ES查询
相关度搜索,需要计算评分
_score
相关度评分用于对搜索结果排序,评分越高则认为其结果和搜索的预期值相关度越高,即越符合搜索预期值。在7.x之前相关度评分默认使用TF/IDF算法计算而来,7.x之后默认为BM25。
源数据:_source
- 禁用_source:
-
好处:节省存储开销
-
坏处:
- 不支持update、update_by_query和reindex API。
- 不支持高亮。
- 不支持reindex、更改mapping分析器和版本升级。
- 通过查看索引时使用的原始文档来调试查询或聚合的功能。
- 将来有可能自动修复索引损坏。
总结:如果只是为了节省磁盘,可以压缩索引比禁用_source更好。
- 数据源过滤器:
Including:结果中返回哪些field
Excluding:结果中不要返回哪些field,不返回的field不代表不能通过该字段进行检索,因为元数据不存在不代表索引不存在
-
在mapping中定义过滤:支持通配符,但是这种方式不推荐,因为mapping不可变
PUT product { "mappings": { "_source": { "includes": [ "name", "price" ], "excludes": [ "desc", "tags" ] } } } -
常用过滤规则
- “_source”: “false”, # 表示不要元数据
- “_source”: “obj.*”, # 支持通配符配置
- “_source”: [ “obj1.", "obj2.” ],
- “_source”: {
“includes”: [ “obj1.", "obj2.” ],
“excludes”: [ “*.description” ]
}
source不要定义在mapping中这样以后不允许修改了,可以在查询中使用_source进行动态过滤
PUT test_mapping_manual1/_doc/1
{
"name":"hell",
"age":10,
"owner":{
"name":"23",
"id": 5
}
}
PUT test_mapping_manual1/_doc/2
{
"name":"hell",
"age":10,
"owner.name":33
}
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search
{
"_source": ["owner.name"],
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
## 冲突以excelude为准
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search
{
"_source":{
"includes": ["age*"],
"excludes": ["age*"]
},
"query":{
"match_all": {}
}
}
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search
{
"_source":{
"includes": ["*"],
"excludes": ["owner.*"]
},
"query":{
"match_all": {}
}
}
DSL Domain Specific Language
我们在Kibana中使用的RESt查询脚本叫domain special language(就是写的json)
简单查询 Query String Search
带条件查询
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search?q=name:hello
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search?from=0&size=3&sort=age:asc
尝试了text类型排序需要特别处理下. "reason" : "Text fields are not optimised for operations that require per-document field data like aggregations and sorting, so these operations are disabled by default. Please use a keyword field instead. Alternatively, set fielddata=true on [name] in order to load field data by uninverting the inverted index. Note that this can use significant memory."
这种查询方式是创建索引的字段都会被检索
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search?q=hell
关闭字段索引,在mapping中设置
"cloName": {
"type": "text",
"index": false
}
全文检索 Fulltext search
match
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "John Smith"
}
}
}
# name包含John或者Smith都会被检索出来即这里对搜索词做了分词,且对source data也做了分词
这种把条件放到json体中
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "keyword1 keyword2 keyword2"
}
}
}
# 上边查询的含义是任何包含关键字 keyword1 或者 keyword2 或者keyword3都会查询出来
# 前提是设置好分词器,如果中文使用英文分词器可能会存在问题
# 查询结构顺序按照_score进行排序,内部排序算法是bm25
查询结果会统计命中几个关键字
match_all
# 查询所有全部数据
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
}
}
# 等同于
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search
# 查询集群所有数据
GET _search
multi_match
# 这段含义是在字段name和desc中查找包含"John或者IT的内容的
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "John IT",
"fields": ["name","desc"]
}
}
}
# 语义: 默认分词器的对`John Smith`的分词结果为`John`和`Smith`
# name.last 中包含 `John` 或者 `Smith`
# OR
# name.first 中包含 `John` 或者 `Smith`
# 如果设置了"operator": "and",则中间 OR 的关系变为 AND
GET teacher/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "John Smith",
"type": "most_fields",
"fields": [
"name.last",
"name.first"
]
// ,"operator": "and"
}
}
}
match_phrase
短语搜索
短语搜索内部原理是先分词,分词之后需要命中每个分词,并且顺序要一直
# 这段含义先把name查询条件分词为John 和Tim
# 然后去source中把name字段的内容分词
# 分词之后需要同时命中John 和Tim并且顺序要一致
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"name": "John Tim"
}
}
}
验证分词
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "John Sam desc IT"
}
exact match
使用关键字term
term不会对搜索词分词
记住分词分两个部分,搜索词分词和源数据分词
keyword是不对source data的值分词
match_phase是分词的
所以重点来了:
如果搜索词部分词,但是source data内容分词了,这时是无法查询数据的,因为建索引的时候索引已经分词了; 另外还需要注意一点一个字段要被搜索到一定要被索引到
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name": "John Smith"
}
}
}
# 测试数据1
POST test_mapping_manual1/_doc
{
"name": "John Smith",
"age": 18,
"desc": "IT phone"
}
# 此案例无法查询出数据
term没有查到数据分析
match 一般要结合 text 类型一起使用
而 term 要结合 keyword 类型一起使用,这样才是有意义的
这里的理解有些人可能有误区,
"name" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
这里的name并不是keyword, name.keyword才是keyword,是不是keyword要看其type
先总结几点:
- term查询要查询keyword字段
- term搜索词不会分词,也不会normalization化
- 源数据会normalization化
这样就会导致无法匹配,甚至你改成小写会有匹配的错视感.
text 类型在创建索引的时候会执行分词,分词过程有一个步骤叫 normalization 也叫文档归一化处理,在这个处理过程中,源数据字段会被统一时态、大小写等,具体还会执行哪些操作取决于你使用了哪个分词器,也就是说你的搜索词会保留大写,而源文档的索引数据会被转换为小写,注意这里说的是倒排索引会被转换为小写,而不是源数据,所以相当于 你用 John 去匹配了 john,所以无法命中
所以一般查询命中情况, 一定要注意分词器情况以及具体type如text和keyword
- keyword不会被分词,会保留源数据原样
- text会做文档标准化, 大小写,单复数,时态等等
- 搜索的分词器和源数据分词器是两回事,一定要注意这个区别
- term搜索词不分词,保留词源信息
常量评分
GET test_mapping_manual3/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"name": "john"
}
},
// 可以不写,不写默认1.0
"boost": 1.2
}
}
}
布尔查询
布尔查询可以组合前边的一些查询,比如组合filter和must/must_not等等
它的目的就是提高性能,比如先通过filter过滤一些数据之后,然后再计算评分,这样节省一些评分时间
POST test_goods/_doc
{
"name": "apple watch",
"price": 6999,
"date": "2023-06-27"
}
POST test_goods/_doc
{
"name": "apple ring",
"price": 999,
"date": "2023-06-27"
}
POST test_goods/_doc
{
"name": "apple phone",
"price": 7999,
"date": "2023-06-27"
}
POST test_goods/_doc
{
"name": "apple",
"price": 9999,
"date": "2023-06-27"
}
GET test_goods/_search
GET test_goods/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 0,
"lte": 99999
}
}
}
],
"must": [
{
"match": {
"name.keyword": "apple"
}
}
]
}
}
}
must
GET test_mapping_manual1/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
// 可以设置多个查询条件, 所有条件必须满足
{},{}
]
}
}
}
"must": [
// 可以设置多个查询条件, 所有条件必须满足
should
must:必须满足子句(查询)必须出现在匹配的文档中,并将有助于得分。
filter:过滤器 不计算相关度分数,cache☆子句(查询)必须出现在匹配的文档中。但是不像 must查询的分数将被忽略。Filter子句在filter上下文中执行,这意味着计分被忽略,并且子句被考虑用于缓存。
should:可能满足 or子句(查询)应出现在匹配的文档中。
should:参数指定should返回的文档必须匹配的子句的数量或百分比。可以写多个条件,这些条件中它要求最低要满足几个条件才算命中, 默认[如果bool查询包含至少一个 should 子句,而没有 must 或 filter 子句,则默认值为 1。否则,默认值为0],可以配置.minimum_should_match:
minimum_should_match可以接受以下几种不同的取值:
- 固定数量值:可以指定一个具体的数字,例如
minimum_should_match: 2,表示至少需要两个should条件匹配。- 百分比值:可以指定一个百分比值,例如
minimum_should_match: 50%,表示至少需要should条件的一半匹配。- Combination values:可以结合固定数量值和百分比值,例如
minimum_should_match: "2<75%",表示至少需要两个should条件匹配,或者匹配百分之75的should条件。
# 我的filter有2个条件, should设置为0才能查询数据; filter和should的条件不冲突, filter只是影响should的默认值
# 如果有你filter则should的最小数量是0,如果没有should的最小数量就是1
GET test_goods/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 99999
}
}
},
{
"term": {
"name.keyword": "apple phone"
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match_phrase": {
"name": "huawei"
}
},
{
"match_phrase": {
"name": "phone"
}
}
,{
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 7000
}
}
}
]
}
}
],
"minimum_should_match": 2
}
}
}
must_not:必须不满足 不计算相关度分数 not子句(查询)不得出现在匹配的文档中。子句在过滤器上下文中执行,这意味着计分被忽略,并且子句被视为用于缓存。由于忽略计分,0因此将返回所有文档的分数。
分词器
normalization : 文档规范化
先切词,然后规范化.
规范化要规范哪些内容?
大小写; 标点符号; 时态; 复数;
规范化主要是为了匹配更精准
character filter : 字符过滤器. 标点符号
分词之前的预处理,过滤无用字符
-
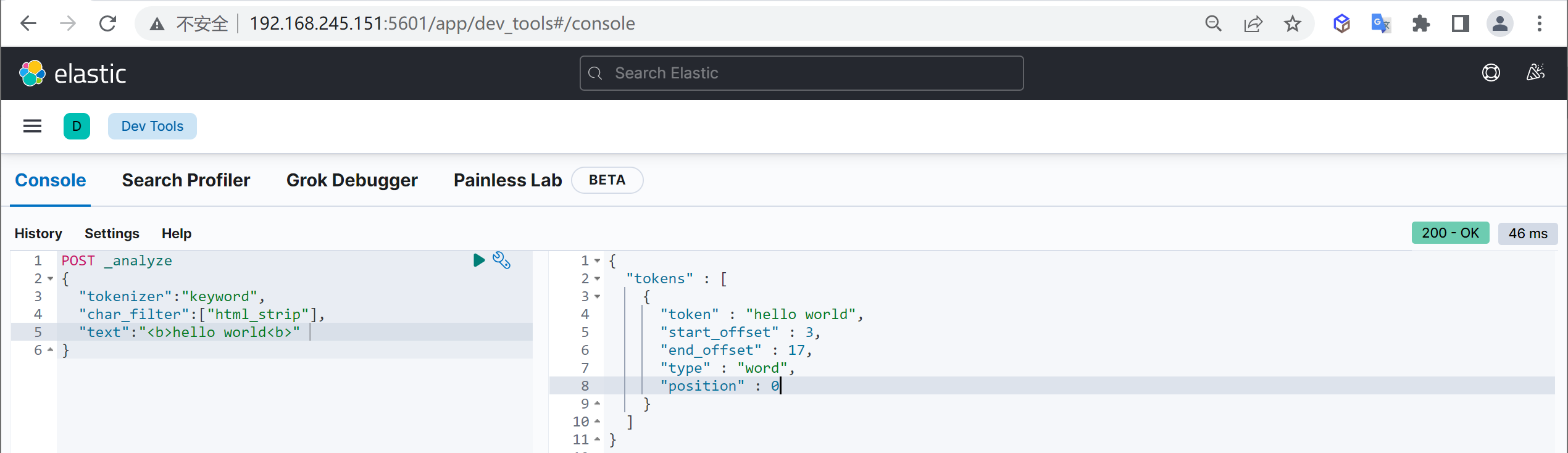
HTML Strip Character Filter
:html_strip
- 参数:escaped_tags 需要保留的html标签
-
Mapping Character Filter:type mapping
-
Pattern Replace Character Filter:type pattern_replace
> normalization 通过分词器把单词分词然后规范化 查看具体分词器效果
```json
GET _analyze
{
"text": "the computer Apple is the best Tools, Teacher's notebood",
"analyzer": "english"
}
GET _analyze
{
"text": "the computer Apple is the best Tools",
"analyzer": "standard"
}
```
- HTML strip 过滤html标签
- mapping 映射替换的标点符号等
- pattern Replace 正则替换
- 分词器在创建时指定
DELETE test_idx_analyzer1
PUT test_idx_analyzer1
{
"settings": {
// 这里是分析器 不是分词器; 分词器可以包含设置过滤器和分词器
"analysis": {
// 这个有四种类型具体看官方文档
"char_filter": {
// 分词器名称
"test_char_filter1": {
// 指定具体的类型, 具体类型看官方文档,
"type": ["html_strip"],
"escaped_tags": ["a"]
}
},
"analyzer": {
"test_analyzer1": {
"tokenizer": "keyword",
"char_filter": "test_char_filter1"
}
}
}
}
}
```html
<p> I'm so <a>Happy</a></p>
```
GET test_idx_analyzer1/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "test_analyzer1"
, "text": "<p> I'm so <a>Happy</a></p>"
}
### mapping
DELETE test_idx_analyzer3
PUT test_idx_analyzer3
{
"settings": {
// 这里是分析器 不是分词器; 分词器可以包含设置过滤器和分词器
"analysis": {
// 这个有四种类型具体看官方文档
"char_filter": {
"test_mapping_filter1": {
"type": "mapping",
"mappings":[
"滚 => *",
"蛋 => x"
]
}
},
"analyzer": {
"test_analyzer2": {
"tokenizer": "keyword",
"char_filter": ["test_mapping_filter1"]
}
}
}
}
}
GET test_idx_analyzer3/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "test_analyzer2"
, "text": "滚蛋球"
}
### Pattern replace
### pattern replace
DELETE test_idx_analyzer3
PUT test_idx_analyzer3
{
"settings": {
// 这里是分析器 不是分词器; 分词器可以包含设置过滤器和分词器
"analysis": {
// 这个有四种类型具体看官方文档
"char_filter": {
"test_mapping_filter1": {
"type": "pattern_replace",
"pattern": "(\\d{3})(\\d{4})(\\d{4})",
"replacement": "$1***$2"
}
},
"analyzer": {
"test_analyzer2": {
"tokenizer": "keyword",
"char_filter": ["test_mapping_filter1"]
}
}
}
}
}
GET test_idx_analyzer3/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "test_analyzer2"
, "text": "12345677890"
}
tokenizer : 分词器
安装IK分词器
IK地址:
https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/blob/master/README.md
分词器安装目录
es_home/plugins/ik
分词器安装方式
// 此例子可能需要安装插件, 插件安装有单独一节进行讲解见后
每个节点同义词文件都要同步吗?是的
// ik每个node都要安装; 如果版本不对有两种办法
- 手动编译安装
- 相近的版本可以直接修改版本
如何手动安装?
git clone https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik
cd elasticsearch-analysis-ik
git checkout tags/{version}
mvn clean
mvn compile
mvn package
拷贝和解压release下的文件: #{project_path}/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/target/releases/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-*.zip 到你的 elasticsearch 插件目录, 如: plugins/ik 重启elasticsearch
相近的版本可以直接修改版本
vim plugin-descriptor.properties
修改
elasticsearch.version=your_version
> 如果修改plugin-descriptor.properties里的版本号不行的话,还有elasticsearch-analysis-ik-xxx.jar内pom.properties里的版本号。
常见分词器
- standard analyzer:默认分词器,中文支持的不理想,会逐字拆分。
- pattern tokenizer:以正则匹配分隔符,把文本拆分成若干词项。
- simple pattern tokenizer:以正则匹配词项,速度比pattern tokenizer快。
- whitespace analyzer:以空白符分隔 Tim_cookie
自定义分词器:custom analyzer
char_filter:内置或自定义字符过滤器 。
token filter:内置或自定义token filter 。
tokenizer:内置或自定义分词器。
中文分词器IK
IK分词器
安装和部署
- ik下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik
- Github加速器:https://github.com/fhefh2015/Fast-GitHub
- 创建插件文件夹 cd your-es-root/plugins/ && mkdir ik
- 将插件解压缩到文件夹 your-es-root/plugins/ik
- 重新启动es
- 主词库:main.dic
- 英文停用词:stopword.dic,不会建立在倒排索引中
- 特殊词库:
- quantifier.dic:特殊词库:计量单位等
- suffix.dic:特殊词库:行政单位
- surname.dic:特殊词库:百家姓
- preposition:特殊词库:语气词
- 自定义词库:网络词汇、流行词、自造词等
扩展IK词库
修改IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml中自定义词库的路径,路径原则上可以随便放,管理是跟ik放一起,建一个custome目录

token filter : 令牌过滤器
停用词、时态转换、大小写转换、同义词转换、语气词处理等。比如:has=>have him=>he apples=>apple the/oh/a=>干掉
处理大小写
// why get not PUT
// I miss the keyword _analyze,why? cannot understand better?
// this way is operate exists index to do query
GET /test_index02/_analyze
{
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": {
"type": "condition",
"filter": "uppercase",
"script": {
"source": "token.getTerm().length() < 5"
}
},
"text": ["abdsfs sdf dsfdsf dsf dsfdsf sd fds fds f dsf sd f dsf sd fs df sdf dsfdsfdsfs dfdsfds"]
}
token_filter同义词替换
-
定义同义词词典文件 格式
src1,src2 => target -
vim analysis/synonyms.txt Mengdiudiu,mengdiudiu => MDO -
同步到目录 es_home/config/analysis/your_dict.txt
-
如何验证是否生效:
-
DELETE test_index01 PUT /test_index01 { "settings": { "index": { "analysis": { "analyzer": { "test_index01_synonym": { "tokenizer": "whitespace", "filter": [ "test_index01_synonym" ] } }, "filter": { "test_index01_synonym": { "type": "synonym", "synonyms_path": "analysis/synonyms.txt" } } } } } } GET /test_index01/_analyze { "text": "Mengdiudiu", "analyzer": "test_index01_synonym" }
第二种方式
DELETE test_index02
PUT /test_index02
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"test_index02_search_synonyms": {
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter": [ "test_index02_graph_synonyms" ]
}
},
"filter": {
"test_index02_graph_synonyms": {
"type": "synonym_graph",
"synonyms_path": "analysis/synonyms.txt"
}
}
}
}
}
}
GET /test_index02/_analyze
{
"text": "Mengdiudiu",
"analyzer": "test_index02_search_synonyms"
}
自定义切词器,分析器
DELETE test_index03
PUT /test_index03
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"char_filter": {
// 自定义char_filter: 转换单词
"test_myfilter03": {
"type": "mapping",
"mappings": ["& => and", "| => or"]
}
// 可以定义多个char_filter,其余的是否可以定义多个可以尝试
},
"filter": {
// 自定义过滤器: 过滤停用词
"test_mystop01":{
"type": "stop",
"stopwords": ["is", "the"]
}
},
"tokenizer": {
// 自定义切词器
"test_mytokenizer01":{
"type": "pattern",
"pattern": "[.,!? ]"
}
},
"analyzer": {
// 自定义分析器
"test_myanalyzer01": {
// 分词器类型,自定义
"type": "custom",
"char_filter": ["test_myfilter03"],
"tokenizer": "test_mytokenizer01",
"filter": ["test_mystop01","lowercase"]
}
}
}
}
}
GET test_index03/_analyze
{
// 使用自定义的analyzer
"analyzer": "test_myanalyzer01",
"text": "is,the.New? Apple! & |"
}
常用分词器
中文分词器
已定义分词器
词库热更新
如果每次更新词库都要重启服务这是生产环境无法忍受的.
所以现在支持热更新;
使用方式就是配置IK config文件的remote_ext_dict的url地址进行热更新(默认是location)
具体的热更新见IK github说明
https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik
热更新的坑
- 你本地启动的服务只是告诉es要不要更新,并不是由这个服务返回最新内容,即最终reload操作还是es node从自己本地目录去加载
- node 对应的停用词文件, 分词文件必须有,理由见第一条.
- 停用词和分词文件目录一定要放对plugins/ik/config/custome, 一定要在ik的config内,它是相对这里的, 其他地方不生效,除非配置绝对路径
- 正更新流程是这样的: 修改各个node本地文件-> 三方服务告诉es需要更新->es reload本地文件

synonym_graph与synonym
esThe synonym_graph token filter allows to easily handle synonyms, including multi-word synonyms correctly during the analysis process.这里的including multi-word synonyms correctly指的是什么? 举个例子说明?解释这块和synonym的区别
在 Elasticsearch 中,普通的 synonym 过滤器无法正确处理多词同义词。当使用普通的 synonym 过滤器时,多词同义词会被拆分成单独的词,并分别进行处理,而无法保持它们之间的关联性。
而 synonym_graph token 过滤器则能够正确处理多词同义词。它在分析过程中能够识别并保留多词同义词的关联性,使其作为一个整体进行处理。这样可以确保多词同义词在搜索和索引过程中的行为更加准确和一致。
举个例子,假设有以下的同义词映射关系:
"big apple, new york"
如果使用普通的 synonym 过滤器,在分析过程中,输入文本 “I love big apple” 会被分析成 “I love big” 和 “apple”。这就导致了 “big apple” 这个多词同义词被拆分了,并失去了其作为一个整体的意义。
而使用 synonym_graph 过滤器,输入文本 “I love big apple” 会被分析成 “I love big apple”,保留了多词同义词的完整性。这样,在搜索或索引时,就能够正确匹配包含多词同义词的文本。
因此,synonym_graph 与普通的 synonym 过滤器相比,能够更好地处理多词同义词,保持其完整性和关联性,从而提供更准确的搜索结果。
如果没生效如何跟踪日志分析原因?
- 检查文件及目录是否存在
- 所有节点配置完之后都要重启
- 检查测试脚本是否正确的,我遇到的问题就是脚本不正确但是确能执行,就是拿不到正确结果
错误脚本:
PUT test_idx_analyzer3
{
"settings": {
// 这里是分析器 不是分词器; 分词器可以包含设置过滤器和分词器
"analysis": {
// 这个有四种类型具体看官方文档
"char_filter": {
"test_mapping_filter1": {
"type": "pattern_replace",
"pattern": "(\\d{3})(\\d{4})(\\d{4})",
"replacement": "$1***$2"
}
},
"analyzer": {
"test_analyzer2": {
"tokenizer": "keyword",
"char_filter": ["test_mapping_filter1"]
}
}
}
}
}
正确脚本:
PUT /test_index02
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"test_index02_search_synonyms": {
"tokenizer": "ik_max_word",
"filter": [ "test_index02_graph_synonyms" ]
}
},
"filter": {
"test_index02_graph_synonyms": {
"type": "synonym_graph",
"synonyms_path": "analysis/synonyms.txt"
}
}
}
}
}
}
疑问
为什么返回值变小写?
ik_max_word什么含义?
analysis与analyzer
analyzer和tokenizer
在 Elasticsearch 中,
analyzer和tokenizer是用于处理文本的重要组件。
Tokenizer是一个将输入文本分割成一个个词汇单元(tokens)的过程。它根据指定的规则,如空格、标点符号、字母边界等,将文本拆分成独立的词汇单元。例如,将句子 “Hello, world!” 分割成 “Hello” 和 “world” 两个词汇单元。Tokenizer 是分析过程的第一步。
Analyzer是由多个组件组成的文本分析器。它在分析过程中使用了一个或多个 Tokenizer 和其他的文本处理器(如过滤器、字符映射等)。Analyzer 接收输入文本,将其分割成词汇单元,并对这些词汇单元应用一系列的处理步骤,如去除停用词、转换为小写、词干提取等。最终,Analyzer 生成了一个分析后的文本结果,用于索引和搜索。因此,Tokenizer 是分割文本的组件,而 Analyzer 是一系列处理组件的集合,用于对文本进行更深入的分析和处理。Tokenizer 通常是 Analyzer 中的一个重要组成部分,负责将文本分割成词汇单元,然后交给其他组件进行进一步的处理和转换。
如何验证分词
GET _analyze
{
“analyzer”: “standard”,
“text”: “John Sam desc IT”
}
插件更新方式
插件不支持热更新,必须重新启动.
每个Node都必须配置