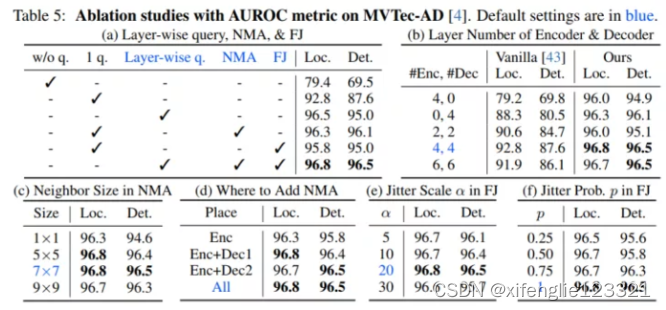
主要参考:What is the “eval” command in bash
简而言之,它让一个输入行被解析两次。
它是如何做到这一点的?
shell有一系列步骤来解析一行命令。
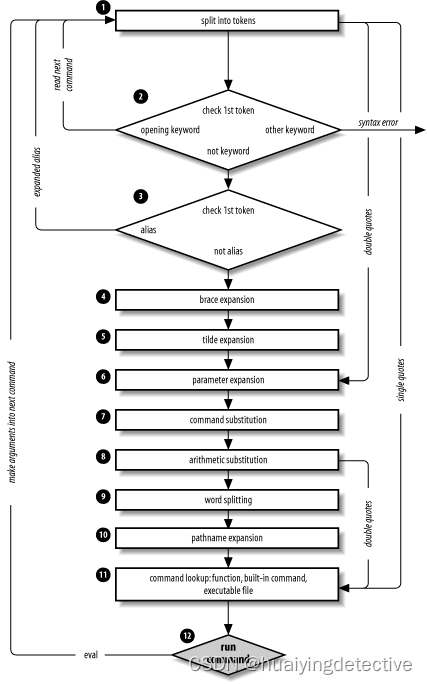
- shell读取它的输入
- shell将输入放入token:分为运算符和单词
- The shell parses the input into simple and compound commands.
- The shell performs various expansions (separately) …
- The shell performs redirection and removes redirection operators and their operands from the parameter list.
- The shell executes a function, built-in, executable file, or script …
- The shell optionally waits for the command to complete and collects the exit status.
在第六步,eval导致被处理好的命令行重新被发送到第一步。
$(…)这个命令将小括号内的命令在新的进程中执行,即继承了当前shell变量和设置的子shell,并接收它的输出。
它会接收参数并且根据这个参数构造一个命令,这个命令将会被shell执行。
例子:
foo=10 x=foo # 1
y='$'$x # 2
echo $y # 3
$foo
eval y='$'$x # 5
echo $y # 6
10
在第一行,定义 foo的值为10,定义x的值为foo
第二行,定义了y
第三行命令,显示了y的值为字符串$foo
总之前三行命令结束后,各个变量的值如下所示。

现在我们用eval命令重复这个分配过程。它首先会把$x翻译为字符串foo.现在我们有了表达式: y=$foo,这会给y赋值为10.
现在运行echo $y的结果就是10.