中的那个值进行CAS操作,这样热点就被分散了,冲突的概率就小很多。如果要获取真正的long值,只要将各个槽中的变量值累加返回。
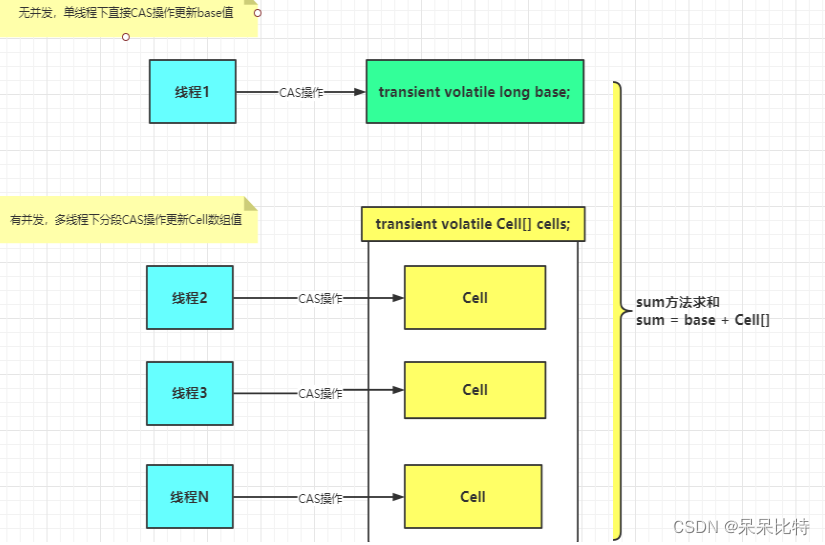
LongAdder在无竞争的情况,跟AtomicLong一样,对同一个base进行操作,当出现竞争关系时则是采用化整为零的做法,从空间换时间,用一个数组cells,将一个value拆分进这个数组cells。多个线程需要同时对value进行操作时候,可以对线程id进行hash得到hash值,再根据hash值映射到这个数组cells的某个下标,再对该下标所对应的值进行自增操作。当所有线程操作完毕,将数组cells的所有值和无竞争值base都加起来作为最终结果。
使用总结
- AtomicLong:线程安全,可允许一些性能损耗,要求高精度时可使用,AtomicLong是多个线程针对单个热点值value进行原子操作。
- LongAdder:当需要在高并发下有较好的性能表现,且对值的精确度要求不高时可以使用,LongAdder是每个线程拥有自己的槽,各个线程一般只对自己槽中的那个值进行CAS操作。







![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django自行车租赁管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5cd83157cf1843349bce625ef336448a.png)