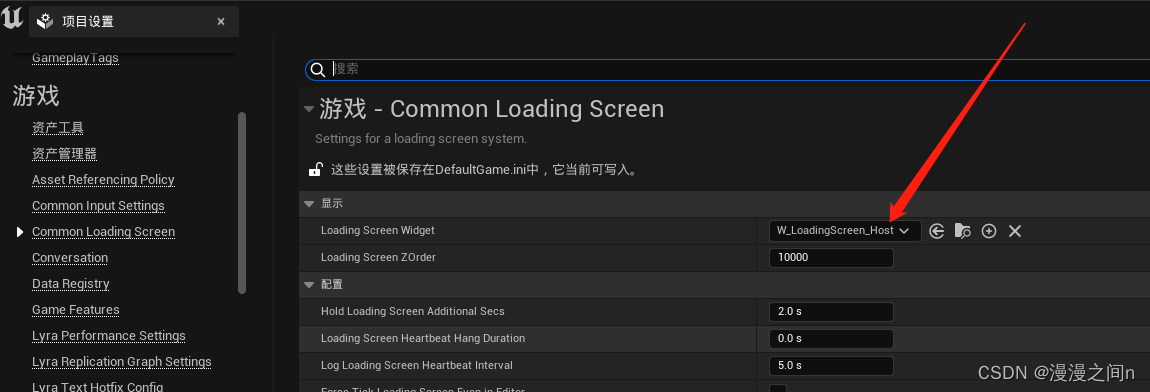
一.auto
1.介绍:
auto是一个用于类型推导的关键字。它允许变量的类型在编译时根据其初始化值自动推断
例子:
(1)自动类型推导变量
// C++ program to demonstrate working of auto
// and type inference
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// auto a; this line will give error
// because 'a' is not initialized at
// the time of declaration
// a=33;
// see here x ,y,ptr are
// initialised at the time of
// declaration hence there is
// no error in them
auto x = 4;
auto y = 3.37;
auto z = 3.37f;
auto c = 'a';
auto ptr = &x;
auto pptr = &ptr; //pointer to a pointer
cout << typeid(x).name() << endl
<< typeid(y).name() << endl
<< typeid(z).name() << endl
<< typeid(c).name() << endl
<< typeid(ptr).name() << endl
<< typeid(pptr).name() << endl;
return 0;
}
output:

(2) 自动类型迭代器
// C++ program to demonstrate that we can use auto to
// save time when creating iterators
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Create a set of strings
set<string> st;
st.insert({ "geeks", "for", "geeks", "org" });
// 'it' evaluates to iterator to set of string
// type automatically
for (auto it = st.begin(); it != st.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
return 0;
}
(3)自动类型推导 lambda 表达式参数:
auto lambda = [](int x, double y) {
return x + y;
};2. 特点
(1)auto的使用必须马上初始化,否则无法推导出类型
(2)auto在一行定义多个变量时,各个变量的推导不能产生二义性,否则编译失败
(3)auto不能用作函数参数(因为函数参数必须具有明确的类型,以便在函数调用时进行类型匹配和参数传递)
void processValue(auto value) {
// 函数体
}
int main() {
int num = 10;
processValue(num); // 错误!不能使用auto作为函数参数类型
return 0;
}(4)在类中auto不能用作非静态成员变量 (非静态成员变量是属于类的对象的成员)
class MyClass {
public:
auto myVariable = 10; // 错误!auto不能用于非静态成员变量
};(5)auto不能定义数组,可以定义指针
int func()
{
int array[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };//ok
auto t1 = array;//ok,t1 -> int *
auto t3[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };//error,auto无法定义数组
}
auto array1 = new int[2];
cout << typeid(array1).name(); //(int*)(6)auto无法推导出模板参数(对于模板参数,我们需要明确指定其类型,而不能使用auto进行类型推导)
template <typename T>
class Test
{
//To do something
};
int func()
{
Test<double> t;
Test<auto> t1 = t;//error,无法推导模板类型
return 0;
}