跳跃链表的概念
跳跃链表是有序链表的一个变种,在一个有序链表中,查找一个链表中的元素需要进行一次遍历,时间复杂度为O(n),为了加快查找的过程,能够跳过某些元素呢?一个思路就是牺牲一定的空间换时间,对有序链表建立类似索引的结构加快查找过程,跳跃链表基本上就是通过维护一个多层次的链表,每一层链表中的元素是前一层链表元素的子集,搜索时,最开始在最稀疏的层次进行搜索,直至需要查找的元素在该层两个相邻元素中间,这时,将跳转到下一个层次,重复刚才的搜索,直到找到需要查找的元素为止。
跳跃链表的创建
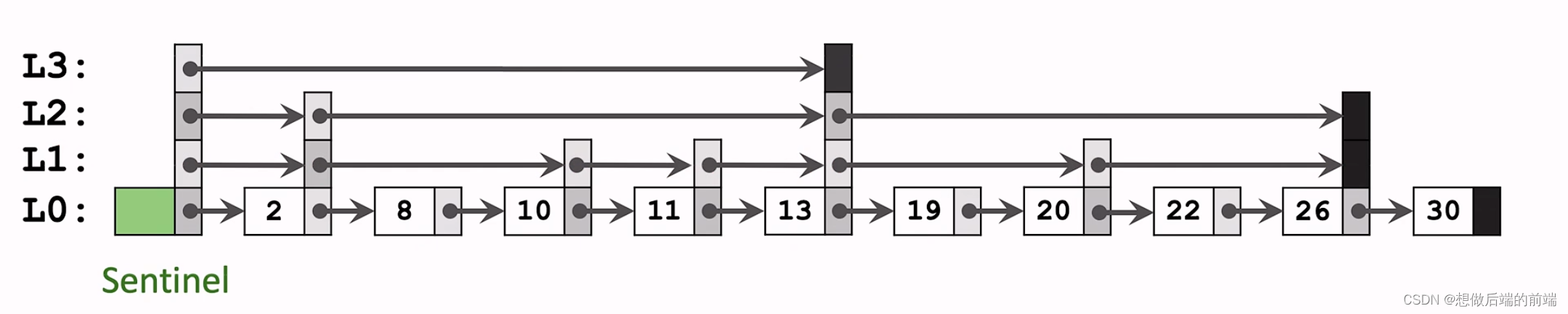
如果给定一个固定的有序链表,构造跳跃链表的话,思路非常简单,就是每一层都取上一层的1/2个元素就可以了(例如,按奇偶,每次都取第偶数个元素作为下一层元素…),这样查找就相当于二分查找的过程,查找一个元素的时间复杂度变为了log(n)。但是实际应用中,有序链表往往不是固定元素个数的,会动态的增删,这种静态的构建过程就不合适了,那该怎么办呢?
可以看到,跳跃链表构建索引的关键是每一层都取上一层的部分元素作为该层的元素,即第i层的元素按某个固定的概率p(例如1/2或1/4)出现在第i+1层中。可通过这个概率p值对空间和时间进行平衡,p越大,占用空间越多。所以,构建的思路就是在插入一个新的元素时,随机的生成该元素的层数,算法描述如下:
randomLevel()
lvl := 1
// random() return a random value in [0..1)
while random() < p && lvl < MaxLevel do
lvl := lvl + 1
return lvl
即,层次越高,概率越低,但层数也不能太高,太高了无意义,一般根据元素的个数n计算MaxLevel = log(n)作为最高层数。这样,跳跃链表就适应动态变化的情况了。
跳跃链表的插入、查找、删除
查找
查找的思路就是先在最上层查找,找到不到再转向下一层继续查找,这样就可以跳过很多元素,缩小查找范围。
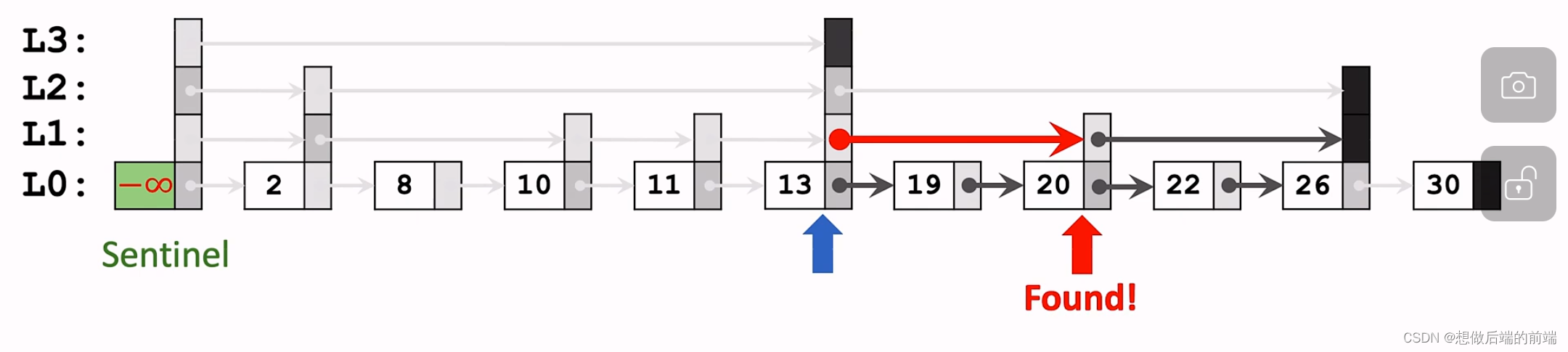
比如寻找key =20:
第一步:从L3出发,找到第一个节点13,因为13是L3的最后一个节点了,所以向下寻找;
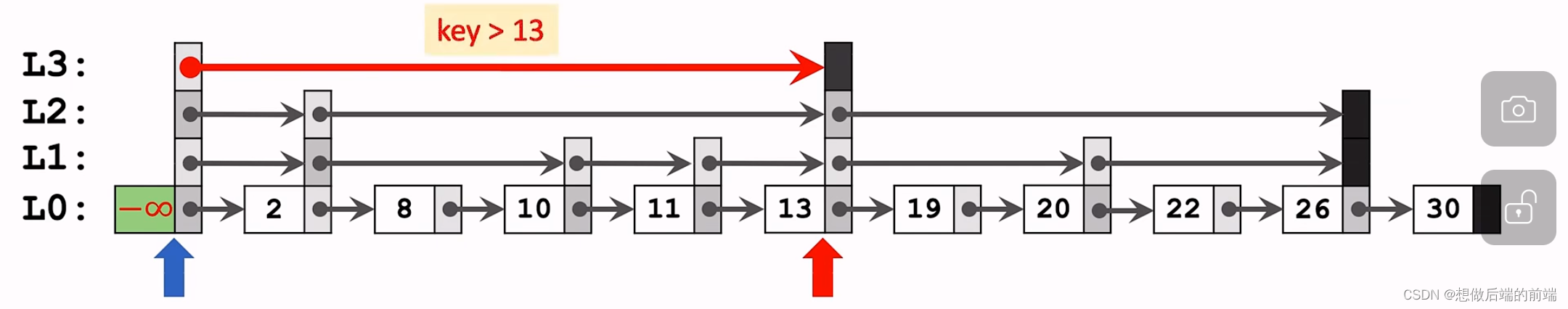
第二步:因为20>13,所以到L2后往右出发,找到L2的第二个节点26,并且26为L2的最后一个节点,所以继续向下寻找;
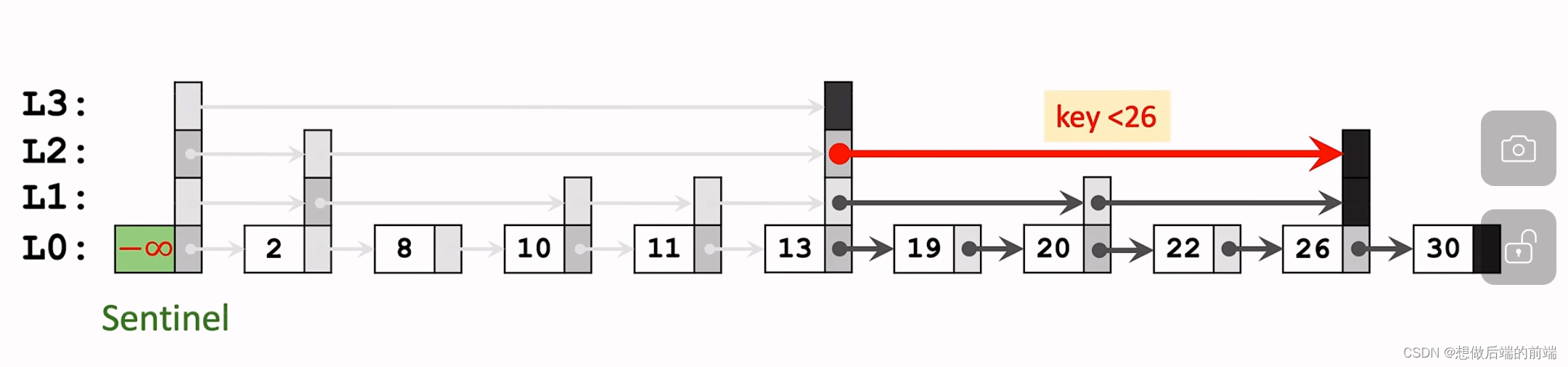
第三步:因为26>20所以在L1中我们继续从节点13开始向右寻找,找到下一个节点即为20
算法描述如下:
Search(list, searchKey)
x := list->header // loop invariant: x->key < searchKey
for i := list->level downto 1 do // downto的意思是从最高层,每次下降一层
while x->forward[i]->key < searchKey do
x := x->forward[i] // x->key < searchKey <= x->forward[1]->key
x := x->forward[1]
if x->key = searchKey then return x->value
else return failure
插入
插入的关键步骤是随机决定节点层数,算法前面已经描述过,与普通链表不同的是跳跃链表是多层的,所以确定层数后每一层都需要插入该元素。
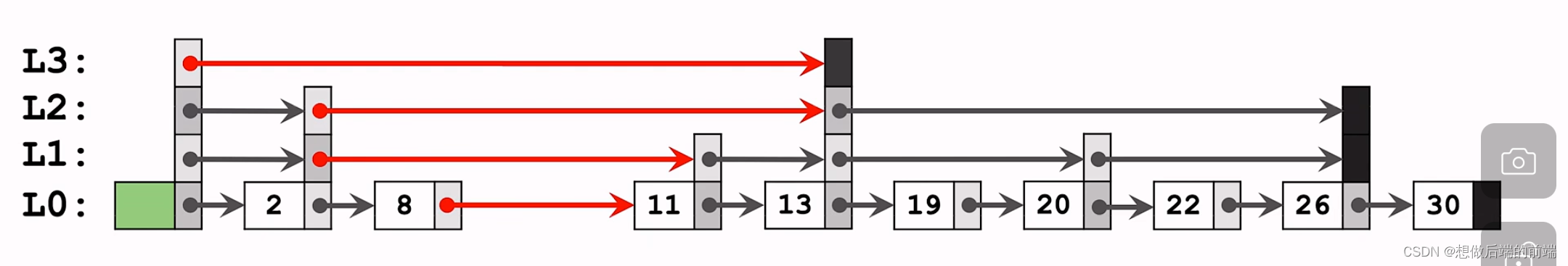
比如插入key =9:
第一步:查找key=9的位置,并且记录下位置
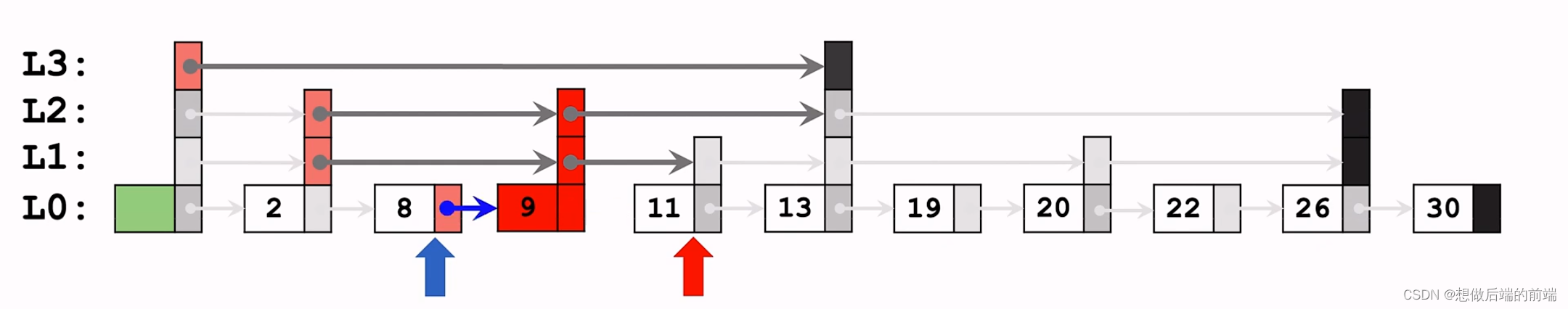
第二步:创建一个新的节点,它的高度是随机算法生成的的,然后把节点插入到跳跃链表中

第三步:将新的节点与跳跃链表连接起来
算法描述如下:
Insert(list, searchKey, newValue)
local update[1.. MaxLevel]
x := list->leader
for i:= list->level downto 1 do
while x->forward[i]->key < searchKey do
x := x->forward[i] // x->key < searchKey <= x->forward[1]->key
update[i] := x //这里是找出这个元素在每一层的前驱节点
x := x->forward[1]
if x->key = searchKey then x->value := newValue
else
lvl := randomLevel()
if lvl > list->level then
for i := list->level + 1 to lvl do
update[i] := list->header
list->level := lvl
x := makeNode(lvl, searchKey, value)
for i := 1 to level do // 这里与普通链表插入节点操作类似,只不过是每层都要插入
x->forward[i] := update[i]->forward[i]
update[i]->forward[i] := x
删除
删除操作与普通链表删除操作类似,不同的地方在于找到该元素后要每一层都做删除操作,算法描述如下:
Delete(list, searchKey)
local update[1..MaxLevel]
x := list->header
for i := list->level downto 1 do
while x->forward[i]->key < searchKey do
x := x->forward[i]
update[i] := x
x := x->forward[1]
if x->key = searchKey then
for i := 1 to list->level do
if update[i]->forward[i] neq x then break
update[i]->forward[i] := x->foreard[i]
free(x)
while list->level > 1 and list->header->forward[list->level] =NIL do
list->level := list->level -1
完整算法
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<ctime>
#include<random>
#include<cmath>
#include<climits>
#include<vector>
#include<cassert>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_LEVEL = 8; // 用户定义的最大层数
const float P = 0.5; // 用户设置的概率P
//跳跃列表节点类
template<class K, class V>
class SkipListNode {
public:
SkipListNode() {}
SkipListNode(K key, V value, int level);
K key;
V value;
typedef SkipListNode<K, V>* NodePtr;
NodePtr forward[MAX_LEVEL];
};
template<class K, class V>
SkipListNode<K, V>::SkipListNode(K key, V value, int level):key(key),value(value) {
for (int i = 0; i < level; ++i) {
this->forward[i] = nullptr;
}
}
// 跳跃列表类
template<class K, class V>
class SkipList {
public:
typedef SkipListNode<K, V>* NodePtr;
SkipList();
SkipList(NodePtr header, NodePtr tail);
~SkipList();
V* search(const K& key);
void insert(const K& key,const V& value);
void remove(const K& key);
void print();
private:
int randomLevel() const;
NodePtr header; // header节点
NodePtr tail; // tail节点
int level; // 当前层数
int n; // 节点数量
};
template<class K, class V>
void SkipList<K, V>::print() {
assert(this->header != nullptr);
std::cout << "level=" << this->level << " count=" << this->n << endl;
for (int i = this->level - 1; i >= 0 ; --i) {
cout << "level" << i + 1 << ":";
NodePtr pNode = this->header->forward[i];
while (pNode != this->tail) {
cout << "<" << pNode->key << ", " << pNode->value << "> ";
pNode = pNode->forward[i];
}
cout << endl;
}
}
template<class K, class V>
SkipList<K, V>::SkipList() {
this->header = nullptr;
this->tail = nullptr;
this->level = 0;
this->n = 0;
}
template<class K, class V>
SkipList<K, V>::SkipList(NodePtr header, NodePtr tail) {
this->header = header;
this->tail = tail;
this->level = 1;
this->n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_LEVEL; ++i) {
this->header->forward[i] = tail;
}
}
template<class K, class V>
SkipList<K, V>::~SkipList() {
NodePtr p = this->header;
while (p->forward[0] != nullptr) {
NodePtr tmp = p;
p = p->forward[0];
delete tmp;
}
}
template<class K, class V>
int SkipList<K, V>::randomLevel() const {
int lvl = 1;
int maxLevel = (int)log(this->n) + 1;
while (rand() % 100 < P * 100 && lvl < min(maxLevel, MAX_LEVEL)) {
++lvl;
}
return lvl;
}
template<class K, class V>
V* SkipList<K, V>::search(const K& key) {
NodePtr x = this->header;
for (int i = 0; i < this->level; ++i) {
while (x->forward[i]->key < key) {
x = x->forward[i];
}
}
x = x->forward[0];
if (x->key == key) {
return &x->value;
} else {
return nullptr;
}
}
template<class K, class V>
void SkipList<K, V>::insert(const K& key,const V& value) {
// 找到待调整的项
NodePtr update[MAX_LEVEL];
NodePtr ptr = this->header;
for (int i = this->level - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
while (ptr->forward[i]->key < key) {
ptr = ptr->forward[i];
}
update[i] = ptr;
}
if (update[0]->forward[0]->key == key) {
update[0]->forward[0]->value = value;
return;
}
// 进行节点加入操作(与链表插入类似)
const int lvl = this->randomLevel(); // 随机生成该节点层数
if (lvl > this->level) {
for (int i = this->level; i< lvl; ++i) {
update[i] = this->header;
}
this->level = lvl;
}
NodePtr x = new SkipListNode<K, V>(key, value, lvl);
for (int i = 0; i < this->level; ++i) {
x->forward[i] = update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i] = x;
}
this->n++;
}
template<class K, class V>
void SkipList<K, V>::remove(const K& key) {
NodePtr update[MAX_LEVEL];
NodePtr x = this->header;
for (int i = this->level -1; i >= 0; --i) {
while (x->forward[i]->key < key) {
x = x->forward[i];
}
update[i] = x;
}
x = x->forward[0];
if (x->key == key) {
for (int i = 0; i < this->level; ++i) {
if (update[i]->forward[i] != x)
break;
update[i]->forward[i] = x->forward[i];
}
delete x;
this->n--;
while (this->level > 1 && this->header->forward[this->level - 1] == this->tail) {
this->level--;
}
}
}
int main() {
srand(time(nullptr));
SkipListNode<int, int> *header = new SkipListNode<int, int>(INT_MIN, 0, 1);
SkipListNode<int, int> *tail = new SkipListNode<int, int>(INT_MAX, 0, 1);
SkipList<int, int>* pSkiplist = new SkipList<int, int>(header, tail);
pSkiplist->insert(10, 10);
pSkiplist->insert(15, 15);
pSkiplist->insert(12, 12);
pSkiplist->insert(18, 18);
pSkiplist->insert(1, 1);
pSkiplist->insert(121, 121);
pSkiplist->insert(118, 118);
pSkiplist->insert(10, 100);
pSkiplist->print();
int* v = pSkiplist->search(121);
cout << "value is :" << *v << endl;
pSkiplist->remove(118);
pSkiplist->print();
pSkiplist->insert(11860, 1180);
pSkiplist->insert(11850, 1180);
pSkiplist->insert(11840, 1180);
pSkiplist->insert(11830, 1180);
pSkiplist->insert(11820, 1180);
pSkiplist->print();
delete pSkiplist;
}