C:\ProgramData\NVIDIA Corporation\CUDA Samples\v11.0\0_Simple\asyncAPI
这个例子说明了CUDA事件在GPU计时和CPU与GPU重叠执行方面的应用。 事件被插入到CUDA的调用流中。
由于CUDA流调用是异步的,CPU可以在GPU执行时进行计算(包括主机和设备之间的DMA记忆复制)。
CPU可以查询CUDA事件以确定 GPU是否已经完成任务。
// includes, system
#include <stdio.h>
// includes CUDA Runtime
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
// includes, project
#include <helper_cuda.h>
#include <helper_functions.h> // helper utility functions
__global__ void increment_kernel(int *g_data, int inc_value)
{
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
g_data[idx] = g_data[idx] + inc_value;
}
bool correct_output(int *data, const int n, const int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (data[i] != x)
{
printf("Error! data[%d] = %d, ref = %d\n", i, data[i], x);
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int devID;
cudaDeviceProp deviceProps;
printf("[%s] - Starting...\n", argv[0]);
// 这将挑选出尽可能好的具有CUDA能力的设备
devID = findCudaDevice(argc, (const char **)argv);
// get device name
checkCudaErrors(cudaGetDeviceProperties(&deviceProps, devID));
printf("CUDA device [%s]\n", deviceProps.name);
int n = 16 * 1024 * 1024;
int nbytes = n * sizeof(int);
int value = 26;
// allocate host memory
int *a = 0;
checkCudaErrors(cudaMallocHost((void **)&a, nbytes));
memset(a, 0, nbytes);
// allocate device memory
int *d_a=0;
checkCudaErrors(cudaMalloc((void **)&d_a, nbytes));
checkCudaErrors(cudaMemset(d_a, 255, nbytes));
// set kernel launch configuration
dim3 threads = dim3(512, 1);
dim3 blocks = dim3(n / threads.x, 1);
// create cuda event handles
cudaEvent_t start, stop;
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventCreate(&start));
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventCreate(&stop));
StopWatchInterface *timer = NULL;
sdkCreateTimer(&timer);
sdkResetTimer(&timer);
checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceSynchronize());
float gpu_time = 0.0f;
// 异步发布工作到GPU(全部为流0)。
sdkStartTimer(&timer);
cudaEventRecord(start, 0);
cudaMemcpyAsync(d_a, a, nbytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, 0);
increment_kernel<<<blocks, threads, 0, 0>>>(d_a, value);
cudaMemcpyAsync(a, d_a, nbytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, 0);
cudaEventRecord(stop, 0);
sdkStopTimer(&timer);
// 在等待第1阶段完成的过程中,CPU要做一些工作
unsigned long int counter=0;
while (cudaEventQuery(stop) == cudaErrorNotReady)
{
counter++;
}
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventElapsedTime(&gpu_time, start, stop));
// print the cpu and gpu times
printf("time spent executing by the GPU: %.2f\n", gpu_time);
printf("time spent by CPU in CUDA calls: %.2f\n", sdkGetTimerValue(&timer));
printf("CPU executed %lu iterations while waiting for GPU to finish\n", counter);
// 检查输出是否正确
bool bFinalResults = correct_output(a, n, value);
// release resources
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventDestroy(start));
checkCudaErrors(cudaEventDestroy(stop));
checkCudaErrors(cudaFreeHost(a));
checkCudaErrors(cudaFree(d_a));
exit(bFinalResults ? EXIT_SUCCESS : EXIT_FAILURE);
给出的代码是一个用于检查数组中元素是否全部为指定值的函数。该函数会遍历数组,如果发现有任何一个元素不等于给定的值,则输出错误信息并返回 false;如果数组中的所有元素都等于给定的值,则返回 true。
该函数的工作流程如下:
- 接收一个指向整型数组的指针 data,数组长度 n,以及要比较的值 x。
- 使用循环遍历数组元素。
- 如果找到任何一个元素不等于 x,则输出错误信息,包括错误元素的索引、其实际值和参考值,并返回 false 表示输出不正确。
- 如果遍历完数组中的所有元素,都没有发现不等于 x 的元素,则返回 true,表示输出正确。
- 该函数可以用于验证特定数据集的输出是否与预期结果一致。如果返回 true,则表示数据输出正确;如果返回 false,则表示存在输出错误。*/
sdkStartTimer(&timer);
cudaEventRecord(start, 0);
cudaMemcpyAsync(d_a, a, nbytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, 0);
increment_kernel<<<blocks, threads, 0, 0>>>(d_a, value);
cudaMemcpyAsync(a, d_a, nbytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, 0);
cudaEventRecord(stop, 0);
sdkStopTimer(&timer);
给出的代码片段涉及了CUDA的异步内存传输和核函数调用。以下是对代码的解释:
sdkStartTimer(&timer);:启动计时器,用于测量代码片段的执行时间。
cudaEventRecord(start, 0);:记录起始时间点,以便后续计算执行时间。
cudaMemcpyAsync(d_a, a, nbytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, 0);:将主机内存中的数据异步复制到设备内存中。该函数使用指定的流(stream)来进行异步传输,这里的流指定为 0。
increment_kernel<<<blocks, threads, 0, 0>>>(d_a, value);:启动并行的CUDA核函数。该核函数称为 increment_kernel,使用指定的线程块(blocks)和线程(threads)配置启动。此外,也使用指定的流进行并行执行,这里的流同样指定为 0。
cudaMemcpyAsync(a, d_a, nbytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, 0);:将设备内存中的数据异步复制回主机内存。同样,该函数使用指定的流进行异步传输。
cudaEventRecord(stop, 0);:记录结束时间点,用于计算执行时间。
sdkStopTimer(&timer);:停止计时器。
该代码片段展示了一种典型的异步数据传输和核函数调用的模式,旨在提高CUDA程序的性能。通过异步传输和执行,可以在数据传输和计算之间进行重叠,从而减少整体执行时间。使用合适的流设置可以更好地利用GPU并行性。
需要注意的是,代码中的计时器函数(如 sdkStartTimer 和 sdkStopTimer)可能是特定的SDK或库函数,需要确认代码所使用的具体环境和库。此外,代码中的变量(如 blocks、threads、d_a、a、nbytes、value)需要在代码上下文中定义和初始化。
exit(bFinalResults ? EXIT_SUCCESS : EXIT_FAILURE);
给出的代码片段使用了 exit() 函数来退出程序,并根据条件 bFinalResults 的值决定返回的退出状态码。
具体解释如下:
bFinalResults 是一个布尔类型的变量,可能是根据程序的某些条件或结果来判断的。
EXIT_SUCCESS 和 EXIT_FAILURE 是标准库中定义的常量,表示程序正常结束和异常结束的状态码。EXIT_SUCCESS 通常被定义为 0,表示程序成功完成,而 EXIT_FAILURE 通常被定义为非零值,表示程序异常结束。
exit() 是一个标准库函数,它用于终止程序的执行并返回到操作系统。在这里,根据条件 bFinalResults 的值,如果为真(true),则调用 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS),表示程序成功结束;如果为假(false),则调用 exit(EXIT_FAILURE),表示程序异常结束。
通过使用 exit() 函数,可以在程序的任何地方进行终止,并根据条件决定程序的退出状态码,从而可以在后续的处理中识别程序的执行结果
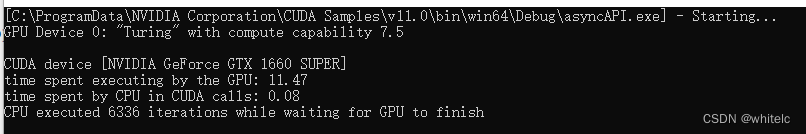
GPU设备0:“图灵”,计算能力7.5
CUDA设备[NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1660 SUPER]
GPU执行时间:11.47
CPU在CUDA调用中花费的时间:0.08
CPU执行6336次迭代,等待GPU完成