文章目录
- 一、栈
- 1.1 什么是栈
- 1.2 栈的模拟实现
- 二、Java中的Stack
- 2.1 构造方法
- 2.2 操作方法
- 2.3 应用场景
- 三、队列
- 3.1 什么是队列
- 3.2 队列的模拟实现
- 四、Java中的Queue
- 4.1 实例化方法
- 4.2 操作方法
- 4.3 应用场景
一、栈
1.1 什么是栈
栈(Stack)是一种常见的数据结构,它遵循"后进先出"(Last-In-First-Out,LIFO)的原则。在栈中,最后添加的元素首先被访问或删除,而最先添加的元素则最后被访问或删除。
栈具有以下特点:
- 插入操作称为"入栈"(push):将元素添加到栈的顶部。
- 删除操作称为"出栈"(pop):从栈的顶部移除元素。
- 只能访问栈顶的元素:栈是一种限制性访问的数据结构,只允许访问或操作栈顶的元素。
- 栈的大小是动态的:栈的大小可以根据需要自动增长或缩小。
1.2 栈的模拟实现
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyStack {
private int[] elem;
private int usedSize;
public static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;
public MyStack(){
elem = new int[DEFAULT_SIZE];
}
public void push(int val){
// 如果栈满了就扩容
if(isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2 * Arrays.stream(this.elem).sum());
}
this.elem[usedSize] = val;
usedSize++;
}
private boolean isFull(){
return usedSize == elem.length;
}
private boolean isEmpty(){
return usedSize == 0;
}
public int pop(){
if(usedSize == 0){
throw new MyEmptyException("栈已经空!");
}
return elem[--usedSize];
}
public int size(){
return usedSize;
}
public int peek(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new MyEmptyException("栈已经空!");
}
return elem[usedSize - 1];
}
}
二、Java中的Stack
在Java中,Stack类是一个继承自Vector类的类,它实现了一个后进先出(LIFO)的堆栈数据结构。Stack类提供了一些方法来实现栈的常见操作,例如压栈(push)、弹栈(pop)、查看栈顶元素(peek)等。
Stack的继承体系如图:

2.1 构造方法
在Java中,Stack类提供了以下几个构造方法:
- Stack():创建一个空的Stack对象。
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
- Stack(Collection<? extends E> c):创建一个包含指定集合中的元素的Stack对象。集合中的元素将按照迭代器返回的顺序添加到Stack中。
List<String> collection = new ArrayList<>();
collection.add("Element 1");
collection.add("Element 2");
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>(collection);
另外,需要注意的是,Stack类在Java 1.0中引入,但自Java 1.6起,官方推荐使用更加通用的Deque接口(如ArrayDeque或LinkedList)来代替Stack类,因为Deque提供了更丰富的操作方法,并且更加高效。
2.2 操作方法
Stack类提供了一些常见的操作方法,可以用于实现栈的功能。以下是一些常用的Stack操作方法:
- push(E item):将元素item压入栈顶。
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push("Element 1");
stack.push("Element 2");
- pop():弹出并返回栈顶的元素。
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push("Element 1");
stack.push("Element 2");
String topElement = stack.pop(); // 返回"Element 2",栈顶的元素被弹出
- peek():返回栈顶的元素,但不对栈进行修改。
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push("Element 1");
stack.push("Element 2");
String topElement = stack.peek(); // 返回"Element 2",栈顶的元素不会被弹出
- empty():检查栈是否为空。
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
boolean isEmpty = stack.empty(); // 返回true,栈为空
- search(Object o):查找元素o在栈中的位置,返回距离栈顶的距离(栈顶元素的位置为1,依次递增)。
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push("Element 1");
stack.push("Element 2");
int position = stack.search("Element 1"); // 返回2,"Element 1"距离栈顶的位置为2
除了上述方法外,Stack类还继承了Vector类的其他方法,例如size()、isEmpty()、clear()等。
另外,由于Stack类是线程安全的,使用同步方法来实现的,而在Java的并发编程中,建议使用更高效的并发类(如ConcurrentLinkedDeque)代替Stack类。
2.3 应用场景
- 括号匹配问题
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {
if(ch == '('){
stack.push(')');
} else if (ch == '{') {
stack.push('}');
} else if (ch == '[') {
stack.push(']');
} else if(stack.isEmpty() || ch != stack.pop()) {
return false;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
- 逆波兰表达式求值
class Solution {
// tokens = ["2","1","+","3","*"] 9
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (String str : tokens) {
switch (str) {
case "+" -> {
int right = stack.pop();
int left = stack.pop();
stack.push(left + right);
}
case "-" -> {
int right = stack.pop();
int left = stack.pop();
stack.push(left - right);
}
case "*" -> {
int right = stack.pop();
int left = stack.pop();
stack.push(left * right);
}
case "/" -> {
int right = stack.pop();
int left = stack.pop();
stack.push(left / right);
}
default -> {
Integer integer = Integer.valueOf(str);
stack.push(integer);
}
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
}
三、队列
3.1 什么是队列
队列(Queue)是一种常见的数据结构,它遵循"先进先出"(First-In-First-Out,FIFO)的原则。在队列中,最先添加的元素首先被访问或删除,而最后添加的元素则最后被访问或删除。
队列具有以下特点:
- 插入操作称为"入队"(enqueue):将元素添加到队列的末尾。
- 删除操作称为"出队"(dequeue):从队列的头部移除元素。
- 只能访问队列头部和尾部的元素:队列是一种限制性访问的数据结构,只允许访问或操作队列的头部和尾部元素。
- 队列的大小是动态的:队列的大小可以根据需要自动增长或缩小。
3.2 队列的模拟实现
public class MyQueue {
static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
private ListNode head; // 队头出
private ListNode tail; // 队尾入
public void offer(int val) {
if (head == null){
head = new ListNode(val);
tail = head;
} else {
ListNode node = new ListNode(val);
tail.next = node;
tail = node;
}
}
public int poll() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new MyEmptyException("队列为空!");
}
int tmp = head.val;
head = head.next;
if (head == null)
tail = null;
return tmp;
}
public int peek() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new MyEmptyException("队列为空!");
}
return head.val;
}
public int size() {
if(isEmpty()){
return 0;
}
int cnt = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
cnt++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cnt;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
public void display(){
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
四、Java中的Queue
在Java中,Queue是一个接口,它表示一种先进先出(FIFO)的队列数据结构。它是Java集合框架的一部分,定义了一些方法来操作队列。Queue接口的常见实现类包括LinkedList和ArrayDeque。其继承体系如下:
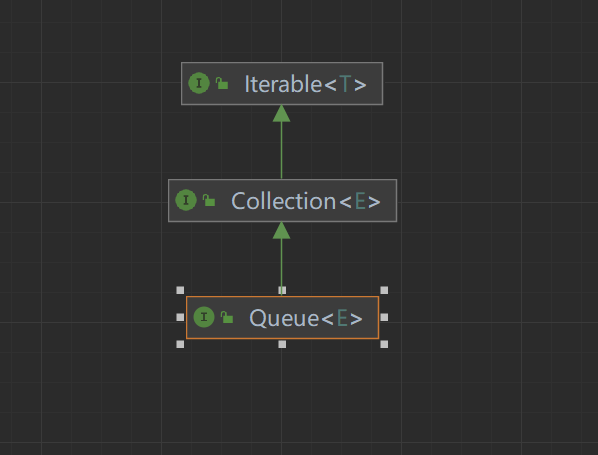
4.1 实例化方法
Queue接口本身是一个接口,不能直接实例化。在Java中,我们可以使用具体的实现类来创建Queue对象,常用的实现类有LinkedList和ArrayDeque。
- LinkedList实现的Queue:
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
- ArrayDeque实现的Queue:
Queue<String> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
这些构造方法创建了一个空的Queue对象,可以根据需要将元素添加到队列中。
4.2 操作方法
Queue接口提供了一系列方法来操作队列。以下是Queue接口的一些常见操作方法:
- add(E e):将元素e插入队列的尾部,如果成功则返回true,如果队列已满则抛出异常。
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean result = queue.add("Element 1");
- offer(E e):将元素e插入队列的尾部,如果成功则返回true,如果队列已满则返回false。
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean result = queue.offer("Element 1");
- remove():移除并返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空则抛出异常。
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
String element = queue.remove();
- poll():移除并返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空则返回null。
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
String element = queue.poll();
- element():返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空则抛出异常。
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
String element = queue.element();
- peek():返回队列头部的元素,如果队列为空则返回null。
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
String element = queue.peek();
此外,Queue接口还继承了Collection接口和Iterable接口中的方法,例如size()、isEmpty()、clear()、iterator()等。
4.3 应用场景
- 队列实现栈
// 两个队列
// 入栈:入到不为空的队列
// 出栈:找到不为空的队列,出size - 1个元素到空队列,返回最后一个元素
// 使用队列实现栈
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue1;
private Queue<Integer> queue2;
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
// 两个队列都为空的时候
if(empty()){
queue1.offer(x);
return;
}
if(queue1.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(x);
} else {
queue1.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(queue1.isEmpty()){
int size = queue2.size();
while (size - 1 != 0){
queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
size--;
}
return queue2.poll();
} else {
int size = queue1.size();
while (size - 1 != 0){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
size--;
}
return queue1.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
int tmp = pop();
push(tmp);
return tmp;
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
}
}
- 栈实现队列
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> inStack; // 入栈
private Stack<Integer> outStack; // 出栈
public MyQueue() {
inStack = new Stack<>();
outStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
inStack.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (empty()){
return -1;
}
if (outStack.isEmpty()) {
while (!inStack.empty()) {
outStack.push(inStack.pop());
}
}
return outStack.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(outStack.empty()){
while (!inStack.empty()){
outStack.push(inStack.pop());
}
}
return outStack.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return inStack.isEmpty() && outStack.isEmpty();
}
}