目录
- 什么是Vuex
- 安装和配置Vuex
- 安装Vuex
- 配置Vuex
- 使用Vuex
- State
- 定义State
- 访问State
- Mutations
- Mutations 的特点
- 定义Mutations
- 触发Mutations 修改State中的状态
- Action
- Action 的特点和作用
- 定义Action
- 触发Action
- Getter
- Getter 的特点和作用
- 定义Getter
- 获取Getter
- Module
- Module 的特点和作用
- 定义和使用Module
- Vuex中的辅助函数
- mapState
- mapGetters
- mapMutations
- mapActions
Vuex 曾经是Vue.js的官方状态管理库。为什么说是曾经呢,因为在Vue.js官方网站的生态系统的官方系统中找不到Vuex的影子了,取而代之的是Pinia。那么问题来了,既然Vue官方已经舍弃了Vuex,使用Pinia取而代之,我们还有必要去深入了解Vuex吗?
我觉得还是由必要深入了解下Vuex的,虽然Vue.js的官方网站生态系统中已经不再推荐使用Vuex了,但是在目前市面上大多项目中仍然有大量使用Vuex的项目,而且Vuex的核心概念也可以应用于其他状态管理库中。因此,学习Vuex可以帮助我们更好地理解Vue.js的状态管理机制,提高我们处理Vue.js应用中的状态管理的能力,并且能够更好地适应已有的Vue.js项目。因此,今天我们就花费一个章节来详细的聊一聊Vuex
什么是Vuex
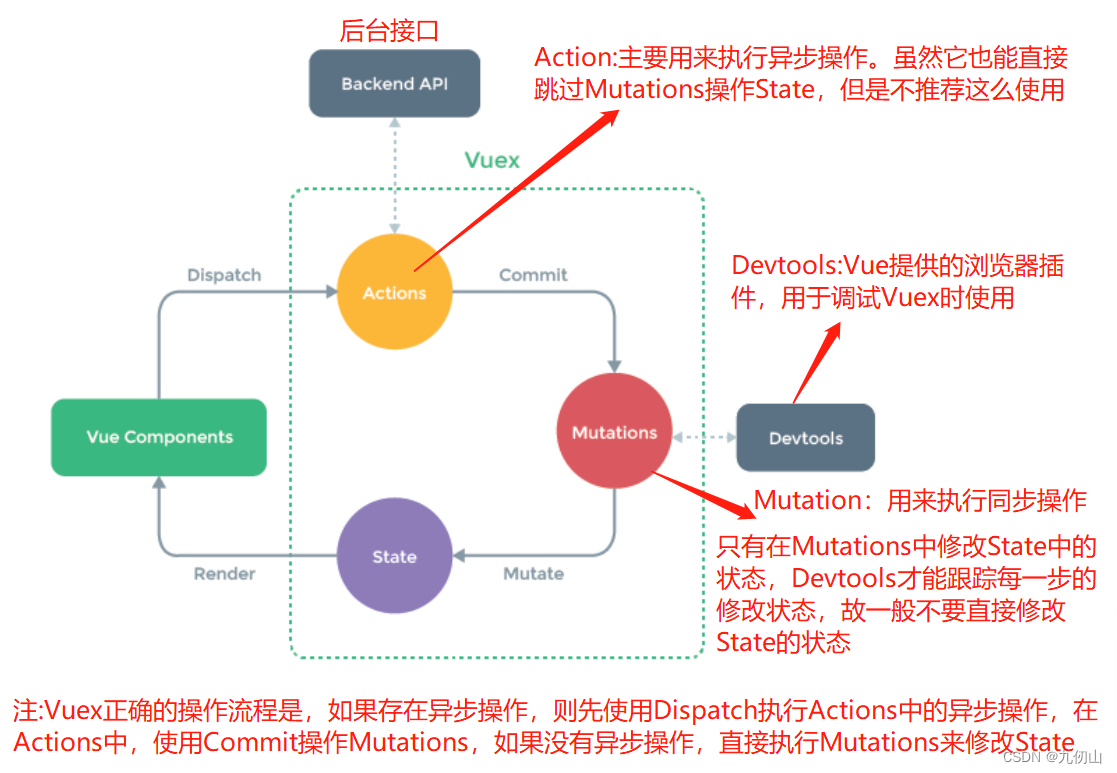
Vuex是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理库,它允许我们以集中的方式管理应用程序中的所有状态。
官方给出的vuex状态管理执行的流程图下图所示
安装和配置Vuex
安装Vuex
通过下面的指令按照Vuex
npm install vuex@next --save
# or
yarn add vuex@next --save
配置Vuex
为了代码可读性及便于后期维护管理,我们一般将Vuex相关的代码统一放到一个文件夹中。因此,配置Vuex的步骤如下:
- 在src文件夹新建一个store文件夹,在该文件夹下新建index.js文件
- 在index.js中引入Vuex中的createStore 方法
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
- 使用createStore创建Vuex实例对象,
const store = createStore({
state:{
//状态管理器中定义的数据源
},
mutations:{
//同步操作
},
actions:{
//异步操作
},
//getters相当于计算属性
getters:{
}
})
- 将上面创建的store导出
export default store
- 在main.js文件中引入上面创建的sotre.js,并注册到app中
import store from './store'
app.use(store) //注册vuex
经过上面的步骤,Vuex就配置完成了,下面就可以在我们的程序中进行使用了。
使用Vuex
在使用Vuex之前,我们需要了解Vuex中的几个核心概念,即:State,Mutation,Action,Getter 和 Module
State
在Vuex中,state是应用程序的状态管理模式中定义的数据源,它是一个单一的JavaScript对象,在一个应用程序中只使用一个store对象,来存储所有共享的状态信息。该对象具有被访问和修改的方法,可以帮助简化数据的共享和传递。
定义State
定义State有两种方式,分别是使用对象方式和函数方式进行定义,下面是两种定义方式的示例代码,两种方式选一种即可
//对象方式
state:{
isTabbarShow:true
},
//函数方式
state() {
return {
isTabbarShow:true
}
},
访问State
由于Vue3中即支持选项是API,也支持组合式API,因此访问State也有两种方式
在选项是API中,通过如下代码进行访问到上面定义的isTabbarShow
console.lgo(this.$store.state.isTabbarShow)
在组合式API中,通过如下代码访问上面定义的isTabbarShow
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
const store = useStore()
console.lgo(store.state.isTabbarShow)
Mutations
Mutations是用来管理和修改 state 状态的工具,通过Mutations更新的状态,Vuex 可以更容易地追踪状态的变化。
Mutations 的特点
- Mutations 是同步修改 state 状态的。
- Mutations 修改 state 必须是通过 store.commit() 来触发。
- Mutations 只能处理同步操作。
定义Mutations
和上面的State一样,定义Mutations也有对象式和函数式两种方式,这里以对象式为例
mutations:{
changeState(state,payload) {
state.isTabbarShow = payload
}
},
触发Mutations 修改State中的状态
通访问State的方法一样,触发Mutations 修改State中的状态也有两种方式。
在选项是API中,通过如下代码进行访问
this.$store.commit('changeState',true)
在组合式API中,通过如下代码访问上面定义的isTabbarShow
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
const store = useStore()
store.commit('changeState',true)
Action
Action 用于处理异步操作或复杂的操作逻辑,类似于 Mutations,但是 Action 支持异步操作,而且一般不直接修改 state 状态,而是提交 Mutations 完成具体的状态变更。
Action 的特点和作用
- Action 是异步的,用于处理异步操作或复杂的操作逻辑。
- Action 一般不直接修改 state 状态,而是提交 Mutations 完成具体的状态变更。
- Action 可以提交 Mutations,也可以赋值 state 状态。
- Action 通过 store.dispatch 触发。
Action 的主要作用是处理异步操作或复杂的操作逻辑,并将操作变更提交给 Mutations 完成更新状态的操作。
定义Action
定义Action和上面定义Mutations类似,以对象方式定义Action的示例代码如下:
actions:{
ayncChangeState(context) {
context.commit('changeState',true)
}
}
触发Action
和触发Mutations一样,触发Action 也有两种方式。
在选项是API中,通过如下代码进行访问
this.$store.dispatch('ayncChangeState')
在组合式API中,通过如下代码访问上面定义的isTabbarShow
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
const store = useStore()
store.dispatch('ayncChangeState')
Getter
Getter 用于从 store 中的 state 中派生出一些状态,例如对 state 中的数据进行计算和过滤。也可以通过 Getter 访问定义在 store 中的 state。我们可以认为是Getter 是 store 的计算属性。
Getter 的特点和作用
- Getter 访问时不需要调用,是在模块中对 state 进行一个辅助性的处理。
- Getter 不会对 state 数据进行修改,只是对 state 数据进行加工处理。
- Getter 的作用是从 store 中派生状态,即从 store 中获取状态。
- 组件中很少直接使用 state,因为 state 的结构可能会改变,这会导致需要修改组件中的所有使用到这些 state 的地方。而使用 Getter,可以维护一种稳定的接口。
定义Getter
Getter 接受 state 作为其第一个参数:
定义Getter的方式如下
getters: {
doneTodos: state => {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
}
}
获取Getter
在选项式API中获取 Getter:
computed: {
doneTodos() {
return this.$store.getters.doneTodos
}
}
在组合式API中获取Getter
store.getters.doneTodos
Module
在 Vuex 中,Module 可以帮助我们把 Store 分割成多个小的 Store,每个 Module 可以有自己的 State、Mutation、Action、Getter。
Module 的特点和作用
- 命名空间: Module 可以减少把 State、Mutation、Action、Getter 加入到全局命名空间中的问题,避免团队开发时命名冲突的问题。
- 优化组织结构:当一个 Store 变得非常大时,使用Module将它们拆分成较小而简单的部分可以更轻松地理解和维护。
- 代码重复使用:可以为多个模块中共享代码提供便利。
定义和使用Module
在实际开发中,当我们需要共享和管理的数据越来越多时,可以使用Module将需要管理的数据进行分类创建,比如,我们需要同时管理user的信息和book的信息,我们就可以通过下面的步骤来定义和使用Module
- 在store文件夹下再创建一个module文件夹,创建userModule.js和bookModule.js两个文件,各个文件的代码如下:
userModule.js代码如下:
const user = {
namespaced: true,
state: {
name: 'John Doe',
age: 30,
email: 'johndoe@example.com'
},
getters: {
fullName (state) {
return state.name
}
},
mutations: {
setName (state, newName) {
state.name = newName
}
},
actions: {
updateName ({ commit }, newName) {
commit('setName', newName)
}
}
}
export default user
bookModule.js代码如下
const books = {
namespaced: true,
state: {
name: 'Vue入门',
price: 30,
author: 'John Doe'
},
getters: {
totalMoney (state) {
return state.price
}
},
mutations: {
setName (state, newName) {
state.name = newName
}
},
actions: {
updateName ({ commit }, newName) {
commit('setName', newName)
}
}
}
export default books
- 在store文件夹下的index.js中使用如下方法将上面的两个module整合到一起引入
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
import userModule from './module/userModule.js'
import bookModule from './module/bookModule.js'
const store = createStore({
modules:{
userModule,
bookModule
}
})
export default store
-
使用Module:在上面第3步中,我们创建了userModule和 bookModule两个js文件,他们都定义了单独的state、mutations、actions、getters。我们可以通过 store 对象中的「模块命名空间」来访问它们
在选项是API中,通过如下代码进行访问
this.$store..state.userModule this.$store..state.bookModule在组合式 API 中,使用
useStore来获取store对象,从而访问模块中的 state, mutation, action 或 getterimport { useStore } from 'vuex' const store = useStore() const userModuleState = computed(() => store.state.userModule.stateName) // userModule mutation的使用 const updateName = name => { store.commit('userModule/updateName', name) }
Vuex中的辅助函数
在组件中使用大量的$store访问和调用操作会导致代码缺乏可读性和可维护性。为此,Vuex提供了一些辅助函数来简化在Vue组件中访问和操作store中的state、getter、mutation和action的代码,这些函数包括mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations和mapActions
mapState
mapState用于将state映射到Vue组件的计算属性中。
示例代码如下:
// 在组件中使用 mapState
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapState({
count: state => state.count,
message: state => state.message
})
}
}
mapGetters
mapGetters用于将getter映射到Vue组件的计算属性中。
示例代码如下:
// 在组件中使用 mapGetters
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapGetters({
doneTodos: 'doneTodos',
doneTodosCount: 'doneTodosCount'
})
}
}
mapMutations
mapMutations用于将mutation映射到Vue组件的methods中。
示例代码如下:
// 在组件中使用 mapMutations
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
'add' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('add')`
])
}
}
mapActions
mapActions用于将action映射到Vue组件的methods中。
示例代码如下:
// 在组件中使用 mapActions
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
...mapActions([
'incrementAsync', // 将 `this.incrementAsync()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementAsync')`
'addAsync' // 将 `this.addAsync()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('addAsync')`
])
}
}
在选项式API中,上述函数都可以通过对象展开符...将计算属性和方法添加到组件中。
注意:
这里需要注意的是,当我们使用组合式API时,如在<script setup>语法糖中,我们无法使用上面介绍的辅助函数,因为这些辅助函数的底层是调用的this.$store,而在组合式API中,不存在this,所以上面的几个辅助函数在组合式API中无法使用
好了,关于vue中使用Vuex的相关特性和方法就聊到这里,喜欢的小伙伴点赞关注收藏哦!