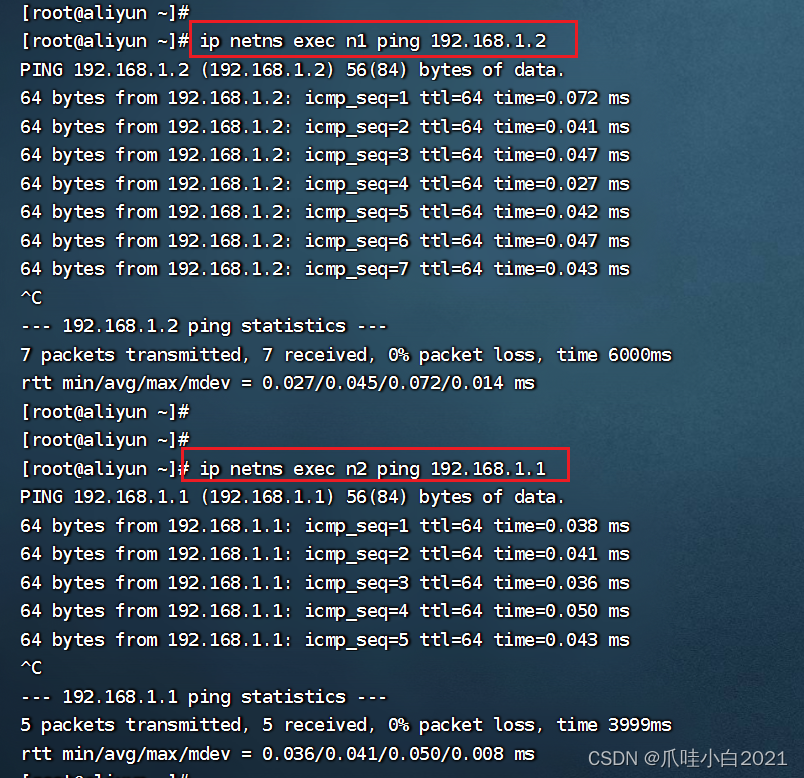
参考文献:微信公众号“程序猿声”关于分支定价求解VRPTW的代码
A tutorial on column generation and branch-and-price for vehicle routing problems
框架
对于VRPTW问题,先做线性松弛,调用列生成算法(一种解决大型线性规划问题的精确算法),得到最终RMP(Restricted master problem)。此时,如果得到的是整数解,那么结束算法;否则,更新上界、下界并分支,再在分支节点上重复上述步骤。
- 列生成算法的具体步骤:对原松弛问题Min(主问题,MP),选择一些列,得到限制性主问题(RLMP)并求解它,得到对偶变量的值;用对偶变量的值,更新子问题的目标函数,目的是找到检验数为负的列,把新列添加给RLMP,继续求解,直到没有检验数为负的列生成了为止。
- 分支定界算法的具体步骤:
初始化上界、下界分别为系统最大值、系统最小值,下面我们希望通过分支来缩小他们之间的gap。
对MIP做线性松弛,用单纯形法求解,如果解中满足Integer feasibility,那么结束算法;否则,更新下界并选择分支变量,做两个分支,对分支用单纯性算法求解,
如果得到更好的整数解,更新上界;
如果得到整数解但是没有更好,那么剪枝;
如果得到的是非整数解,更新下界;
如此循环,直到上界、下界之间的gap在可接受范围内为止。
细节
VRP问题的表述方式
分两种模型,一种是Arc-flow model,还有一种是set-covering model.
下面这种的是Arc-flow model

或者


下面是set-covering model
翻译:上面的模型太弱了,无法使用分支定界算法。上面的模型可以通过Dantzig-Wolfe decomposition,得到下面的模型。下面的模型会有更好的线性松弛。

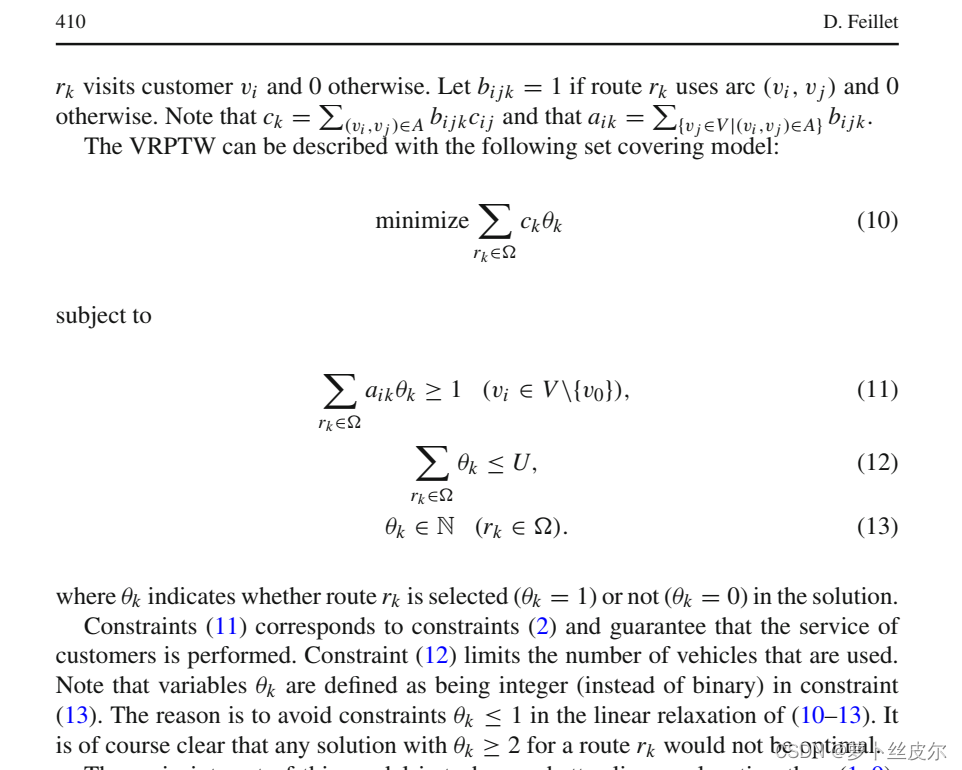
set-covering model的松弛解 可以转化为 arc-flow model的松弛解,但是 反过来不行。
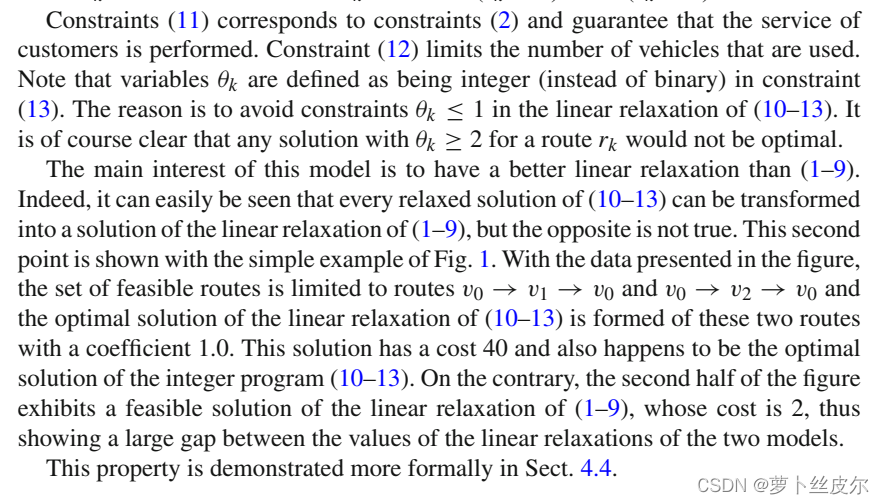
这里列生成算法作用的是 set-covering model.
分支策略
分支策略添加的约束要和列生成算法相兼容。
基于路径的分支策略可能会导致整个BB树的不平衡,推荐使用基于弧段的分支策略,且后者更具代表性。
基于弧段的分支策略:
针对路径
r
k
r_k
rk,选择一个弧段,当弧段的流量值为分数(介于0到1之间),进行分支:
分支1:解不能包含该弧段;
分支2:解必须包含该弧段;
-
如何得到分支1?
在主问题中,只要含有该弧段的列都被删除掉;
在子问题中,该弧段被删除,确保没有使用该弧段的列被生成; -
如何得到分支2?
禁用那些”沾亲带故“的弧段,在代码中通过将弧段dist设置为无穷大做到这一点。
代码(Java调用Cplex)
- 主函数 Main.java
package BranchAndPrice;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
branchandbound bp = new branchandbound(); // build bb tree
paramsVRP instance = new paramsVRP();
instance.initParams("D:\\VRP问题实践\\DengFahengBPVRPTW-master\\BPVRPTW-master\\dataset\\C101.TXT");
ArrayList<route> initRoutes = new ArrayList<route>();
ArrayList<route> bestRoutes = new ArrayList<route>();
// create root node for bb tree
bp.BBNode(instance, initRoutes, null, bestRoutes, 0); // fill bestRoutes
double optCost = 0;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("solution >>>");
for (route bestRoute : bestRoutes) {
System.out.println(bestRoute.path);
optCost += bestRoute.cost;
}
System.out.println("\nbest Cost = " + optCost);
}
}
- 分支定界算法
package BranchAndPrice;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class branchandbound {
double lowerbound;
double upperbound;
public branchandbound() {
lowerbound = -1E10;
upperbound = 1E10;
}
// try to update these two bound s.t. they are closer to each others
class treeBB { // BB树上的节点
// this is a linked tree list recording all the branching during Branch and Bound
treeBB father; // link to the node processed before branching
treeBB son0; // link to the son on the left of the tree (edge=0; first processed) => need it to compute the global lowerbound
int branchFrom; // we branch on edges between cities => city origin of the edge
int branchTo; // we branch on edges between cities => city destination of the edge
int branchValue; // we branch on edges between cities => value of the branching (remove edge=0; set edge=1)
double lowestValue; // lower bound on the solution if we start from this node (i.e. looking only down for this tree)
boolean toplevel; // to compute the global lowerBound, need to know if everything above has been considered
}
// 对于给定分支节点branching,按照它的branchFrom和branchTo,重置dist[][],把某些边给禁了
public void EdgesBasedOnBranching(paramsVRP userParam, treeBB branching,
boolean recur) {
int i;
if (branching.father != null) { // stop before root node
if (branching.branchValue == 0) { // forbid this edge (in this direction) // 左分支禁用此弧
// associate a very large distance to this edge to make it unattractive
userParam.dist[branching.branchFrom][branching.branchTo] = userParam.verybig;
} else {// 右分支 只允许 该弧被用, 禁用其他”沾亲带故“的弧
// impose this edge (in this direction)
// associate a very large and unattractive distance to all edges
// starting from "branchFrom" excepted the one leading to "branchTo"
// and excepted when we start from depot (several vehicles)
if (branching.branchFrom != 0) { // except 'branchTo'
for (i = 0; i < branching.branchTo; i++)
userParam.dist[branching.branchFrom][i] = userParam.verybig;
// I guess, in this way, it can skip setting the distance between i and 'branchTo' this node
for (i++; i < userParam.nbclients + 2; i++)
userParam.dist[branching.branchFrom][i] = userParam.verybig;
}
// associate a very large and unattractive distance to all edges ending
// at "branchTo" excepted the one starting from "branchFrom"
// and excepted when the destination is the depot (several vehicles)
if (branching.branchTo != userParam.nbclients + 1) {
for (i = 0; i < branching.branchFrom; i++)
userParam.dist[i][branching.branchTo] = userParam.verybig;
for (i++; i < userParam.nbclients + 2; i++)
userParam.dist[i][branching.branchTo] = userParam.verybig;
}
// forbid the edge in the opposite direction
userParam.dist[branching.branchTo][branching.branchFrom] = userParam.verybig;
}
if (recur) EdgesBasedOnBranching(userParam, branching.father, true);// ??
}
}
public boolean BBNode(paramsVRP userParam, ArrayList<route> routes,
treeBB branching, ArrayList<route> bestRoutes, int depth)
throws IOException {// bestRoutes用于记录目前收集到的最好的可行路径
// userParam (input) : all the parameters provided by the users (cities,
// roads...)
// routes (input) : all (but we could decide to keep only a subset) the
// routes considered up to now (to initialize the Column generation process)
// branching (input): BB branching context information for the current node
// to process (branching edge var, branching value, branching from...)
// bestRoutes (output): best solution encountered
// routes 收集了 很多路径,那些.getQ>0的路径表示 被使用了
int i, j, bestEdge1, bestEdge2, prevcity, city, bestVal;// previous city
double coef, bestObj, change, CGobj;
boolean feasible;
try {
// check first that we need to solve this node. Not the case if we have
// already found a solution within the gap precision
if ((upperbound - lowerbound) / upperbound < userParam.gap)
return true;
// init
if (branching == null) { // root node - first call
// first call - root node
treeBB newNode = new treeBB();
newNode.father = null;
newNode.toplevel = true; // ??
newNode.branchFrom = -1;
newNode.branchTo = -1;
newNode.branchValue = -1;
newNode.son0 = null;
branching = newNode;
}
// display some local info
if (branching.branchValue < 1) {// 这条弧段 被禁用
System.out.println("\nEdge from " + branching.branchFrom + " to "
+ branching.branchTo + ": forbid");
} else {// 这条弧段 被选择
System.out.println("\nEdge from " + branching.branchFrom + " to "
+ branching.branchTo + ": set");
}
int MB = 1024 * 1024;
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.print("Java Memory=> Total:" + (runtime.totalMemory() / MB)
+ " Max:" + (runtime.maxMemory() / MB) + " Used:"
+ ((runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory()) / MB) + " Free: "
+ runtime.freeMemory() / MB);
// Compute a solution for this node using Column generation
columngen CG = new columngen();
CGobj = CG.computeColGen(userParam, routes);// objValue of RLMP, relaxed linear master problem
// 生成的新列都会加入到 route中
// feasible ? Does a solution exist?
if ((CGobj > 2 * userParam.maxlength) || (CGobj < -1e-6)) {
// can only be true when the routes in the solution include forbidden edges (can happen when the BB set branching values)
System.out.println("RELAX INFEASIBLE | Lower bound: " + lowerbound
+ " | Upper bound: " + upperbound + " | Gap: "
+ ((upperbound - lowerbound) / upperbound) + " | BB Depth: "
+ depth + " | " + routes.size() + " routes");
return true; // stop this branch
}
branching.lowestValue = CGobj;// 当前分支的下界, 当前分支节点处的最终的RMP的最优值
// routes 是 最终的RLMP的最优基 对应的路径
// update the global lowerBound when required
if ((branching.father != null) && (branching.father.son0 != null)
&& branching.father.toplevel) {// 有父节点,且父节点有左孩子,父节点的lowerbound已经计算过了
// all nodes above and on the left have been processed=> we can compute
// a new lowerBound
lowerbound = Math.min(branching.lowestValue, branching.father.son0.lowestValue);
branching.toplevel = true;
} else if (branching.father == null) {
// root node
lowerbound = CGobj;
}
if (branching.lowestValue > upperbound) {
CG = null;
System.out.println("CUT | Lower bound: " + lowerbound
+ " | Upper bound: " + upperbound + " | Gap: "
+ ((upperbound - lowerbound) / upperbound) + " | BB Depth: "
+ depth + " | Local CG cost: " + CGobj + " | " + routes.size()
+ " routes");
return true; // cut this useless branch
} else {
// ///
// check the (integer) feasibility. Otherwise search for a branching
// variable
feasible = true;
bestEdge1 = -1;
bestEdge2 = -1;
bestObj = -1.0;
bestVal = 0;
// 基于路段的分支策略,书上的第二种
// 路径的使用次数 转成 边的使用次数,切换了 决策变量
// transform the path variable (of the CG model) into edges variables
for (i = 0; i < userParam.nbclients + 2; i++) {
java.util.Arrays.fill(userParam.edges[i], 0.0); // initialize the ith row
// userParam.egdes is an array
}
for (route r : routes) {
if (r.getQ() > 1e-6) {// 使用路径r的次数 大于 0,但是因为CG解的是线性松弛问题,所以r.getQ是double型
// we consider only the routes in the current local solution
ArrayList<Integer> path = r.getpath(); // get back the sequence of
// cities (path for this route)
prevcity = 0;
for (i = 1; i < path.size(); i++) {
city = path.get(i);
// 把 路径上的Q值 赋予到 路径的边上
userParam.edges[prevcity][city] += r.getQ(); // convert into edges
prevcity = city;
}
}
}
// find a fractional edge 选择分支弧段
for (i = 0; i < userParam.nbclients + 2; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < userParam.nbclients + 2; j++) {
coef = userParam.edges[i][j];
if ((coef > 1e-6) && ((coef < 0.9999999999) || (coef > 1.0000000001))) {
// ?? what if coef=2, 这种情况也同样被标记成feasible=false??有可能出现么? 答:不会,值介于 0到1之间
// coef 大于0, 且, 小于1或大于1
// coef is fractional// 介于 0到1之间
// this route has a fractional coefficient in the solution =>
// should we branch on this one?
feasible = false;
// what if we impose this route in the solution? Q=1
// keep the ref of the edge which should lead to the largest change
change = Math.min(coef, Math.abs(1.0 - coef));// min(0.2,0.8) = 0.2
change *= routes.get(i).getcost();
if (change > bestObj) { // ??
bestEdge1 = i;
bestEdge2 = j;
bestObj = change;
bestVal = (Math.abs(1.0 - coef) > coef) ? 0 : 1;// bestVal=1 if coef>0.5
} // 选择分支弧段 (i_q,i_(q+1))
}
}
}
// 如果需要分支,选定 分支弧段为 [bestEdge1,bestEdge2]
if (feasible) { // 说明 没有 取值为分数的 edge
if (branching.lowestValue < upperbound) { // new incumbant feasible solution!
upperbound = branching.lowestValue;
bestRoutes.clear();
for (route r : routes) {
if (r.getQ() > 1e-6) {// 投入使用的路径,记录到bestRoutes中
// 创建复制品,存到bestRoutes中
route optim = new route();
optim.setcost(r.getcost());
optim.path = r.getpath();
optim.setQ(r.getQ());
bestRoutes.add(optim);
}
}
System.out.println("OPT | Lower bound: " + lowerbound
+ " | Upper bound: " + upperbound + " | Gap: "
+ ((upperbound - lowerbound) / upperbound) + " | BB Depth: "
+ depth + " | Local CG cost: " + CGobj + " | " + routes.size()
+ " routes");
System.out.flush();
} else { //?? feasible && branching.lowerestValue>=upperbound
// since we already got '>' done, so here, (feasible && branching.lowerestValue=upperbound)
// 是整数解,但不是比upperbound更好的整数解,所以 无需记录
System.out.println("FEAS | Lower bound: " + lowerbound
+ " | Upper bound: " + upperbound + " | Gap: "
+ ((upperbound - lowerbound) / upperbound) + " | BB Depth: "
+ depth + " | Local CG cost: " + CGobj + " | " + routes.size()
+ " routes");
}
return true;
} else {// infeasible 、、 fraction
System.out.println("INTEG INFEAS | Lower bound: " + lowerbound
+ " | Upper bound: " + upperbound + " | Gap: "
+ ((upperbound - lowerbound) / upperbound) + " | BB Depth: "
+ depth + " | Local CG cost: " + CGobj + " | " + routes.size()
+ " routes");
System.out.flush();
// ///
// branching (diving strategy)
// 分支1: 删除掉含有弧段[bestEdge1,bestEdge2]的列/路径
// first branch -> set edges[bestEdge1][bestEdge2]=0
// record the branching information in a tree list
treeBB newNode1 = new treeBB();
newNode1.father = branching;
newNode1.branchFrom = bestEdge1;
newNode1.branchTo = bestEdge2;
newNode1.branchValue = bestVal; // ?!first version was not with bestVal
// but with 0
newNode1.lowestValue = -1E10;
newNode1.son0 = null;
// branching on edges[bestEdge1][bestEdge2]=0
//在函数EdgesBasedOnBraning函数中, newNode1.branchValue 提示此分支是被禁用的
EdgesBasedOnBranching(userParam, newNode1, false); // 修改了dist[][]
// ?? 为什么recur取值为false??
// the initial lp for the CG contains all the routes of the previous
// solution less(去掉分支的边) the routes containing this arc (arc bestEdge1-->bestEdge2)
// 在routes的基础上,删除掉含有弧段[bestEdge1,bestEdge2]的列/路径;记录余下路径到nodeRoutes中
ArrayList<route> nodeRoutes = new ArrayList<route>();
for (route r : routes) {
ArrayList<Integer> path = r.getpath();
boolean accept = true;
if (path.size() > 3) { // we must keep trivial routes
// Depot-City-Depot in the set to ensure
// feasibility of the CG
prevcity = 0;
for (j = 1; accept && (j < path.size()); j++) {
city = path.get(j);
if ((prevcity == bestEdge1) && (city == bestEdge2))
accept = false;
prevcity = city;
}
}
if (accept) nodeRoutes.add(r);
}
boolean ok;
ok = BBNode(userParam, nodeRoutes, newNode1, bestRoutes, depth + 1);
nodeRoutes = null; // free memory
if (!ok) {// “没结果”会返回false, "有结果"指 因最优性或可行性被剪枝、找到最优解等。
return false;
}
branching.son0 = newNode1;
// 分支2:必须“直接”含有弧段[bestEdge1,bestEdge2]的路径,排除掉 “沾亲带故”的路径
// second branch -> set edges[bestEdge1][bestEdge2]=1
// record the branching information in a tree list
treeBB newNode2 = new treeBB();
newNode2.father = branching;
newNode2.branchFrom = bestEdge1;
newNode2.branchTo = bestEdge2;
newNode2.branchValue = 1 - bestVal; // first version: always 1
newNode2.lowestValue = -1E10;
newNode2.son0 = null;
// branching on edges[bestEdge1][bestEdge2]=1
// second branching=>need to reinitialize the dist matrix
// why, Ans: 因为branch newNode1之后,调用了EdgeBasedOnBranching函数,修改到了dist[][]
for (i = 0; i < userParam.nbclients + 2; i++) {
System.arraycopy(userParam.distBase[i], 0, userParam.dist[i], 0,
userParam.nbclients + 2);
}// 从这里看到distBase的作用在于,为 dist矩阵 存根
//reinitialize了,因此需要recur递归一下
EdgesBasedOnBranching(userParam, newNode2, true); // 为什么这里recur取值true?
// the initial lp for the CG contains all the routes of the previous
// solution less the routes incompatible with this arc,这些路径的弧段都被EdgeBasedOnBranching函数标记为verybig
// “沾亲带故”: 那些路径要么含节点bestEdge1,但不是直接去向bestEdge2; 要么含节点bestEdge2,但不是直接从bestEdge1来
// 从routes中 选 含有此弧段的路径, 记录在 nodeRoute2中
ArrayList<route> nodeRoutes2 = new ArrayList<route>();
for (route r : routes) {
ArrayList<Integer> path = r.getpath();
boolean accept = true;
if (path.size() > 3) { // we must keep trivial routes
// Depot-City-Depot in the set to ensure
// feasibility of the CG
prevcity = 0;
for (i = 1; accept && (i < path.size()); i++) {
city = path.get(i);
if (userParam.dist[prevcity][city] >= userParam.verybig - 1E-6) accept = false;
prevcity = city;
}
}
if (accept) nodeRoutes2.add(r);
}
ok = BBNode(userParam, nodeRoutes2, newNode2, bestRoutes, depth + 1);
nodeRoutes2 = null;
// update lowest feasible value of this node
branching.lowestValue = Math.min(newNode1.lowestValue, newNode2.lowestValue);
return ok;// boolean
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Error: " + e);
}
return false;
}
}
- 列生成算法 columngen.java
package BranchAndPrice;
/**
* Asymetric VRP with Resources Constraints (Time Windows and Capacity)
* Branch and Price algorithm (Branch and Bound + Column generation)
* For educational purpose only! No code optimization. Just to understand the main basic steps of the B&P algorithm.
* Pricing through Dynamic Programming of the Short Path Problem with Resources Constraints (SPPRC)
* Algorithm inspired by the book
* Desrosiers, Desaulniers, Solomon, "Column Generation", Springer, 2005 (GERAD, 25th anniversary)
* => Branch and bound (class BPACVRPTW)
* => Column generation (class columngen) : chapter 3
* => Pricing SPPRC (class SPPRC): chapter 2
* CPLEX code for the column generation inspired by the example "CutStock.java" provided in the examples directory of the IBM ILOG CPLEX distribution
*
* @author mschyns
* M.Schyns@ulg.ac.be
*/
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import ilog.concert.*;
import ilog.cplex.*;
public class columngen {
static class IloNumVarArray {
// Creation of a new class similar to an ArrayList for CPLEX unknowns
// taken from "cutsotck.java"
int _num = 0;
IloNumVar[] _array = new IloNumVar[32];
void add(IloNumVar ivar) {// automative expansion
if (_num >= _array.length) {
IloNumVar[] array = new IloNumVar[2 * _array.length];
System.arraycopy(_array, 0, array, 0, _num);
_array = array;
}
_array[_num++] = ivar;
}
IloNumVar getElement(int i) {
return _array[i];
}
int getSize() {
return _num;
}
}
public double computeColGen(paramsVRP userParam, ArrayList<route> routes)
throws IOException {// 生成的新列都会加入到 routes中
int i, j, prevcity, city;
double cost, obj;
double[] pi; // p_i, the value of dual variables
boolean oncemore;
try {
// ---------------------------------------------------------
// construct the model for the Restricted Master Problem
// ---------------------------------------------------------
// warning: for clarity, we create a new cplex env each time we start a
// Column Generation
// this class contains (nearly) everything about CG and could be used
// independently
// However, since the final goal is to encompass it inside 锟� Branch and
// Bound (BB),
// it would (probably) be better to create only once the CPlex env when we
// initiate the BB and to work with the same (but adjusted) lp matrix each
// time
IloCplex cplex = new IloCplex();
IloObjective objfunc = cplex.addMinimize();
// for each vertex/client, one constraint (chapter 3, 3.23 )
IloRange[] lpmatrix = new IloRange[userParam.nbclients];// start from 0
for (i = 0; i < userParam.nbclients; i++)
lpmatrix[i] = cplex.addRange(1.0, Double.MAX_VALUE); // 表示每个客户都要被服务到
// for each constraint, right member >=1
// lpmatrix[i] = cplex.addRange(1.0, 1.0);
// or for each constraint, right member=1 ... what is the best?
// Declaration of the variables
IloNumVarArray y = new IloNumVarArray(); // y_p to define whether a path p
// is used
// y_p 表示这条路是否使用
// 集覆盖模型
// Populate the lp matrix and the objective function
// first with the routes provided by the argument 'routes' of the function
// (in the context of the Branch and Bound, it would be a pity to start
// again the CG from scratch at each node of the BB!)
// (we should reuse parts of the previous solution(s))
// 复用之前的路径们,建立他们对应的列
for (route r : routes) {
int v;
cost = 0.0;
prevcity = 0;
// total cost of route r
for (i = 1; i < r.getpath().size(); i++) {
city = r.getpath().get(i);
cost += userParam.dist[prevcity][city];
prevcity = city;
}
r.setcost(cost);
// 上面计算新路径的成本c_p
// 按列建模,为RLMP添加新的列
IloColumn column = cplex.column(objfunc, r.getcost());// obj coefficient
// constraint coefficient
for (i = 1; i < r.getpath().size() - 1; i++) { // nodes this route passed, except two depots
v = r.getpath().get(i) - 1;// the ith customer on the route r
column = column.and(cplex.column(lpmatrix[v], 1.0));
// coefficient of y_i in (3.23) => 0 for the other y_p
}// say 0-2-3-6-0, 这一列第1,2,5行处是1,其余都是0
// creation of the variable y_i whose range is [0,+++]
y.add(cplex.numVar(column, 0.0, Double.MAX_VALUE));
}
// 新建一些列
// complete the lp with basic route to ensure feasibility
// initially choose several columns, 初始基可行解,每条路径只访问一个客户,构造得RLMP,并将此路径添加到routes
if (routes.size() < userParam.nbclients) { // a priori true only the first time
for (i = 0; i < userParam.nbclients; i++) { // customer i
cost = userParam.dist[0][i + 1]
+ userParam.dist[i + 1][userParam.nbclients + 1];
// 新列加到目标函数上
IloColumn column = cplex.column(objfunc, cost); // obj coefficient
// 新列加到约束上
column = column.and(cplex.column(lpmatrix[i], 1.0)); // coefficient of
// y_i in (3.23)
// => 0 for the
// other y_p
// 新列产生的新变量
y.add(cplex.numVar(column, 0.0, Double.MAX_VALUE)); // creation of the
// variable y_i
// 新列对应的 新路径
route newroute = new route();
newroute.addcity(0);
newroute.addcity(i + 1);
newroute.addcity(userParam.nbclients + 1);
newroute.setcost(cost);
routes.add(newroute);
}
}
// cplex.exportModel("model.lp");
// CPlex params
cplex.setParam(IloCplex.IntParam.RootAlgorithm, IloCplex.Algorithm.Primal);
cplex.setOut(null);
// cplex.setParam(IloCplex.DoubleParam.TiLim,30); // max number of
// seconds: 2h=7200 24h=86400
// ---------------------------------------------------------
// column generation process
// ---------------------------------------------------------
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#0000.00"); // 保留两位小数的十进制格式
oncemore = true;
double[] prevobj = new double[100]; // previous objective values, used to check stability
int nbroute; // number of routes
int previ = -1; // previous index
while (oncemore) { // oncemore 表示 是否找到了新列,是那么继续找,否那么结束列生成
oncemore = false;// 后面如果找到了新列,就会被更新成true
// ---------------------------------------s------------------
// solve the current RMP
// ---------------------------------------------------------
if (!cplex.solve()) {
System.out.println("CG: relaxation infeasible!");
return 1E10;
}// now, CG: relaxation is feasible
prevobj[(++previ) % 100] = cplex.getObjValue();
// store the 30 last obj values to check stability afterwards
// System.out.println(cplex.getStatus());
// cplex.exportModel("model.lp");
// ---------------------------------------------------------
// solve the subproblem to find new columns (if any)
// ---------------------------------------------------------
// 利用对偶变量的值, 更新子问题的目标函数
// first define the new costs for the subproblem objective function
// (SPPRC)
pi = cplex.getDuals(lpmatrix); // dual variables of those constraints 'lpmatrix'
for (i = 1; i < userParam.nbclients + 1; i++) // from customer i
for (j = 0; j < userParam.nbclients + 2; j++) // to any sites
userParam.cost[i][j] = userParam.dist[i][j] - pi[i - 1];
// 修改到 userParams.cost[][], 后面解子问题SPPRC会使用到这一结果
// 详细见,SPPRC.java的结尾部分,扩展路径得到的新标签的cost的计算
// 因为已经在paramVRP.initParam设置过不可行边的距离为 正无穷, 所以 这里第二个for循环是0~nbclients+2
// start dynamic programming
SPPRC sp = new SPPRC();// subproblem
ArrayList<route> routesSPPRC = new ArrayList<route>();
nbroute = userParam.nbclients; // arbitrarily limit to the 5 first
// shortest paths with negative cost
// if ((previ>100) &&
// (prevobj[(previ-3)%100]-prevobj[previ%100]<0.0003*Math.abs((prevobj[(previ-99)%100]-prevobj[previ%100]))))
// {
// System.out.print("/");
// complete=true; // it the convergence is too slow, start a "complete"
// shortestpast
// }
sp.shortestPath(userParam, routesSPPRC, nbroute); // fill routesSPPRC, 收集到 检验数为负 的可行最短路径
sp = null;
// /
// parameter here
// 根据子问题求解结果,添加新列、新决策变量
if (routesSPPRC.size() > 0) {
for (route r : routesSPPRC) {
// if (userParam.debug) {
// System.out.println(" "+r.getcost());
// }
ArrayList<Integer> rout = r.getpath();
prevcity = rout.get(1);
cost = userParam.dist[0][prevcity];
IloColumn column = cplex.column(lpmatrix[rout.get(1) - 1], 1.0);
for (i = 2; i < rout.size() - 1; i++) {
city = rout.get(i);
cost += userParam.dist[prevcity][city];
prevcity = city;
column = column.and(cplex.column(lpmatrix[rout.get(i) - 1], 1.0));
// coefficient of y_i in (3.23) => 0 for the other y_p
}
cost += userParam.dist[prevcity][userParam.nbclients + 1];
// obj func
column = column.and(cplex.column(objfunc, cost));
// decision variable
y.add(cplex.numVar(column, 0.0, Double.MAX_VALUE, // 根据新建列,创建一个变量,加入模型中
"P" + routes.size())); // creation of the variable y_i
// new route
r.setcost(cost);
routes.add(r);
oncemore = true;// 已经找到了新路径,提示下一轮接着找
}
System.out.print("\nCG Iter " + previ + " Current cost: "
+ df.format(prevobj[previ % 100]) + " " + routes.size()
+ " routes"); // routes.size 表示 当前已经有多少条路径了
System.out.flush();// ??
}
//if (previ % 50 == 0)
routesSPPRC = null;
}// end while(oncemore)
// finished finding and adding new columns
System.out.println();
// final result fo cplex
for (i = 0; i < y.getSize(); i++) // variables
// route's Q value means whether this route is chosed or not
routes.get(i).setQ(cplex.getValue(y.getElement(i)));// set Q value of route i as y_i
obj = cplex.getObjValue(); // mmmmhhh: to check. To be entirely safe, we
// should recompute the obj using the distBase
// matrix instead of the dist matrix
// ?? I thought disBase and dist matrix are the same....
cplex.end();
return obj;
} catch (IloException e) {
System.err.println("Concert exception caught '" + e + "' caught");
}
return 1E10;
}
}
- 用标号法求解带资源约束的最短路径问题
package BranchAndPrice;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
// shortest path with resource constraints
// inspired by Irnish and Desaulniers, "SHORTEST PATH PROBLEMS WITH RESOURCE CONSTRAINTS"
// for educational demonstration only - (nearly) no code optimization
//
// four main lists will be used:
// labels: array (ArrayList) => one dimensional unbounded vector
// list of all labels created along the feasible paths (i.e. paths satisfying the resource constraints)
//
// U: sorted list (TreeSet) => one dimensional unbounded vector
// sorted list containing the indices of the unprocessed labels (paths that can be extended to obtain a longer feasible path)
//
// P: sorted list (TreeSet) => one dimensional unbounded vector
// sorted list containing the indices of the processed labels ending at the depot with a negative cost
//
// city2labels: matrix (array of ArrayList) => nbClients x unbounded
// for each city, the list of (indices of the) labels attached to this city/vertex
// before processing a label at vertex i, we compare pairwise all labels at the same vertex to remove the dominated ones
public class SPPRC {
paramsVRP userParam;// #vehicles, capacity, ready time, due time,...
ArrayList<label> labels; // list of labels
class label { //路径和资源消耗情况,组成标签
// we use a labelling algorithm. 标签算法
// labels are attached to each vertex to specify the state of the resources 标签标识了各种资源的使用状态
// when we follow a corresponding feasible path ending at this vertex 沿可行路径到达当前顶点
public int city; // current vertex
public int indexPrevLabel; // previous label in the same path (i.e. previous vertex in the same path with the state of the resources)
// cost,tTime,demand表示这个标签的资源消耗情况
public double cost; // first resource: cost (e.g. distance or strict travel time)
public float tTime; // second resource: travel time along the path (including wait time and service time)
public double demand; // third resource: demand,i.e. total quantity delivered to the clients encountered on this path
public boolean dominated; // is this label dominated by another one? i.e. if dominated, forget this path.
public boolean[] vertexVisited;
label(int a1, int a2, double a3, float a4, double a5, boolean a6, boolean[] a7) {
city = a1;
indexPrevLabel = a2;
cost = a3;
tTime = a4;
demand = a5;
dominated = a6;
vertexVisited = a7;
}
} // end class label
class MyLabelComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
// the U treeSet is an ordered list
// to maintain the order, we need to define a comparator: cost is the main criterium
public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) {
label A = labels.get(a);
label B = labels.get(b);
// Be careful! When the comparator returns 0, it means that the two labels are considered EXACTLY the same ones!
// This comparator is not only used to sort the lists! When adding to the list, a value of 0 => not added!!!!!
// 因为这里的cost等都是double型,在计算机中存在精度的问题,所以需要自己定义
// 先比较cost, --> city when cities are the same, 继续比较 time,demand, 访问节点顺序
if (A.cost - B.cost < -1e-7)
return -1;
else if (A.cost - B.cost > 1e-7)
return 1;
else {
if (A.city == B.city) {
if (A.tTime - B.tTime < -1e-7)
return -1;
else if (A.tTime - B.tTime > 1e-7)
return 1;
else if (A.demand - B.demand < -1e-7)
return -1;
else if (A.demand - B.demand > 1e-7)
return 1;
else {
int i = 0;
while (i < userParam.nbclients + 2) {
if (A.vertexVisited[i] != B.vertexVisited[i]) {
if (A.vertexVisited[i])// 相比于B, A提前访问了i,所以返回A
return -1;
else
return 1;
}
i++;
}
return 0;
}
} else if (A.city > B.city)
return 1;
else
return -1;
}
}
}
public void shortestPath(paramsVRP userParamArg, ArrayList<route> routes, int nbRoute) {
// 标号算法的主体部分,因为有删除标签的行为,所以标签校正算法
label current;
int i, j, idx, nbsol, maxSol;
double d, d2;//cumutive demand of the next customer and the next and next customer
int[] checkDom;
float tt, tt2; // timePoint when we arrive the next customer i and the next and next customer j
Integer currentidx; // the index of current label
this.userParam = userParamArg;
// unprocessed labels list => ordered TreeSet List (?optimal: need to be sorted like this?)
// 这里的“未处理”表示“未拓展”的
TreeSet<Integer> U = new TreeSet<Integer>(new MyLabelComparator()); // unprocessed labels list
// processed labels list => ordered TreeSet List , “处理过的”表示“已经拓展的”
TreeSet<Integer> P = new TreeSet<Integer>(new MyLabelComparator()); // processed labels list
// array of labels // 一个标签,很像一个状态:从哪里来,现在在哪里,路上访问了谁,耗费了多少资源
labels = new ArrayList<label>(2 * userParam.nbclients); // initial size at least larger than nb clients
boolean[] cust = new boolean[userParam.nbclients + 2];
// for depot 0
cust[0] = true;// vertexVisited
for (i = 1; i < userParam.nbclients + 2; i++) cust[i] = false;
labels.add(new label(0, -1, 0.0, 0, 0, false, cust)); // first label: start from depot (client 0)
U.add(0);
// for each city, an array with the index of the corresponding labels (for dominance)
checkDom = new int[userParam.nbclients + 2];// 每个客户节点 被检查过“占优性”的节点有多少个
ArrayList<Integer>[] city2labels = new ArrayList[userParam.nbclients + 2];
for (i = 0; i < userParam.nbclients + 2; i++) {
city2labels[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
checkDom[i] = 0; // index of the first label in city2labels that needs to be checked for dominance (last labels added)
}
city2labels[0].add(0);
nbsol = 0;
maxSol = 2 * nbRoute;
while ((U.size() > 0) && (nbsol < maxSol)) {
// second term if we want to limit to the first solutions encountered to speed up the SPPRC (perhaps not the BP)
// remark: we'll keep only nbRoute, but we compute 2 x nbRoute!
// It makes a huge difference => we'll keep the most negative ones
// this is something to analyze further! how many solutions to keep and which ones?
// process one label => get the index AND remove it from U
currentidx = U.pollFirst(); // 从队首弹出一个 待拓展的路径的下标
current = labels.get(currentidx);
// check for dominance 查看 当前城市的标签们 有没有 被占优的,要删除掉 被占优的标签
// code not fully optimized:
int l1, l2;
boolean pathdom;
label la1, la2;
ArrayList<Integer> cleaning = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// check for dominance between the labels added since the last time
// we came here with this city and all the other ones
// ?? checkDom?? here, why not directly use i=0
for (i = checkDom[current.city]; i < city2labels[current.city].size(); i++) {
for (j = 0; j < i; j++) {
l1 = city2labels[current.city].get(i);
l2 = city2labels[current.city].get(j);
la1 = labels.get(l1);
la2 = labels.get(l2);
// could happen since we clean 'city2labels' thanks
// to 'cleaning' only after the double loop
if (!(la1.dominated || la2.dominated)) { // 两个标签暂时都没有被占优
// Q1: 判断 标签2 是否被占优了
pathdom = true;
for (int k = 1; pathdom && (k < userParam.nbclients + 2); k++) {
//la1没有访问节点k 或者 la2访问了节点k 、、说明 la1对应的路径比la2短
// if pathdom=true, then it means la1来过的 la2必定也来过
// 看书! la1 访问过的节点 少于 la2 访问过的节点
pathdom = (!la1.vertexVisited[k] || la2.vertexVisited[k]);
}
if (pathdom && (la1.cost <= la2.cost) && (la1.tTime <= la2.tTime)
&& (la1.demand <= la2.demand)) {
labels.get(l2).dominated = true;// l2 被占优了
U.remove((Integer) l2);
cleaning.add(l2);
pathdom = false; // ?? why bother to do this
//System.out.print(" ###Remove"+l2);
}
// Q2: 判断 标签1 是否被占优了
pathdom = true;
for (int k = 1; pathdom && (k < userParam.nbclients + 2); k++) {
//la2没有访问节点k或者la1访问了节点k
//如果pathdom=true, that means la2 的沿途节点数 比 la1少, 因为la2访问过的,la1必然访问过
pathdom = (!la2.vertexVisited[k] || la1.vertexVisited[k]);
}
if (pathdom && (la2.cost <= la1.cost) && (la2.tTime <= la1.tTime) && (la2.demand <= la1.demand)) {
labels.get(l1).dominated = true;// l1被占优了
U.remove(l1);
cleaning.add(l1);
//System.out.print(" ###Remove"+l1);
j = city2labels[current.city].size();// ?? get out of this for loop, so I guess it's kind of speed-up
}
}
}
}
for (Integer c : cleaning)
city2labels[current.city].remove((Integer) c); // a little bit confusing but ok since c is an Integer and not an int!
cleaning = null;
// for current.city, how many non-denominant labels have we checked?
checkDom[current.city] = city2labels[current.city].size(); // update checkDom: all labels currently in city2labels were checked for dom.
// expand REF
if (!current.dominated) {// 当前的这个label没有被占优
//System.out.println("Label "+current.city+" "+current.indexPrevLabel+" "+current.cost+" "+current.ttime+" "+current.dominated);
if (current.city == userParam.nbclients + 1) { // ??shortest path candidate to the depot! 此时 不能再扩展路径了
if (current.cost < -1e-7) { // SP candidate for the column generation
P.add(currentidx);// 当前标签没有被占优,将它加到 已处理的集合P 中
nbsol = 0; // 数 集合P 中 未被占优的标签 的个数
for (Integer labi : P) { // labi : label index
label s = labels.get(labi);
if (!s.dominated)
nbsol++;
}
}
} else {
// if not the depot, we can consider extensions of the path
for (i = 0; i < userParam.nbclients + 2; i++) { // try to reach Customer i
// don't go back to a vertex already visited or along a forbidden edge
// expand this label to some customer i
if ((!current.vertexVisited[i]) &&
(userParam.dist[current.city][i] < userParam.verybig - 1e-6)) {
// ttime
tt = (float) (current.tTime + userParam.ttime[current.city][i]
+ userParam.s[current.city]);
if (tt < userParam.a[i])// 提前到了,等到时间窗开放,才能服务
tt = userParam.a[i];
// demand
d = current.demand + userParam.d[i];
//System.out.println(" -- "+i+" d:"+d+" t:"+tt);
//the potential next customer is feasible?
if ((tt <= userParam.b[i]) && (d <= userParam.capacity)) {
// satisfy the time window constraint and capacity constraint
// current.city --> i
idx = labels.size();
boolean[] newCust = new boolean[userParam.nbclients + 2]; // vertextVisited
System.arraycopy(current.vertexVisited, 0, newCust,
0, userParam.nbclients + 2);
newCust[i] = true;
//speedup: third technique - Feillet 2004 as mentioned in Laporte's paper 、、??
// current.city --> i --X--> j, so we marke all infeasible points j as 'visited'
// then we could skip this point
for (j = 1; j <= userParam.nbclients; j++) {
if (!newCust[j]) {
tt2 = (float) (tt + userParam.ttime[i][j] + userParam.s[i]);
d2 = d + userParam.d[j];
if ((tt2 > userParam.b[j]) || (d2 > userParam.capacity)) {
newCust[j] = true; // useless to visit this client , so marker it as 'visited'
}
}
}
// expand this label and then we obtain a new label( whose city is i) that is seen as unprocessed, so push it into U
// label: city, indexPrevLabel, cost,tTime,demand, dominated, vertexVisited
// !! 这里 current.cost + userParam.cost[current.city][i] 用到了 列生成算法 解主问题,得到对偶变量的值,然后更新了userParams.cost[][]
labels.add(new label(i, currentidx, current.cost + userParam.cost[current.city][i], tt, d, false, newCust)); // first label: start from depot (client 0)
if (!U.add((Integer) idx)) { // idx: index of this new label
// only happens if there exists already a label at this vertex with the same cost, time and demand and visiting the same cities before
// It can happen with some paths where the order of the cities is permuted
// I guess, e,g, 0-1-2-3-0, 0-3-1-2-0
labels.get(idx).dominated = true; // => we can forget this label and keep only the other one?? only keep the previous one
// ?? but how can you do this? why?
}
else {
city2labels[i].add(idx);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
// clean
checkDom = null;
// filtering: find the path from depot to the destination
Integer lab;
i = 0;
while ((i < nbRoute) && ((lab = P.pollFirst()) != null)) {
label s = labels.get(lab);
if (!s.dominated) {
if (/*(i < nbroute / 2) ||*/ (s.cost < -1e-4)) {
// System.out.println(s.cost);
// if(s.cost > 0) {
// System.out.println("warning >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
// }
route newRoute = new route();
newRoute.setcost(s.cost);
newRoute.addcity(s.city);
// 按照indexPreLabel回溯,找到最优解
int path = s.indexPrevLabel;
while (path >= 0) {// 这里和前面depot0的标签中indexPreLabel=-1相呼应
newRoute.addcity(labels.get(path).city);
path = labels.get(path).indexPrevLabel;
}
newRoute.switchpath();
routes.add(newRoute);
i++;
}
}
}// end while
}
}
- 路径 route.java
package BranchAndPrice;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class route implements Cloneable {
public double cost, Q; // Q 表示 这条路径的使用次数的线性松弛版
// first resource: cost (e.g. distance or strict travel time)
public ArrayList<Integer> path;
public route() { // non-param constructor
this.path = new ArrayList<Integer>();
this.cost = 0.0;
}
public route(int pathSize) {
this.path = new ArrayList<Integer>(pathSize);
this.cost = 0.0;
}
/*
* @update 2013. 6. 8
* @modify Geunho Kim
*/
// method for deep cloning // 深拷贝
public route clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
route route = (route) super.clone();// ?? 强制转型
route.path = (ArrayList<Integer>) path.clone();
return route;
}
public void removeCity(int city) {
this.path.remove(Integer.valueOf(city));
}
public void addcity(int f_city, int city) {// 在f_city 之后,add city,
int index = this.path.indexOf(f_city);
this.path.add(index + 1, city);
}
public void addcity(int city) {
this.path.add(city);
}
public void setcost(double c) {
this.cost = c;
}
public double getcost() {
return this.cost;
}
public void setQ(double a) {
this.Q = a;
}
public double getQ() {
return this.Q;
}
public ArrayList<Integer> getpath() {
return this.path;
}
public void switchpath() {// 将path前后置换
Integer swap;
int nb = path.size() / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++) {
swap = path.get(i);
path.set(i, path.get(path.size() - 1 - i));// !!! not add
path.set(path.size() - 1 - i, swap);
}
}
}
- VRP问题的参数 paramsVRP.java
package BranchAndPrice;
// this class contains the inputs and methods to read the inputs
// for the Branch and Price CVRP with TW
// ...I'm afraid that it is not pure OO code
// ...but it is not so bad
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class paramsVRP {
public int mvehic;
public int nbclients;// number of clients
public int capacity; // vehicle capacity
public double[][] cost; // for the SPPRC subProblem
public double[][] distBase; // 为dist存根,original distances for the Branch and Bound
public double[][] dist; // distances that will be updated during the B&B before being used in the CG & SPPRC
public double[][] ttime;// travel time
public double[][] edges; // weight of each edge during branch and bound
public double[] posx, posy, d, wval; // ?? what is wval
public int[] a; // time windows: a=early, b=late, s=service
public int[] b;
public int[] s;
public double verybig;
public double speed; // vehicle's speed
public double gap;
public double maxlength;
public boolean serviceInTW;
String[] citieslab;
public paramsVRP() {
gap = 0.00000000001;
serviceInTW = false;
nbclients = 100;
speed = 1;
mvehic = 0;
verybig = 1E10;
}
public void initParams(String inputPath) throws IOException {
int i, j;
try {
/**
* @update 2013. 6. 12
* @modify Geunho Kim
*
* for Hadoop distributed file system
*/
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(inputPath));
String line = new String();
// //
// for local file system
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(inputPath));
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
line = br.readLine();
String[] tokens = line.split("\\s+");
mvehic = Integer.parseInt(tokens[1]);
capacity = Integer.parseInt(tokens[2]);
citieslab = new String[nbclients + 2];
d = new double[nbclients + 2]; // demand
a = new int[nbclients + 2]; // ready time
b = new int[nbclients + 2];// due time
s = new int[nbclients + 2];// service time
posx = new double[nbclients + 2];
posy = new double[nbclients + 2];
distBase = new double[nbclients + 2][nbclients + 2];
cost = new double[nbclients + 2][nbclients + 2];
dist = new double[nbclients + 2][nbclients + 2];
ttime = new double[nbclients + 2][nbclients + 2];
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
line = br.readLine();
for (i = 0; i < nbclients + 1; i++) {
line = br.readLine();
//System.out.println(line);
tokens = line.split("\\s+");
citieslab[i] = tokens[1]; // customer number
posx[i] = Double.parseDouble(tokens[2]); // x coordinate
posy[i] = Double.parseDouble(tokens[3]); // y coordinate
d[i] = Double.parseDouble(tokens[4]); // demand
a[i] = Integer.parseInt(tokens[5]); // ready time
b[i] = Integer.parseInt(tokens[6]); // due time
s[i] = Integer.parseInt(tokens[7]); // service
// check if the service should be done before due time
if (serviceInTW) // ??
b[i] -= s[i];
}
br.close();
// second depot : copy of the first one for arrival
citieslab[nbclients + 1] = citieslab[0];
d[nbclients + 1] = 0.0;
a[nbclients + 1] = a[0];
b[nbclients + 1] = b[0];
s[nbclients + 1] = 0;// !!
posx[nbclients + 1] = posx[0];
posy[nbclients + 1] = posy[0];
// ---- distances
double max;
maxlength = 0.0;// 一个路径长度的上限,用于列生成算法
for (i = 0; i < nbclients + 2; i++) {
max = 0.0;
for (j = 0; j < nbclients + 2; j++) {
// dist[i][j]=Math.round(10*Math.sqrt((posx[i]-posx[j])*(posx[i]-posx[j])+(posy[i]-posy[j])*(posy[i]-posy[j])))/10.0;
distBase[i][j] = ((int) (10 * Math
.sqrt((posx[i] - posx[j]) * (posx[i] - posx[j])
+ (posy[i] - posy[j]) * (posy[i] - posy[j])))) / 10.0; //只保留到小数点后一位
// truncate to get the same results as in Solomon
if (max < distBase[i][j]) max = distBase[i][j];
}
maxlength += max; // a route with a length longer than this is not
// possible (we need it to check the feasibility of
// the Column Gen sol.
}
// some edges are not available to pass in some direction
for (i = 0; i < nbclients + 2; i++) {
distBase[i][0] = verybig;// any node can't go back to Depot 0
distBase[nbclients + 1][i] = verybig; // Depot nbclients+1 cannot visit any other node
distBase[i][i] = verybig; // any node can't form a loop on its own
}
/*
* for(i = 0; i < 20; i++)
* distBase[10][i] = verybig;
* for(i = 21; i < nbclients+2; i++)
* distBase[10][i] = verybig;
* for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
* distBase[i][20] = verybig;
* for(i = 11; i < nbclients+2; i++)
* distBase[i][20] = verybig;
* distBase[20][10] = verybig;
*/
for (i = 0; i < nbclients + 2; i++)
for (j = 0; j < nbclients + 2; j++) {
dist[i][j] = distBase[i][j];
}
// ---- time
for (i = 0; i < nbclients + 2; i++)
for (j = 0; j < nbclients + 2; j++)
ttime[i][j] = distBase[i][j] / speed;
// ------- cost
for (j = 0; j < nbclients + 2; j++) {
cost[0][j] = dist[0][j];
cost[j][nbclients + 1] = dist[j][nbclients + 1];
}
// !!cost for the other edges are determined during column generation
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Error: " + e);
}
wval = new double[nbclients + 2];
for (i = 1; i < nbclients + 2; i++) // ??
wval[i] = 0.0;
edges = new double[nbclients + 2][nbclients + 2];
}
}