状态
- R —— 运行
- S(
TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE) —— 等待,可中断,IO - D(
TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE) —— 等待,不可中断 - K(
TASK_KILLABLE) —— 等待,可删除,IO完成 - I(
TASK_REPORT_IDLE) —— 等待, - T(
TASK_STOPPED) —— 暂停,监听信号 - t(
TASK_TRACED) —— 暂停,监听信号 - Z(
EXIT_ZOMBLE) —— 终止,等待回收 - X(
EXIT_DEAD) —— 终止,已回收
启停、信号
- kill, killall, pkill
- 中断
- tmux
eval
监控
- 排查负载
- uptime
- lscpu
- TOP https://www.howtogeek.com/668986/how-to-use-the-linux-top-command-and-understand-its-output/
h帮助Z切换profile、配置profileW保存配置- 配置存储在
~/procps/toprc
- 配置存储在
R、x/y、</>排序M内存排序pcpu排序
u用户V树展示- 样式调整
tcpul负载 - uptime
H线程
- htop
systemd
RHEL启动管理进程
- RHEL 5 – Sys ini 是启动速度最慢的,串行启动过程,无论进程相互之间有无依赖关系
- RHEL 6.0 – update init 相对启动速度快一点有所改进。有依赖的进程之间依次启动而其他与之没有依赖关系的则并行同步驱动
- RHEL7 systemd 与以上都不同。所有进程无论有无依赖关系则都是并行启动(很多时候进程没有真正启动而是只有一个信号或者说是标记而已,在真正利用的时候才会正真启动)。systemnd为了解决上文的问题而诞生。它的目标是为系统的启动和管理提供一套完整的解决方案。
- systemd守护进程管理Linux的启动,包括服务启动和服务管理。在系统启动时或者正在运行的系统上激活系统资源、服务器守护程序和其他进程。
- 守护进程时在后台等待或运行,执行各种任务的进程。通常,守护进程在引导时自动启动并继续运行直到关闭或者手动停止。许多守护程序的名称约定以字母d结尾。(deamon)
- 服务通常包含一个或多个守护进程。
- RHEL启动的第一个进程(PID1)时 systemd,提供功能包括:
- 并行化功能(同时启动多个服务),可以提高系统的启动速度。
- 按需启动后台程序而无需单独的服务。
- 自动服务依赖关系管理,可防止长时间超时。例如,网络相关服务在网络可用之前不会尝试启动。
- 使用 [[Linux]]控制组一起跟踪相关进程的方法。
架构图
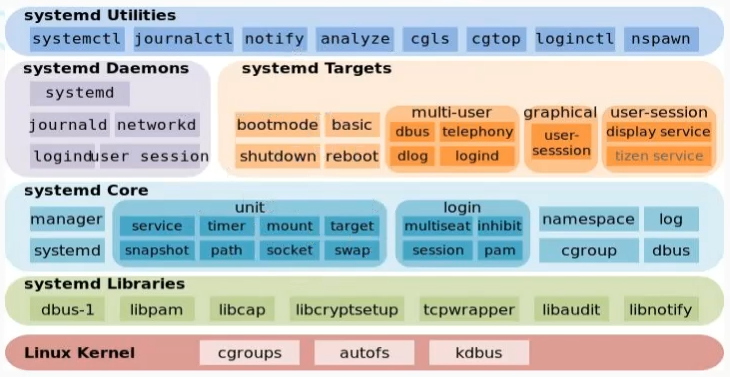
系统对象
systemctl命令用于管理不同类型的系统对象,这些对象称为units
-
unit类型
- service unit —— 用于定义系统服务,文件扩展名
.service - target unit —— 用于模拟实现“运行级别”,文件扩展名
.target#[[runlevel]] #[[init ]] - device unit —— 用于定义内核识别的设备,文件扩展名
.device - mount unit —— 用于顶i一文件系统挂载点,文件扩展名
.mount - socket unit —— 管理系统快照,文件扩展名
.snapshot - swap unit —— 用于标识swap设备,文件扩展名
.swap - automount unit —— 文件系统的自动挂载点,文件扩展名为
.automount - path unit —— 用于根据文件系统上特定对象的变化来启动其他服务,文件扩展名
.path - timer unit —— 用于管理计划任务,文件扩展名
.timer - slice unit —— 用于资源管理,文件扩展名
.slice
- service unit —— 用于定义系统服务,文件扩展名
-
文件、依赖
$ systemctl list-units --type=service $ systemctl list-unit-files --type=service # 查看依赖 $ systemctl list-dependencies default.target ● ├─atd.service ● ├─auditd.service ● ├─chronyd.service ● ├─crond.service ● ├─dbus.service ... $ systemctl list-dependencies --reverse -
配置文件(优先级排序)
/etc/systemd/system本地配置的系统单元/run/systemd/system运行时配置的系统单元/usr/lib/systemd/system软件包安装的系统单元
-
命令
```bash
systemctl start sshd.service
systemctl stop sshd.servicesystemctl restart sshd.service # 服务没有停止,只是重新加载一次配置 systemctl reload sshd.service # 开机启动 systemctl enable sshd.service systemctl disable sshd.service # e.g. $ systemctl restart sshd.service Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/sshd.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service. $ systemctl disable sshd.service Removed /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/sshd.service. # 开机禁止启动 systemctl mask sshd.service systemctl unmask sshd.service # e.g. $ systemctl mask sshd.service Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/sshd.service → /dev/null. $ systemctl unmask sshd.service Removed /etc/systemd/system/sshd.service. ```