目录
第一种方法:使用LockSupport的park和unpark功能(推荐)
第二种方式:synchronized+wait+notify
第三种:暴力循环方法(不推荐)
第一种方法:使用LockSupport的park和unpark功能(推荐)
简单来说我们有一个名为LockSupport的方法
park就是阻塞当前进程
unpark就是取消阻塞让其继续执行
我们要循环打印ABC三个线程的三个字母
那么我们就可以让三个线程按顺序阻塞和解锁,就能完成打印
代码
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class demo2 {
static Thread t1,t2,t3;
public static void main(String[] args) {
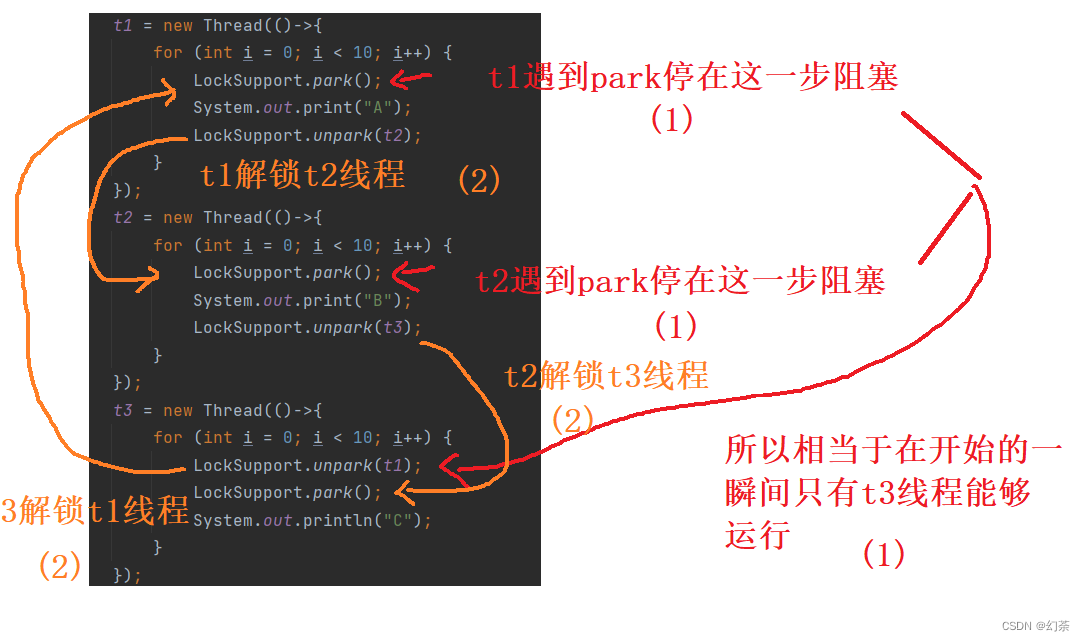
t1 = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
LockSupport.park();
System.out.print("A");
LockSupport.unpark(t2);
}
});
t2 = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
LockSupport.park();
System.out.print("B");
LockSupport.unpark(t3);
}
});
t3 = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
LockSupport.park();
System.out.println("C");
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
第二种方式:synchronized+wait+notify
实际上就是把第一种方式换为用这种方式实现
同样还是控制加锁顺序和解锁顺序罢了
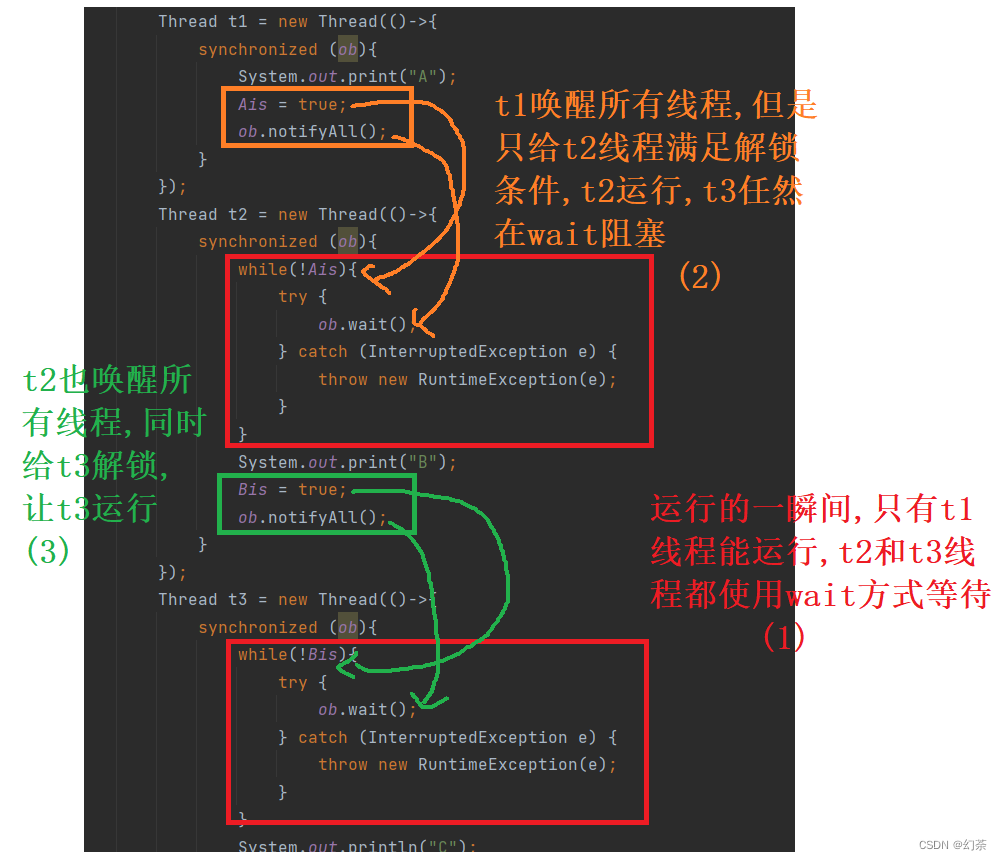
public class demo3 {
public static Object ob = new Object();
static boolean Ais = false;
static boolean Bis = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
synchronized (ob){
System.out.print("A");
Ais = true;
ob.notifyAll();
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
synchronized (ob){
while(!Ais){
try {
ob.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.print("B");
Bis = true;
ob.notifyAll();
}
});
Thread t3 = new Thread(()->{
synchronized (ob){
while(!Bis){
try {
ob.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("C");
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
t1.run();
t2.run();
t3.run();
}
}
}
第三种:暴力循环方法(不推荐)
就...相当于创建三十个线程了....如果实在想不起来其他方法就用这个吧....
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
System.out.print("A");
});
t1.start();
t1.join();
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
System.out.print("B");
});
t2.start();
t2.join();
Thread t3 = new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("C");
});
t3.start();
t3.join();
}
}
}


![[Eigen中文文档] 稀疏矩阵操作](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c691a960e075455caab3de3d0fceae45.jpeg#pic_center)