RVEA
- 1 目标函数
- 2 预备知识
- 3 参考向量引导选择
- 4 更新参考向量
- 5 流程
- 6 代码
- 7 运行效果
1 目标函数
min X f ( X ) = ( f 1 ( X ) , f 2 ( X ) , . . . , f M ( X ) ) \min_{\small{X}} \pmb{f(\small{X})} = (f_1(\small{X}), f_2(\small{X}), ..., f_M(\small{X})) Xminf(X)=(f1(X),f2(X),...,fM(X))
2 预备知识
参考向量个数 N = C H + M − 1 M − 1 N = C_{H+M-1}^{M-1} N=CH+M−1M−1, H H H为边长分成的份数, M M M是目标的个数
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-XkhezIHc-1687679692188)(C:\Users\24220\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230615115213486.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/acc6af6f5ef4484f82b1a171341e9deb.png#pic_center)
from pymoo.algorithms.moo.rvea import RVEA
from pymoo.optimize import minimize
from pymoo.problems import get_problem
from pymoo.util.ref_dirs import get_reference_directions
from pymoo.visualization.scatter import Scatter
problem = get_problem("dtlz1", n_obj=3)
ref_dirs = get_reference_directions("das-dennis", 3, n_partitions=12)
algorithm = RVEA(ref_dirs)
res = minimize(problem,
algorithm,
termination=('n_gen', 400),
seed=1,
verbose=False)
plot = Scatter()
plot.add(problem.pareto_front(ref_dirs), plot_type="surface", color="black", alpha=0.7)
plot.add(res.F, color="red")
plot.show(block=True)
此代码中 H = n _ p a r t i t i o n s = 12 M = n _ o b j = 3 H =n\_partitions = 12 \;\;\;\; M = n\_obj = 3 H=n_partitions=12M=n_obj=3
故最终的参考向量个数 N = C 12 + 3 − 1 3 − 1 = C 14 2 = 91 N = C_{12+3-1}^{3-1} = C_{14}^2 = 91 N=C12+3−13−1=C142=91
每个参考向量需要单位化: v i = u i ∣ ∣ u i ∣ ∣ v_i=\frac{u_i}{ ||u_i||} vi=∣∣ui∣∣ui
参考向量的相似度 c o s θ = v 1 ∙ v 2 ∣ ∣ v 1 ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ v 2 ∣ ∣ cos \theta = \frac{\pmb{v_1} \bullet\pmb{ v_2}}{||\pmb{v_1} ||||\pmb{v_2}||} cosθ=∣∣v1∣∣∣∣v2∣∣v1∙v2
3 参考向量引导选择
-
理想向量: Z t m i n = ( Z t , 1 m i n , Z t , 2 m i n , . . . , Z t , m m i n ) \small{Z_t^{min}} = (\small{Z_{t, 1}^{min}}, \small{Z_{t, 2}^{min}}, ..., \small{Z_{t, m}^{min}}) Ztmin=(Zt,1min,Zt,2min,...,Zt,mmin)代表每个目标函数的最小值组成的向量
-
目标向量平移:因为参考向量是以坐标系原点为中心的,因此需要将目标函数都平移到坐标系原点: f t , i ′ = f t , i − Z t m i n \text{f}_{t, i}^{\prime} = \text{f}_{t, i} - \small{Z_t^{min}} ft,i′=ft,i−Ztmin, f t , i \text{f}_{t, i} ft,i表示第 t t t次迭代中第 i i i个个体的目标函数向量
-
种群划分:种群里面的每个个体按照到参考向量的最小夹角,与离得最近的目标向量归为一个集合体【与目标向量的余弦值最大】
c o s θ t , i , j = f t , i ′ ∙ v t , j ∣ ∣ f t , i ′ ∣ ∣ P ˉ t , k = { I t , i ∣ k = argmax i ∈ { 1 , 2 , . . . , N } c o s θ t , i , j } \begin{align} & cos \theta_{t, i, j} = \frac{\text{f}_{t, i}^{\prime} \bullet \pmb{v}_{t, j}}{||\text{f}_{t, i}^{\prime}||} \\ & \bar{P}_{t, k} = \{I_{t, i}|k = \underset{i \in \{1, 2, ..., N\}}{\text{argmax}} cos \theta_{t, i, j}\} \end{align} cosθt,i,j=∣∣ft,i′∣∣ft,i′∙vt,jPˉt,k={It,i∣k=i∈{1,2,...,N}argmaxcosθt,i,j}
- 角度惩罚距离
d t , i , j = ( 1 + P ( θ t , i , j ) ) ∙ ∣ ∣ f t , i ′ ∣ ∣ P ( θ t , i , j ) = M . ( t t m a x ) α . θ t , i , j γ v t , j γ v t , j = min i ∈ { 1 , 2 , . . . , N } , i ≠ j < v t , i , v t , j > 最小角 \begin{align} d_{t, i, j} &= (1 + P(\theta_{t, i, j})) \bullet ||\text f_{t, i}^{\prime}|| \\ P(\theta_{t, i, j}) &= M . (\frac{t}{t_{max}}) ^\alpha . \frac{\theta_{t, i, j}}{\gamma_{\pmb v_{t, j}}} \\ \gamma_{\pmb v_{t, j}} &= \min_{i \in \{1, 2, ..., N\}, i \neq j} <\pmb v_{t, i}, \pmb v_{t, j}> \;\;\;\; \text{最小角} \end{align} dt,i,jP(θt,i,j)γvt,j=(1+P(θt,i,j))∙∣∣ft,i′∣∣=M.(tmaxt)α.γvt,jθt,i,j=i∈{1,2,...,N},i=jmin<vt,i,vt,j>最小角
4 更新参考向量
v t + 1 , i = v 0 , i ∘ ( Z t + 1 m a x − Z t + 1 m i n ) ∣ ∣ v 0 , i ∘ ( Z t + 1 m a x − Z t + 1 m i n ) ∣ ∣ \pmb v_{t+1, i} = \frac{\pmb v_{0, i} \circ (\small Z_{t+1}^{max} - Z_{t+1}^{min})}{||\pmb v_{0, i} \circ (\small Z_{t+1}^{max} - Z_{t+1}^{min})||} vt+1,i=∣∣v0,i∘(Zt+1max−Zt+1min)∣∣v0,i∘(Zt+1max−Zt+1min)
5 流程
整体流程

参考向量指导选择

更新参考向量

fr通常设置为
0.2
0.2
0.2
alpha通常设置为
2
2
2
t_max通常设置为
400
400
400
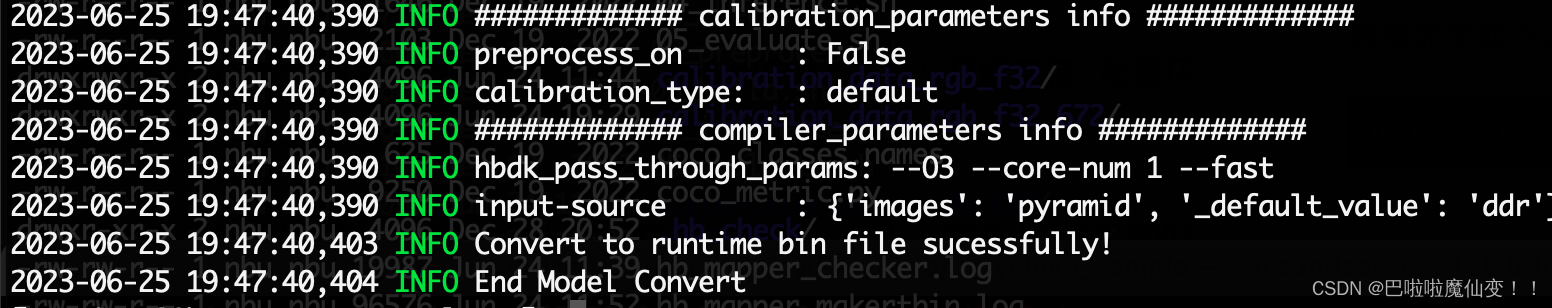
6 代码
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from pymoo.util.ref_dirs import get_reference_directions
import geatpy as ea
from pymoo.visualization.scatter import Scatter
class DTLZ1(ea.Problem): # 继承Problem父类
def __init__(self, M=3, Dim=None): # M : 目标维数;Dim : 决策变量维数
name = 'DTLZ1' # 初始化name(函数名称,可以随意设置)
maxormins = [1] * M # 初始化maxormins(目标最小最大化标记列表,1:最小化该目标;-1:最大化该目标)
if Dim is None:
Dim = M + 4 # 初始化Dim(决策变量维数)
varTypes = np.array([0] * Dim) # 初始化varTypes(决策变量的类型,0:实数;1:整数)
lb = [0] * Dim # 决策变量下界
ub = [1] * Dim # 决策变量上界
lbin = [1] * Dim # 决策变量下边界(0表示不包含该变量的下边界,1表示包含)
ubin = [1] * Dim # 决策变量上边界(0表示不包含该变量的上边界,1表示包含)
# 调用父类构造方法完成实例化
ea.Problem.__init__(self, name, M, maxormins, Dim, varTypes, lb, ub, lbin, ubin)
def evalVars(self, Vars): # 目标函数
XM = Vars[:, (self.M - 1):]
g = 100 * (self.Dim - self.M + 1 + np.sum(((XM - 0.5) ** 2 - np.cos(20 * np.pi * (XM - 0.5))), 1,
keepdims=True))
ones_metrix = np.ones((Vars.shape[0], 1))
f = 0.5 * np.hstack([np.fliplr(np.cumprod(Vars[:, :self.M - 1], 1)), ones_metrix]) * np.hstack(
[ones_metrix, 1 - Vars[:, range(self.M - 2, -1, -1)]]) * (1 + g)
return f
if __name__ == '__main__':
M = 3 # 目标函数的个数
ref_dirs0 = get_reference_directions("das-dennis", M, n_partitions=12) # 初始化参考向量
N = ref_dirs0.shape[0] # 参考向量的大小
dim = 7 # 决策变量的维度
for i in range(ref_dirs0.shape[0]):
ref_dirs0[i] = ref_dirs0[i] / np.linalg.norm(ref_dirs0[i])
ref_dirs = np.copy(ref_dirs0)
pop = np.random.random((100, dim))
crossover = ea.Recsbx(XOVR=1, n=30) # 交叉
mutation = ea.Mutpolyn(Pm=1 / dim) # 变异
lb = np.array([0] * dim)
ub = np.array([1] * dim)
varsType = np.array([0] * dim)
problem = DTLZ1()
t_max = 400
alpha = 2
fr = 0.2
for t in range(t_max):
print(t)
children = crossover.do(pop)
children = mutation.do('RI', children, np.array([lb, ub, varsType]))
pop = np.row_stack((pop, children)) # 合并种群
ObjV = problem.evalVars(pop) # 计算种群的目标值
# ================== 参考向量指导选择 ==================
z_min = np.min(ObjV, axis=0) # 计算最优点
# ======================= 更新参考向量 ==============================
if np.mod(t / t_max, fr) == 0:
z_max = np.max(ObjV, axis=0) # 计算最差点
for j in range(N):
ref_dirs[j] = np.multiply(ref_dirs0[j], z_max - z_min)
ref_dirs[j] = ref_dirs[j] / np.linalg.norm(ref_dirs[j])
# ======================= 更新参考向量 ==============================
ObjV_1 = ObjV - z_min # 目标值转换到坐标轴
pop_size = pop.shape[0]
theta_set = np.full((pop_size, N), np.nan) # 根据目标值与参考点之间的夹角,划分种群
for i in range(pop_size):
for j in range(N):
cos_theta = ObjV_1[i].dot(ref_dirs[j]) / np.maximum(np.linalg.norm(ObjV_1[i]), 1e-64)
theta_set[i, j] = np.arccos(cos_theta)
partition = [[] for _ in range(N)] # 划分为 N 个种群
for i in range(pop_size):
k = np.argmin(theta_set[i])
partition[k].append(i)
gamma = np.full((N, N), np.nan) # 参考向量之间的夹角
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if i == j:
gamma[i, j] = np.pi
continue
gamma[i, j] = np.arccos(ref_dirs[i].dot(ref_dirs[j]))
gamma = np.min(gamma, axis=1)
apd_partition = [[] for _ in range(N)]
for j in range(N): # 设置角度惩罚
partiton_j = partition[j]
for i in partiton_j:
p_theta = M * np.power(t / t_max, alpha) * (theta_set[i, j] / gamma[j])
apd = (1 + p_theta) * np.linalg.norm(ObjV_1[i])
apd_partition[j].append(apd)
# ================== 参考向量指导选择 =====================
# ==================== 精英选择 ========================
survivor = []
for j in range(N):
partiton_j = partition[j]
if not partiton_j:
continue
k = np.argmin(apd_partition[j])
survivor.append(partiton_j[k])
pop = pop[survivor]
# ==================== 精英选择 =======================
ObjV = problem.evalVars(pop)
print(ObjV.shape)
plot = Scatter()
plot.add(ObjV)
plot.show()
7 运行效果