目录
- 引出
- 一、为啥用mybatis?
- 二、多表查询之一对多【待续】
- 1.一对多的情况
- 方案一:采用多表联查的方式
- (1)resultMap
- (2)查询的java接口和xml的SQL语句
- (3)对应关系分析
- (4)进阶版本,根据业主id查询房屋的sql不在当前的mapper中
- 方案二:延迟加载 fetchType="lazy"
- 方案三:业务拆解,查两次【建议】
- (1)根据id查询业主
- (2)根据业主id查询房子的list
- (3)在service层【可变长度参数】
- (4)在controller层调用service
- 三、延迟加载
- 为什么会有延迟加载
- association例子
- collection例子
- 四、缓存【待续】
- 总结
引出
1.mybatis可以实现SQL语句和Java代码的解耦;
2.多表查询,一对多情况的延迟加载 fetchType=“lazy”;
3.一对多的查询方式,建议查询两次,从业务和速度的角度;
4.延迟加载的association和 collection;
5.mybatis缓存,一级缓存,二级缓存;
一、为啥用mybatis?
mybatis 是一个优秀的基于 java 的持久层框架,主要应用于关系型数据库(sql),它内部封装了 jdbc,使开发者只需要关注 sql 语句本身,而不需要花费精力去处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建 statement ,封装数据等繁杂的过程。
在之前没有mybatis的时候,SQL语句和Java耦合
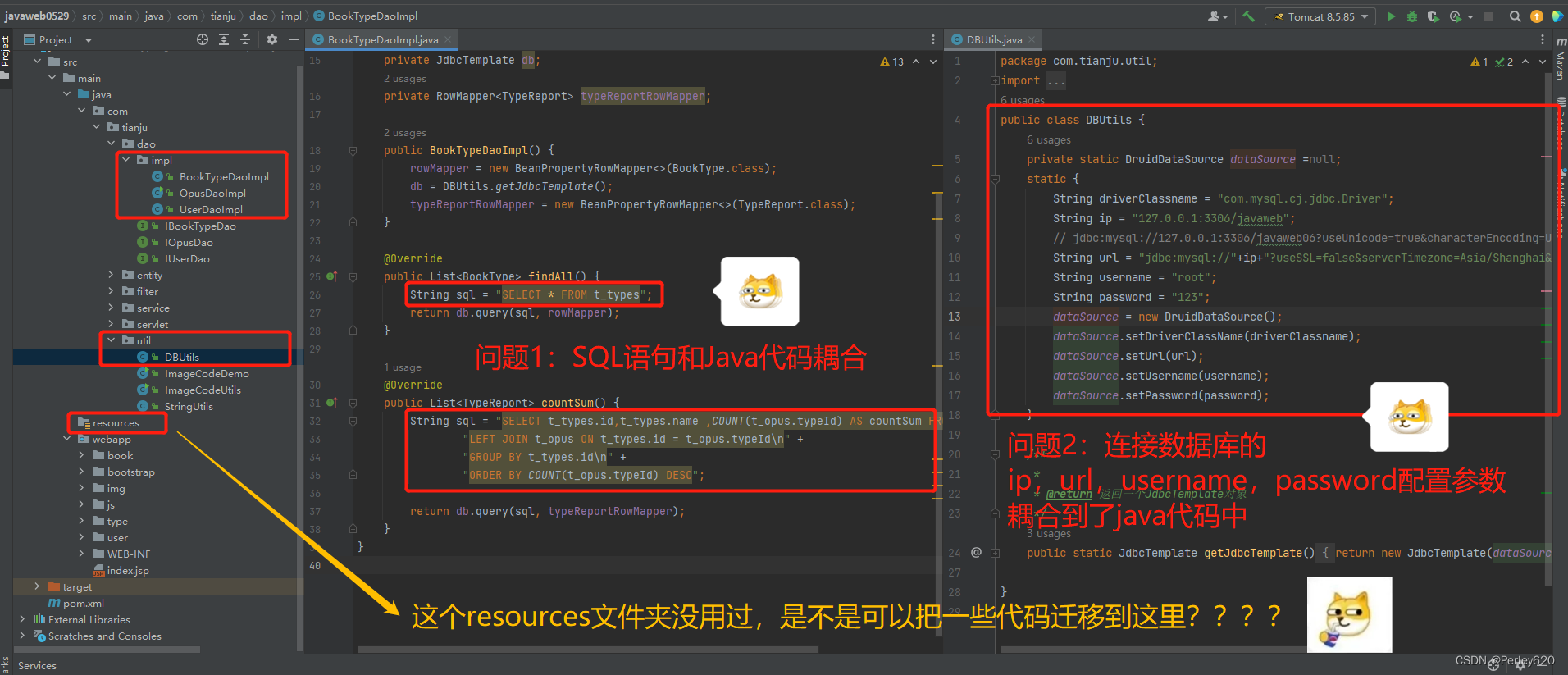
通过mybatis框架,就可以实现SQL和Java代码的解耦;
此外,在mybatis框架下,开发者只需要关注 sql 语句本身,而不需要花费精力去处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建 statement ,封装数据等繁杂的过程。
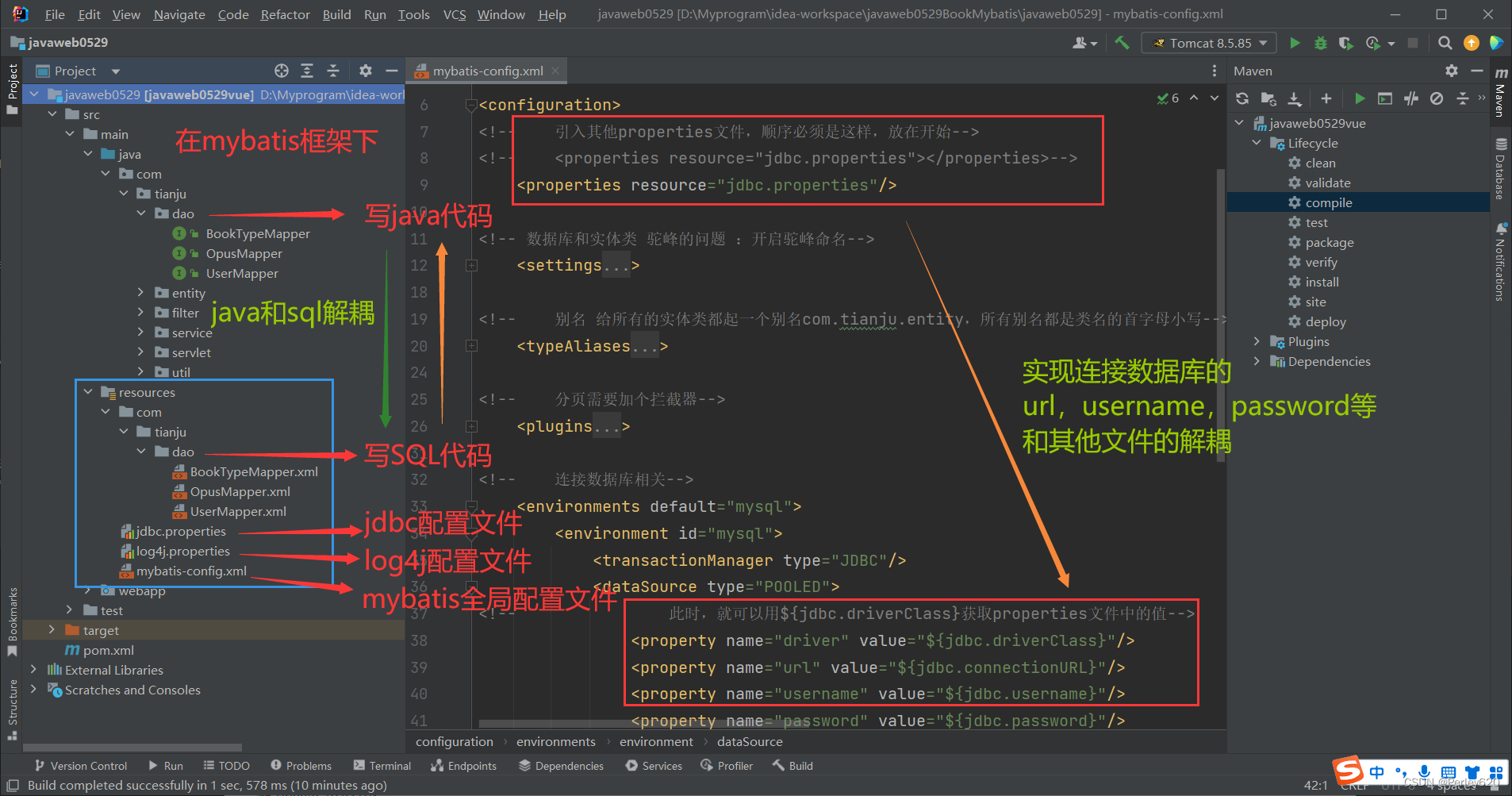
二、多表查询之一对多【待续】
1.一对多的情况
一对多的表查询,比如想要查询一个人名下有多少套房子,也就是查询业主的时候,想要把业主名下的所有房子也查询出来
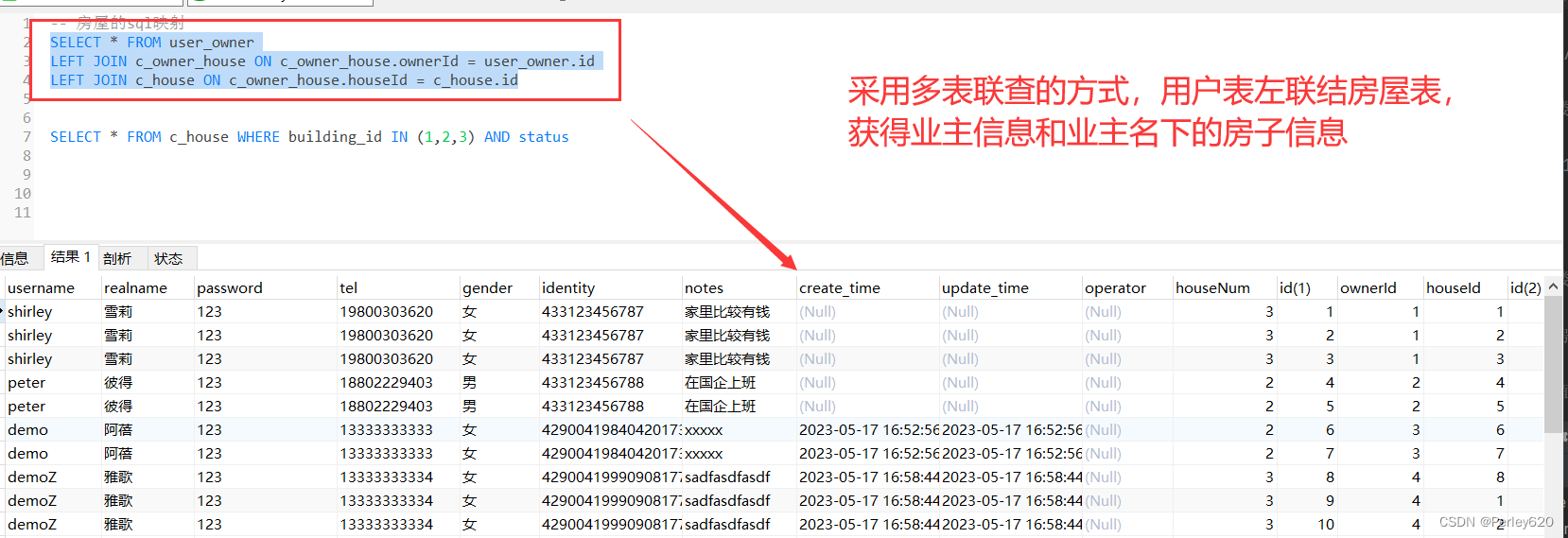
方案一:采用多表联查的方式
SELECT * FROM user_owner
LEFT JOIN c_owner_house ON c_owner_house.ownerId = user_owner.id
LEFT JOIN c_house ON c_owner_house.houseId = c_house.id
在mybatis里面,提供了多对一的查询方式
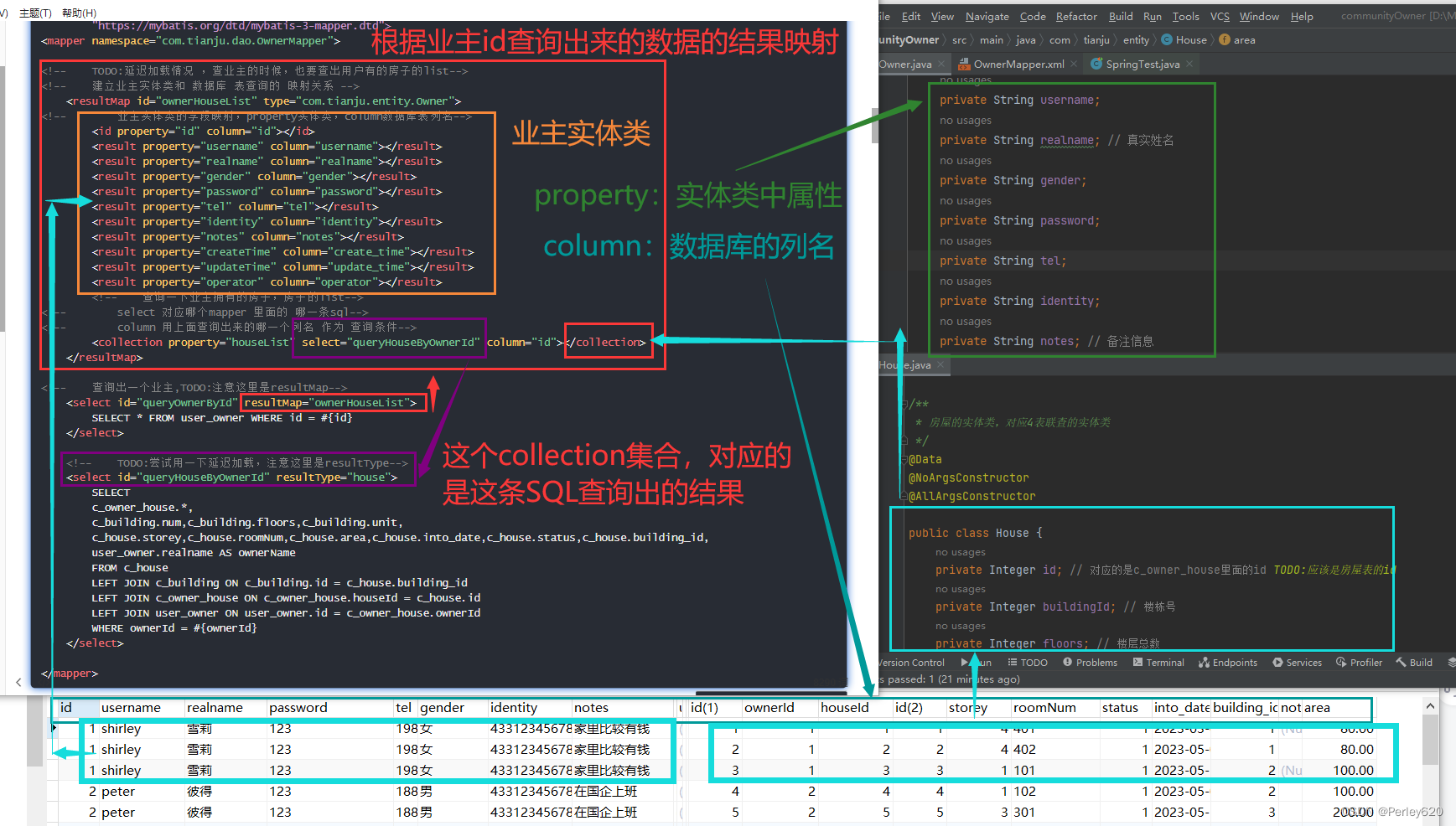
(1)resultMap
- 用resultMap,建立业主实体类 和 数据库 表查询的 映射关系,property表示实体类的属性,column表示对应表的字段;
- 查出来的list用collection定义关系,select 表示对应哪个mapper.xml中的哪条sql语句,column表示用上面查询出来的哪一个列名作为查询条件,property表示对应owner实体类的属性;
- 其中,select 表示对应哪个mapper.xml中的哪条sql语句,在本案例中位于同一个mapper中;
<!-- 建立业主实体类和 数据库 表查询的 映射关系 -->
<resultMap id="ownerHouseList" type="com.tianju.entity.Owner">
<!-- 业主实体类的字段映射,property实体类,column数据库表列名-->
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="realname" column="realname"></result>
<result property="gender" column="gender"></result>
<result property="password" column="password"></result>
<result property="tel" column="tel"></result>
<result property="identity" column="identity"></result>
<result property="notes" column="notes"></result>
<result property="createTime" column="create_time"></result>
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time"></result>
<result property="operator" column="operator"></result>
<!-- 查询一下业主拥有的房子,房子的list-->
<!-- select 对应哪个mapper 里面的 哪一条sql-->
<!-- column 用上面查询出来的哪一个列名 作为 查询条件-->
<collection property="houseList" select="queryHouseByOwnerId" column="id"></collection>
</resultMap>
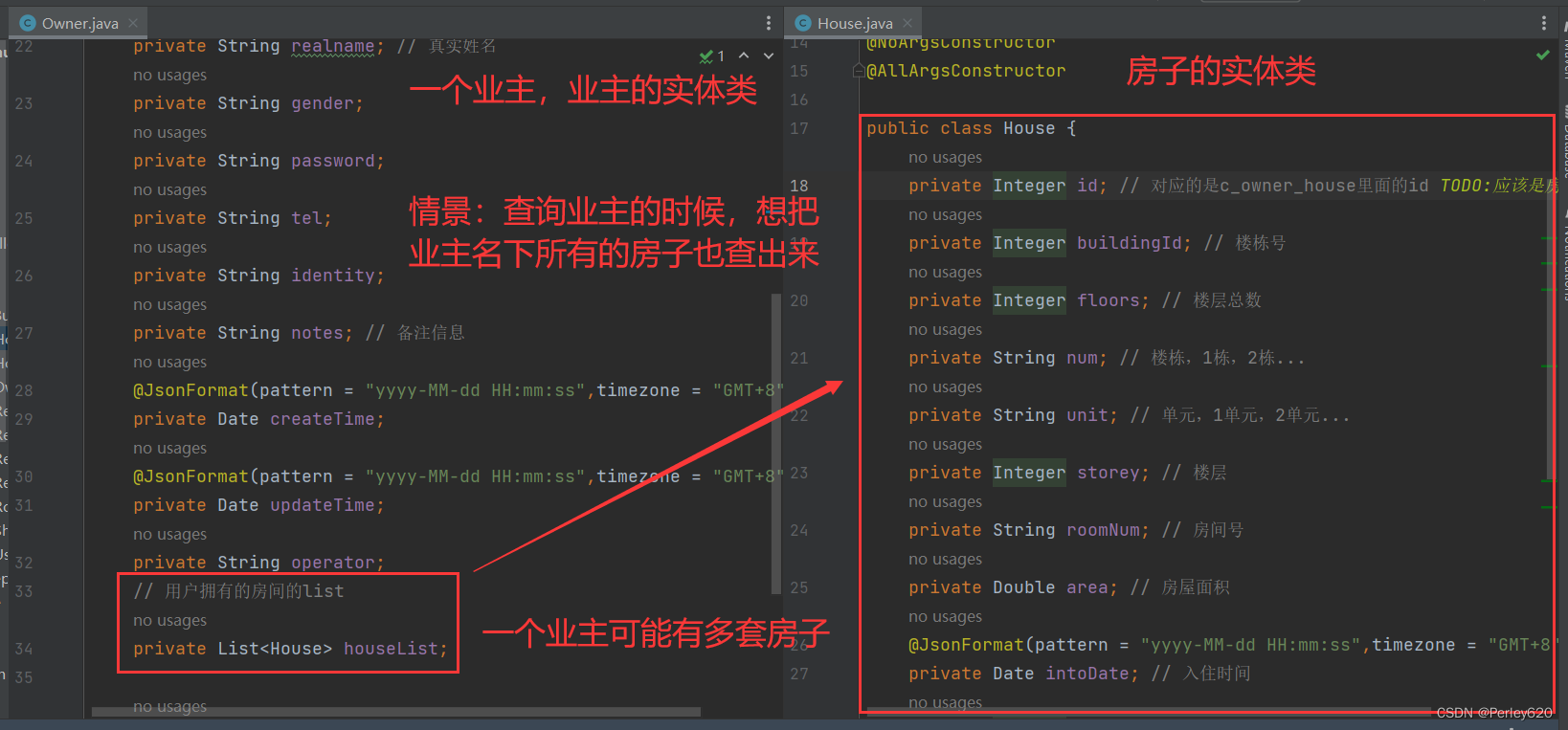
上面的resultmap对应的实体类如下:
package com.tianju.entity;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 业主的实体类
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Owner implements Serializable { // 序列化
//public class Owner { // TODO:序列化,序列化是一级缓存和二级缓冲的事情
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String realname; // 真实姓名
private String gender;
private String password;
private String tel;
private String identity;
private String notes; // 备注信息
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8")
private Date createTime;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8")
private Date updateTime;
private String operator;
// 用户拥有的房间的list
private List<House> houseList;
// 拥有房子的数量
private Integer houseNum;
}
House的实体类如下:
package com.tianju.entity;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 房屋的实体类,对应4表联查的实体类
*/
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class House {
private Integer id; // 对应的是c_owner_house里面的id TODO:应该是房屋表的id
private Integer buildingId; // 楼栋号
private Integer floors; // 楼层总数
private String num; // 楼栋,1栋,2栋...
private String unit; // 单元,1单元,2单元...
private Integer storey; // 楼层
private String roomNum; // 房间号
private Double area; // 房屋面积
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8")
private Date intoDate; // 入住时间
private Integer status;// 入住状态,0未入住,1入住
private Integer ownerId; // 业主的id;
private String ownerName; // 业主的真实姓名;
}
(2)查询的java接口和xml的SQL语句
/**
* TODO:延迟加载
* 查询业主信息,同时获取业主名下所有的房屋信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
Owner queryOwnerById(Integer id);
对应的xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tianju.dao.OwnerMapper">
<!-- TODO:延迟加载情况 ,查业主的时候,也要查出用户有的房子的list-->
<!-- 建立业主实体类和 数据库 表查询的 映射关系 -->
<resultMap id="ownerHouseList" type="com.tianju.entity.Owner">
<!-- 业主实体类的字段映射,property实体类,column数据库表列名-->
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="realname" column="realname"></result>
<result property="gender" column="gender"></result>
<result property="password" column="password"></result>
<result property="tel" column="tel"></result>
<result property="identity" column="identity"></result>
<result property="notes" column="notes"></result>
<result property="createTime" column="create_time"></result>
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time"></result>
<result property="operator" column="operator"></result>
<!-- 查询一下业主拥有的房子,房子的list-->
<!-- select 对应哪个mapper 里面的 哪一条sql-->
<!-- column 用上面查询出来的哪一个列名 作为 查询条件-->
<collection property="houseList" select="queryHouseByOwnerId" column="id"></collection>
</resultMap>
<!-- 查询出一个业主,TODO:注意这里是resultMap-->
<select id="queryOwnerById" resultMap="ownerHouseList">
SELECT * FROM user_owner WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
<!-- TODO:尝试用一下延迟加载,注意这里是resultType-->
<select id="queryHouseByOwnerId" resultType="house">
SELECT
c_owner_house.*,
c_building.num,c_building.floors,c_building.unit,
c_house.storey,c_house.roomNum,c_house.area,c_house.into_date,c_house.status,c_house.building_id,
user_owner.realname AS ownerName
FROM c_house
LEFT JOIN c_building ON c_building.id = c_house.building_id
LEFT JOIN c_owner_house ON c_owner_house.houseId = c_house.id
LEFT JOIN user_owner ON user_owner.id = c_owner_house.ownerId
WHERE ownerId = #{ownerId}
</select>
</mapper>
(3)对应关系分析
一个简化版本的例子,新闻和新闻的评论

(4)进阶版本,根据业主id查询房屋的sql不在当前的mapper中
则原来的collection改成:
<collection property="houseList" select="com.tianju.dao.HouseMapper.queryHouseByOwnerId" column="id"></collection>
在houseMapper.xml文件中
<!-- TODO:尝试用一下延迟加载-->
<!-- TODO:一个卡了一会儿的bug,这里要用resultType,而不是resultMap-->
<select id="queryHouseByOwnerId" parameterType="integer" resultType="house">
SELECT
c_owner_house.*,
c_building.num,c_building.floors,c_building.unit,
c_house.storey,c_house.roomNum,c_house.area,c_house.into_date,c_house.status,c_house.building_id,
user_owner.realname AS ownerName
FROM c_house
LEFT JOIN c_building ON c_building.id = c_house.building_id
LEFT JOIN c_owner_house ON c_owner_house.houseId = c_house.id
LEFT JOIN user_owner ON user_owner.id = c_owner_house.ownerId
WHERE ownerId = #{ownerId}
</select>
方案二:延迟加载 fetchType=“lazy”
在查看业主的基础信息时,其实并不需要知道业主名下的房屋信息,就比如看新闻的时候并不需要把评论也放出来,因此,可以采用需要的时候再查询房屋信息来实现一定程度的减少和数据库频繁交互;
延迟加载其实很简单,只需要加上在xml文件中的resultMap加上fetchType="lazy"即可
<resultMap id="ownerHouseList" type="com.tianju.entity.Owner">
<!-- 业主实体类的字段映射,property实体类,column数据库表列名-->
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="realname" column="realname"></result>
<result property="gender" column="gender"></result>
<result property="password" column="password"></result>
<result property="tel" column="tel"></result>
<result property="identity" column="identity"></result>
<result property="notes" column="notes"></result>
<result property="createTime" column="create_time"></result>
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time"></result>
<result property="operator" column="operator"></result>
<!-- 查询一下业主拥有的房子,房子的list-->
<!-- select 对应哪个mapper 里面的 哪一条sql-->
<!-- column 用上面查询出来的哪一个列名 作为 查询条件-->
<!-- fetchType lazy表示开启延迟加载 -->
<collection property="houseList" select="com.tianju.dao.HouseMapper.queryHouseByOwnerId" column="id" fetchType="lazy"></collection>
</resultMap>
对应的接口java
/**
* TODO:延迟加载
* 查询业主信息,同时获取业主名下所有的房屋信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
Owner queryLazyOwnerById(Integer id);
进行延迟加载的测试,只有用到houseList的时候,mybatis才会去查业主名下的房屋信息
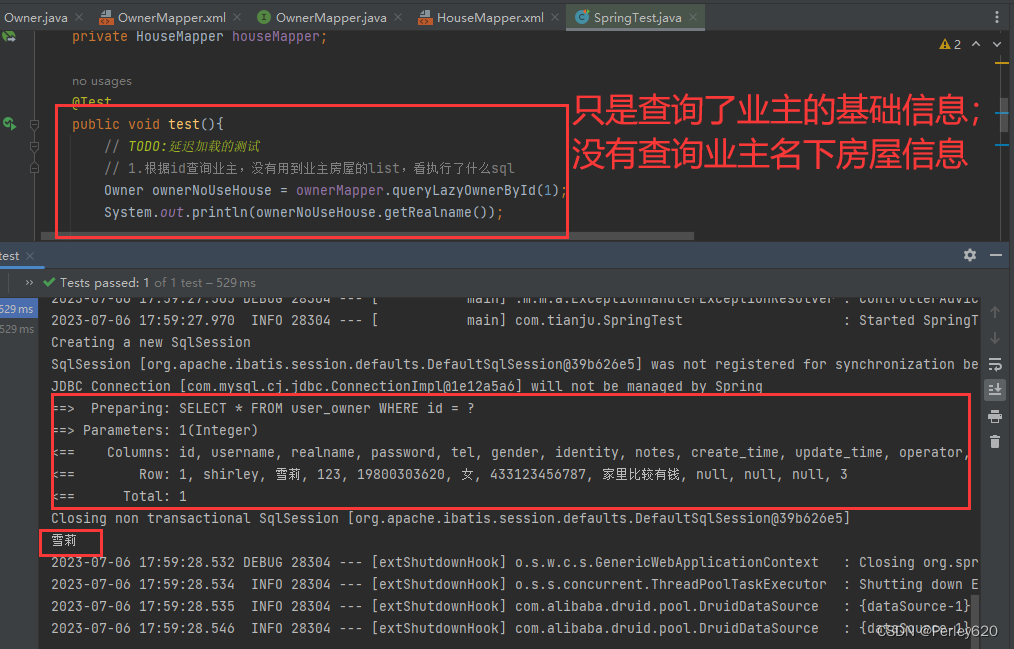
(1)没有用到业主房屋的list
@Test
public void test(){
// TODO:延迟加载的测试
// 1.根据id查询业主,没有用到业主房屋的list,看执行了什么sql
Owner ownerNoUseHouse = ownerMapper.queryLazyOwnerById(1);
System.out.println(ownerNoUseHouse.getRealname());
// 2.如果用到了业主房屋的list,看执行了什么sql
}
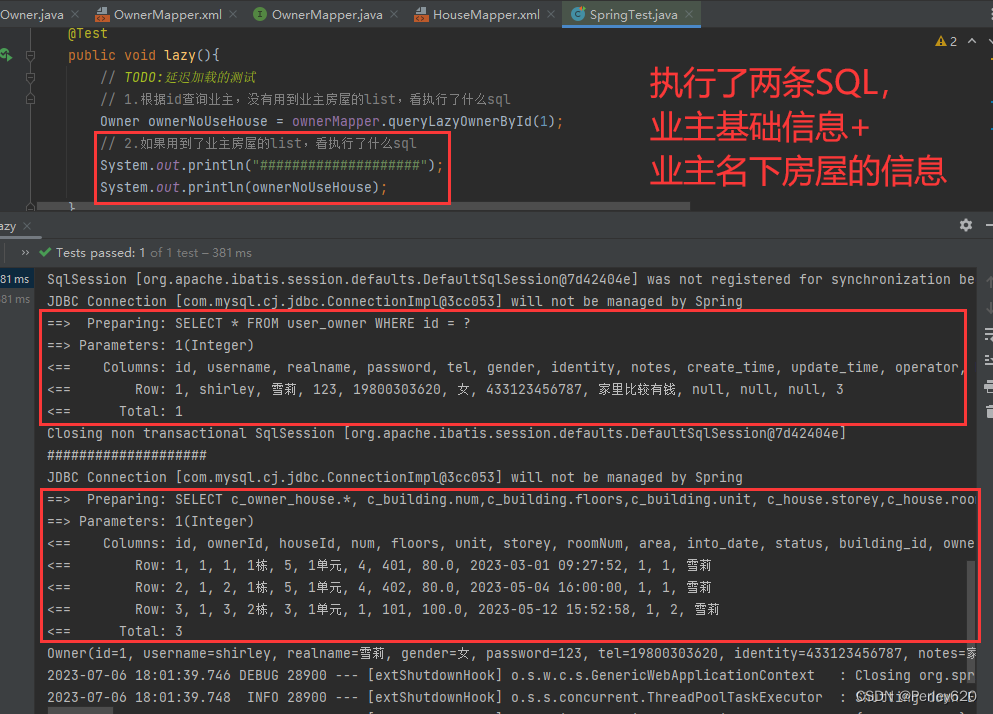
(2)用到业主的房屋信息
@Test
public void lazy(){
// TODO:延迟加载的测试
// 1.根据id查询业主,没有用到业主房屋的list,看执行了什么sql
Owner ownerNoUseHouse = ownerMapper.queryLazyOwnerById(1);
// 2.如果用到了业主房屋的list,看执行了什么sql
System.out.println("####################");
System.out.println(ownerNoUseHouse);
}
完整的SpringBootTest代码
package com.tianju;
import com.tianju.dao.HouseMapper;
import com.tianju.dao.OwnerMapper;
import com.tianju.entity.House;
import com.tianju.entity.Owner;
import org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* spring的测试类 @SpringBootTest
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringTest {
@Autowired
private OwnerMapper ownerMapper;
@Autowired
private HouseMapper houseMapper;
@Test
public void test(){
// TODO:延迟加载的测试
// 1.根据id查询业主,没有用到业主房屋的list,看执行了什么sql
Owner ownerNoUseHouse = ownerMapper.queryLazyOwnerById(1);
System.out.println(ownerNoUseHouse.getRealname());
// 2.如果用到了业主房屋的list,看执行了什么sql
}
@Test
public void lazy(){
// TODO:延迟加载的测试
// 1.根据id查询业主,没有用到业主房屋的list,看执行了什么sql
Owner ownerNoUseHouse = ownerMapper.queryLazyOwnerById(1);
// 2.如果用到了业主房屋的list,看执行了什么sql
System.out.println("####################");
System.out.println(ownerNoUseHouse);
}
}
方案三:业务拆解,查两次【建议】
从业务的角度,以及速度的角度,应该如下操作:
- 1.一般情况下,只需要根据id查询出业主的基础信息,此时只执行一条SQL语句;
- 2.如果需要用到业主名下的房屋信息,就再执行一条SQL,根据id查询业主名下的房屋数据;
第一种情况:只需要业主的基础信息,此时不需要查询房屋信息
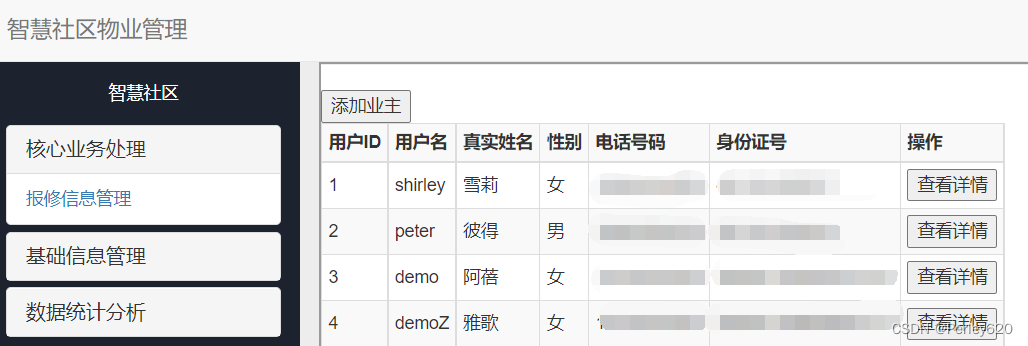
第二种情况,如果点击查看详情,此时既要业主的基础信息,也要查询房屋信息,就执行两条SQL
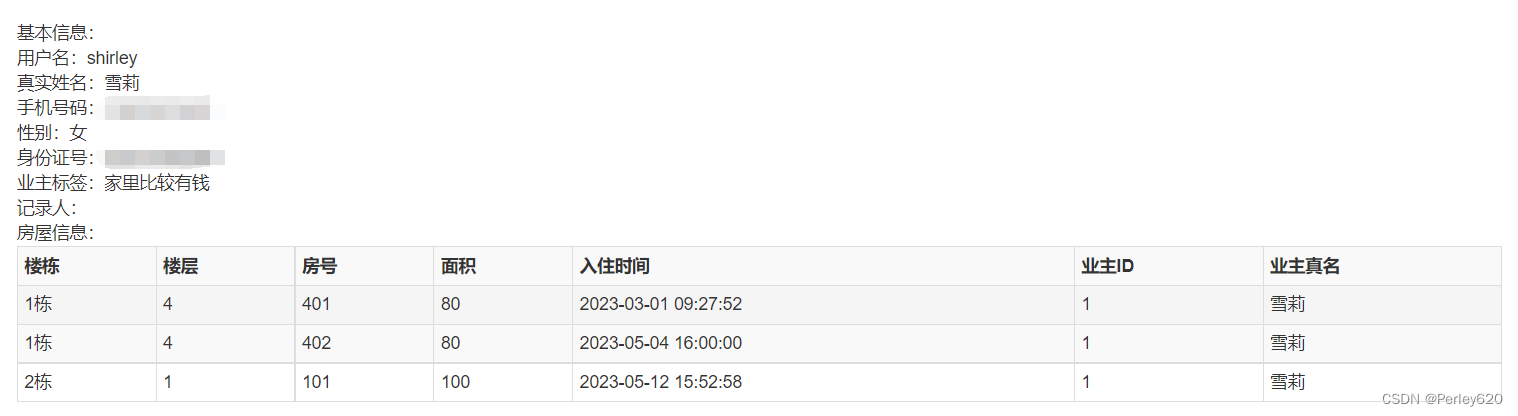
(1)根据id查询业主
/**
* 上面这种延迟加载的方式不建议,应该这样做
* TODO:从业务角度,和速度角度
* 1.一般情况下,只需要根据id查询出业主;
* 2.如果需要用到业主名下的房屋,再根据业主id查方法
*/
Owner queryById(Integer id);
<select id="queryById" resultType="owner">
SELECT * FROM user_owner WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
(2)根据业主id查询房子的list
/**
* 根据业主的id,查询该业主名下有哪些房子
* @param ownerId 业主的id
* @return 名下房子的list
*/
List<House> queryHouseByOwnerId(Integer ownerId);
<select id="queryHouseByOwnerId" parameterType="integer" resultType="house">
SELECT
c_owner_house.*,
c_building.num,c_building.floors,c_building.unit,
c_house.storey,c_house.roomNum,c_house.area,c_house.into_date,c_house.status,c_house.building_id,
user_owner.realname AS ownerName
FROM c_house
LEFT JOIN c_building ON c_building.id = c_house.building_id
LEFT JOIN c_owner_house ON c_owner_house.houseId = c_house.id
LEFT JOIN user_owner ON user_owner.id = c_owner_house.ownerId
WHERE ownerId = #{ownerId}
</select>
(3)在service层【可变长度参数】
package com.tianju.service;
import com.tianju.entity.Owner;
public interface IOwnerService {
/**
* 默认情况下只查询这个用户的基础信息,
* 如果需要房屋信息,就再查一下房屋信息
* @param id 查询的业主的id
* @param isGetHouse 是否获取房屋信息,默认不获取,true表示获取
* @return
*/
Owner queryById(Integer id,Boolean... isGetHouse);
/**
* 新增一条用户信息
*/
Integer add(Owner owner);
}
package com.tianju.service.impl;
import com.tianju.dao.HouseMapper;
import com.tianju.dao.OwnerMapper;
import com.tianju.entity.House;
import com.tianju.entity.Owner;
import com.tianju.service.IOwnerService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
@Service
@Transactional
public class OwnerServiceImpl implements IOwnerService {
@Autowired
private OwnerMapper ownerMapper;
@Autowired
private HouseMapper houseMapper;
@Override
public Owner queryById(Integer id,Boolean... isGetHouse) {
// TODO:尽量减少和数据库的交互
Owner owner = ownerMapper.queryById(id);
if (isGetHouse!=null && isGetHouse[0]){
// 表示既要业主的信息,也要业主名下的房屋的信息
List<House> houseList = houseMapper.queryHouseByOwnerId(id);
owner.setHouseList(houseList);
// 既然查询了一下该业主的房屋数量,那就更新一下拥有房间数量
ownerMapper.updateOwnerHouseNum(id, houseList.size());
return owner;
}
return owner;
}
@Override
public Integer add(Owner owner) {
// 如果新用户只是意向客户
if (owner.getHouseList().size()<1){
owner.setHouseNum(0);
return ownerMapper.add(owner);
}
// 买房的客户变成了业主
Integer num = 0; //影响数据库的数据的行数
ownerMapper.add(owner);
for (House house:owner.getHouseList()){
// 房间状态改为入住的状态
houseMapper.intoHouse(house.getId());
// 房屋-业主对应表新增一条数据
houseMapper.addOwnerHouse(owner.getId(), house.getId());
num +=2;
}
return num;
}
}
(4)在controller层调用service
// 查询出用户的详细信息,需要查用户名下房子的信息
@RequestMapping("/detail")
@ResponseBody
public ResData detail(Integer id){
if (StringUtils.isBlank(id)){
return new ResData(1001, "id为空", null);
}
Owner owner = ownerService.queryById(id, true);
if (owner==null){
return new ResData(1002,"未找到",null);
}
return new ResData(200, "ok", owner);
}
三、延迟加载
实际开发经验中,很多时候可能只是需要用户信息,然后通过用户去查询角色时,也就是说,加载用户信息时不一定要同时加载角色信息。此时就是延迟加载。
为什么会有延迟加载
select * from account where id=1 //先查询出这个账户信息,包含uid
select * from user where uid=1 //再查询用户信息
延迟加载: 延迟加载也叫懒加载,是针对级联使用的,懒加载的目的是减少内存的浪费和减轻系统负担。
好处:
先从单表查询,需要时再从关联表去关联查询,大大提高数据库性能,因为查询单表要比关联查询多张表速度要快。
坏处:
因为只有当需要用到数据时,才会进行数据库查询,这样在大批量数据查询时,其实是二次连接查询,所以速度反而下降,让数据库的压力显得不平滑。
需求:
查询账户(Account)信息并且关联查询用户(User)信息。如果先查询账户(Account)信息即可满足要求,当我们需要查询用户(User)信息时再去查询用户(User)信息。把对用户(User)信息的按需去查询就是延迟加载。
我们使用多对多的关系,主要是通过 association、collection 实现映射。而association、collection 具备延迟加载功能。
如果某个collection不想用懒加载,可以使用 fetchType=“eager”,默认是fetchType=“lazy”,高版本有修改,fetchType需要自己添加
association例子
association用于一对一、多对一场景使用
<resultMap id="accountMap2" type="account">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="uid" property="uid"/>
<result column="money" property="money"/>
<association property="user" javaType="user"
select="com.tianju.mapper.UserMapper.findById" column="uid">
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAll2" resultMap="accountMap2">
select * from account
</select>
@Test
public void findAll2(){
List<Account> all2 = accountMapper.findAll2();
//User user = all2.get(0).getUser();
}
collection例子
<resultMap id="userMap2" type="user">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<result column="address" property="address"/>
<result column="sex" property="sex"/>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday"/>
<collection property="accounts" ofType="account" fetchType="lazy"
select="com.woniu.mapper.AccountMapper.findByUid" column="id">
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAll2" resultMap="userMap2">
select * from user;
</select>
collection:是用于建立一对多中集合属性的对应关系
ofType : 用于指定集合元素的数据类型
select : 是用于指定查询账户的唯一标识(账户的 mapper 全限定类名加上方法名称)
column :是用于指定使用哪个字段的值作为条件查询
四、缓存【待续】
缓存是什么?在mybatis中,缓存就是,第一次查询数据库以后,把结果存起来,如果下一次查询参数没改变,并且对应要查询的表也没有改变,就可以直接从存的地方来拿,这就是缓存技术。
mybatis的缓存分为一级缓存,和二级缓存。
其中一级缓存是系统自带的缓存,只要sqlsession没有变化,他就一直存在
二级缓存是在namespace阶段,也就是每一个mapper.xml中,需要开启才能使用。我们先讲一级缓存
缓存失效的情况:
sqlsession关闭,一级缓存失效
两次查询中间,数据库表有变动,缓存失效
总结
1.mybatis可以实现SQL语句和Java代码的解耦;
2.多表查询,一对多情况的延迟加载 fetchType=“lazy”;
3.一对多的查询方式,建议查询两次,从业务和速度的角度;
4.延迟加载的association和 collection;
5.mybatis缓存,一级缓存,二级缓存;








![[攻防世界] [RE] [APK] app2](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d16d763b4bd94ebe8d699ddb7504e53c.png)