STM32串口DMA双缓冲
1.简介
STM32F429系列DMA支持双缓冲模式进行数据传输,相当于数字电路设计领域的乒乓操作,但是HAL库并没有实现像单缓冲区一样可以简单使用的函数,有的方法是使用单缓冲的方式,但是通过接收半满的中断控制CPU进行数据处理,相当于是把一个缓冲区拆成两半使用。双缓冲的优势是显而易见的,在将串口数据写入到一个缓冲区时,CPU同时可以进行另一个缓冲区的读取,可以加快数据的处理
HAL库没有实现硬件双缓冲的代码,需要自己实现一下。
2.代码分析
要想自己实现一个双缓冲的接收函数,需要首先看一下HAL库是如何实现单缓冲模式的串口接收的。首先使用STM32CubeMX生成一个正常的开启DMA,串口的工程,先确保单缓冲的串口可以正常收发数据。
开启双缓冲,MDA会强制性切换为循环模式,无法调整。
HAL库启动串口DMA使用函数HAL_UART_Receive_DMA
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_UART_Receive_DMA(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size)
{
/* Check that a Rx process is not already ongoing */
if (huart->RxState == HAL_UART_STATE_READY)
{
if ((pData == NULL) || (Size == 0U))
{
return HAL_ERROR;
}
/* Process Locked */
__HAL_LOCK(huart);
/* Set Reception type to Standard reception */
huart->ReceptionType = HAL_UART_RECEPTION_STANDARD;
return (UART_Start_Receive_DMA(huart, pData, Size));
}
else
{
return HAL_BUSY;
}
}
其中主要功能是UART_Start_Receive_DMA函数
HAL_StatusTypeDef UART_Start_Receive_DMA(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size)
{
uint32_t *tmp;
huart->pRxBuffPtr = pData;
huart->RxXferSize = Size;
huart->ErrorCode = HAL_UART_ERROR_NONE;
huart->RxState = HAL_UART_STATE_BUSY_RX;
/* Set the UART DMA transfer complete callback */
huart->hdmarx->XferCpltCallback = UART_DMAReceiveCplt;
/* Set the UART DMA Half transfer complete callback */
huart->hdmarx->XferHalfCpltCallback = UART_DMARxHalfCplt;
/* Set the DMA error callback */
huart->hdmarx->XferErrorCallback = UART_DMAError;
/* Set the DMA abort callback */
huart->hdmarx->XferAbortCallback = NULL;
/* Enable the DMA stream */
tmp = (uint32_t *)&pData;
HAL_DMA_Start_IT(huart->hdmarx, (uint32_t)&huart->Instance->DR, *(uint32_t *)tmp, Size);
/* Clear the Overrun flag just before enabling the DMA Rx request: can be mandatory for the second transfer */
__HAL_UART_CLEAR_OREFLAG(huart);
/* Process Unlocked */
__HAL_UNLOCK(huart);
if (huart->Init.Parity != UART_PARITY_NONE)
{
/* Enable the UART Parity Error Interrupt */
ATOMIC_SET_BIT(huart->Instance->CR1, USART_CR1_PEIE);
}
/* Enable the UART Error Interrupt: (Frame error, noise error, overrun error) */
ATOMIC_SET_BIT(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_EIE);
/* Enable the DMA transfer for the receiver request by setting the DMAR bit
in the UART CR3 register */
ATOMIC_SET_BIT(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_DMAR);
return HAL_OK;
}
UART_Start_Receive_DMA函数的主要过程是
- 给DMA传输完成,传输一半,和串口错误设置回调函数
- 启动中断模式的DMA传输
- 使能串口的DMA触发
然后再来看一下DMA传输完成的回调函数UART_DMAReceiveCplt
/**
* @brief DMA UART receive process complete callback.
* @param hdma Pointer to a DMA_HandleTypeDef structure that contains
* the configuration information for the specified DMA module.
* @retval None
*/
static void UART_DMAReceiveCplt(DMA_HandleTypeDef *hdma)
{
UART_HandleTypeDef *huart = (UART_HandleTypeDef *)((DMA_HandleTypeDef *)hdma)->Parent;
/* DMA Normal mode*/
if ((hdma->Instance->CR & DMA_SxCR_CIRC) == 0U)
{
huart->RxXferCount = 0U;
/* Disable RXNE, PE and ERR (Frame error, noise error, overrun error) interrupts */
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR1, USART_CR1_PEIE);
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_EIE);
/* Disable the DMA transfer for the receiver request by setting the DMAR bit
in the UART CR3 register */
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_DMAR);
/* At end of Rx process, restore huart->RxState to Ready */
huart->RxState = HAL_UART_STATE_READY;
/* If Reception till IDLE event has been selected, Disable IDLE Interrupt */
if (huart->ReceptionType == HAL_UART_RECEPTION_TOIDLE)
{
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR1, USART_CR1_IDLEIE);
}
}
/* Check current reception Mode :
If Reception till IDLE event has been selected : use Rx Event callback */
if (huart->ReceptionType == HAL_UART_RECEPTION_TOIDLE)
{
#if (USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS == 1)
/*Call registered Rx Event callback*/
huart->RxEventCallback(huart, huart->RxXferSize);
#else
/*Call legacy weak Rx Event callback*/
HAL_UARTEx_RxEventCallback(huart, huart->RxXferSize);
#endif /* USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS */
}
else
{
/* In other cases : use Rx Complete callback */
#if (USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS == 1)
/*Call registered Rx complete callback*/
huart->RxCpltCallback(huart);
#else
/*Call legacy weak Rx complete callback*/
HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(huart);
#endif /* USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS */
}
}
UART_DMAReceiveCplt函数的主要内容是
- 进行一些状态的更新、对一些中断标志位进行清除
- 调用HAL开放出来让用户编写的中断服务函数
HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(huart);
整体的流程是,HAL_UART_Receive_DMA->UART_Start_Receive_DMA->( 回调函数+HAL_DMA_Start_IT)
要想实现双缓冲,可以仿造HAL库的方式,自己实现一个启动的流程,大体上直接复制HAL库的即可,关键部分进行自己的修改,最好不要直接在HAL库改,在其他的地方重新写。
1.实现HAL_UART_Receive_DMA_double,主要复制HAL_UART_Receive_DMA,最后调用的函数改为UART_Start_Receive_DMA_double
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_UART_Receive_DMA_double(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart, uint8_t *pData,uint8_t *pData1 ,uint16_t Size)
{
/* Check that a Rx process is not already ongoing */
if (huart->RxState == HAL_UART_STATE_READY)
{
if ((pData == NULL) || (Size == 0U))
{
return HAL_ERROR;
}
/* Process Locked */
__HAL_LOCK(huart);
/* Set Reception type to Standard reception */
huart->ReceptionType = HAL_UART_RECEPTION_STANDARD;
return (UART_Start_Receive_DMA_double(huart, pData,pData1, Size));
}
else
{
return HAL_BUSY;
}
}
2.实现UART_Start_Receive_DMA_double
HAL_StatusTypeDef UART_Start_Receive_DMA_double(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart, uint8_t *pData,uint8_t *pData1, uint16_t Size)
{
uint32_t *tmp;
uint32_t *tmp1;
huart->pRxBuffPtr = pData;
huart->RxXferSize = Size;
huart->ErrorCode = HAL_UART_ERROR_NONE;
huart->RxState = HAL_UART_STATE_BUSY_RX;
/* Set the UART DMA transfer complete callback */
huart->hdmarx->XferCpltCallback = UART_DMAReceiveCplt_M0;
huart->hdmarx->XferM1CpltCallback = UART_DMAReceiveCplt_M1;
/* Set the UART DMA Half transfer complete callback */
huart->hdmarx->XferHalfCpltCallback = NULL;
/* Set the DMA error callback */
huart->hdmarx->XferErrorCallback = UART_DMAError;
/* Set the DMA abort callback */
huart->hdmarx->XferAbortCallback = NULL;
/* Enable the DMA stream */
tmp = (uint32_t *)&pData;
tmp1 = (uint32_t *)&pData1;
//HAL_DMA_Start_IT(huart->hdmarx, (uint32_t)&huart->Instance->DR, *(uint32_t *)tmp, Size);
HAL_DMAEx_MultiBufferStart_IT(huart->hdmarx, (uint32_t)&huart->Instance->DR, *(uint32_t *)tmp,*(uint32_t *)tmp1 ,Size);
/* Clear the Overrun flag just before enabling the DMA Rx request: can be mandatory for the second transfer */
__HAL_UART_CLEAR_OREFLAG(huart);
/* Process Unlocked */
__HAL_UNLOCK(huart);
if (huart->Init.Parity != UART_PARITY_NONE)
{
/* Enable the UART Parity Error Interrupt */
ATOMIC_SET_BIT(huart->Instance->CR1, USART_CR1_PEIE);
}
/* Enable the UART Error Interrupt: (Frame error, noise error, overrun error) */
ATOMIC_SET_BIT(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_EIE);
/* Enable the DMA transfer for the receiver request by setting the DMAR bit
in the UART CR3 register */
ATOMIC_SET_BIT(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_DMAR);
return HAL_OK;
}
后面启动DMA传输的函数更改为HAL_DMAEx_MultiBufferStart_IT,此函数要求必须要有两个缓冲区满的回调函数以及传输错误的回调函数,因此必须实现这三个回调函数。
3.实现回调函数,直接复制HAL库原本的回调函数
/**
* @brief DMA UART receive process complete callback.
* @param hdma Pointer to a DMA_HandleTypeDef structure that contains
* the configuration information for the specified DMA module.
* @retval None
*/
static void UART_DMAReceiveCplt_M0(DMA_HandleTypeDef *hdma)
{
UART_HandleTypeDef *huart = (UART_HandleTypeDef *)((DMA_HandleTypeDef *)hdma)->Parent;
/* DMA Normal mode*/
if ((hdma->Instance->CR & DMA_SxCR_CIRC) == 0U)
{
huart->RxXferCount = 0U;
/* Disable RXNE, PE and ERR (Frame error, noise error, overrun error) interrupts */
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR1, USART_CR1_PEIE);
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_EIE);
/* Disable the DMA transfer for the receiver request by setting the DMAR bit
in the UART CR3 register */
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_DMAR);
/* At end of Rx process, restore huart->RxState to Ready */
huart->RxState = HAL_UART_STATE_READY;
/* If Reception till IDLE event has been selected, Disable IDLE Interrupt */
if (huart->ReceptionType == HAL_UART_RECEPTION_TOIDLE)
{
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR1, USART_CR1_IDLEIE);
}
}
/* Check current reception Mode :
If Reception till IDLE event has been selected : use Rx Event callback */
if (huart->ReceptionType == HAL_UART_RECEPTION_TOIDLE)
{
#if (USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS == 1)
/*Call registered Rx Event callback*/
huart->RxEventCallback(huart, huart->RxXferSize);
#else
/*Call legacy weak Rx Event callback*/
HAL_UARTEx_RxEventCallback(huart, huart->RxXferSize);
#endif /* USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS */
}
else
{
/* In other cases : use Rx Complete callback */
#if (USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS == 1)
/*Call registered Rx complete callback*/
huart->RxCpltCallback(huart);
#else
/*Call legacy weak Rx complete callback*/
//HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(huart);
printf("000\r\n");
#endif /* USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS */
}
}
/**
* @brief DMA UART receive process complete callback.
* @param hdma Pointer to a DMA_HandleTypeDef structure that contains
* the configuration information for the specified DMA module.
* @retval None
*/
static void UART_DMAReceiveCplt_M1(DMA_HandleTypeDef *hdma)
{
UART_HandleTypeDef *huart = (UART_HandleTypeDef *)((DMA_HandleTypeDef *)hdma)->Parent;
/* DMA Normal mode*/
if ((hdma->Instance->CR & DMA_SxCR_CIRC) == 0U)
{
huart->RxXferCount = 0U;
/* Disable RXNE, PE and ERR (Frame error, noise error, overrun error) interrupts */
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR1, USART_CR1_PEIE);
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_EIE);
/* Disable the DMA transfer for the receiver request by setting the DMAR bit
in the UART CR3 register */
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_DMAR);
/* At end of Rx process, restore huart->RxState to Ready */
huart->RxState = HAL_UART_STATE_READY;
/* If Reception till IDLE event has been selected, Disable IDLE Interrupt */
if (huart->ReceptionType == HAL_UART_RECEPTION_TOIDLE)
{
ATOMIC_CLEAR_BIT(huart->Instance->CR1, USART_CR1_IDLEIE);
}
}
/* Check current reception Mode :
If Reception till IDLE event has been selected : use Rx Event callback */
if (huart->ReceptionType == HAL_UART_RECEPTION_TOIDLE)
{
#if (USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS == 1)
/*Call registered Rx Event callback*/
huart->RxEventCallback(huart, huart->RxXferSize);
#else
/*Call legacy weak Rx Event callback*/
HAL_UARTEx_RxEventCallback(huart, huart->RxXferSize);
#endif /* USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS */
}
else
{
/* In other cases : use Rx Complete callback */
#if (USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS == 1)
/*Call registered Rx complete callback*/
huart->RxCpltCallback(huart);
#else
/*Call legacy weak Rx complete callback*/
//HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(huart);
printf("11111\r\n");
#endif /* USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS */
}
}
static void UART_DMAError(DMA_HandleTypeDef *hdma)
{
uint32_t dmarequest = 0x00U;
UART_HandleTypeDef *huart = (UART_HandleTypeDef *)((DMA_HandleTypeDef *)hdma)->Parent;
/* Stop UART DMA Tx request if ongoing */
dmarequest = HAL_IS_BIT_SET(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_DMAT);
if ((huart->gState == HAL_UART_STATE_BUSY_TX) && dmarequest)
{
huart->TxXferCount = 0x00U;
UART_EndTxTransfer(huart);
}
/* Stop UART DMA Rx request if ongoing */
dmarequest = HAL_IS_BIT_SET(huart->Instance->CR3, USART_CR3_DMAR);
if ((huart->RxState == HAL_UART_STATE_BUSY_RX) && dmarequest)
{
huart->RxXferCount = 0x00U;
UART_EndRxTransfer(huart);
}
huart->ErrorCode |= HAL_UART_ERROR_DMA;
#if (USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS == 1)
/*Call registered error callback*/
huart->ErrorCallback(huart);
#else
/*Call legacy weak error callback*/
HAL_UART_ErrorCallback(huart);
#endif /* USE_HAL_UART_REGISTER_CALLBACKS */
}
在这里的回调函数中简单测试,如果第一个缓冲区满就输出0,第二个缓冲区满就输出1,
定义两个缓冲区
uint8_t rx_buf[10];
uint8_t rx_buf1[10];
在主函数中调用
HAL_UART_Receive_DMA_double(&huart1,rx_buf,rx_buf1,10);
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-70TGixxb-1686544064828)(https://assets.b3logfile.com/siyuan/1675829124924/assets/串口发送-20230610194158-8imrwc7.gif)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/143d6550227046038ddb0b09cef5c112.gif)
双缓冲基本实现
3.数据转发实现
在上述简单的接收双缓冲实现的情况下,尝试实现将接收到的数据转发出去,首先将双缓冲区的大小设置为10字节,因为在双缓冲发挥作用的场景下,应该是接收大量的数据,只有将缓冲设置的小一点,才能测试在相对于缓冲区大量的数据接收,如果缓冲区就设置1k字节,那我得发多少才算得上是大量呢?
数据转发的原理如下:
- 首先设置两个发送缓冲区
- 接收缓冲区1满就将数据复制到发送缓冲区1,接收缓冲区2满就将数据复制到发送缓冲区2
- 数据复制完毕后,主函数中根据状态控制将准备好的发送缓冲区1或者2通过串口DMA再发送出去
while (1)
{
if (rx_state == 1)//接收缓冲区1完成
{
if (tx_state == 2)//发送缓冲区2发送完成
{
tx_state_strat = 1;
tx_state = 0;
HAL_UART_Transmit_DMA(&huart1,tx_buf,buf_size);//开始发送 发送缓冲区1的数据
}
}
if (rx_state == 2)//接收缓冲区2完成
{
if (tx_state == 1)//发送缓冲区1发送完成
{
tx_state_strat = 2;
tx_state = 0;
HAL_UART_Transmit_DMA(&huart1,tx_buf1,buf_size);//开始发送 发送缓冲区2的数据
}
}
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
上述原理不难理解,看起来也没什么问题,简单测试也没问题,但是在继续增大数据量的时候数据的转发出现了问题。
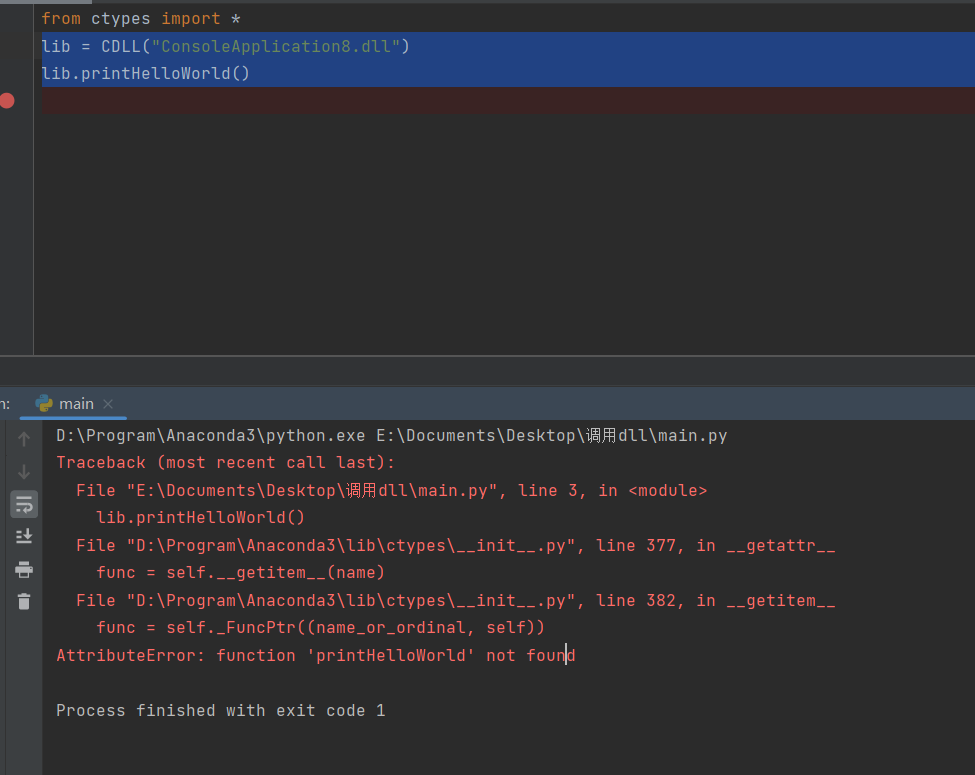
数据出现了丢失!!!!!数据量少一点的时候一切正常,数据量超过某个值之后就会稳定的丢20个字节的数据。
接逻辑分析仪进行观察。

发现在数据传输中途缺失数据。
为了分析执行过程,在双缓冲切换回调函数以及串口DMA发送完成回调函数进行管脚电平翻转,
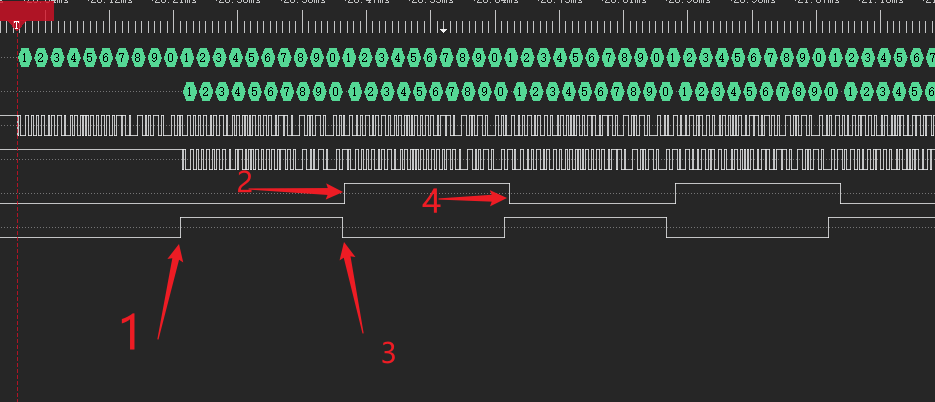
在1的位置接收缓冲区1满,2的位置是发送缓冲区1发送完毕,3是接受缓冲区2满,4是发送缓冲区2发送完成
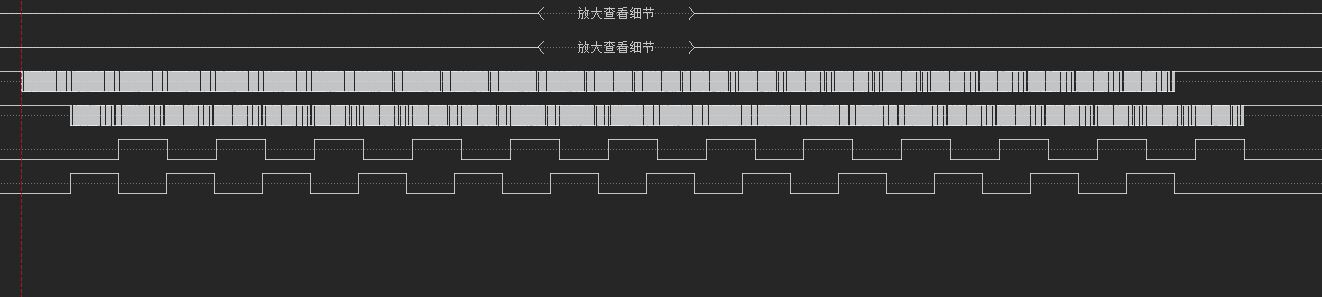
数据变多之后,二者的相位差越来越大,原因是,接收来的数据每个字节的间隔比较短,而转发之后,由于每个字节之间需要执行程序,就会导致两个发送字节之间的间隔比接收的间隔长,这样一直累计起来就会导致发送和接收的相位差越来越大。
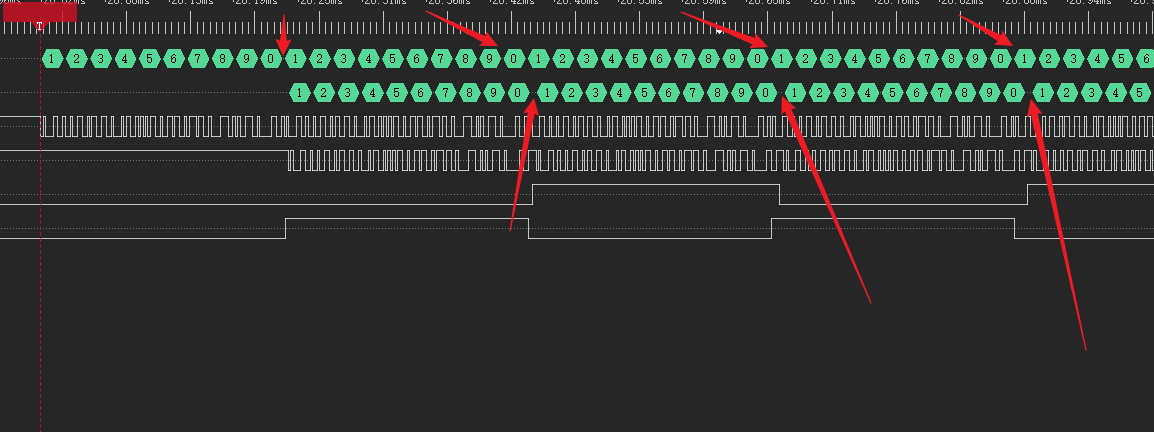
最终发送和接收的时间差累计到一个缓冲区接收的时间后,就会导致数据丢失。
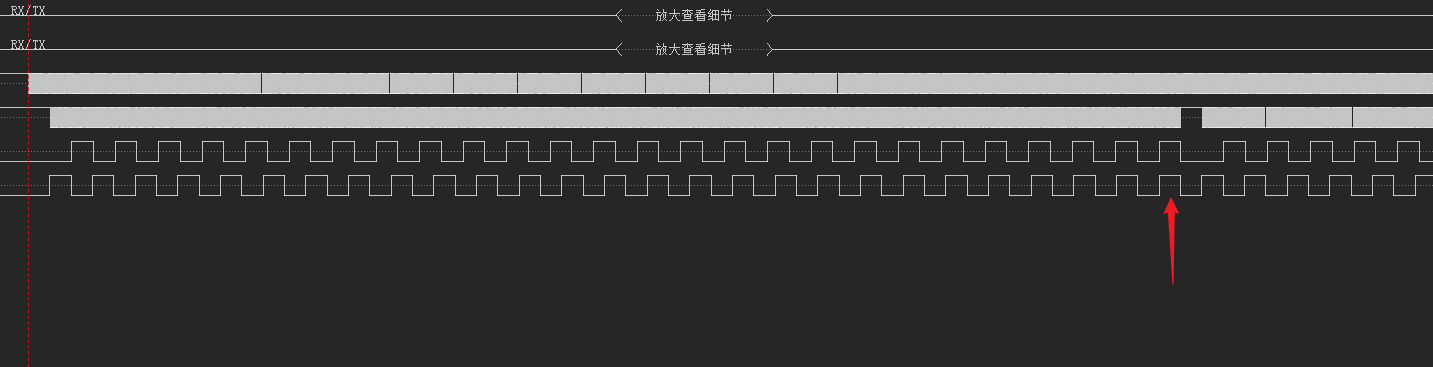
现在这个情况相当于是对接收到的速度进行处理的速度比接收的速度慢,因为波特率相同,而发送数据还需要一段处理的时间,就导致发送速度慢于接收的速度,这样就会导致数据丢失,如果不从根本上提升数据发送的速度,永远会有数据丢失,所以应该换一个串口以更快的波特率发送数据。
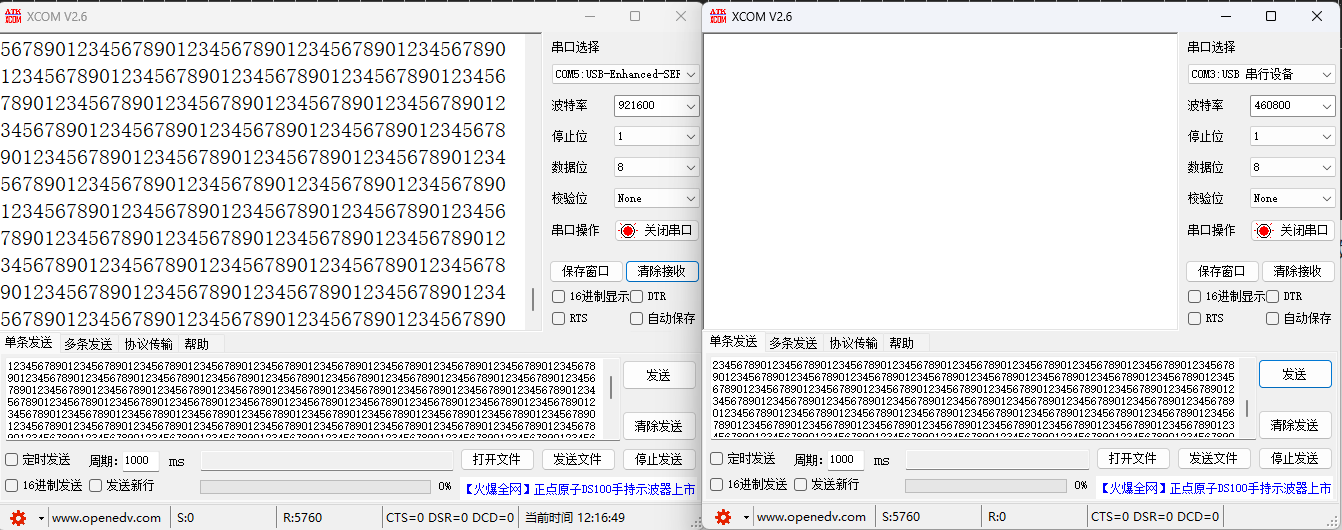
增加一个串口,波特率设置为921600,缓冲区仍然为10字节,一次性发送5760字节,转发也没有问题

4.总结
接收使用双缓冲,好处是可以使CPU在处理接收到的数据的同时,新的数据接收还可以正常进行。但是也需要保证对数据的处理速度是要比接收的速度快的,否则一定会导致数据丢失。
如果需要接收的数据长度不可知,还需要结合空闲中断实现数据不定长的接收,可以参考http://t.csdn.cn/vFnt8
工程代码已经上传
https://download.csdn.net/download/Master_0_/87897707
参考链接
https://blog.csdn.net/zhang1079528541/article/details/121049656
https://www.sohu.com/a/260229041_807475
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_51368339/article/details/124439407
https://www.cnblogs.com/puyu9499/archive/2022/02/19/15914090.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_20553613/article/details/108367512
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_19999465/article/details/81054680
http://t.csdn.cn/XCan6











![KYOCERA Programming Contest 2023(AtCoder Beginner Contest 305)(A、B、C、D)[施工中]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0c9e8452f4a04777a1ef883a1c09f0b8.png)