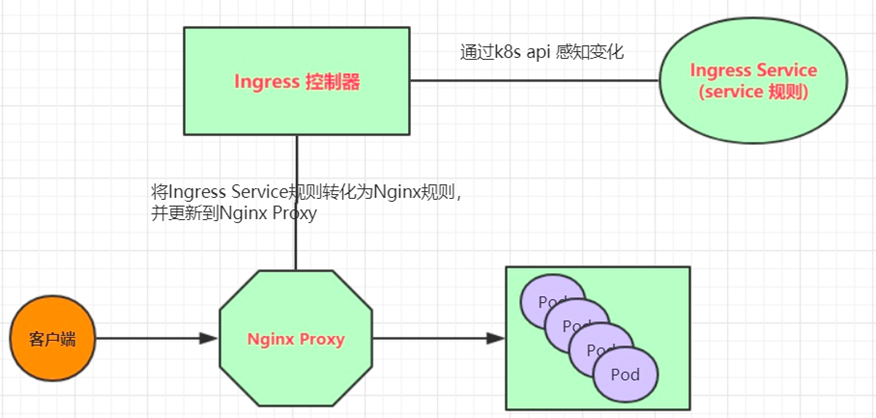
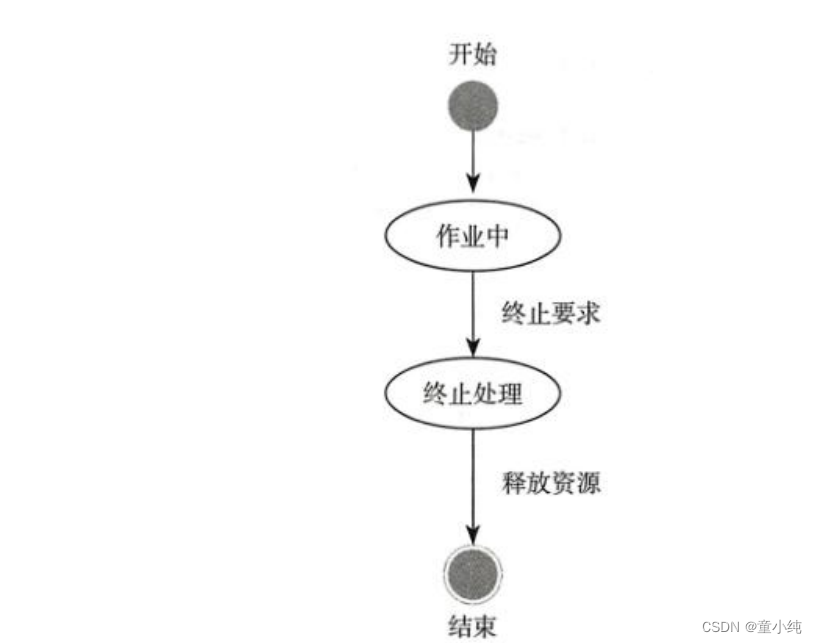
介绍
在前一天我们介绍了Android中有两种启动Service的方法。并擅述了startService和bindService的区别。同时我们着重讲了startService。
因此今天我们就来讲bindService。bindService大家可以认为它是和Android的一个共生体。即这个service所属的activity如果消亡那么bindService也会消亡。
因此今天我们以一个比较复杂的例子,activity<->service间互相传值来讲透这个bindService的使用,同时我们在这个例子中故意留下一个坑即:在Service里使用Thread处理大事务是不是就一定安全呢?也不安全,它也会引起ANR即:Application Not Responding-安卓崩溃。从而以这个坑来引出IntentService的使用。
来看例子

我们设有三个按钮:
- 【BIND SERVICE】-点击后运行Service
- 【STOP BINDING】-点击后结束Service
- 【GET VALUE FROM BINDER】-通过Activity获取正在BINDING的Service内的值,此处我们留下了一个ANR的坑,即获取Service内的值时我们留了一个Thread.Sleep(30000)的长事务,来观察ANR;
此处记得按钮的点击顺序为:先点【BIND SERVICE】->再点【GET VALUE FROM BINDER】->再点【STOP BINDING】不过此处你没有机会点这个【STOP BINDING】按钮,因为在GET时你已经ANR(崩溃)了。
来看全代码展示。
全代码
Service注册
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:dataExtractionRules="@xml/data_extraction_rules"
android:fullBackupContent="@xml/backup_rules"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.DemoBindService"
tools:targetApi="31">
<service
android:name=".SampleBindService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action
android:name="org.mk.android.demo.SampleBindService"/>
</intent-filter>
</service>
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.app.lib_name"
android:value="" />
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>Service类(坑来了)
package org.mk.android.demo;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class SampleBindService extends Service {
private final String TAG = "SimpleBindService";
private int count;
private boolean quit;
private CountNumBinder countNumBinder = new CountNumBinder();
public SampleBindService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>onBind方法被调用");
return countNumBinder;
}
//Service被关闭前回调
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
this.quit = true;
Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>onDestroyed方法被调用!");
}
@Override
public void onRebind(Intent intent) {
Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>onRebind方法被调用!");
super.onRebind(intent);
}
//Service被创建时调用
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>onCreate方法被调用");
super.onCreate();
//创建一个线程动态地修改count的值
new Thread() {
public void run() {
while (!quit) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
}
}
;
}.start();
}
//Service断开连接时回调
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>onUnbind方法被调用!");
return true;
}
//Service被启动时调用
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>onStartCommand方法被调用");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
public class CountNumBinder extends Binder {
public int getCount() {
Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>into long waiting");
try {
Thread.sleep(300000);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return -1;
}
}
}我们可以看到,这个Service以每秒对着count+1.
然后通过bindService的onBind生命体里以一个CountNumBinder暴露出去,给到外部可以通过一个getCount方法来调用获取Service里当前count的值,但是这个值在获取前我们会使用Thread.sleep(30000)-30秒来模拟ANR。
主运行类-MainActivity.java
- 在调用Service的activity里我们使用bindService(intent, conn, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);来启动。
- 这边这个conn是一个ServiceConnection类,new出一个ServiceConnection类并覆盖里面的
- onServiceConnected方法,用于接受bindService返回的对象;
- onServiceDisconnected方法,用于在这个bindService被销毁时作处理;
具体代码如下:
package org.mk.android.demo;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private final String TAG = "SimpleBindService";
private Button buttonBindService;
private Button buttonStopBinding;
private Button buttonGetValueFromBinder;
private Context ctx;
private Intent intent;
private SampleBindService.CountNumBinder countNumBinder;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
buttonBindService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.buttonBindService);
buttonStopBinding = (Button) findViewById(R.id.buttonStopBinding);
buttonGetValueFromBinder = (Button) findViewById(R.id.buttonGetValueFromBinder);
ctx = MainActivity.this;
intent = new Intent(ctx, SampleBindService.class);
buttonBindService.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener());
buttonStopBinding.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener());
buttonGetValueFromBinder.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener());
}
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
//Activity与Service断开连接时回调该方法
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>Service DisConnected");
}
//Activity与Service连接成功时回调该方法
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Log.i(TAG, ">>>>>>Service Connected");
countNumBinder = (SampleBindService.CountNumBinder) service;
}
};
class OnClickListener implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Intent eIntent;
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.buttonBindService:
bindService(intent, conn, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
break;
case R.id.buttonStopBinding:
unbindService(conn);
break;
case R.id.buttonGetValueFromBinder:
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Service的count" + "的值为:" + countNumBinder.getCount(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
break;
}
}
}
}运行效果
- 先点【BIND SERVICE】;
- 再点【GET VALUE FROM BINDER】;
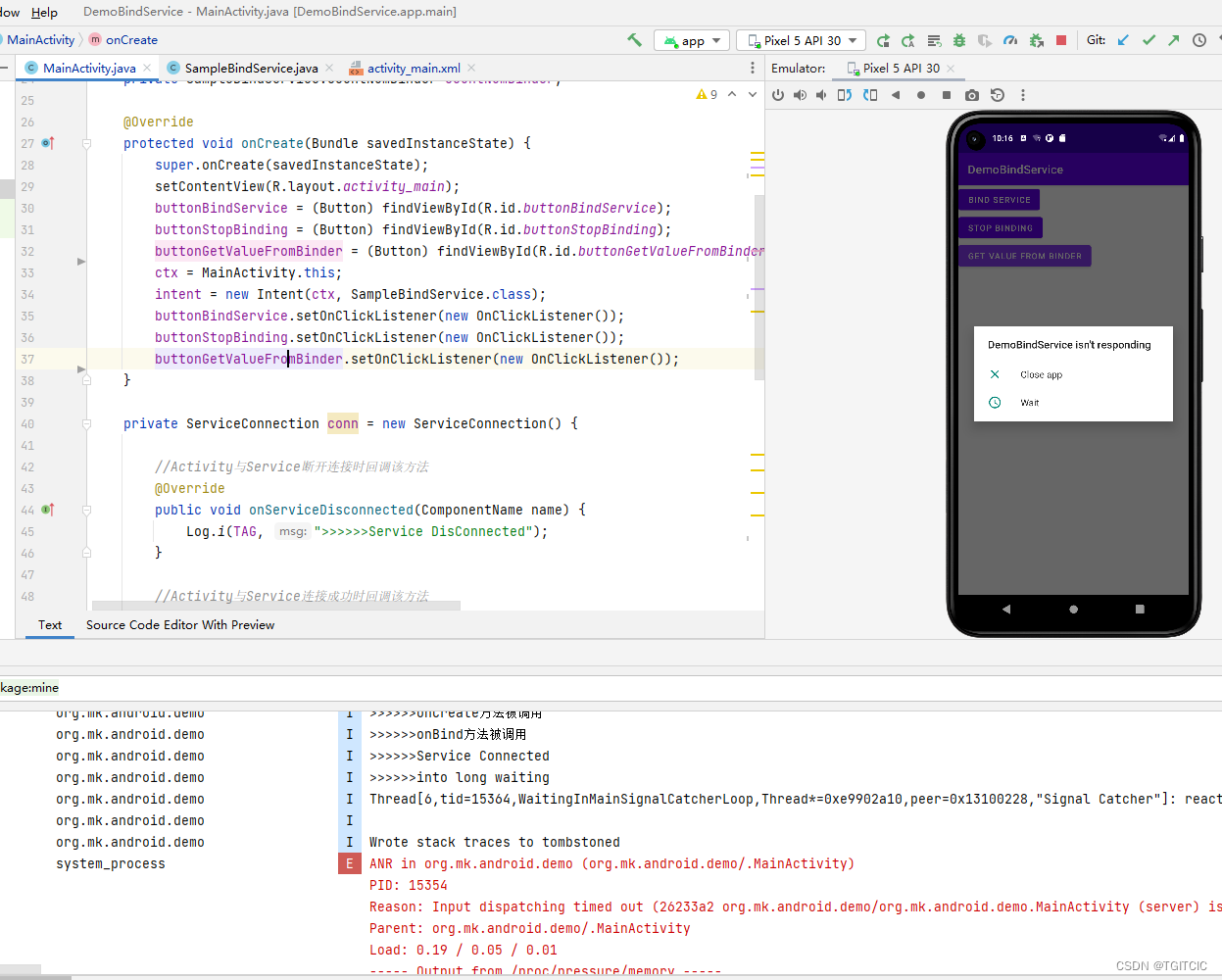
看,ANR出现了。
这就是我说的坑,怎么解决这个坑,请听下回分解。