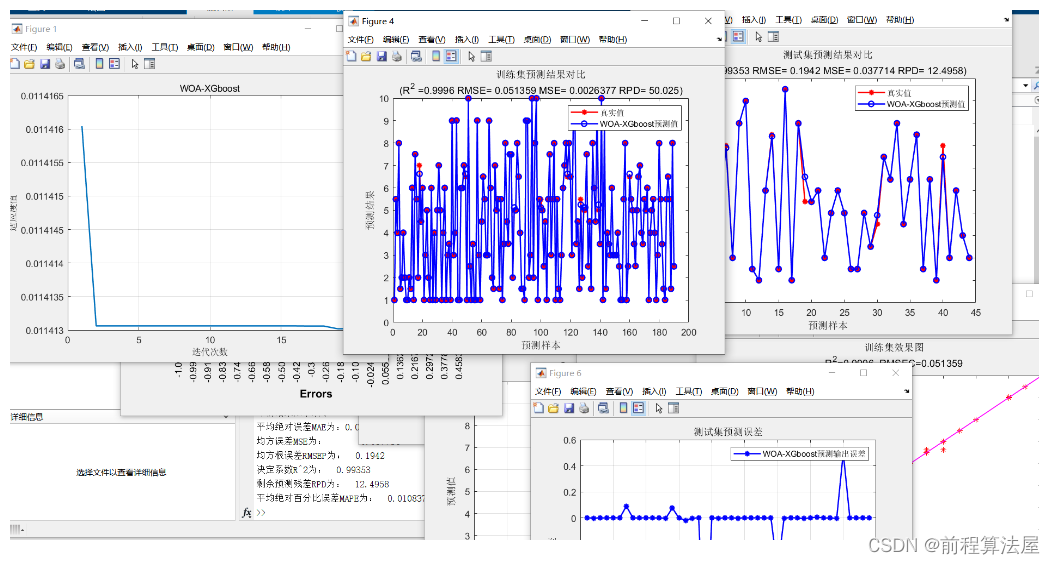
spring之ApplicationContext
- ApplicationContext
- ApplicationContext源码
- ApplicationContext继承接口分析
- ApplicationContext两个比较重要的实现类
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
- 国际化---MessageSource
- 资源加载---ResourceLoader
- 获取运行时环境---Environment
- 事件发布---ApplicationEventPublisher
ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext是个接口,实际上也是一个BeanFactory,不过比BeanFactory更加强大。
ApplicationContext源码
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
/**
* Return the unique id of this application context.
* @return the unique id of the context, or {@code null} if none
*/
@Nullable
String getId();
/**
* Return a name for the deployed application that this context belongs to.
* @return a name for the deployed application, or the empty String by default
*/
String getApplicationName();
/**
* Return a friendly name for this context.
* @return a display name for this context (never {@code null})
*/
String getDisplayName();
/**
* Return the timestamp when this context was first loaded.
* @return the timestamp (ms) when this context was first loaded
*/
long getStartupDate();
/**
* Return the parent context, or {@code null} if there is no parent
* and this is the root of the context hierarchy.
* @return the parent context, or {@code null} if there is no parent
*/
@Nullable
ApplicationContext getParent();
/**
* Expose AutowireCapableBeanFactory functionality for this context.
* <p>This is not typically used by application code, except for the purpose of
* initializing bean instances that live outside of the application context,
* applying the Spring bean lifecycle (fully or partly) to them.
* <p>Alternatively, the internal BeanFactory exposed by the
* {@link ConfigurableApplicationContext} interface offers access to the
* {@link AutowireCapableBeanFactory} interface too. The present method mainly
* serves as a convenient, specific facility on the ApplicationContext interface.
* <p><b>NOTE: As of 4.2, this method will consistently throw IllegalStateException
* after the application context has been closed.</b> In current Spring Framework
* versions, only refreshable application contexts behave that way; as of 4.2,
* all application context implementations will be required to comply.
* @return the AutowireCapableBeanFactory for this context
* @throws IllegalStateException if the context does not support the
* {@link AutowireCapableBeanFactory} interface, or does not hold an
* autowire-capable bean factory yet (e.g. if {@code refresh()} has
* never been called), or if the context has been closed already
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#getBeanFactory()
*/
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
ApplicationContext继承接口分析
-
HierarchicalBeanFactory:拥有获取父BeanFactory的功能
-
ListableBeanFactory:拥有获取beanNames的功能
-
ResourcePatternResolver:资源加载器,可以一次性获取多个资源(文件资源等等)
-
EnvironmentCapable:可以获取运行时环境(没有设置运行时环境功能)
-
ApplicationEventPublisher:拥有广播事件的功能(没有添加事件监听器的功能)
-
MessageSource:拥有国际化功能
ApplicationContext两个比较重要的实现类
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
类继承实现结构:
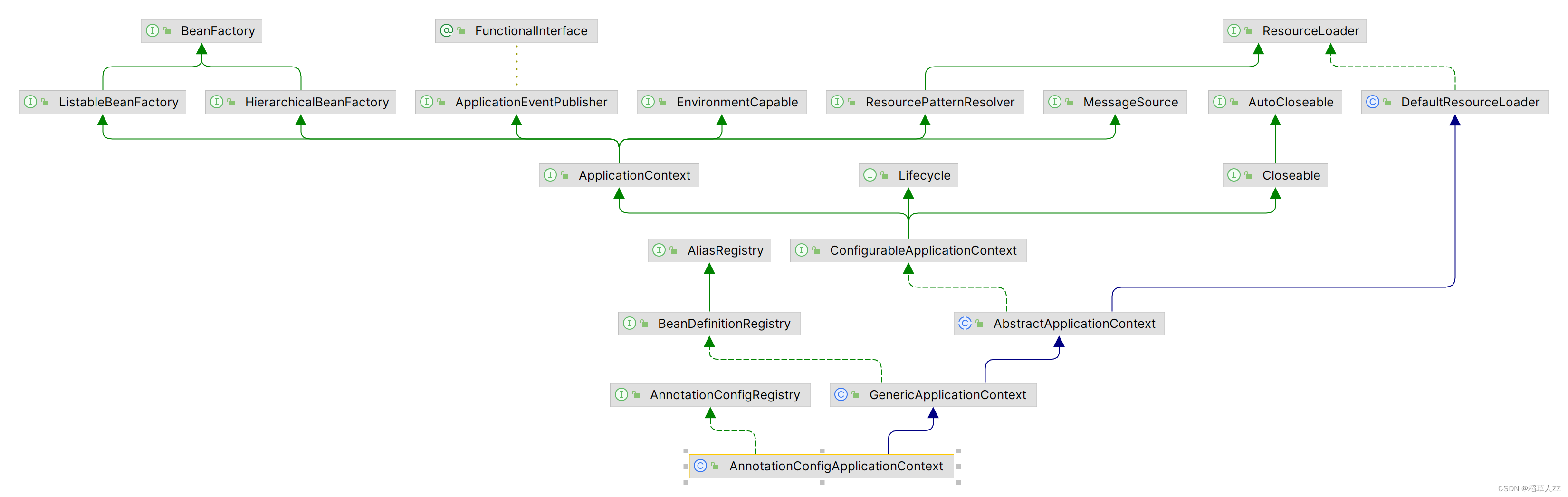
类图说明:
-
ConfigurableApplicationContext:继承了ApplicationContext接口,增加了,添加事件监听器、添加BeanFactoryPostProcessor、设置Environment,获取ConfigurableListableBeanFactory等功能
-
AbstractApplicationContext:实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext接口
-
GenericApplicationContext:继承了AbstractApplicationContext,实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,拥有了所有ApplicationContext的功能,并且可以注册BeanDefinition,注意这个类中有一个属性(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
-
AnnotationConfigRegistry:可以单独注册某个为类为BeanDefinition(可以处理该类上的**@Configuration注解**,已经可以处理**@Bean注解**),同时可以扫描
-
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:继承了GenericApplicationContext,实现了AnnotationConfigRegistry接口,拥有了以上所有的功能
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
类继承实现结构:

它也是继承了AbstractApplicationContext,但是相对于AnnotationConfigApplicationContext而言,功能没有AnnotationConfigApplicationContext强大,比如不能注册BeanDefinition
国际化—MessageSource
messages.properties:
test=你好
demo=测试指定字符串{0}
messages_en.properties:
test=hello
demo=test str{0}
AppConfig:
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
messageSource.setBasename("messages");
return messageSource;
}
Main:
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
//context.refresh();
System.out.println(context.getMessage("test", null, Locale.getDefault()));
System.out.println(context.getMessage("test", null, Locale.CHINA));
System.out.println(context.getMessage("test", null, Locale.US));
System.out.println(context.getMessage("demo", new String[]{"1"}, Locale.getDefault()));
System.out.println(context.getMessage("demo", new String[]{"1"}, Locale.US));
}
资源加载—ResourceLoader
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Resource resource = context.getResource("file://D:\\javaProject\\tuling-code\\spring\\src\\main\\java\\top\\mingempty\\spring\\config\\AppConfig.java");
System.out.println(resource.getFilename());
System.out.println(resource.contentLength());
Resource resource1 = context.getResource("https://www.baidu.com");
System.out.println(resource1.contentLength());
System.out.println(resource1.getURL());
Resource resource2 = context.getResource("classpath:spring.xml");
System.out.println(resource2.contentLength());
System.out.println(resource2.getURL());
//获取多个
Resource[] resources = context.getResources("classpath:top/mingempty/spring/*");
for (Resource resource3 : resources) {
System.out.println(resource3.contentLength());
System.out.println(resource3.getFilename());
}
}
获取运行时环境—Environment
AppConfig :
@PropertySource("classpath:spring.properties")
public class AppConfig {
}
spring.properties:
environment=Environment
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// 操作系统层面的环境变量
Map<String, Object> systemEnvironment = context.getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment();
System.out.println(systemEnvironment);
System.out.println("=======");
// java运行层面,通过-D指定的
Map<String, Object> systemProperties = context.getEnvironment().getSystemProperties();
System.out.println(systemProperties);
System.out.println("=======");
// 前面两者之和
MutablePropertySources propertySources = context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources();
System.out.println(propertySources);
System.out.println("=======");
// 系统中存在的环境变量
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("MVN_HOME"));
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("sun.jnu.encoding"));
// 获取一个不存在的
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("NULL"));
// 获取配置文件内的
// @PropertySource("classpath:spring.properties")
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("environment"));
}
事件发布—ApplicationEventPublisher
AppConfig:注册一个监听事件
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public ApplicationListener applicationListener() {
return event -> {
if (event instanceof PayloadApplicationEvent) {
PayloadApplicationEvent payloadApplicationEvent = (PayloadApplicationEvent) event;
System.out.println("接收到了一个事件:" + payloadApplicationEvent.getPayload());
}
};
}
}
Main:发布消息
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
context.publishEvent("abc");
}