文章目录
- Pre
- Pre
- MyBatis-Spring 组件
- 扩展点org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean
- InitializingBean扩展接口 afterPropertiesSet
- FactoryBean 扩展接口 getObject
- ApplicationListener扩展接口 onApplicationEvent
- 扩展点org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean
- SqlSessionTemplate 解决线程安全问题

Pre
Spring Boot - 扩展接口一览
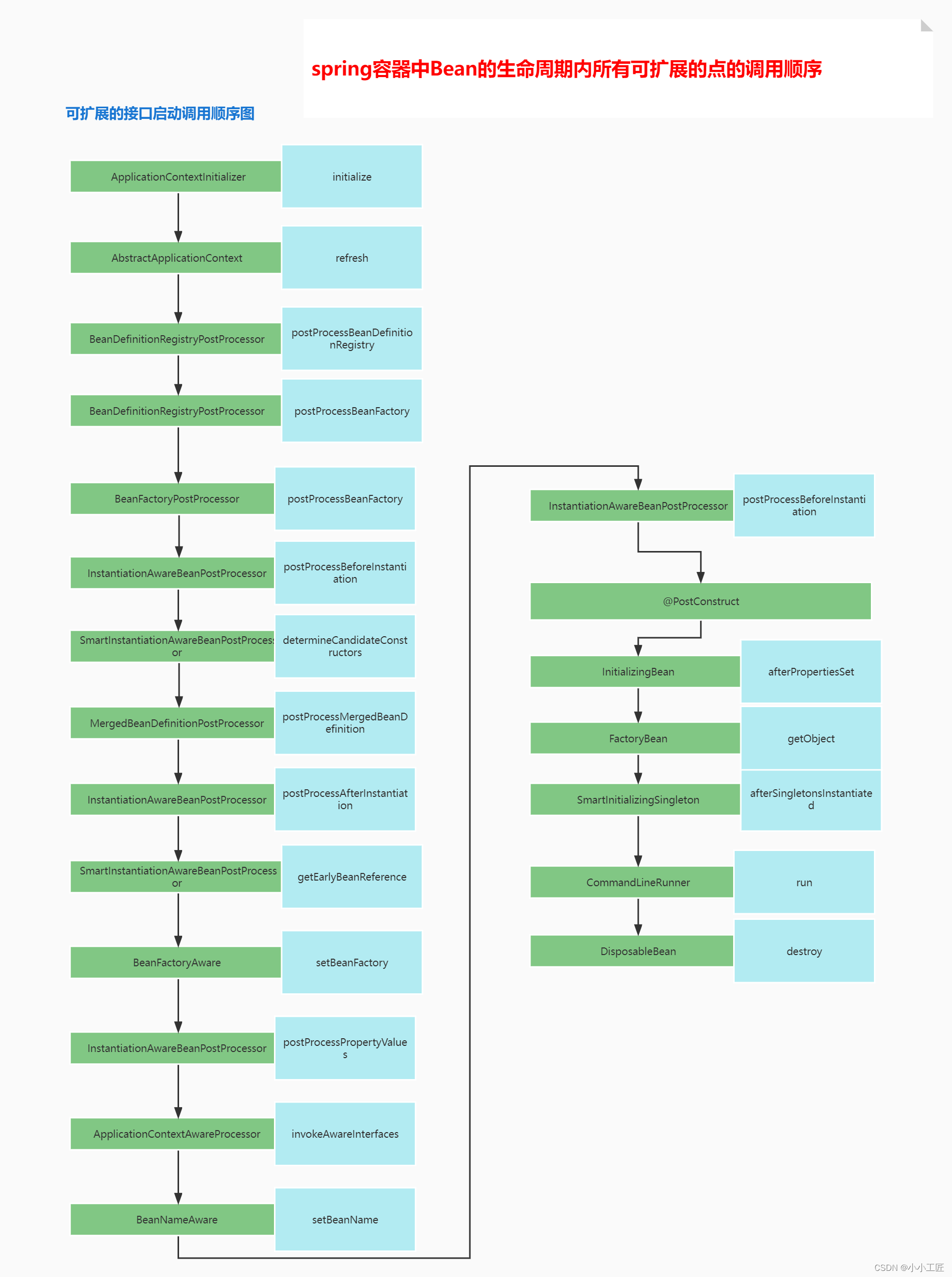
Pre
Spring - FactoryBean扩展接口
Spring-Spring整合MyBatis详解

MyBatis-Spring 组件
MyBatis的启动过程包含了一系列核心对象的创建,而这个过程涉及到对配置文件的读取和处理 。
MyBatis 也专门提供了一个 MyBatis-Spring 组件来完成与 Spring 框架的集成。
对于 MyBatis-Spring 而言,它的启动过程构建在 MyBatis 的启动过程基础之上,融合了 Spring 框架的功能特性。
因此了解Spring的扩展点是非常重要的。
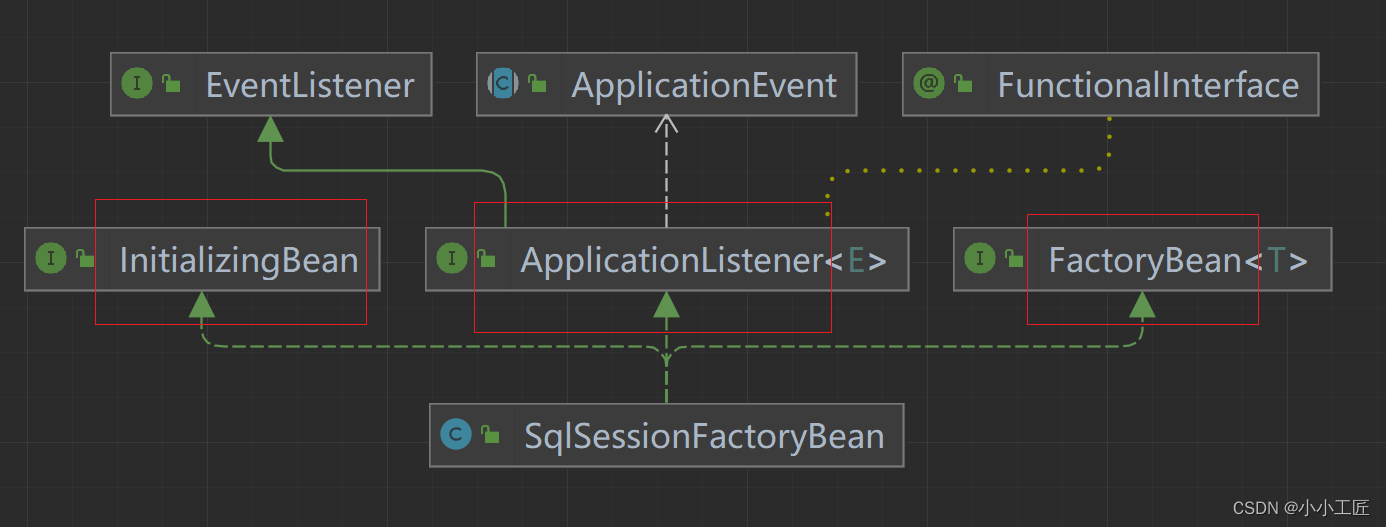
扩展点org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean
基于这些启动扩展点,其他框架实现与 Spring 框架之间的整合变得非常简单。
MyBatis 就是利用了这些扩展点实现与 Spring 框架的整合。扩展点-------------> SqlSessionFactoryBean 类。
public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<SqlSessionFactory>, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
...
private Configuration configuration;
private SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
private String environment = SqlSessionFactoryBean.class.getSimpleName();
...
}
SqlSessionFactoryBean 实现了 FactoryBean、InitializingBean 和 ApplicationListener 这三个扩展点,部分重要的变量如上。
InitializingBean扩展接口 afterPropertiesSet
结合Spring扩展点的执行顺序,我们先看看 InitializingBean,找到 afterPropertiesSet
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
显然,SqlSessionFactoryBean 的主要职责就是完成 SqlSessionFactory 的构建,这也是这个类的类名的由来。
而完成这个操作的最合适阶段就是生命周期中的 InitializingBean 阶段。
buildSqlSessionFactory 方法的具体实现过程,这个方法非常长,但代码结构比较简单。
抛开大量的代码细节,使用如下所示的代码框架来展示这个方法的结构:
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
Configuration configuration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
if (this.configuration != null) {
//如果当前的configuration不为空,这直接使用该对象
configuration = this.configuration;
...
} else if (this.configLocation != null) {
//如果配置文件地址configLocation不为空,则通过XMLConfigBuilder进行解析并创建configuration
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
configuration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
//如果以上两种情况都不满足,则创建一个新的configuration对象并进行参数赋值
configuration = new Configuration();
...
}
//设置objectFactory等各种MyBatis运行时所需的配置信息
...
//基于configuration,通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder构建SqlSessionFactory
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration);
}
继续build
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
首先会加载 XML 配置文件,然后基于这个配置文件构建一个 Configuration 配置类,再通过 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 的 build 方法来创建 SqlSessionFactory。
这里创建的是一个 DefaultSqlSessionFactory,我们可以通过 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 进而获取 SqlSession 对象的实例。
FactoryBean 扩展接口 getObject
继续看 SqlSessionFactoryBean 实现的 FactoryBean接口, 从接口的泛型定义上,我们明白它的 getObject 方法返回的应该是一个 SqlSessionFactory 对象。
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
如果还没有创建目标 SqlSessionFactory,就直接调 afterPropertiesSet 方法完成该对象的创建并返回。
ApplicationListener扩展接口 onApplicationEvent
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (failFast && event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) {
// fail-fast -> check all statements are completed
this.sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getMappedStatementNames();
}
}
在接收到代表容器刷新的 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件时,重新获取各种 MappedStatement。
执行流程如下:
ContextRefreshedEvent ------> onApplicationEvent -------------> getMappedStatementNames
继续看下 getMappedStatementNames
@Override
public Collection<String> getMappedStatementNames() {
//构建所有的Statement
buildAllStatements();
return mappedStatements.keySet();
}
继续跟下去就已经到了Mybatis了,就这么巧妙的集合起来了。
至此,SqlSessionFactoryBean 中与 Spring 整合的相关内容就梳理完了。通过 org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean,我们就可以获取 SqlSessionFactory 对象,这是 MyBatis 框架启动过程的目标生成对象 。

扩展点org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean
继续来看另一个 FactoryBean, MapperFactoryBean 这个类用于生成 MapperFactory, MapperFactory 的作用显然就是获取 Mapper
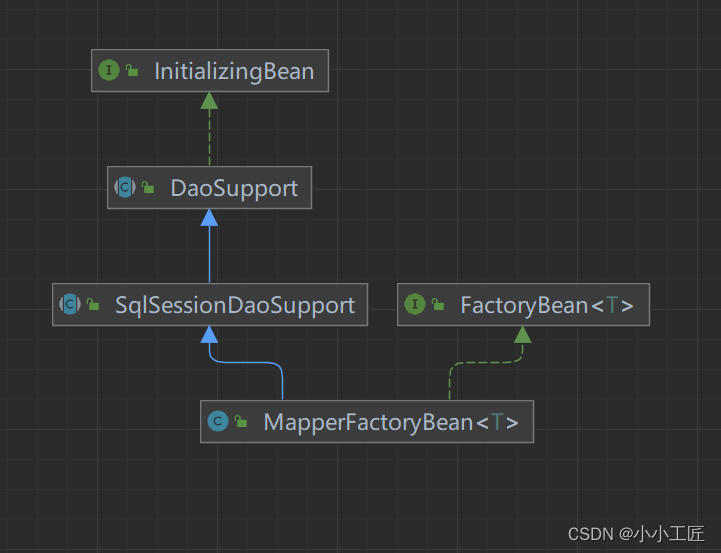
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
private Class<T> mapperInterface;
...
}
MapperFactoryBean 实现了 FactoryBean 接口,那就看下 getObject方法
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
通过 SqlSession 的 getMapper 方法获取 Mapper 对象,这个是 MyBatis 自身所提供的核心功能。
那么这个 SqlSession 是怎么来的呢?
不难发现 MapperFactoryBean 在实现了 FactoryBean 接口的同时,还扩展了 SqlSessionDaoSupport 类。
SqlSessionDaoSupport 是一个抽象类,扩展了 Spring 中的 DaoSupport 抽象类,并提供了如下方法
public abstract class SqlSessionDaoSupport extends DaoSupport {
private SqlSession sqlSession;
private boolean externalSqlSession;
public void setSqlSessionFactory(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
if (!this.externalSqlSession) {
//注意,这个构建SqlSession是一个SqlSessionTemplate对象
this.sqlSession = new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
public void setSqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSessionTemplate;
this.externalSqlSession = true;
}
public SqlSession getSqlSession() {
return this.sqlSession;
}
...
}
看到这里定义了一个 SqlSession 对象用于对外暴露访问入口。
注意,这个 SqlSession 并不是我们所认为的来自 MyBatis 的 DefaultSqlSession,而是构建了一个同样实现了 SqlSession 接口的 SqlSessionTemplate 类。
SqlSessionTemplate 解决线程安全问题
既然 MyBatis 已经提供了 DefaultSqlSession,为什么这里还要构建一个 SqlSessionTemplate 呢?那一起看看这个 SqlSessionTemplate,这是 MyBatis-Spring 中的核心类。
DefaultSqlSession 本身是线程不安全的,所以我们要使用 SqlSession 时,为了确保线程安全,常规做法就是通过 SqlSessionFactory 获取一个新的 SqlSession。但这种做法效率会很低,造成资源的浪费。
更好的实现方法应该是通过全局唯一的 SqlSession 实例来完成 DefaultSqlSession 的工作,而 SqlSessionTemplate 就是这个全局唯一的 SqlSession 实例。
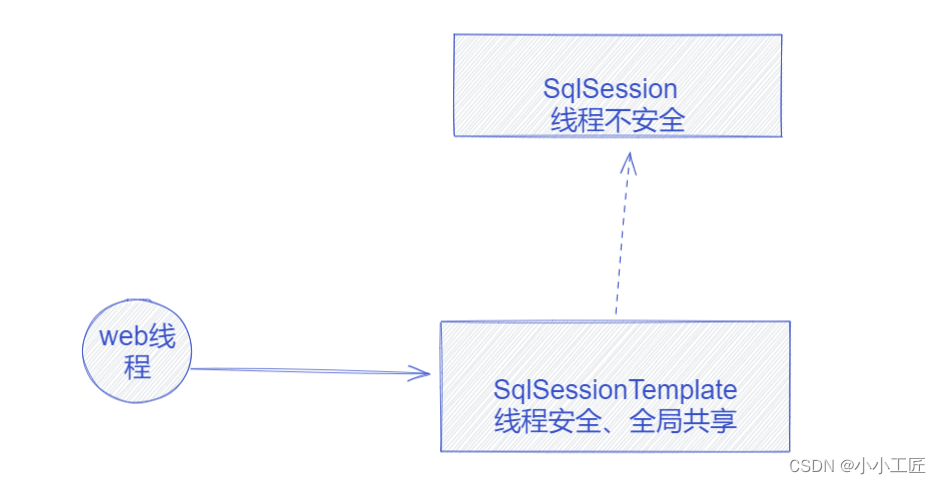
当通过 Web 线程访问同一个 SqlSessionTemplate,也就是同一个 SqlSession 时,它是如何确保线程安全的呢?
分析一下 SqlSessionTemplate 类的构造函数。SqlSessionTemplate 实现了 SqlSession 接口,并提供了如下所示的构造函数
public class SqlSessionTemplate implements SqlSession, DisposableBean {
public SqlSessionTemplate(...) {
//通过动态代理创建一个SqlSession的代理对象
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class },
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
...
}
这里创建了一个名为 sqlSessionProxy 的 SqlSession,但创建过程使用了 JDK 中经典的动态代理实现方案,就是通过 Proxy.newProxyInstance 静态方法注入一个 InvocationHandler 的实例。
这个实例就是 SqlSessionInterceptor 类。SqlSessionInterceptor 类是 SqlSessionTemplate 中的一个内部类,实现了 InvocationHandler 接口,其 invoke 方法实现如下:
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//获取SqlSession实例,该实例是线程不安全的
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
//调用真实SqlSession的方法
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
//判断当前的sqlSession是否被Spring托管,如果未被Spring托管则自动commit
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
//省略异常处理
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
//关闭sqlSession
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
}
核心逻辑其实是在 getSqlSession 方法中,这个方法完成了线程安全性的处理
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(...) {
//根据sqlSessionFactory从当前线程对应的资源Map中获取SqlSessionHolder
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
//从SqlSessionHolder中获取sqlSession实例
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
//如果获取不到sqlSession实例,则根据executorType创建一个新的sqlSession
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
//将sessionFactory和session注册到线程安全的资源Map
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
使用了 Spring 中的一个工具类——TransactionSynchronizationManager,这个类用于存储传入的 SessionHolder,registerSessionHolder 方法的核心代码如下所示:
private static void registerSessionHolder(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator, SqlSession session) {
SqlSessionHolder holder;
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
Environment environment = sessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment();
if (environment.getTransactionFactory() instanceof SpringManagedTransactionFactory) {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registering transaction synchronization for SqlSession [" + session + "]");
holder = new SqlSessionHolder(session, executorType, exceptionTranslator);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(sessionFactory, holder);
TransactionSynchronizationManager
.registerSynchronization(new SqlSessionSynchronization(holder, sessionFactory));
holder.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
holder.requested();
} else {
//......
} else {
//......
}
}
重点是:
holder = new SqlSessionHolder(session, executorType, exceptionTranslator);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(sessionFactory, holder);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(new SqlSessionSynchronization(holder, sessionFactory));
继续
public static void registerSynchronization(TransactionSynchronization synchronization)
throws IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(synchronization, "TransactionSynchronization must not be null");
Set<TransactionSynchronization> synchs = synchronizations.get();
if (synchs == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Transaction synchronization is not active");
}
synchs.add(synchronization);
}
看 synchronizations变量
TransactionSynchronizationManager 中存储 SqlSessionSynchronization 用的是 synchronizations 变量
private static final ThreadLocal<Set<TransactionSynchronization>> synchronizations =
new NamedThreadLocal<Set<TransactionSynchronization>>("Transaction synchronizations");
ThreadLocal 确保了线程的安全性。






![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django校园订餐管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bc1426b693124accaefaebfffdc3306c.png)


![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django小型银行管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5d4ac03ec63a476d9d14259cda608afa.png)