SpringBoot2 核心技术
- (一)、SpringBoot核心技术入门
- 1.Spring能做什么?
- 1.1、Spring 的能力
- 1.2、Spring的生态
- 1.3、Spring5重大升级
- 1.3.1、响应式编程
- 1.3.2、内部源码设计
- 2.为什么用SpringBoot
- 2.1、SpringBoot优点
- 2.2、SpringBoot缺点
- 3.时代背景
- 3.1、微服务
- 3.2、分布式的困难
- 3.3、云原生
- 4.如何学习SpringBoot
- 4.1、查看官方文档
- (二)、SpringBoot2入门
- 1.系统要求
- 1.1、maven设置
- 2.HelloWord
- 2.1、创建maven工程
- 2.3、创建主程序
- 2.4、编写业务
- 2.5、RestController源码 ⭐
- 2.6、测试是否成功
- 2.7、简化配置 ⭐⭐
- 2.8、简化打包 ⭐⭐⭐
- (三)、了解SpringBoot自动配置原理
- 1.SpringBoot特点
- 1.1、依赖管理
- (1).父项目控制版本依赖 (自动版本仲裁机制)
- (2).自定义依赖版本
- (3).starter场景启动器
- (4).版本仲裁
- 1.2、自动配置
- (1).自动配备 Tomcat
- (2).自动配备 SpringMVC
- (3). 自动配备 常用组件
- (4).默认的包结构 (修改默认扫描路径) ⭐
- (5).自动配置 配置有用默认值
- (6).按需加载自动配置项
- 2.IOC容器功能
- 2.1、组件添加
- (1).@Configuration
- (2).@Bean、@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository
- (3).@ComponentScan、@Import
- (4).@Conditional
- 2.2、原生配置文件引入 (只能放在类级别的注解上)
- (1). 尚未使用 @ImportResource
- (2). 引用 @ImportResource
- 2.3、配置绑定
- (1).@ConfigurationProperties (第一种)
- (2).@EnableConfigurationProperties (第二种)
- 3.自动配置原理入门
- 3.1、引导加载自动配置类
- (1). @SpringBootConfiguration
- (2). @ComponentScan
- (3).@EnableAutoConfiguration
- (3.1).@AutoConfigurationPackage (自定义注入组件)
- (3.2).@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) (官方注入)
- 3.2、按需开启自动配置项
- 3.3、 修改默认配置
- 3.4、 总结
- 3.5、最佳实践
- 4.开发技巧
- 4.1 lombok 技术
- 4.2 devtools 技术
(一)、SpringBoot核心技术入门
官方文档: https://www.yuque.com/atguigu/springboot/na3pfd
1.Spring能做什么?
1.1、Spring 的能力
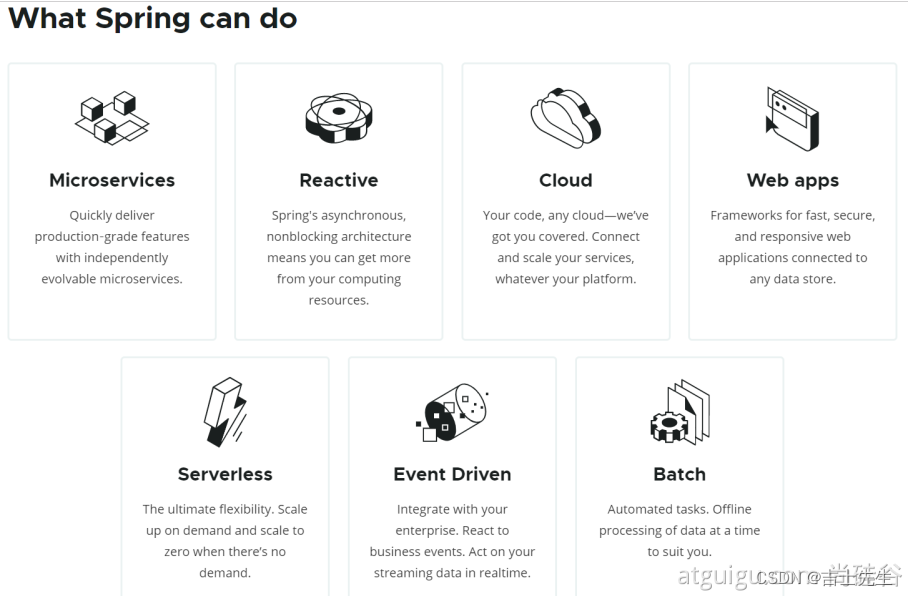
1.2、Spring的生态
https://spring.io/projects/spring-boot
覆盖了:
web开发
数据访问
安全控制
分布式
消息服务
移动开发
批处理
…
1.3、Spring5重大升级
1.3.1、响应式编程
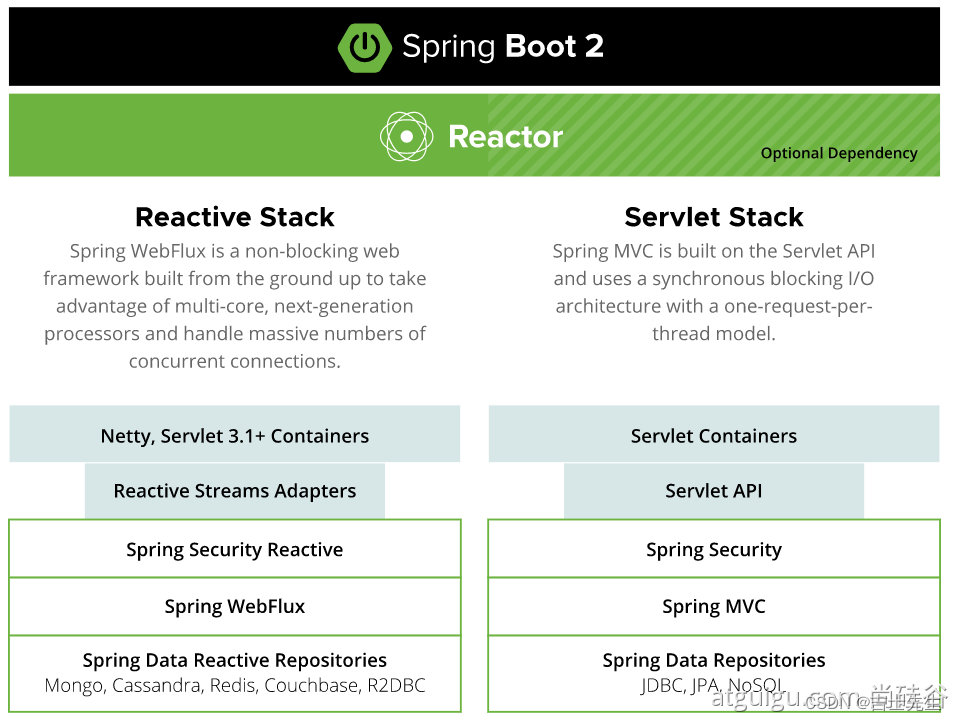
1.3.2、内部源码设计
基于Java8的一些新特性,如:接口默认实现。重新设计源码架构。
2.为什么用SpringBoot
2.1、SpringBoot优点
● Create stand-alone Spring applications
○ 创建独立Spring应用
● Embed Tomcat, Jetty or Undertow directly (no need to deploy WAR files)
○ 内嵌web服务器
● Provide opinionated ‘starter’ dependencies to simplify your build configuration
○ 自动starter依赖,简化构建配置
● Automatically configure Spring and 3rd party libraries whenever possible
○ 自动配置Spring以及第三方功能
● Provide production-ready features such as metrics, health checks, and externalized configuration
○ 提供生产级别的监控、健康检查及外部化配置
● Absolutely no code generation and no requirement for XML configuration
○ 无代码生成、无需编写XML
SpringBoot的底层是Spring.Spring的底层是Java。
2.2、SpringBoot缺点
● 人称版本帝,迭代快,需要时刻关注变化
● 封装太深,内部原理复杂,不容易精通
3.时代背景
3.1、微服务
● 微服务是一种架构风格
● 一个应用拆分为一组小型服务
● 每个服务运行在自己的进程内,也就是可独立部署和升级
● 服务之间使用轻量级HTTP交互
● 服务围绕业务功能拆分
● 可以由全自动部署机制独立部署
● 去中心化,服务自治。服务可以使用不同的语言、不同的存储技术
3.2、分布式的困难
● 远程调用
● 服务发现
● 负载均衡
● 服务容错
● 配置管理
● 服务监控
● 链路追踪
● 日志管理
● 任务调度
● …
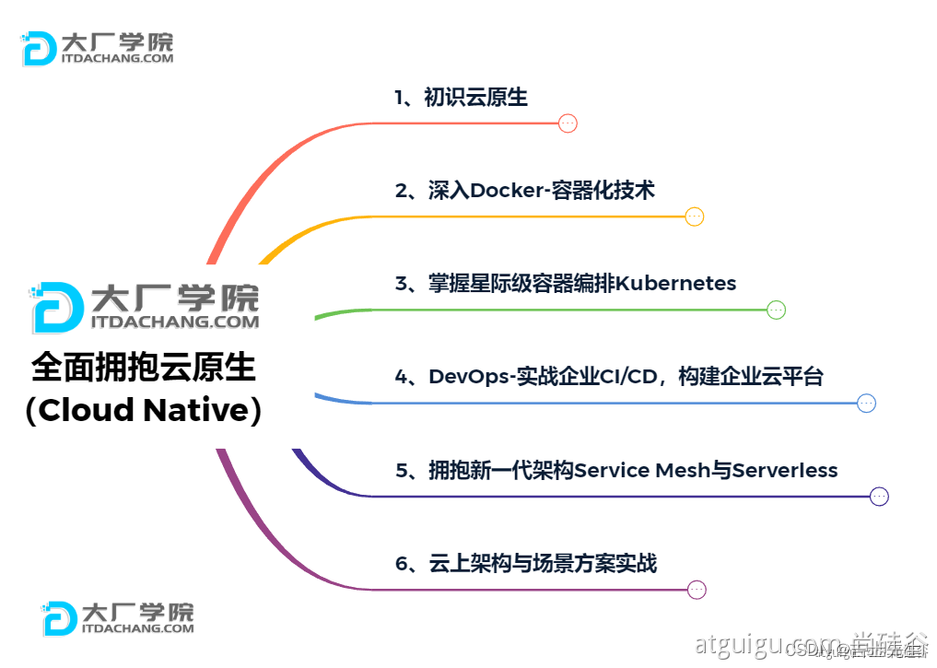
3.3、云原生
原生应用如何上云。 Cloud Native
上云的困难
● 服务自愈
● 弹性伸缩
● 服务隔离
● 自动化部署
● 灰度发布
● 流量治理
● …
上云的解决
4.如何学习SpringBoot
4.1、查看官方文档
SpringBoot 2.4.13 官方文档: https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.4.13/reference/html//

(二)、SpringBoot2入门
1.系统要求
● Java 8 & 兼容java14 .
● Maven 3.3+
● idea 2019.1.2
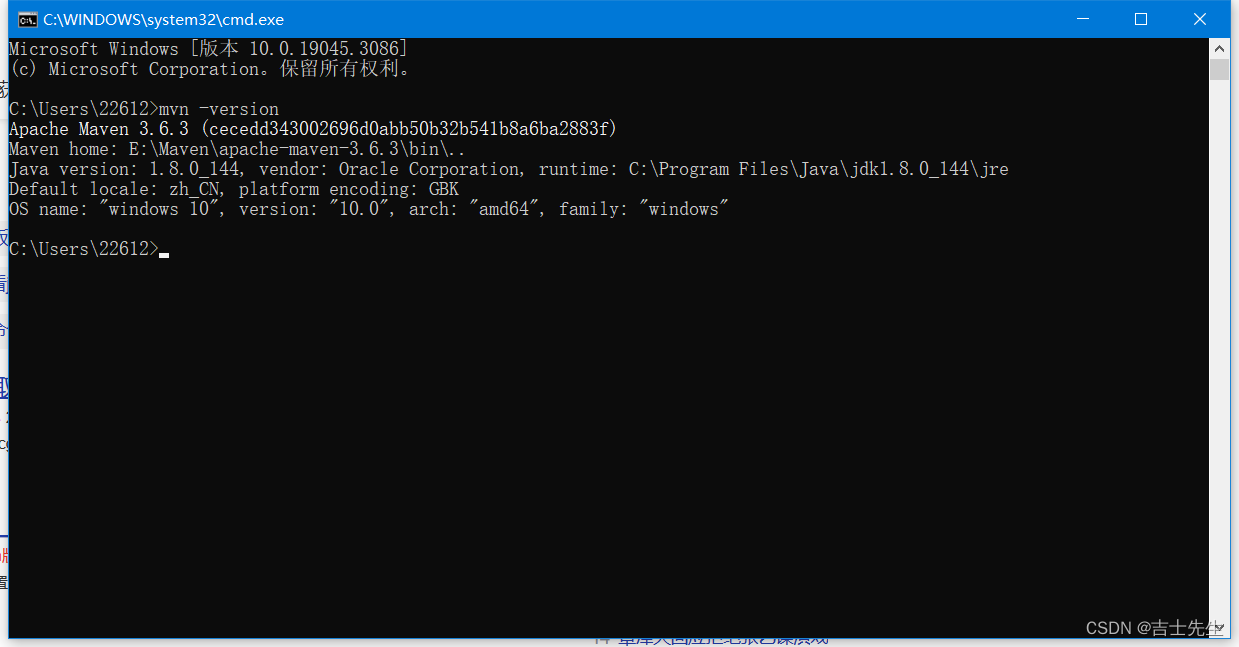
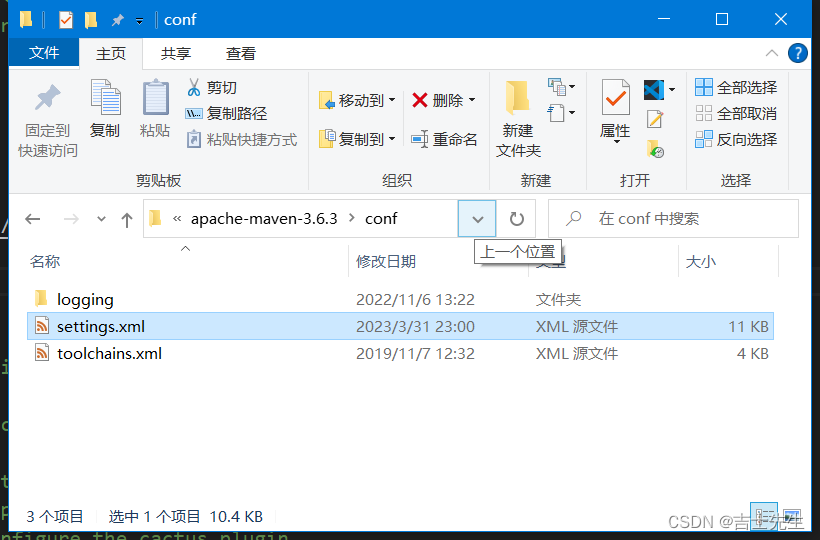
1.1、maven设置
1.查看自己的Maven版本:
mvn -version
2.打开自己的Maven配置文件
// 使用阿里云的镜像进行下载
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<id>nexus-aliyun</id>
<mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf>
<name>Nexus aliyun</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
// 使用jdk1.8进行编译
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
2.HelloWord
2.1、创建maven工程
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.3、创建主程序
/**
* 主程序类
* @SpringBootApplication:这是一个SpringBoot应用
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class,args);
}
}
2.4、编写业务
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String handle01(){
return "Hello, Spring Boot 2!";
}
}
2.5、RestController源码 ⭐
@Controller + @ResponseBody = @RestController
package org.springframework.web.bind.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller ⭐⭐
@ResponseBody ⭐⭐
public @interface RestController {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Controller.class
)
String value() default "";
}
2.6、测试是否成功
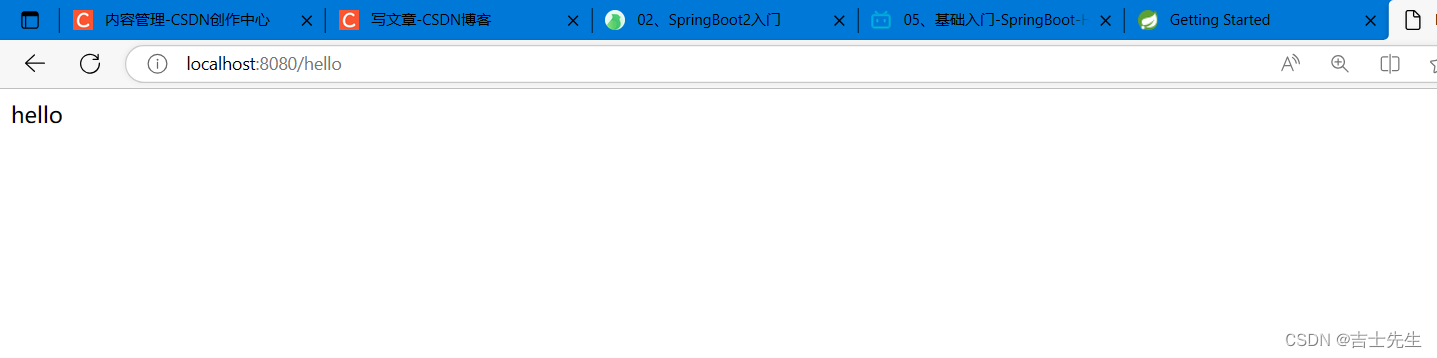
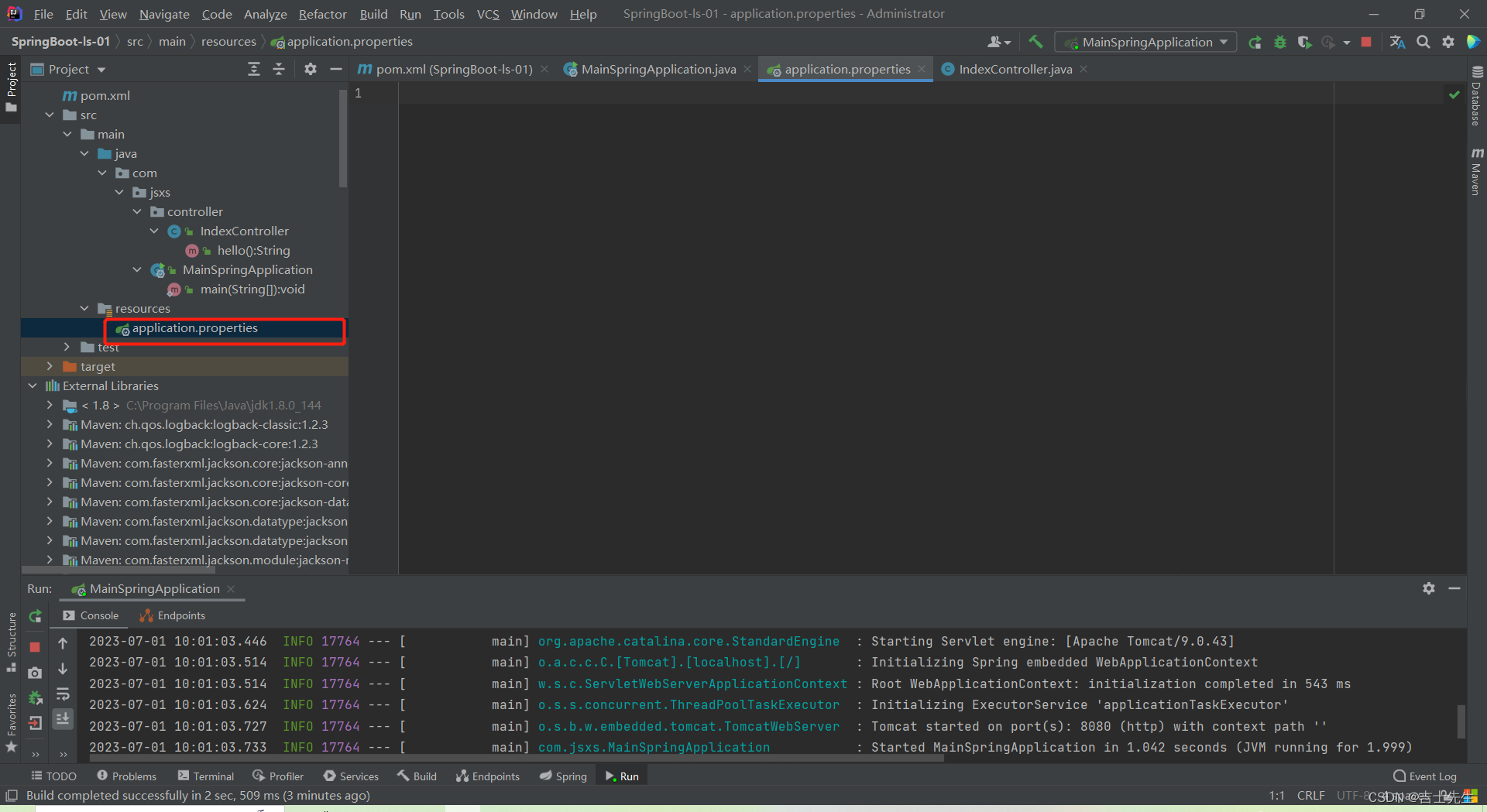
2.7、简化配置 ⭐⭐
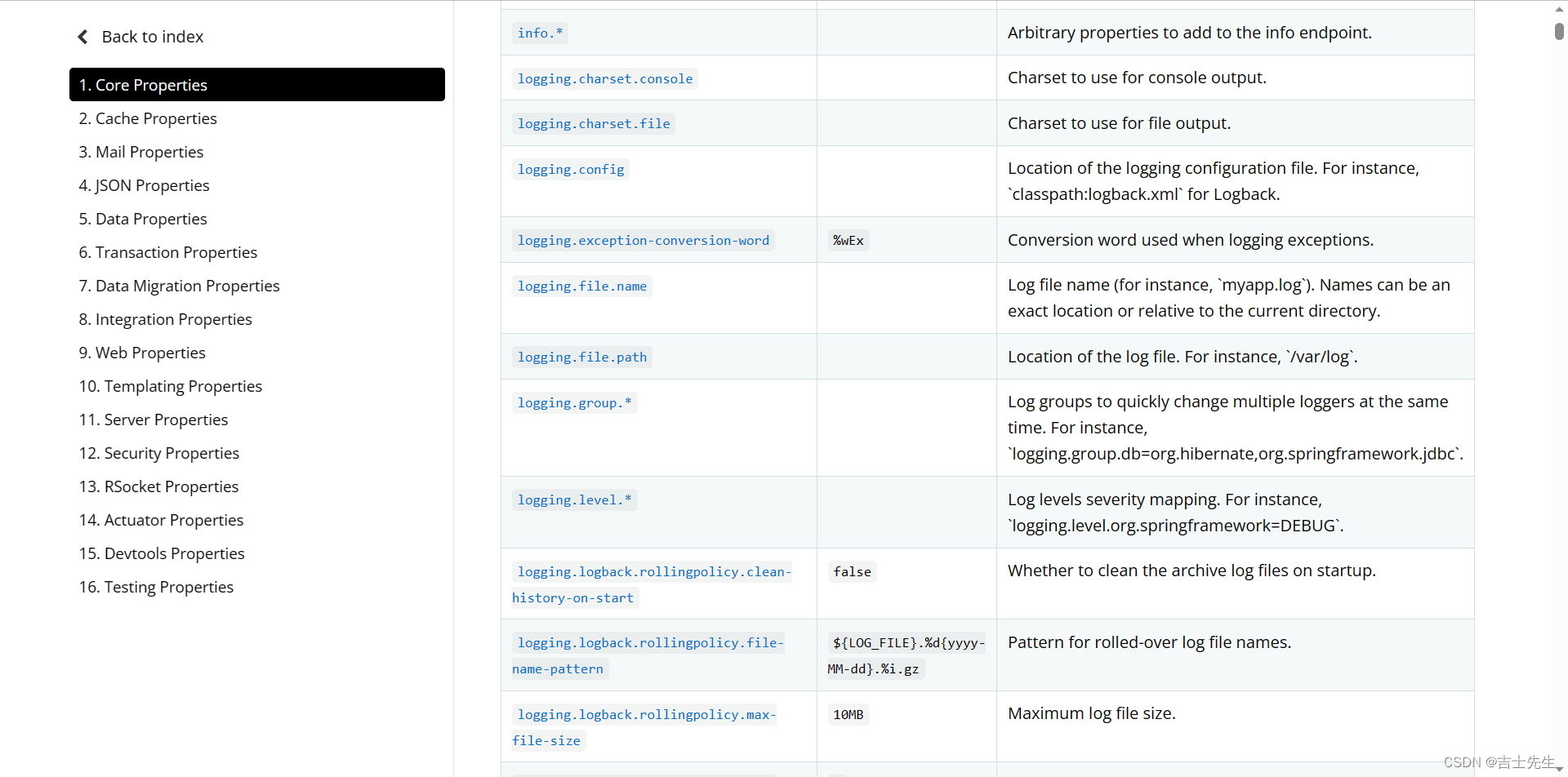
有一个统一的配置文件 : application.properties
官方配置选项: 2.4.3 application.properties配置选项
2.8、简化打包 ⭐⭐⭐
在以前我们如果需要打包一个jar包是非常繁琐的,我们需要先写入配置文件,然后打包成war包,再然后利用第三方工具进行将war包转换为jar包。
现在我们SpringBoot给我们提供了一款便捷的打包工具插件:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
然后我们在终端输入: mvn package 即可打包成功!!!
(三)、了解SpringBoot自动配置原理
1.SpringBoot特点
1.1、依赖管理
在实际开发中: 父项目是为了做依赖管理的,也就是统一管理我们软件开发的版本号。
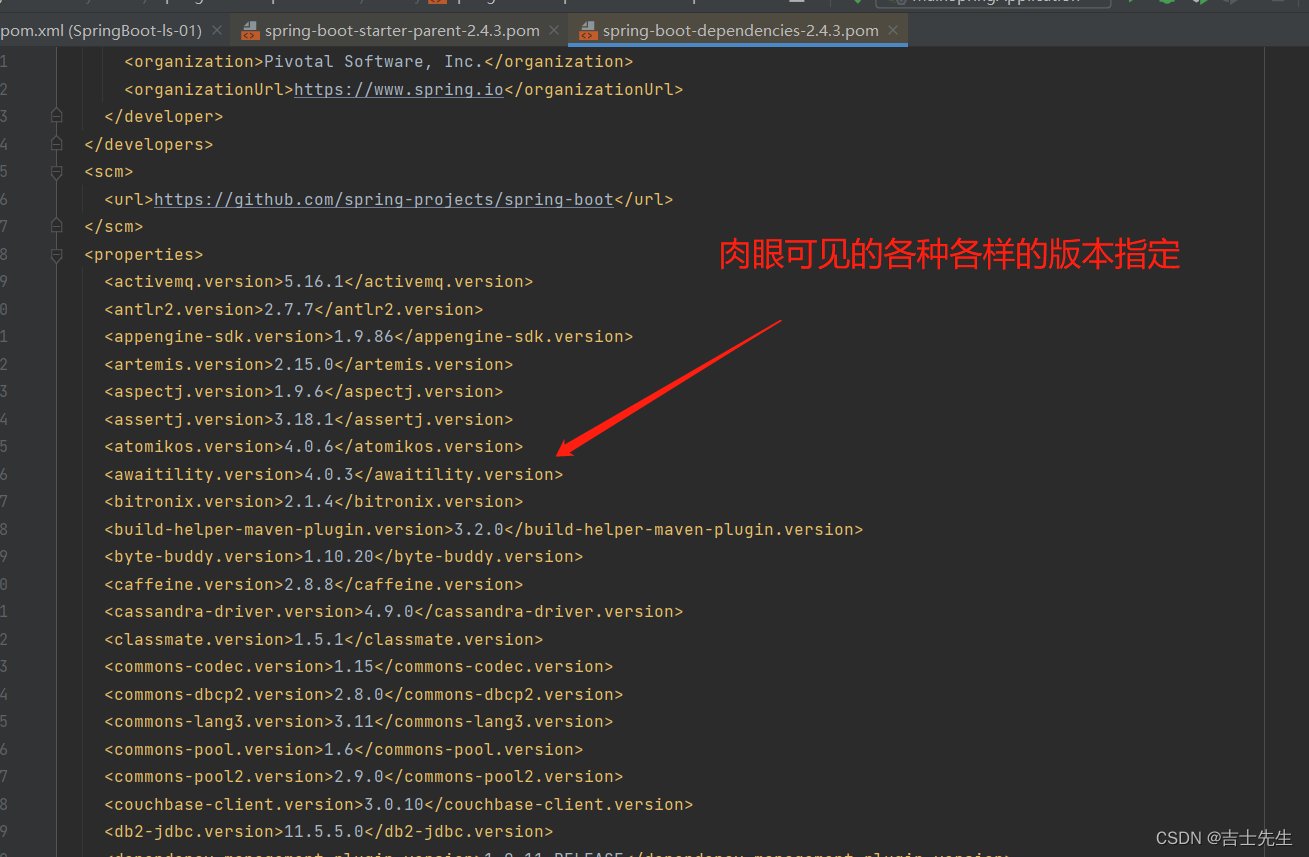
(1).父项目控制版本依赖 (自动版本仲裁机制)
依赖管理
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
他的父项目
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
几乎声明了所有开发中常用的依赖的版本号,自动版本仲裁机制
他的父项目的父项目几乎指定了所有版本信息
(2).自定义依赖版本
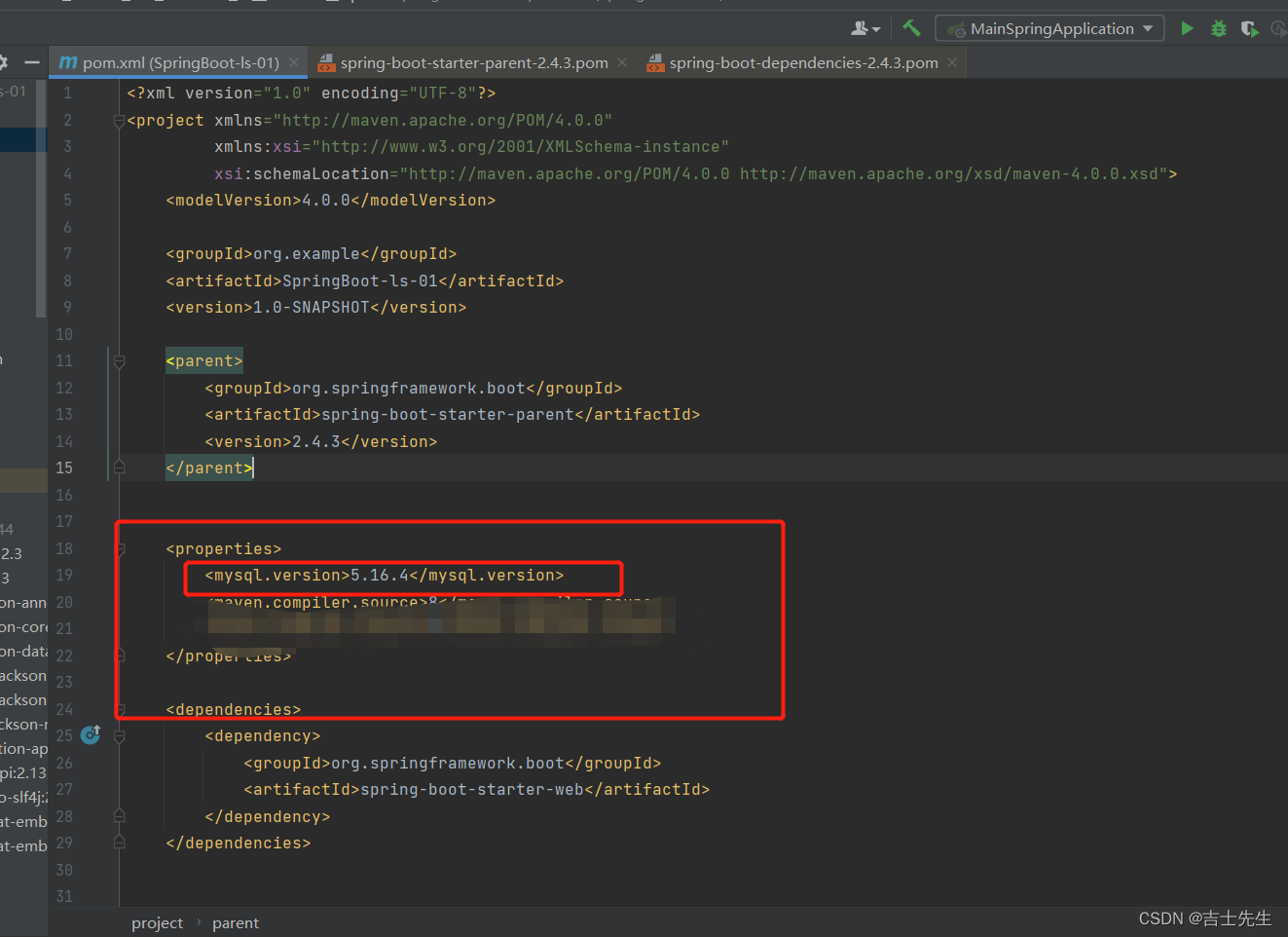
在日常工作和开发中我们会遇到SpringBoot自动生成的很多版本和我们实际需要的版本不一致的问题,我们只需要在当前的的Maven依赖管理文件中新增如下版本指定即可覆盖原有的不合实际的版本。
1、查看spring-boot-dependencies里面规定当前依赖的版本 用的 key。
2、在当前项目里面重写配置
<properties>
<mysql.version>5.16.4</mysql.version>
</properties>
(3).starter场景启动器
1、见到很多 spring-boot-starter-* : *就某种场景
2、只要引入starter,这个场景的所有常规需要的依赖我们都自动引入
3、SpringBoot所有支持的场景
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/using-spring-boot.html#using-boot-starter
4、见到的 *-spring-boot-starter: 第三方为我们提供的简化开发的场景启动器。
5、所有场景启动器最底层的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
(4).版本仲裁
1、引入依赖默认都可以不写版本
2、引入非版本仲裁的jar,要写版本号。
1.2、自动配置
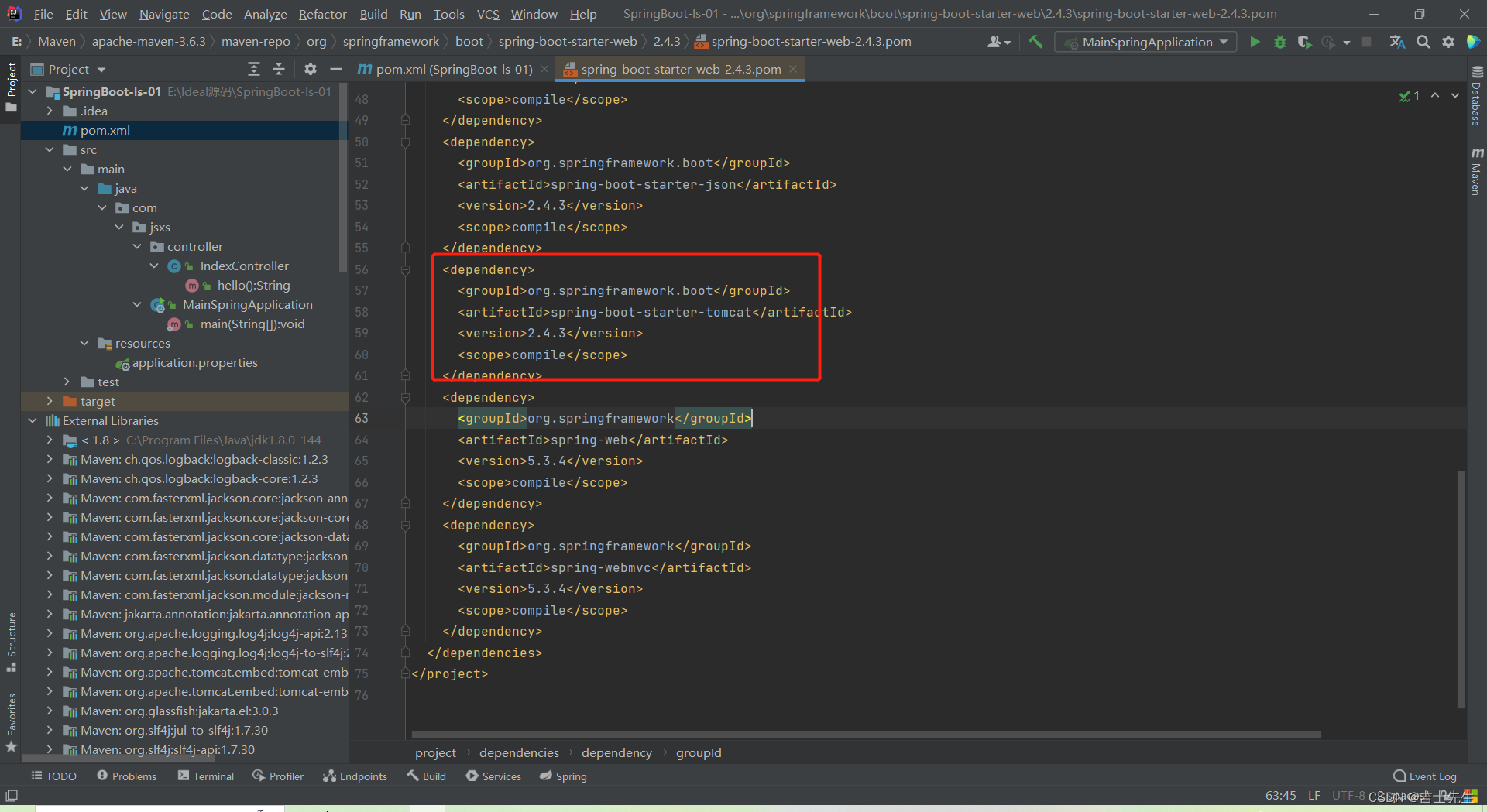
(1).自动配备 Tomcat
引入Tomcat、配置Tomcat。
我们引入的web启动器中,底层帮我们引入了tomcat
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
点击查看web启动器的源码,发现以下Tomcat配置文件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.4.3</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
(2).自动配备 SpringMVC
web启动器的源码依然帮助我们自动配备了webMVC
- 引入SpringMVC全套组件
- 自动配好SpringMVC常用组件(功能)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.3.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
(3). 自动配备 常用组件
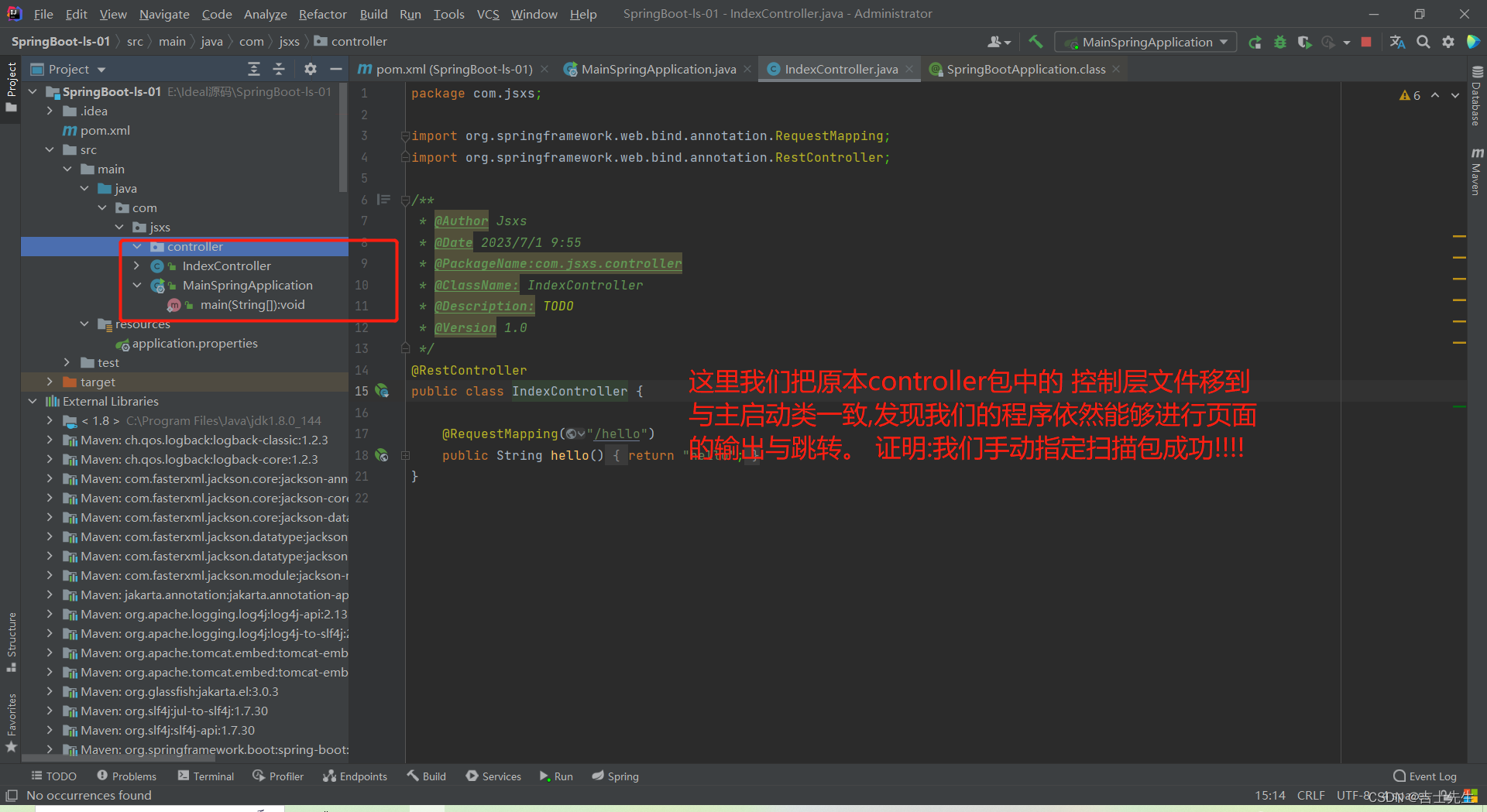
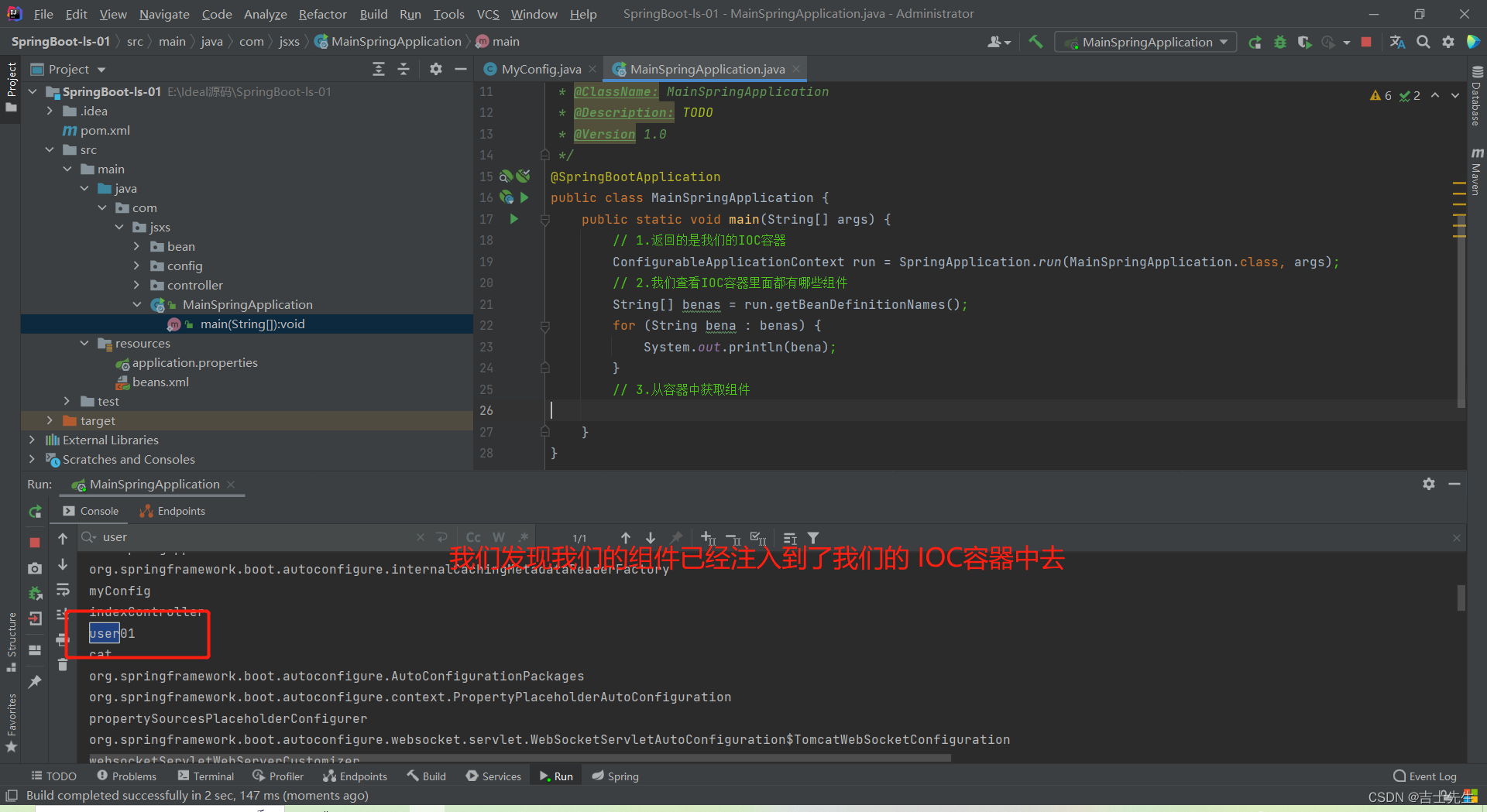
启动类返回的是IOC容器,我们查看这个IOC容器中的组件名都有哪些,就自动帮助我们配备了哪些组件。
package com.jsxs;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 9:53
* @PackageName:com.jsxs
* @ClassName: MainSpringApplication
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainSpringApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.返回的是我们的IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainSpringApplication.class, args);
// 2.我们查看IOC容器里面都有哪些组件
String[] benas = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String bena : benas) {
System.out.println(bena);
}
}
}
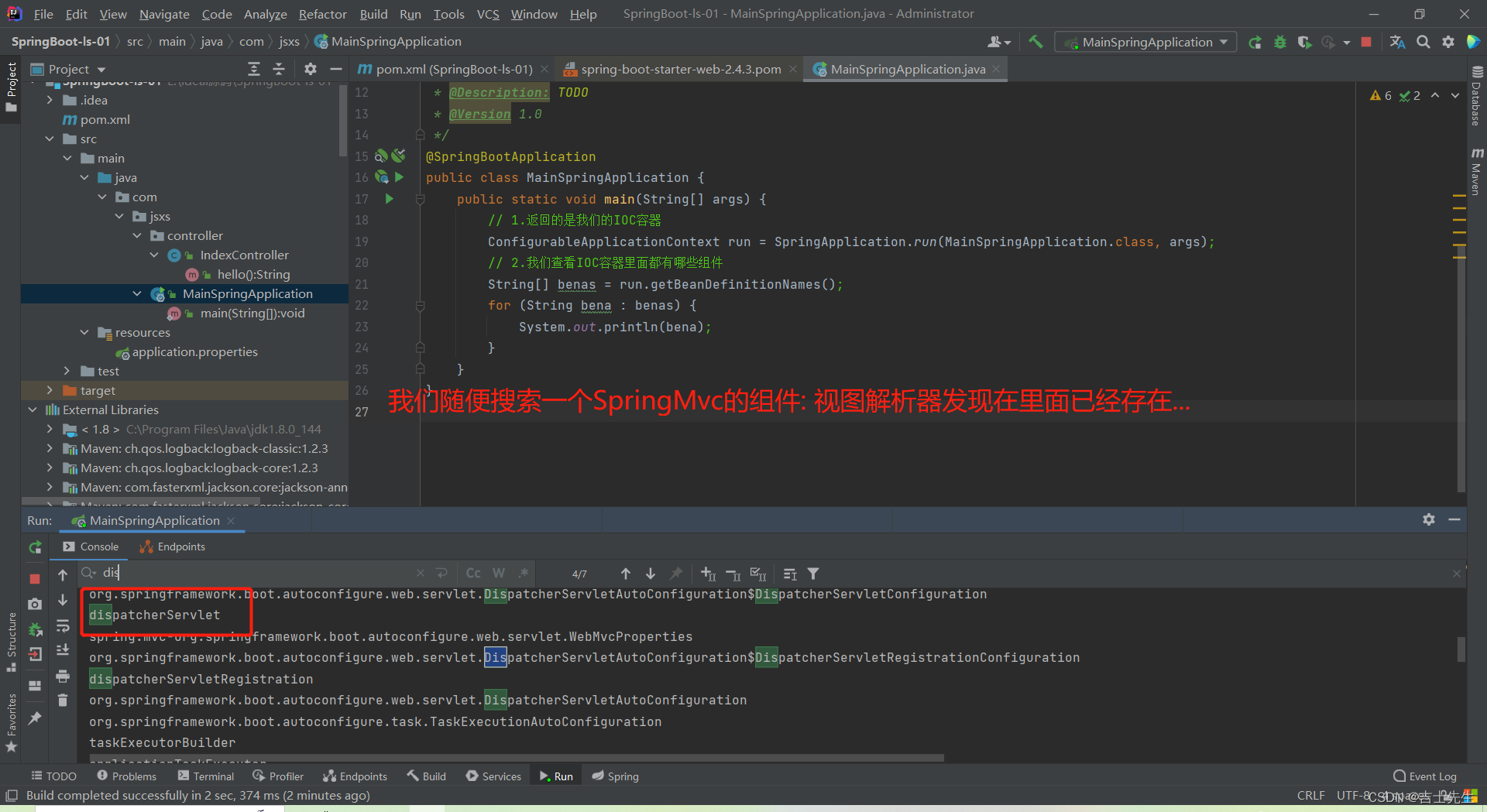
(4).默认的包结构 (修改默认扫描路径) ⭐
- 主程序所在包及其下面的所有子包里面的组件都会被默认扫描进来
com
+- example
+- myapplication
+- Application.java
|
+- customer
| +- Customer.java
| +- CustomerController.java
| +- CustomerService.java
| +- CustomerRepository.java
|
+- order
+- Order.java
+- OrderController.java
+- OrderService.java
+- OrderRepository.java
-
无需以前的包扫描配置
-
想要改变扫描路径,
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="com.atguigu")或者@ComponentScan指定扫描路径
1.在主程序的启动类上进行手动添加要扫描的位置,我们点开SpringBootApplication的注解源码发现里面存在一个value为scanBasePackages
我们只需要在这里指定扫描包的位置路径即可。
@SpringBootConfiguration + @EnableAutoConfiguration + @ComponentScan = @SpringBootApplication
package com.jsxs;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 9:53
* @PackageName:com.jsxs
* @ClassName: MainSpringApplication
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="com.jsxs")
public class MainSpringApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.返回的是我们的IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainSpringApplication.class, args);
// 2.我们查看IOC容器里面都有哪些组件
String[] benas = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String bena : benas) {
System.out.println(bena);
}
}
}
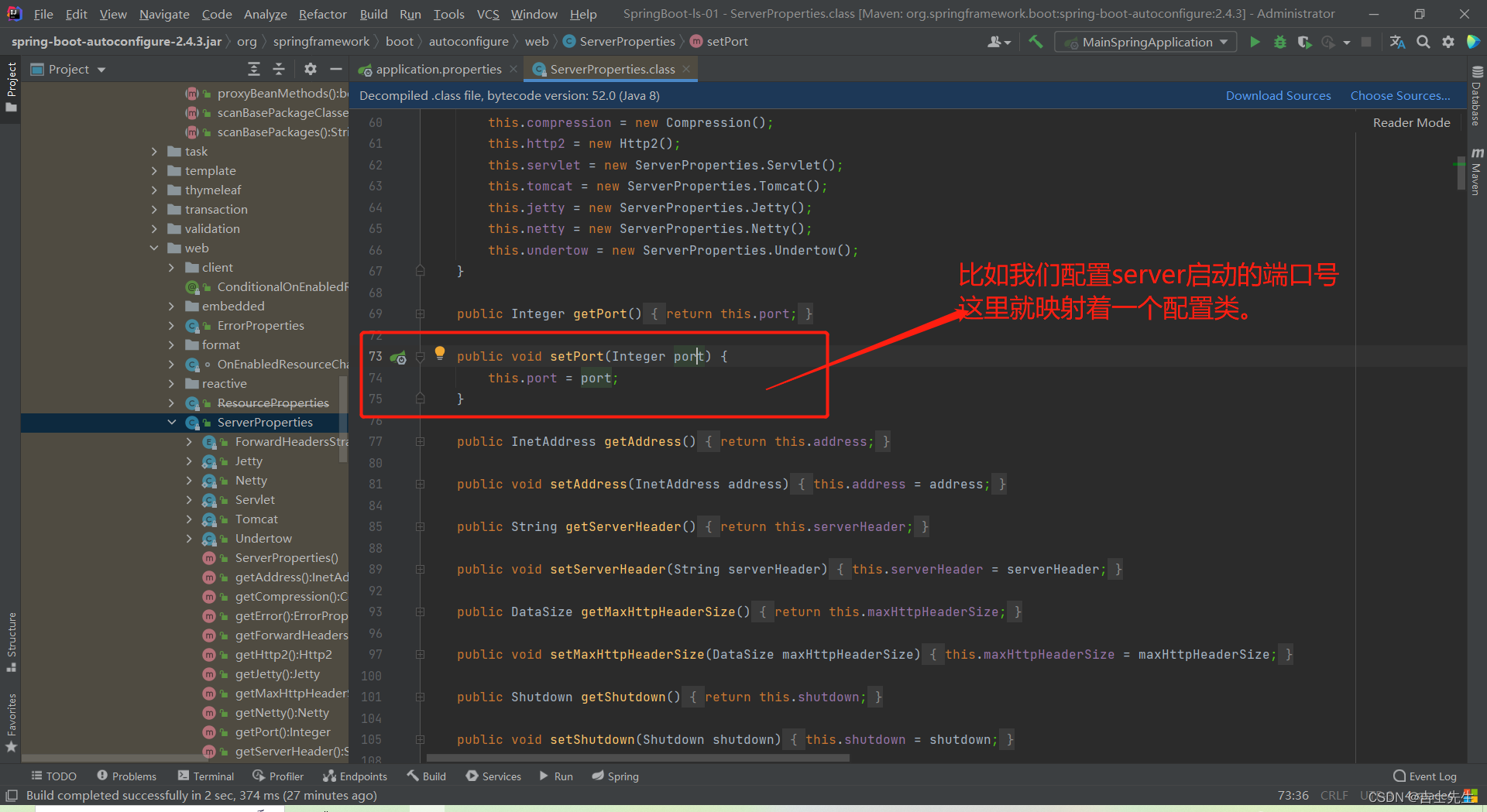
(5).自动配置 配置有用默认值
application.properties: 默认的配置其实都是映射到一个类上的

比如配置端口号映射的类名是 : ServerProperties.java
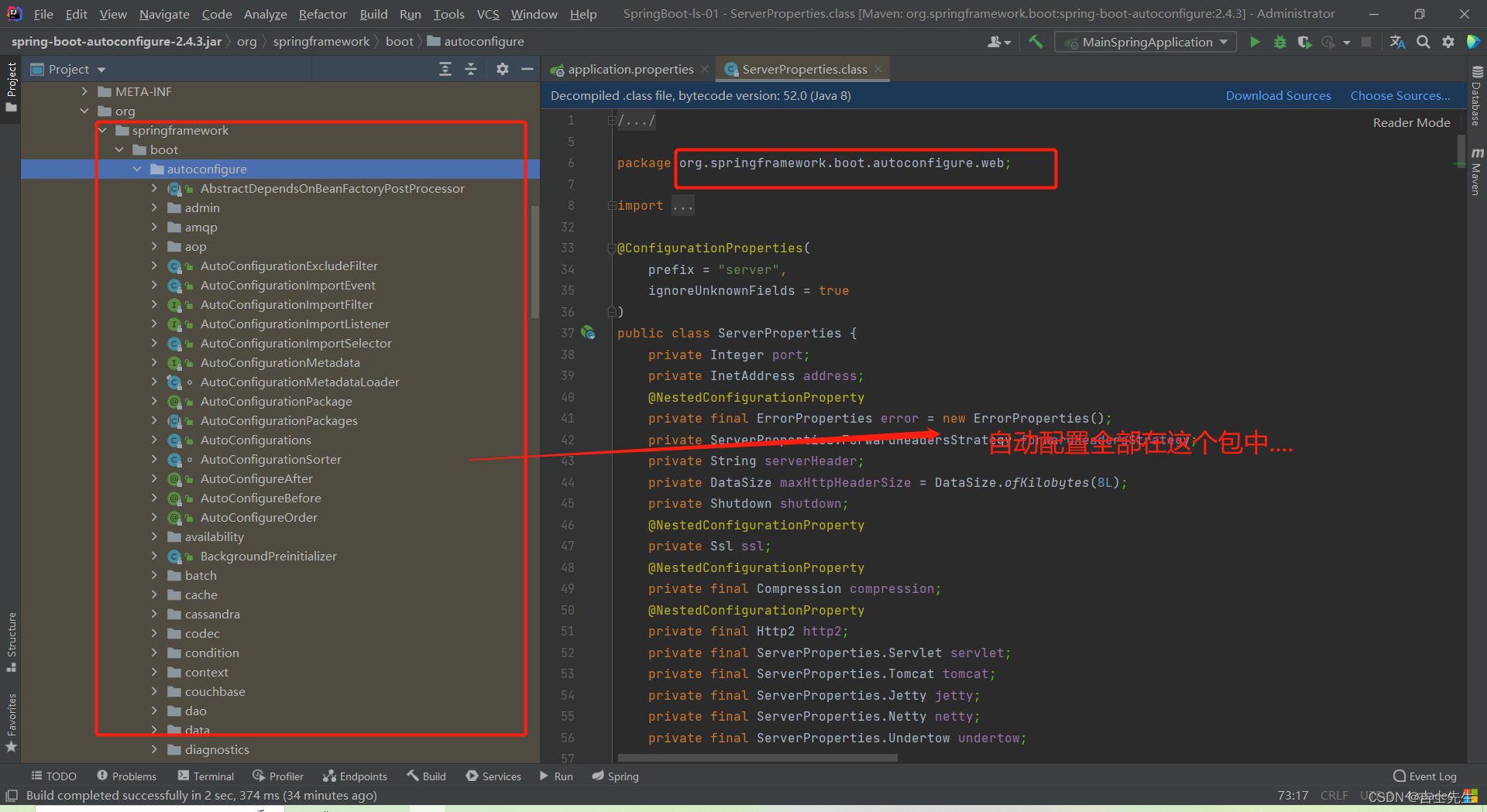
(6).按需加载自动配置项
- 非常多的starter
- 引入了哪些场景这个场景的自动配置才会开启
- SpringBoot所有的自动配置功能都在
spring-boot-autoconfigure包里面
如果我们查看源码的时候爆红,不是因为我们哪里写错了,而是我们的SpringBoot是按需配置的,没有使用上(使用依赖)就会爆红。
2.IOC容器功能
2.1、组件添加
(1).@Configuration
- 基本使用
- Full模式与Lite模式
-
- 示例
-
- 最佳实战
-
-
- 配置 类组件之间无依赖关系用Lite模式加速容器启动过程,减少判断
-
-
-
- 配置类组件之间有依赖关系,方法会被调用得到之前单实例组件,用Full模式
-
1.我们使用SpringMVC的时候如何进行组件添加的
在resources目录下创建 beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 1.指定我们的人类实体类并赋值id -->
<bean id="user01" class="com.jsxs.bean.User">
<!-- 2.给我们实体类进行默认赋值的操作 -->
<property name="name" value="李明"></property>
<property name="age" value="12"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 3.指定宠物实体类并赋值id -->
<bean id="cat" class="com.jsxs.bean.Pet">
<property name="name" value="哈吉米"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
2.现在我们省去了配置文件,直接使用@Configuration注解即可
package com.jsxs.config;
import com.jsxs.bean.Pet;
import com.jsxs.bean.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 12:30
* @PackageName:com.config
* @ClassName: MyConfig
* @Description: TODO 1.配置类里面使用@Bean标注在方法上给容器注册组件,默认也是单实列的,
* @Description: TODO 2.配置类(类名)本身也是一个组件,即在这个列子中有三个组件并不是俩个。
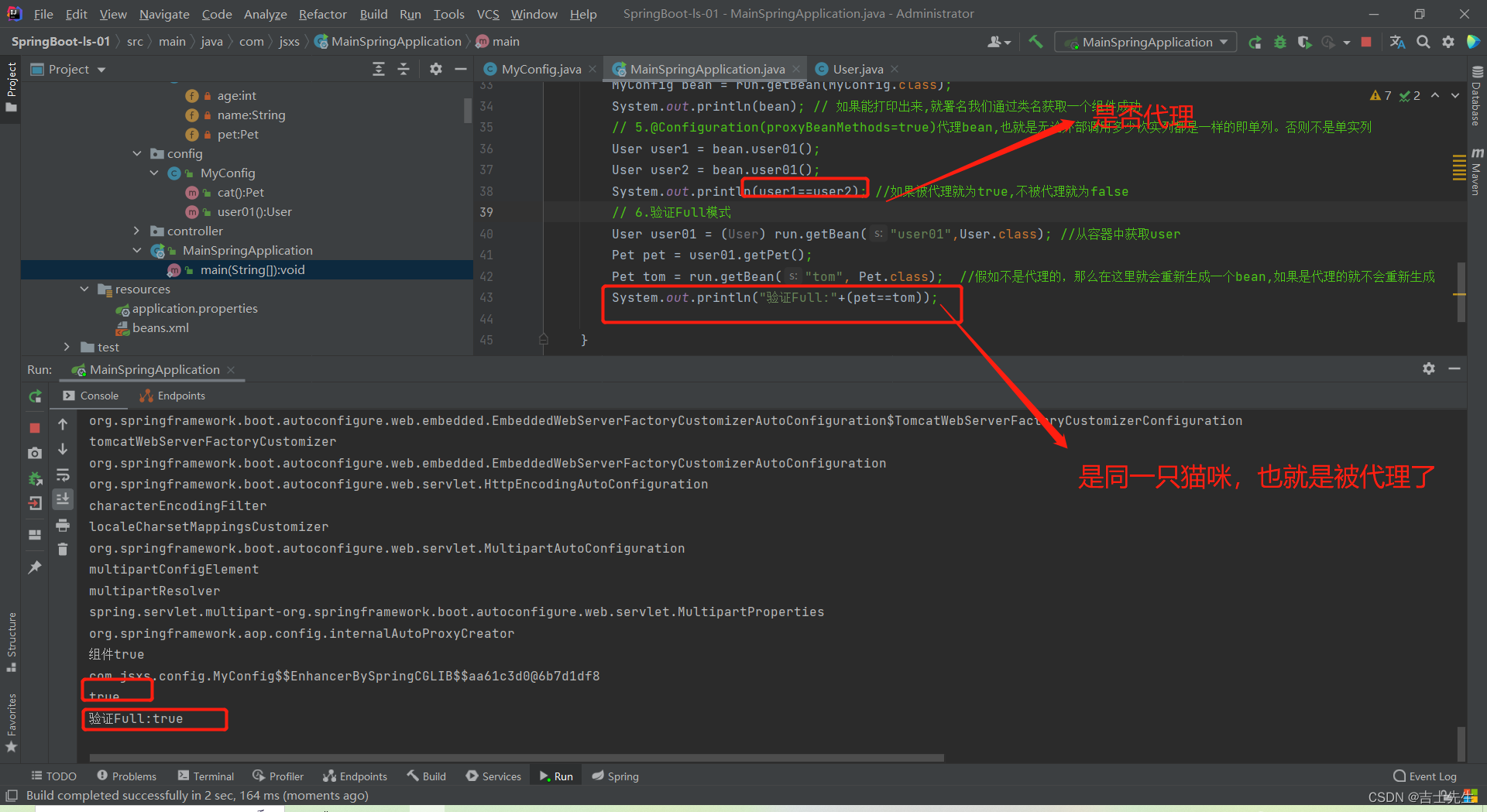
* @Description: TODO 3.@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true)代理bean,也就是无论外部调用多少次实列都是一样的即单列。否则不是单实列
* Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)、【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
* Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
* 组件依赖必须使用Full模式默认。其他默认是否Lite模式
*
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=false) // 告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类,相当于以前的配置文件 beans.xml
public class MyConfig {
@Bean // 1. 这里相当于我们配置文件中的<bena></bean>标签
// 2. User对应的是我们配置文件的class非全限定名, user01对应我们配置文件的id
public User user01() {
// FULL模式人拥有宠物
return new User("李明",12,this.cat());
}
@Bean("tom") // 相当于我们配置文件的bean标签
public Pet cat(){ // Pet指的是calss的非全限定名, cat指定的是id
return new Pet("哈吉米");
}
}
- 什么时候用到Full模式或List模式呢?
组件依赖必须使用Full模式默认。其他默认是否Lite模式。通俗的讲就是如果这个容器下面没人用了我们就设置成false,如果仍然有人是用的话,我们就设置成true。
- 区别: 设置成fasle会跳过检查是否容器中已经存在,提升性能。
列子: 用户拥有容器中注册的哈吉米猫,我们要使用FULL模式,因为要保证用户有的是唯一的,即用户拥有的哈吉米猫和容器中组件的哈吉米猫是一样的。
User.java
package com.jsxs.bean;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 12:11
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.bean
* @ClassName: User
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
//
private Pet pet;
}
config.java 设置为FULL模式
package com.jsxs.config;
import com.jsxs.bean.Pet;
import com.jsxs.bean.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 12:30
* @PackageName:com.config
* @ClassName: MyConfig
* @Description: TODO 1.配置类里面使用@Bean标注在方法上给容器注册组件,默认也是单实列的,
* @Description: TODO 2.配置类(类名)本身也是一个组件,即在这个列子中有三个组件并不是俩个。
* @Description: TODO 3.@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true)代理bean,也就是无论外部调用多少次实列都是一样的即单列。否则不是单实列
* Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)、【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
* Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
* 组件依赖必须使用Full模式默认。其他默认是否Lite模式
*
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true) ⭐// 告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类,相当于以前的配置文件 beans.xml
public class MyConfig {
@Bean // 1. 这里相当于我们配置文件中的<bena></bean>标签
// 2. User对应的是我们配置文件的class非全限定名, user01对应我们配置文件的id
public User user01() {
// FULL模式人拥有宠物
return new User("李明",12,this.cat());
}
@Bean("tom") // 相当于我们配置文件的bean标签
public Pet cat(){ // Pet指的是calss的非全限定名, cat指定的是id
return new Pet("哈吉米");
}
}
(2).@Bean、@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository
1.SpringMVC提供的这些注解,只要在SpringBoot扫描包的范围内仍然可以进行注册组件。
1. @Bean 注册配置类组件
2. @Component 除了配置类组件不能使用,其余万能
3. @Controller 控制层组件
4. @Service 业务层组件
5. @Repository 实体类层组件
(3).@ComponentScan、@Import
1.@ComponentScan 组件
通过这个注解我们可以手动的更改SpringBoot默认的扫描路径。
2. @Import
用法:
1. @imoort 用于放在容器中组件类上。
用途
2. @imoort 用于给容器中导入 自定义组件或第三方组件
结论
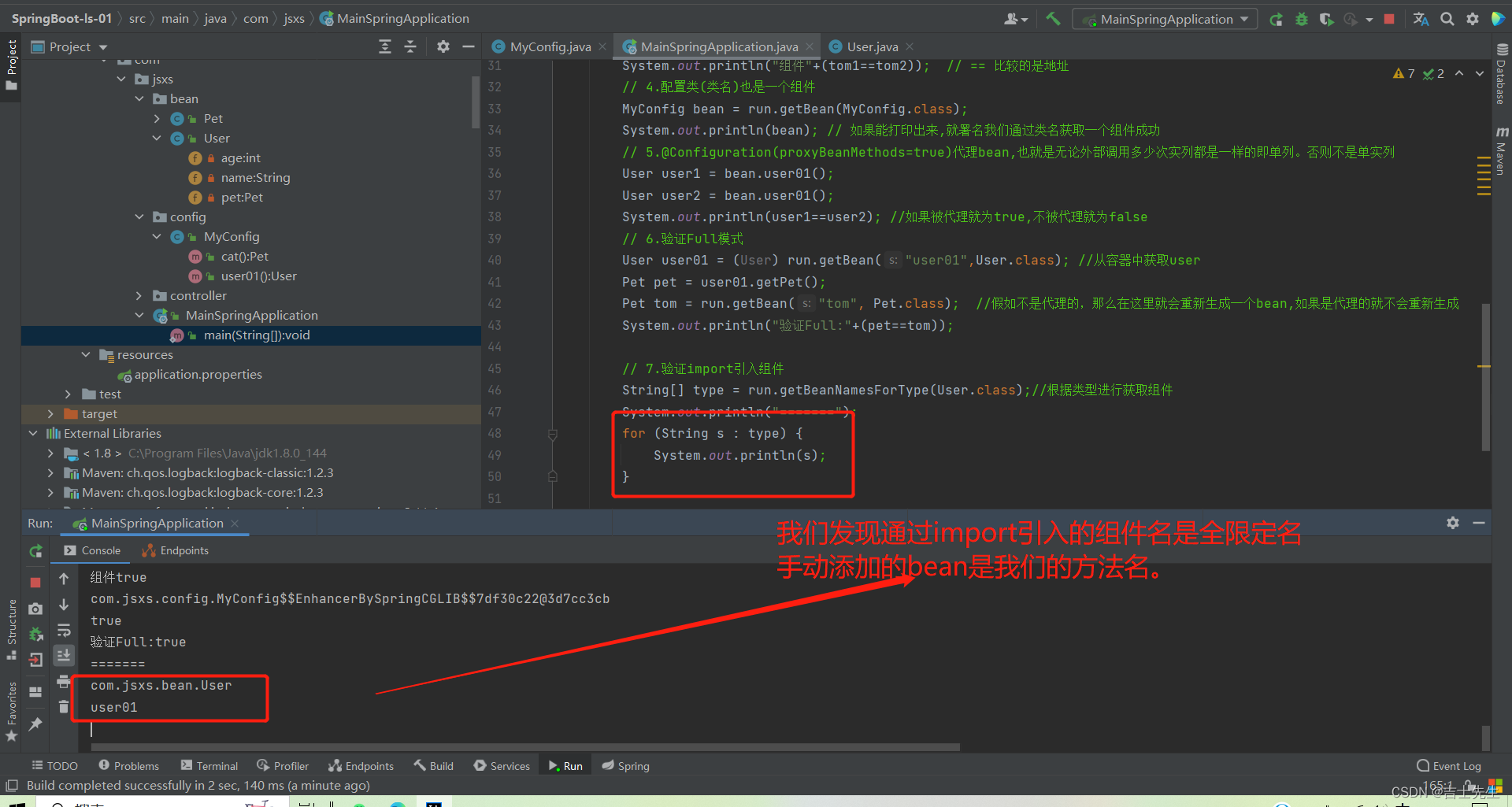
3. @import引入组件和手动添加组件结果都添加到容器中去了,但是获取到的组件名有点区别: 引入的获得的名字是全限定名,手动的不是全限定名。
package com.jsxs.config;
import com.jsxs.bean.Pet;
import com.jsxs.bean.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 12:30
* @PackageName:com.config
* @ClassName: MyConfig
* @Description: TODO 1.配置类里面使用@Bean标注在方法上给容器注册组件,默认也是单实列的,
* @Description: TODO 2.配置类(类名)本身也是一个组件,即在这个列子中有三个组件并不是俩个。
* @Description: TODO 3.@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true)代理bean,也就是无论外部调用多少次实列都是一样的即单列。否则不是单实列
* Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)、【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
* Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
* 组件依赖必须使用Full模式默认。其他默认是否Lite模式
*
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Import({User.class}) ⭐⭐
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true) // 告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类,相当于以前的配置文件 beans.xml
public class MyConfig {
@Bean // 1. 这里相当于我们配置文件中的<bena></bean>标签
// 2. User对应的是我们配置文件的class非全限定名, user01对应我们配置文件的id
public User user01() {
// FULL模式人拥有宠物
return new User("李明",12,this.cat());
}
@Bean("tom") // 相当于我们配置文件的bean标签
public Pet cat(){ // Pet指的是calss的非全限定名, cat指定的是id
return new Pet("哈吉米");
}
}
package com.jsxs;
import com.jsxs.bean.Pet;
import com.jsxs.bean.User;
import com.jsxs.config.MyConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 9:53
* @PackageName:com.jsxs
* @ClassName: MainSpringApplication
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainSpringApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.返回的是我们的IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainSpringApplication.class, args);
// 2.我们查看IOC容器里面都有哪些组件
String[] benas = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String bena : benas) {
System.out.println(bena);
}
// 3.从IOC容器中获取组件,结果为true证明是单实列的。Bean是一个组件
Pet tom1 = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class);
Pet tom2 = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class);
System.out.println("组件"+(tom1==tom2)); // == 比较的是地址
// 4.配置类(类名)也是一个组件
MyConfig bean = run.getBean(MyConfig.class);
System.out.println(bean); // 如果能打印出来,就署名我们通过类名获取一个组件成功
// 5.@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true)代理bean,也就是无论外部调用多少次实列都是一样的即单列。否则不是单实列
User user1 = bean.user01();
User user2 = bean.user01();
System.out.println(user1==user2); //如果被代理就为true,不被代理就为false
// 6.验证Full模式
User user01 = (User) run.getBean("user01",User.class); //从容器中获取user
Pet pet = user01.getPet();
Pet tom = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class); //假如不是代理的,那么在这里就会重新生成一个bean,如果是代理的就不会重新生成
System.out.println("验证Full:"+(pet==tom));
// 7.验证import引入组件
String[] type = run.getBeanNamesForType(User.class);//根据类型进行获取组件
System.out.println("======="); ⭐⭐⭐
for (String s : type) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
(4).@Conditional
条件装配:满足Conditional指定的条件,则进行组件注入
1.当组件中存在某个组件的时候才执行注册
1.作用域: 类上或者方法上。
假如标注到方法上,当这个条件注解为真的时候,这个方法上的注册才生效。当标注到类上的时候,当条件为假的时候,这个类上的所有方法都不生效(也就不会注入到IOC)。
@ConditionalOnBean(name = "tom") // 当整个IOC容器中存在tom这个容器,我们就注册user01这个组件否则不注册
我们这里对tom容器进行了注释,也就是说IOC容器中不存在tom容器了。
package com.jsxs.config;
import com.jsxs.bean.Pet;
import com.jsxs.bean.User;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 12:30
* @PackageName:com.config
* @ClassName: MyConfig
* @Description: TODO 1.配置类里面使用@Bean标注在方法上给容器注册组件,默认也是单实列的,
* @Description: TODO 2.配置类(类名)本身也是一个组件,即在这个列子中有三个组件并不是俩个。
* @Description: TODO 3.@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true)代理bean,也就是无论外部调用多少次实列都是一样的即单列。否则不是单实列
* Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)、【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
* Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
* 组件依赖必须使用Full模式默认。其他默认是否Lite模式
*
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Import({User.class})
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true) // 告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类,相当于以前的配置文件 beans.xml
public class MyConfig {
@ConditionalOnBean(name = "tom") // 当整个IOC容器中存在tom这个容器,我们就注册user01这个组件否则不注册
@Bean // 1. 这里相当于我们配置文件中的<bena></bean>标签
// 2. User对应的是我们配置文件的class非全限定名, user01对应我们配置文件的id
public User user01() {
// FULL模式人拥有宠物
return new User("李明",12,this.cat());
}
// @Bean("tom") // 相当于我们配置文件的bean标签
public Pet cat(){ // Pet指的是calss的非全限定名, cat指定的是id
return new Pet("哈吉米");
}
}
package com.jsxs;
import com.jsxs.bean.Pet;
import com.jsxs.bean.User;
import com.jsxs.config.MyConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 9:53
* @PackageName:com.jsxs
* @ClassName: MainSpringApplication
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainSpringApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.返回的是我们的IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainSpringApplication.class, args);
// 2.我们查看IOC容器里面都有哪些组件
String[] benas = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String bena : benas) {
System.out.println(bena);
}
// 1.测试容器中是否有tom这个组件
boolean flag = run.containsBean("tom");
System.out.println("IOC容器是否有tom容器:"+flag);
boolean b = run.containsBean("user01");
System.out.println("IOC容器中是否有user01这个容器:"+b);
}
}
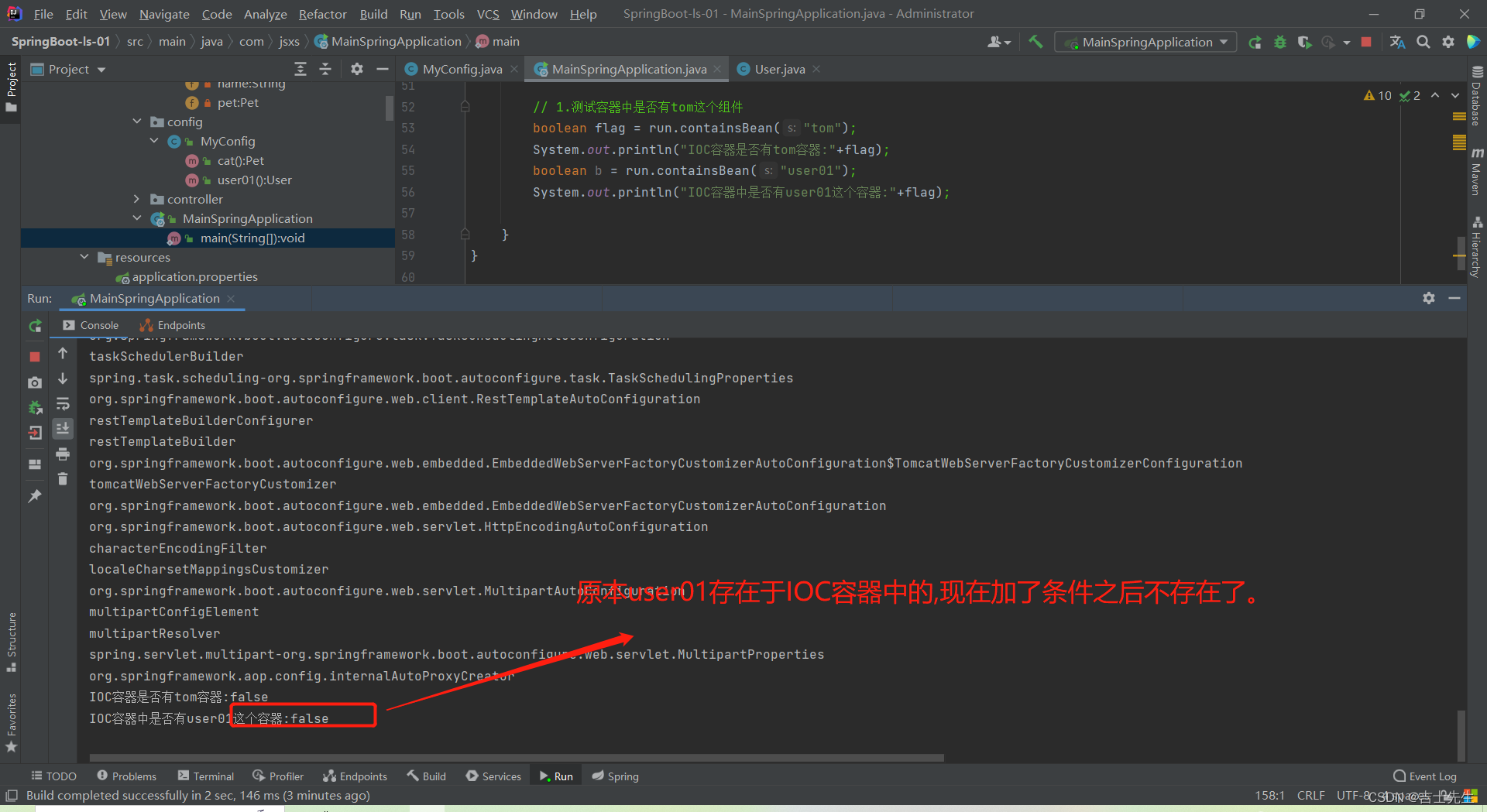
- 当容器中没有指定的组件的时候才执行
package com.jsxs.config;
import com.jsxs.bean.Pet;
import com.jsxs.bean.User;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 12:30
* @PackageName:com.config
* @ClassName: MyConfig
* @Description: TODO 1.配置类里面使用@Bean标注在方法上给容器注册组件,默认也是单实列的,
* @Description: TODO 2.配置类(类名)本身也是一个组件,即在这个列子中有三个组件并不是俩个。
* @Description: TODO 3.@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true)代理bean,也就是无论外部调用多少次实列都是一样的即单列。否则不是单实列
* Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)、【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
* Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
* 组件依赖必须使用Full模式默认。其他默认是否Lite模式
*
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Import({User.class})
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true) // 告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类,相当于以前的配置文件 beans.xml
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "tom") // 当整个IOC容器中存在tom这个容器,我们就注册user01这个组件否则不注册
public class MyConfig {
@Bean // 1. 这里相当于我们配置文件中的<bena></bean>标签
// 2. User对应的是我们配置文件的class非全限定名, user01对应我们配置文件的id
public User user01() {
// FULL模式人拥有宠物
return new User("李明",12,this.cat());
}
// @Bean("tom") // 相当于我们配置文件的bean标签
public Pet cat(){ // Pet指的是calss的非全限定名, cat指定的是id
return new Pet("哈吉米");
}
}
package com.jsxs;
import com.jsxs.bean.Pet;
import com.jsxs.bean.User;
import com.jsxs.config.MyConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 9:53
* @PackageName:com.jsxs
* @ClassName: MainSpringApplication
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainSpringApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.返回的是我们的IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainSpringApplication.class, args);
// 2.我们查看IOC容器里面都有哪些组件
String[] benas = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String bena : benas) {
System.out.println(bena);
}
// 1.测试容器中是否有tom这个组件
boolean flag = run.containsBean("tom");
System.out.println("IOC容器是否有tom容器:"+flag);
boolean b = run.containsBean("user01");
System.out.println("IOC容器中是否有user01这个容器:"+b);
}
}
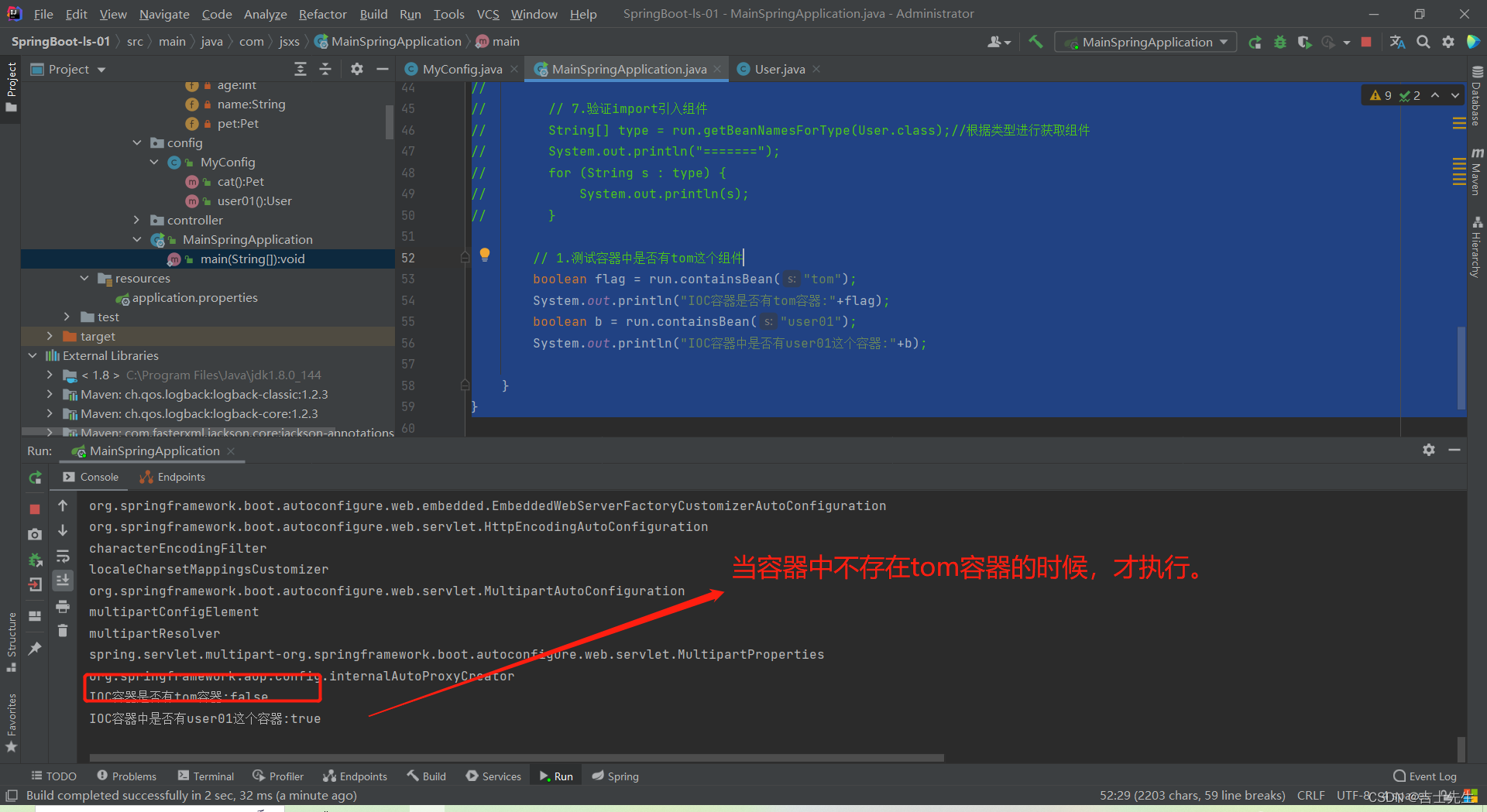
2.2、原生配置文件引入 (只能放在类级别的注解上)
1.作用:
我们使用SpringBoot框架之后,SpringMvc支持的beans.xml配置文件不会被SpringBoot进行解析,这时候我们想要SpringBoot帮助我们解析beans.xml
2.用法:
文件的话,我们可以在任意一个IOC容器组件类上进行@ImportResource()即可
这个注解放在任意一个IOC容器类组件上即可。(放一个即可)
classpath: 指的是resource目录下
@ImportResource("classpath:beans.xml")
(1). 尚未使用 @ImportResource
/resource/benas.xml: 我们对id名进行修改(避嫌),进行查找是否存在这两个组件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 1.指定我们的人类实体类并赋值id -->
<bean id="haha" class="com.jsxs.bean.User">
<!-- 2.给我们实体类进行默认赋值的操作 -->
<property name="name" value="李明"></property>
<property name="age" value="12"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 3.指定宠物实体类并赋值id -->
<bean id="hehe" class="com.jsxs.bean.Pet">
<property name="name" value="哈吉米"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
查询结果:是查询不到的。因为SpringBoot识别不了这个beans.xml文件
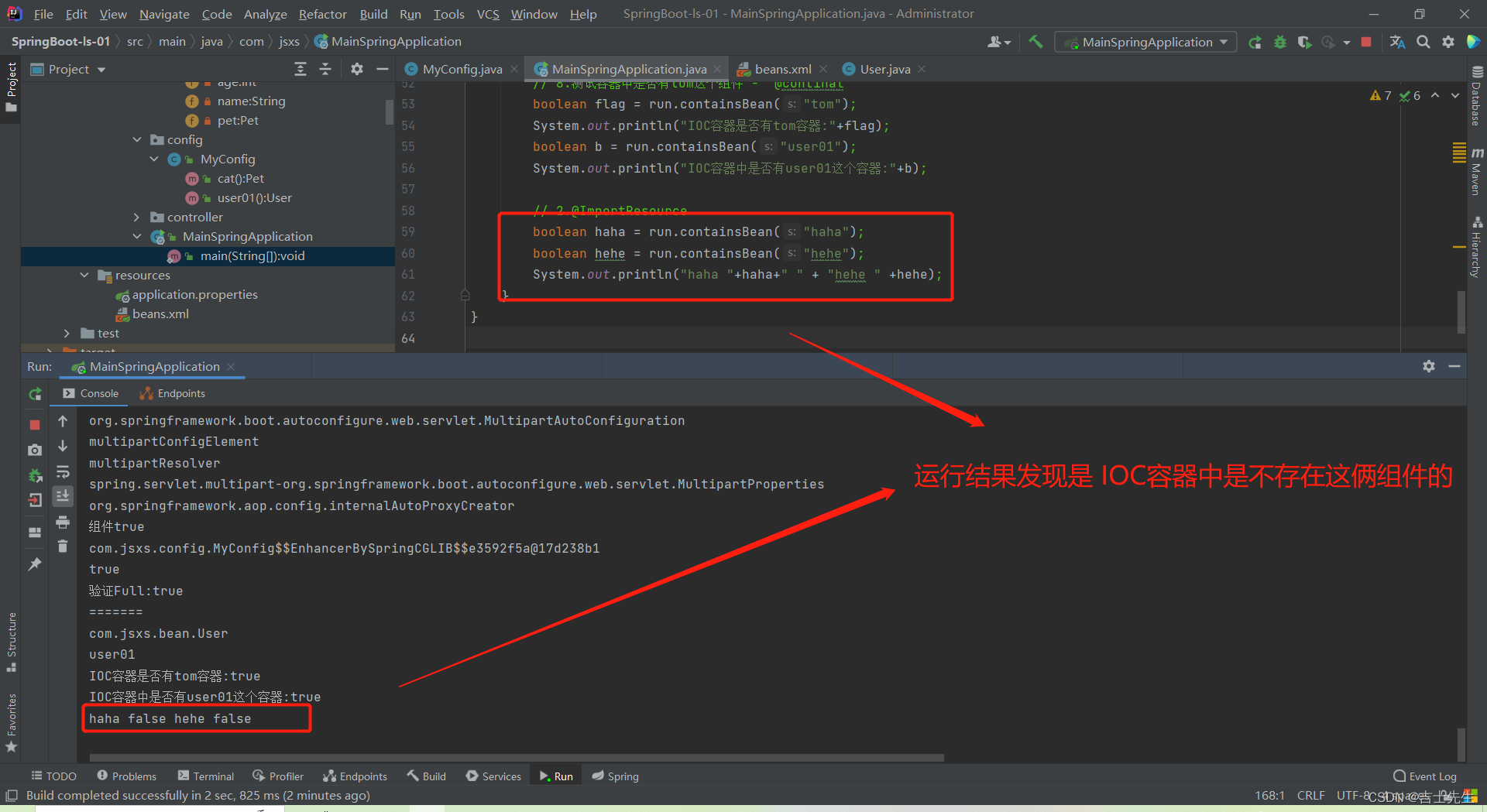
(2). 引用 @ImportResource
package com.jsxs.config;
import com.jsxs.bean.Pet;
import com.jsxs.bean.User;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 12:30
* @PackageName:com.config
* @ClassName: MyConfig
* @Description: TODO 1.配置类里面使用@Bean标注在方法上给容器注册组件,默认也是单实列的,
* @Description: TODO 2.配置类(类名)本身也是一个组件,即在这个列子中有三个组件并不是俩个。
* @Description: TODO 3.@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true)代理bean,也就是无论外部调用多少次实列都是一样的即单列。否则不是单实列
* Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)、【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
* Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
* 组件依赖必须使用Full模式默认。其他默认是否Lite模式
*
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Import({User.class})
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true) // 告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类,相当于以前的配置文件 beans.xml
//@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "tom") // 当整个IOC容器中存在tom这个容器,我们就注册user01这个组件否则不注册
@ImportResource("classpath:beans.xml")
public class MyConfig {
@Bean // 1. 这里相当于我们配置文件中的<bena></bean>标签
// 2. User对应的是我们配置文件的class非全限定名, user01对应我们配置文件的id
public User user01() {
// FULL模式人拥有宠物
return new User("李明",12,this.cat());
}
@Bean("tom") // 相当于我们配置文件的bean标签
public Pet cat(){ // Pet指的是calss的非全限定名, cat指定的是id
return new Pet("哈吉米");
}
}
package com.jsxs;
import com.jsxs.bean.Pet;
import com.jsxs.bean.User;
import com.jsxs.config.MyConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 9:53
* @PackageName:com.jsxs
* @ClassName: MainSpringApplication
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainSpringApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.返回的是我们的IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainSpringApplication.class, args);
// 2.我们查看IOC容器里面都有哪些组件
String[] benas = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String bena : benas) {
System.out.println(bena);
}
// 9.@ImportResource ⭐
boolean haha = run.containsBean("haha");
boolean hehe = run.containsBean("hehe");
System.out.println("haha "+haha+" " + "hehe " +hehe);
}
}

2.3、配置绑定
就是实体类通过配置文件进行赋值。
切记:任何一个注解都只对IOC容器生效,如果注解没有加入IOC容器中去,那么会爆红且报错
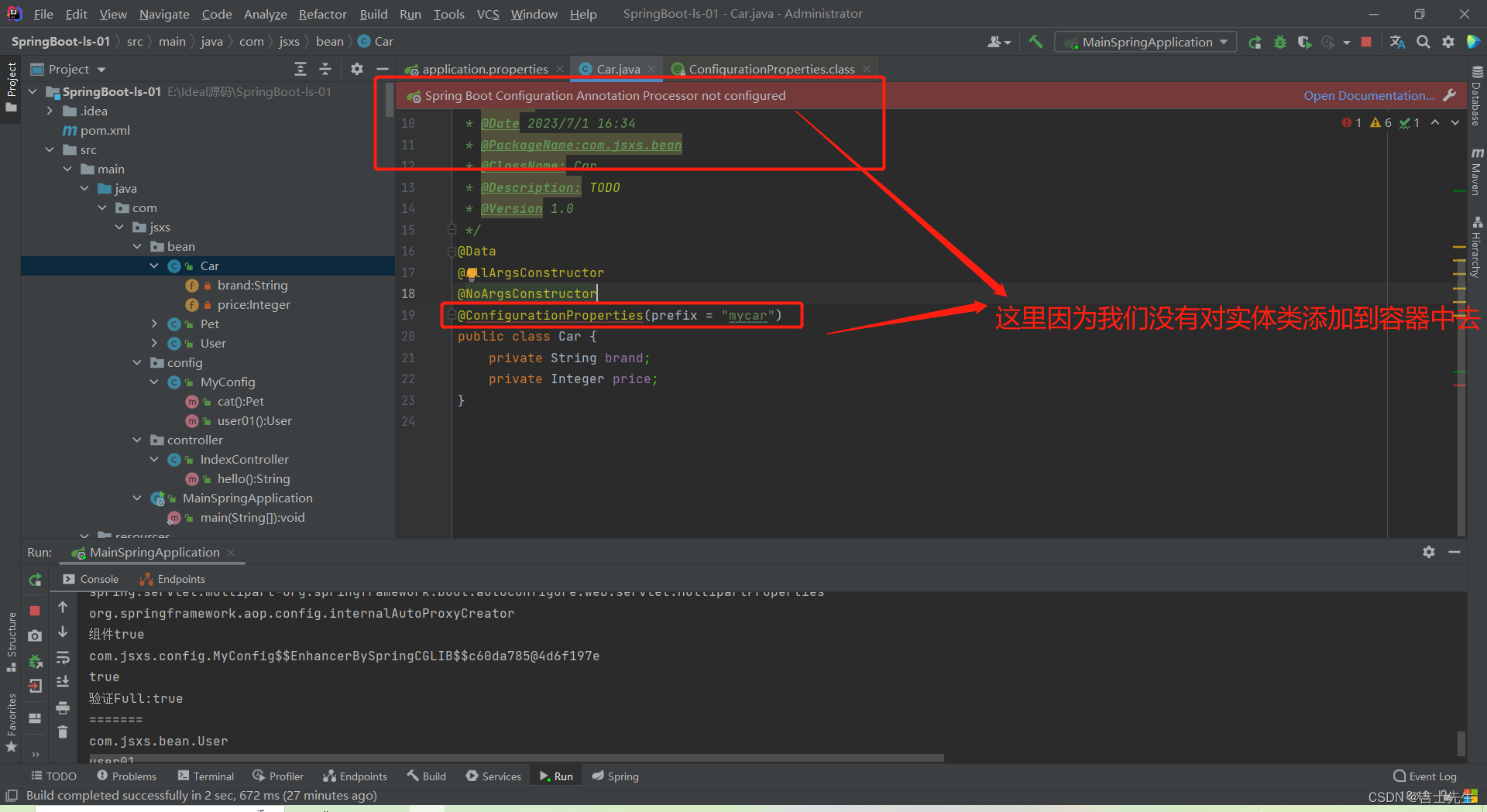
(1).@ConfigurationProperties (第一种)
前缀指的是 .属性 前面的那个单词就是前缀。
我们在使用@ConfigurationProperties注解的时候,指定的前缀就是 .属性前面的那个单词。
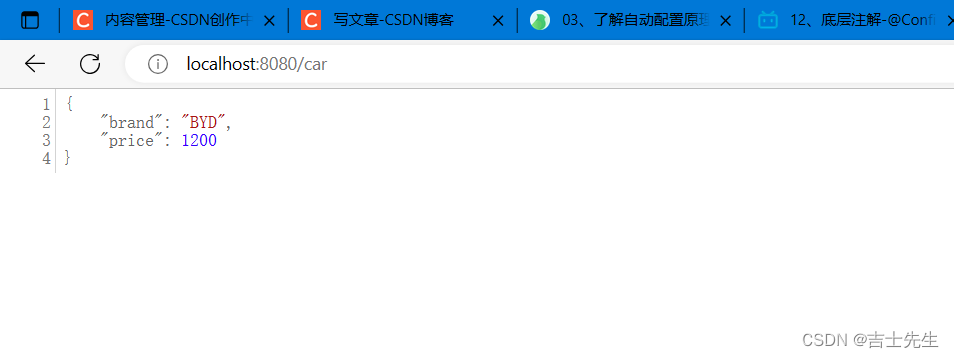
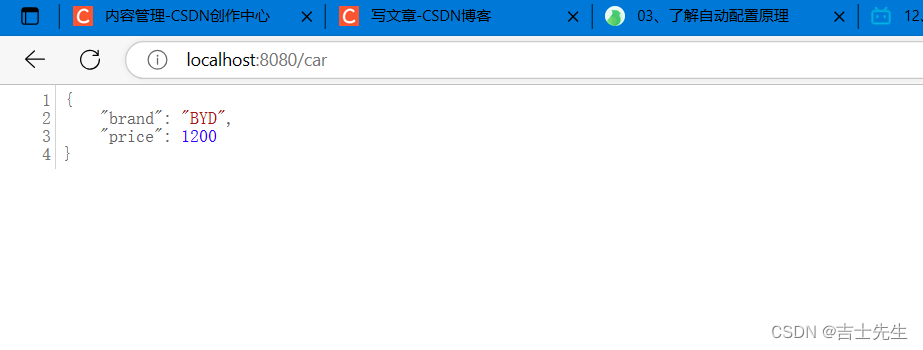
1.application.properties
server.port=8080
mycar.brand=BYD
mycar.price=1200
2.进行配置绑定
package com.jsxs.bean;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 16:34
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.bean
* @ClassName: Car
* @Description: TODO 只会在IOC容器中的组件,才会拥有SprngBoot提供的强大功能
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Data
@Repository
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar") // 添加上前缀
public class Car {
private String brand;
private Integer price;
}
3.注解的源码:
这里prefix与value互为别名
package org.springframework.boot.context.properties;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ConfigurationProperties {
@AliasFor("prefix")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String prefix() default "";
boolean ignoreInvalidFields() default false;
boolean ignoreUnknownFields() default true;
}
4.controller进行测试
package com.jsxs.controller;
import com.jsxs.bean.Car;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 9:55
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.controller
* @ClassName: IndexController
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@RestController
public class IndexController {
@Resource
Car car;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
@RequestMapping("/car")
public Car car(){
return car;
}
}
(2).@EnableConfigurationProperties (第二种)
1. 前提条件
(1).实体类上可以不用加@Compont注入到IOC容器中
(2).实体类上需要指定配置绑定的前缀 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar") // 添加上前缀
(3).@EnableConfigurationProperties(实体类.class) 需要放在任意IOC容器组件类上
2.
@EnableConfigurationProperties(实体类.class) = 配置绑定 + @Component依赖注入
3.使用场景:
当我们引用第三方默认的配置时候,第三方在实体类上没有添加@Component注入到IOC容器的时候,我们需要使用第二种方式。
实体类
package com.jsxs.bean;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 16:34
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.bean
* @ClassName: Car
* @Description: TODO 只会在IOC容器中的组件,才会拥有SprngBoot提供的强大功能
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Data
//@Repository 这次把IOC容器组件给去掉 ⭐
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar") // 添加上前缀 ⭐⭐
public class Car {
private String brand;
private Integer price;
}
配置类上
package com.jsxs.config;
import com.jsxs.bean.Car;
import com.jsxs.bean.Pet;
import com.jsxs.bean.User;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/7/1 12:30
* @PackageName:com.config
* @ClassName: MyConfig
* @Description: TODO 1.配置类里面使用@Bean标注在方法上给容器注册组件,默认也是单实列的,
* @Description: TODO 2.配置类(类名)本身也是一个组件,即在这个列子中有三个组件并不是俩个。
* @Description: TODO 3.@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true)代理bean,也就是无论外部调用多少次实列都是一样的即单列。否则不是单实列
* Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)、【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
* Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
* 组件依赖必须使用Full模式默认。其他默认是否Lite模式
*
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Import({User.class})
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods=true) ⭐⭐⭐ // 告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类,相当于以前的配置文件 beans.xml
//@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "tom") // 当整个IOC容器中存在tom这个容器,我们就注册user01这个组件否则不注册
@ImportResource("classpath:beans.xml")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class) ⭐⭐⭐⭐ // 1.开启配置绑定功能。 2.把Car这个属性自动注入到容器中
public class MyConfig {
@Bean // 1. 这里相当于我们配置文件中的<bena></bean>标签
// 2. User对应的是我们配置文件的class非全限定名, user01对应我们配置文件的id
public User user01() {
// FULL模式人拥有宠物
return new User("李明",12,this.cat());
}
@Bean("tom") // 相当于我们配置文件的bean标签
public Pet cat(){ // Pet指的是calss的非全限定名, cat指定的是id
return new Pet("哈吉米");
}
}
3.自动配置原理入门
3.1、引导加载自动配置类
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication{}
======================
(1). @SpringBootConfiguration
- @Configuration。代表当前是一个配置类
(2). @ComponentScan
- 指定扫描哪些,Spring注解;
(3).@EnableAutoConfiguration
1.@EnableAutoConfiguration的合成
1.注解的合成:
@EnableAutoConfiguration= @AutoConfigurationPackage + @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
2.
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {}
(3.1).@AutoConfigurationPackage (自定义注入组件)
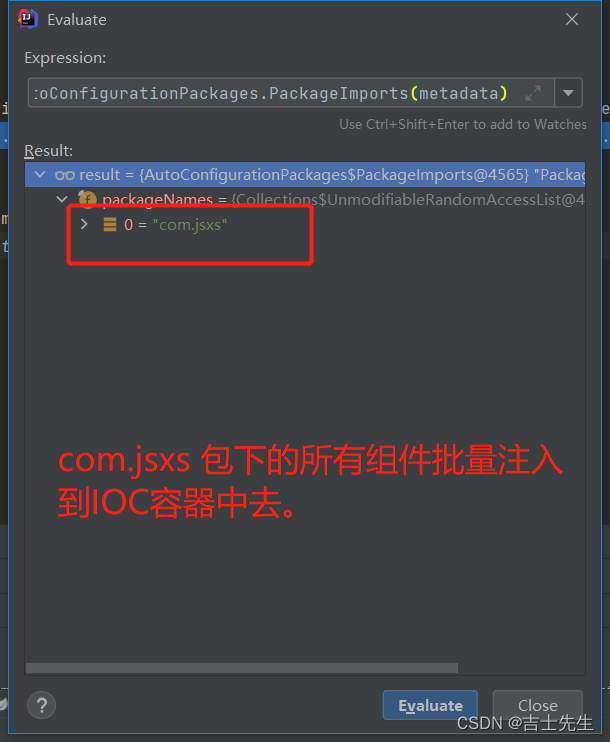
自动配置包?指定了默认的包规则 (即我们主启动类下的包)
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class) //给容器中导入一个组件
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {}
//利用 Registrar 给容器中导入一系列组件
//将指定的一个包下的所有组件导入进来?MainApplication(主启动类) 所在包下。
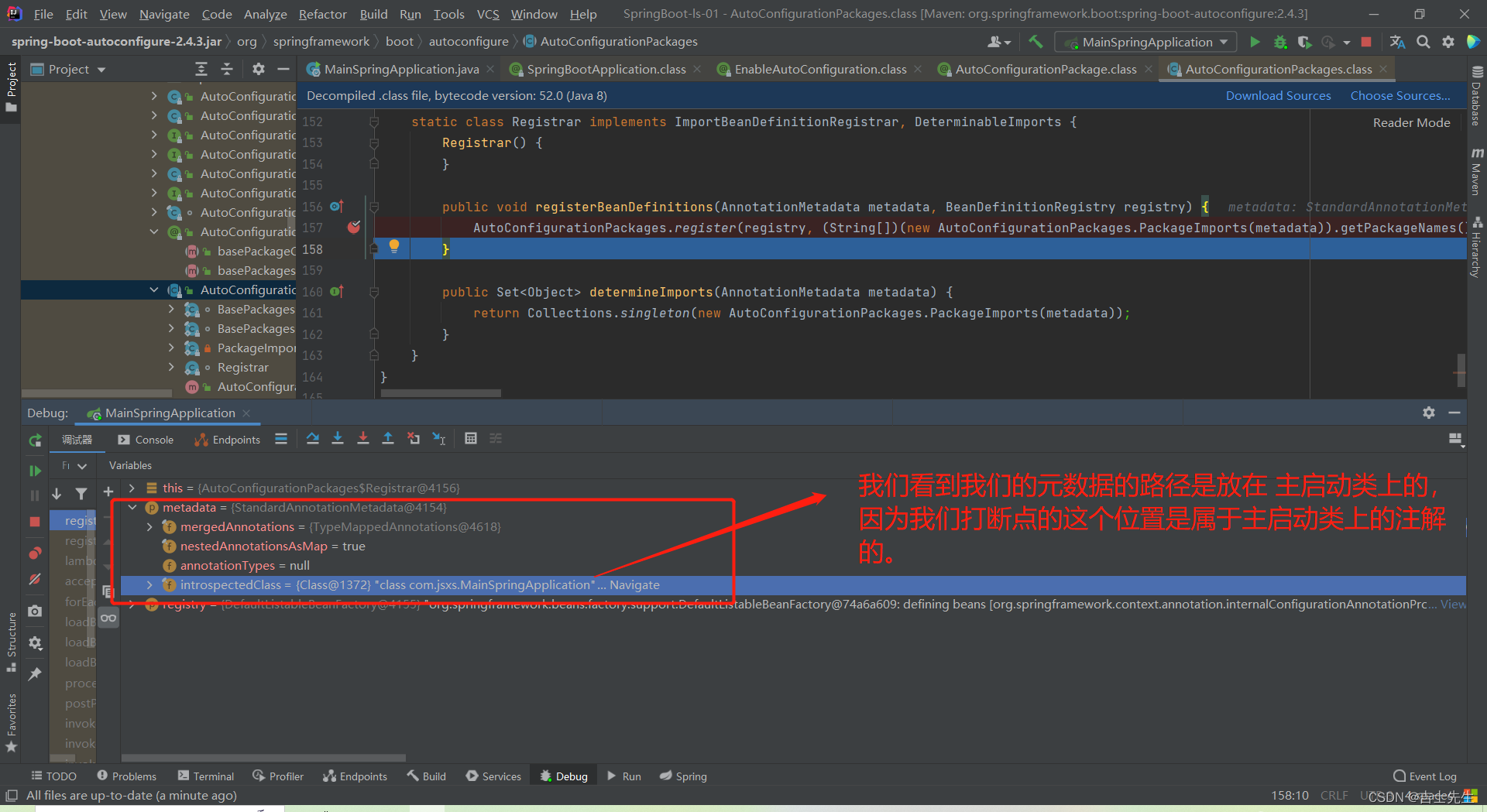
- 我们点开Registar.class这个源代码发现里面存在两个方法
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
Registrar() {
}
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
⭐ AutoConfigurationPackages.register(registry, (String[])(new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImports(metadata)).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0]));
}
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImports(metadata));
}
}
在星星的位置打上断点,发现我们的元数据上的路径在主启动类上。
我们通过计算的到: 导入的是我们主启动类下所在的包中的组件。
(3.2).@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) (官方注入)
- 点进@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})找到
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
} else {
⭐ AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = this.getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
}
1、利用getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);给容器中批量导入一些组件
2、调用List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes)获取到所有需要导入到容器中的配置类
3、利用工厂加载 Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader);得到所有的组件
4、从META-INF/spring.factories位置来加载一个文件。
默认扫描我们当前系统里面所有META-INF/spring.factories位置的文件
⭐⭐⭐ spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar包里面也有META-INF/spring.factories
这里导入的130个包就是 spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar包里面的META-INF/spring.factories
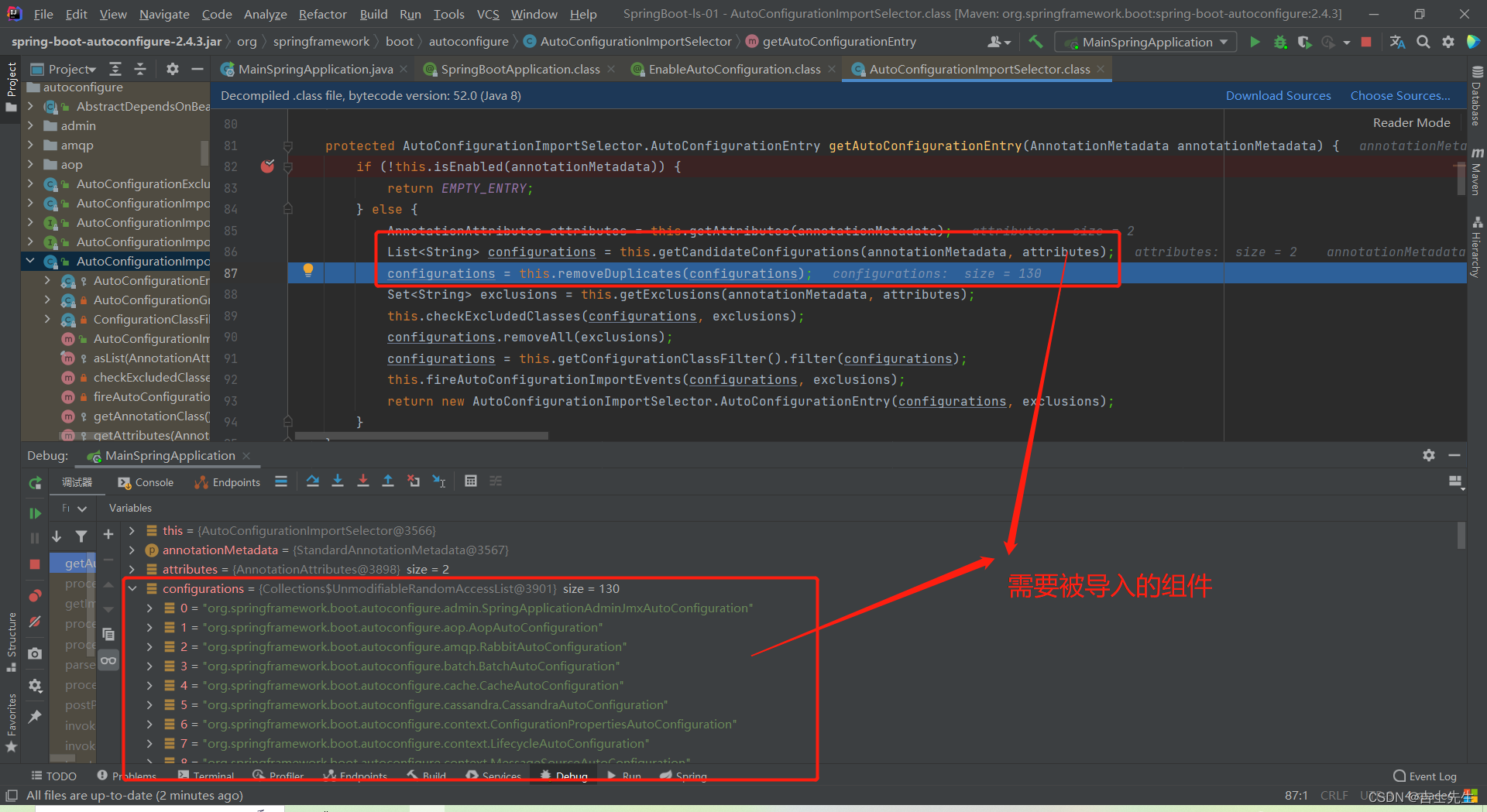
文件里面写死了spring-boot一启动就要给容器中加载的所有配置类
spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar/META-INF/spring.factories
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.availability.ApplicationAvailabilityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.neo4j.Neo4jAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketRequesterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketStrategiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.rsocket.RSocketSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.saml2.Saml2RelyingPartyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
3.2、按需开启自动配置项
虽然我们130个场景的所有自动配置启动的时候默认全部加载。xxxxAutoConfiguration
按照条件装配规则(@Conditional),最终会按需配置。
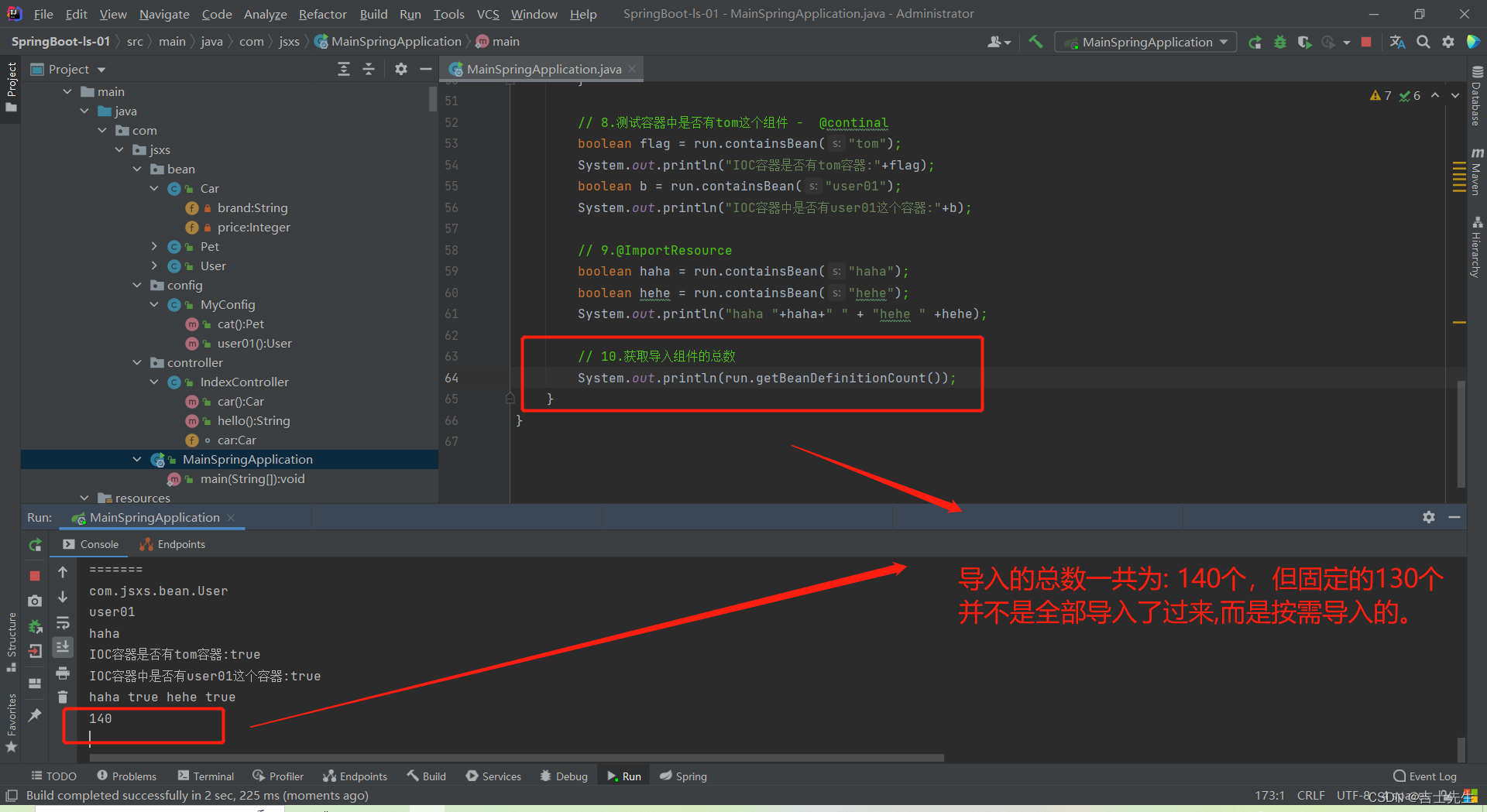
按需开启自动配置的原理是: 按条件注入
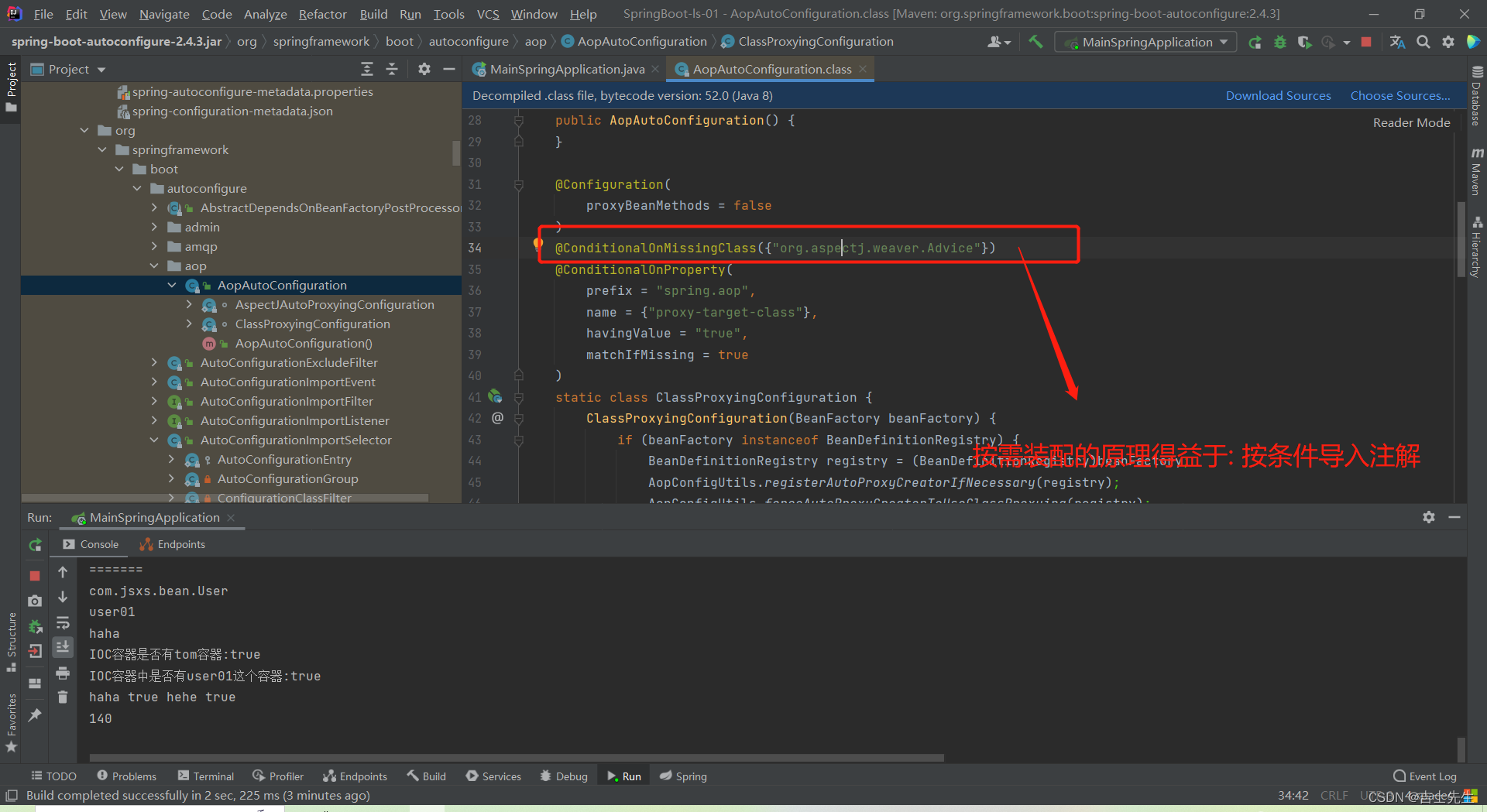
3.3、 修改默认配置
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class) //容器中有这个类型组件
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME) //容器中没有这个名字 multipartResolver 的组件
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
//给@Bean标注的方法传入了对象参数,这个参数的值就会从容器中找。
//SpringMVC multipartResolver。防止有些用户配置的文件上传解析器不符合规范
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;
}
给容器中加入了文件上传解析器;
SpringBoot默认会在底层配好所有的组件。但是如果用户自己配置了以用户的优先
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean //假如没有的时候自动创建,用户创建了就不自动创建了。
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
}
3.4、 总结
- SpringBoot
先加载所有的自动配置类xxxxxAutoConfiguration 每个自动配置类按照条件进行生效,默认都会绑定配置文件指定的值。xxxxProperties里面拿。xxxProperties和配置文件进行了绑定生效的配置类就会给容器中装配很多组件- 只要容器中有这些组件,相当于这些功能就有了
- 定制化配置
-
- 用户直接自己
@Bean替换底层的组件
- 用户直接自己
-
- 用户去看这个组件是获取的配置文件什么值就去修改。
xxxxxAutoConfiguration(自动装配文件) —> 组件 —> xxxxProperties (实体类)里面拿值 ----> application.properties (主配置文件)
3.5、最佳实践
- 引入场景依赖
-
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/using-spring-boot.html#using-boot-starter
- 查看自动配置了哪些(选做)
-
- 自己分析,引入场景对应的自动配置一般都生效了
-
- 配置文件中debug=true开启自动配置报告。Negative(不生效)\Positive(生效)
- 是否需要修改
-
- 参照文档修改配置项
-
-
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/appendix-application-properties.html#common-application-properties
-
-
-
- 自己分析。xxxxProperties绑定了配置文件的哪些。
-
- 自定义加入或者替换组件
-
- @Bean、@Component。。。
-
- 自定义器 XXXXXCustomizer;
-
- …
4.开发技巧
4.1 lombok 技术
1. 可以帮助我们配置实体类
2. 拥有@Slf4j 日志配置注解
===============================简化JavaBean开发===================================
@NoArgsConstructor
//@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Pet pet;
public User(String name,Integer age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
================================简化日志开发===================================
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String handle01(@RequestParam("name") String name){
log.info("请求进来了....");
return "Hello, Spring Boot 2!"+"你好:"+name;
}
}
4.2 devtools 技术
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
项目或者页面修改以后:Ctrl+F9;