学完C语言之后,我就去阅读《C Primer Plus》这本经典的C语言书籍,对每一章的编程练习题都做了相关的解答,仅仅代表着我个人的解答思路,如有错误,请各位大佬帮忙点出!
由于使用的是命令行参数常用于linux系统或者vscode,但此代码是运行于vs2022的,测试截图就不弄了。
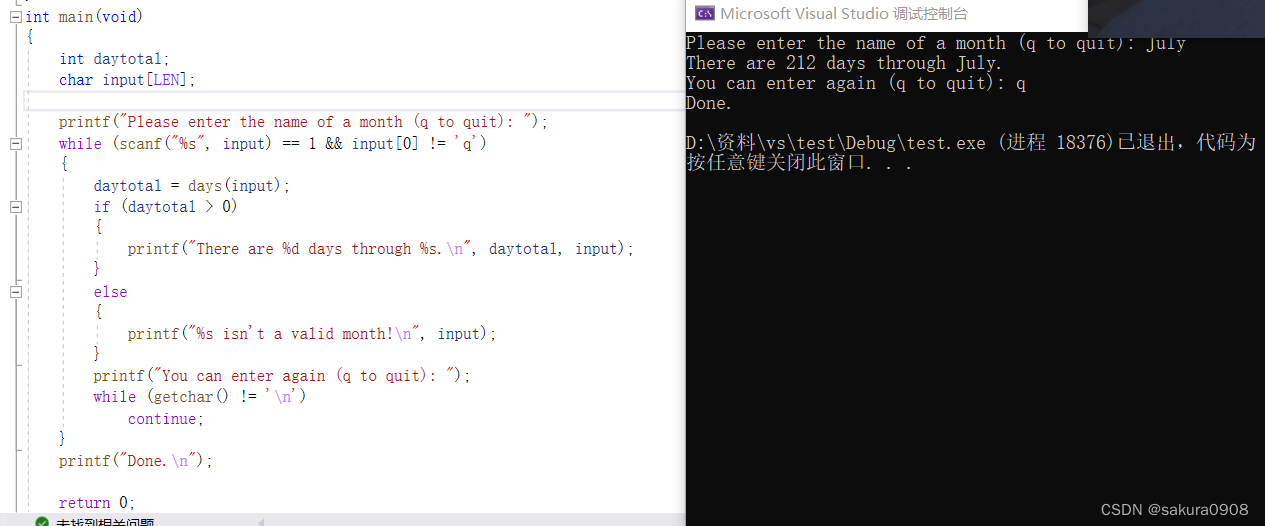
1.重新编写复习题 5,用月份名的拼写代替月份号(别忘了使用 strcmp())。在一个简单的程序中测试该函数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define LEN 12
struct month
{
char name[10];
char abbrev[4];
int days;
int monumb;
};
const struct month months[LEN] ={{"January", "Jan", 31, 1},{"February", "Feb", 28, 2},{"March", "Mar", 31, 3},
{"April", "Apr", 30, 4},{"May", "May", 31, 5},{"June", "Jun", 30, 6},
{"July", "Jul", 31, 7},{"August", "Aug", 31, 8},{"September", "Sep", 30, 9},
{"October", "Oct", 31, 10},{"November", "Nov", 30, 11},{"December", "Dec", 31, 12}};
int days(char* name)
{
int i = 1;
int num = 0;
int total = 0;
name[0] = toupper(name[0]);
while (name[i] != '\0')
{
name[i] = tolower(name[i]);
i++;
}
for (i = 0; i < LEN; i++)
{
if (strcmp(name, months[i].name) == 0)
{
num = months[i].monumb;
break;
}
}
if (num == 0)
{
total = -1;
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
total += months[i].days;
}
}
return total;
}
int main(void)
{
int daytotal;
char input[LEN];
printf("Please enter the name of a month (q to quit): ");
while (scanf("%s", input) == 1 && input[0] != 'q')
{
daytotal = days(input);
if (daytotal > 0)
{
printf("There are %d days through %s.\n", daytotal, input);
}
else
{
printf("%s isn't a valid month!\n", input);
}
printf("You can enter again (q to quit): ");
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
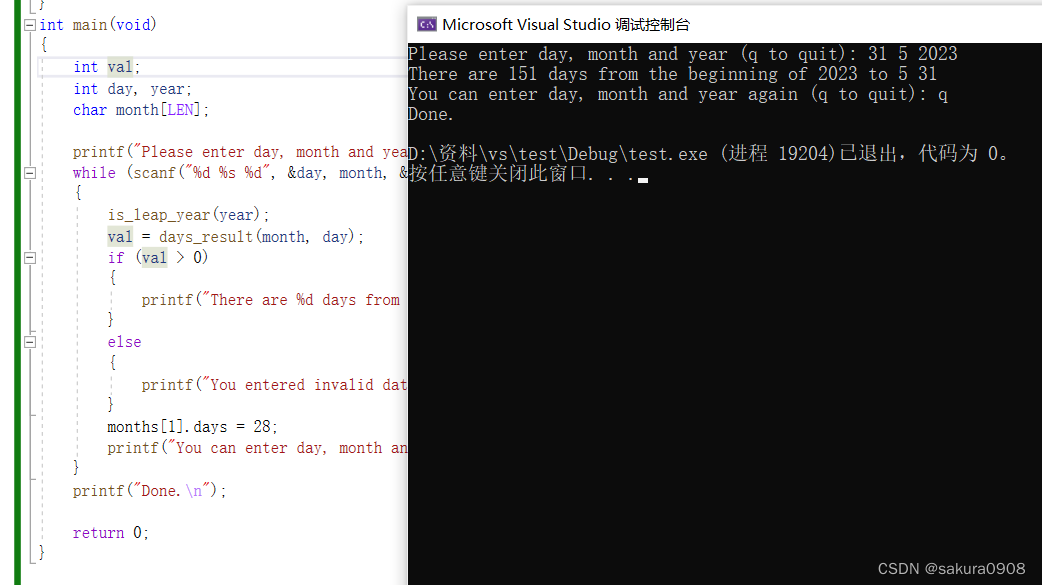
2.编写一个函数,提示用户输入日、月和年。月份可以是月份号、月份 名或月份名缩写。然后该程序应返回一年中到用户指定日子(包括这一天) 的总天数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define LEN 12
struct month
{
char name[10];
char abbrev[4];
int days;
int monumb;
};
struct month months[LEN] ={{"January", "Jan", 31, 1},{"February", "Feb", 28, 2},{"March", "Mar", 31, 3},
{"April", "Apr", 30, 4},{"May", "May", 31, 5},{"June", "Jun", 30, 6},
{"July", "Jul", 31, 7},{"August", "Aug", 31, 8},{"September", "Sep", 30, 9},
{"October", "Oct", 31, 10},{"November", "Nov", 30, 11},{"December", "Dec", 31, 12}};
void is_leap_year(int year)
{
if ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0)
{
months[1].days = 29;
}
}
int days_result(char* month, int days)
{
int i;
int total = 0;
int temp = atoi(month);
if (days < 1 || days > 31)
{
return -1;
}
if (0 == temp)
{
month[0] = toupper(month[0]);
for (i = 1; month[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
month[i] = tolower(month[i]);
}
}
for (i = 0; i < LEN; i++)
{
if ((temp == months[i].monumb) ||
(strcmp(month, months[i].name) == 0) ||
(strcmp(month, months[i].abbrev) == 0))
{
if (days > months[i].days)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
return total + days;
}
}
else
{
total += months[i].days;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int val;
int day, year;
char month[LEN];
printf("Please enter day, month and year (q to quit): ");
while (scanf("%d %s %d", &day, month, &year) == 3)
{
is_leap_year(year);
val = days_result(month, day);
if (val > 0)
{
printf("There are %d days from the beginning of %d to %s %d\n", val, year, month, day);
}
else
{
printf("You entered invalid datas!\n");
}
months[1].days = 28;
printf("You can enter day, month and year again (q to quit): ");
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
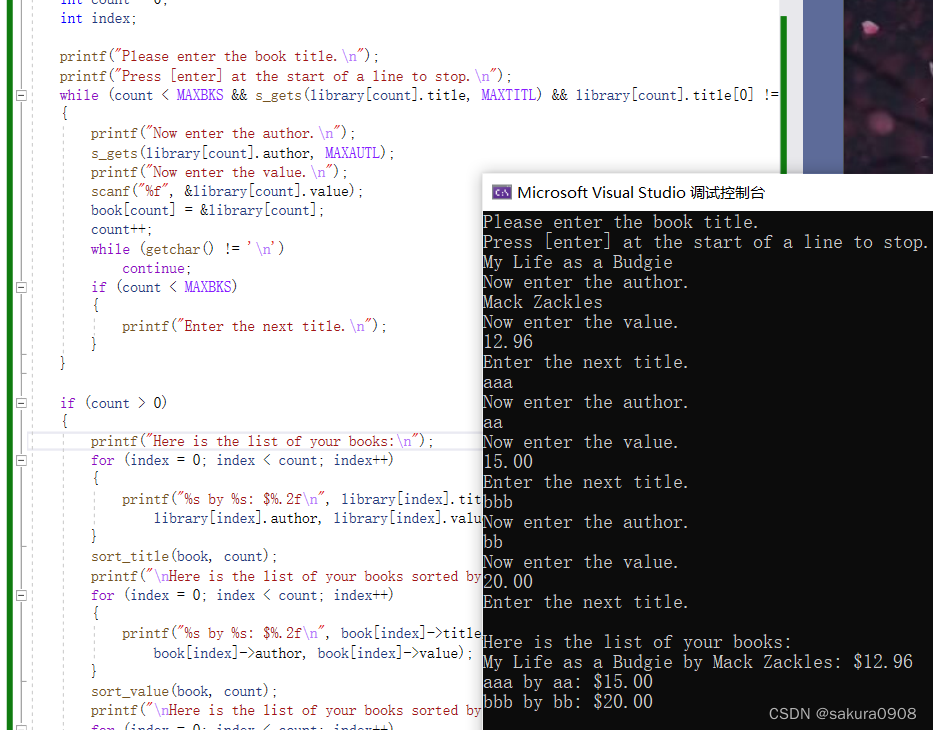
3.修改程序清单 14.2 中的图书目录程序,使其按照输入图书的顺序输出 图书的信息,然后按照标题字母的声明输出图书的信息,最后按照价格的升 序输出图书的信息。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXTITL 40
#define MAXAUTL 40
#define MAXBKS 100
struct book
{
char title[MAXTITL];
char author[MAXAUTL];
float value;
};
void sort_title(struct book* pb[], int n)
{
int i, j;
struct book* temp;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (strcmp(pb[j]->title, pb[i]->title) < 0)
{
temp = pb[j];
pb[j] = pb[i];
pb[i] = temp;
}
}
}
}
void sort_value(struct book* pb[], int n)
{
int i, j;
struct book* temp;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (pb[j]->value < pb[i]->value)
{
temp = pb[j];
pb[j] = pb[i];
pb[i] = temp;
}
}
}
}
char* s_gets(char* st, int n)
{
char* ret_val;
char* find;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
{
*find = '\0';
}
else
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
}
return ret_val;
}
int main(void)
{
struct book library[MAXBKS];
struct book* book[MAXBKS];
int count = 0;
int index;
printf("Please enter the book title.\n");
printf("Press [enter] at the start of a line to stop.\n");
while (count < MAXBKS && s_gets(library[count].title, MAXTITL) && library[count].title[0] != '\0')
{
printf("Now enter the author.\n");
s_gets(library[count].author, MAXAUTL);
printf("Now enter the value.\n");
scanf("%f", &library[count].value);
book[count] = &library[count];
count++;
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
if (count < MAXBKS)
{
printf("Enter the next title.\n");
}
}
if (count > 0)
{
printf("Here is the list of your books:\n");
for (index = 0; index < count; index++)
{
printf("%s by %s: $%.2f\n", library[index].title,
library[index].author, library[index].value);
}
sort_title(book, count);
printf("\nHere is the list of your books sorted by title letters:\n");
for (index = 0; index < count; index++)
{
printf("%s by %s: $%.2f\n", book[index]->title,
book[index]->author, book[index]->value);
}
sort_value(book, count);
printf("\nHere is the list of your books sorted by value(from low to high):\n");
for (index = 0; index < count; index++)
{
printf("%s by %s: $%.2f\n", book[index]->title,
book[index]->author, book[index]->value);
}
}
else
{
printf("No books? Too bad.\n");
}
return 0;
}
4.编写一个程序,创建一个有两个成员的结构模板:
a.第1个成员是社会保险号,第2个成员是一个有3个成员的结构,第1个 成员代表名,第2个成员代表中间名,第3个成员表示姓。创建并初始化一个 内含5个该类型结构的数组。该程序以下面的格式打印数据:
Dribble, Flossie M.–– 302039823
如果有中间名,只打印它的第1个字母,后面加一个点(.);如果没有 中间名,则不用打印点。编写一个程序进行打印,把结构数组传递给这个函 数。
b.修改a部分,传递结构的值而不是结构的地址。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 15
#define LEN 30
struct names
{
char fname[N];
char mname[N];
char lname[N];
};
struct messages
{
char ins_num[LEN];
struct names name;
};
char* s_gets(char* st, int n)
{
char* ret_val;
char* find;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
{
*find = '\0';
}
else
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
}
return ret_val;
}
void show(const struct messages pt[], int n)
{
int i;
printf("All numbers messages:\n");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (pt[i].name.mname[0] == '\0')
{
printf("%s, %s", pt[i].name.fname, pt[i].name.lname);
printf(" -- %s\n", pt[i].ins_num);
}
else
{
printf("%s, %s %c.", pt[i].name.fname, pt[i].name.lname, pt[i].name.mname[0]);
printf(" -- %s\n", pt[i].ins_num);
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
int count = 0;
struct messages m[5];
printf("Please enter the insurance number:\n");
printf("Press [enter] at the start of a line to stop.\n");
while (count < 5 && s_gets(m[count].ins_num, LEN) && m[count].ins_num[0] != '\0')
{
printf("Now enter the former name.\n");
s_gets(m[count].name.fname, N);
printf("Now enter the middle name(Without, [enter] to the next).\n");
s_gets(m[count].name.mname, N);
printf("Now enter the last name.\n");
s_gets(m[count].name.lname, N);
if (count++ < 5)
{
printf("Enter the next insurance number:\n");
}
}
if (count > 0)
{
show(m, count);
}
else
{
printf("No data!\n");
}
return 0;
}
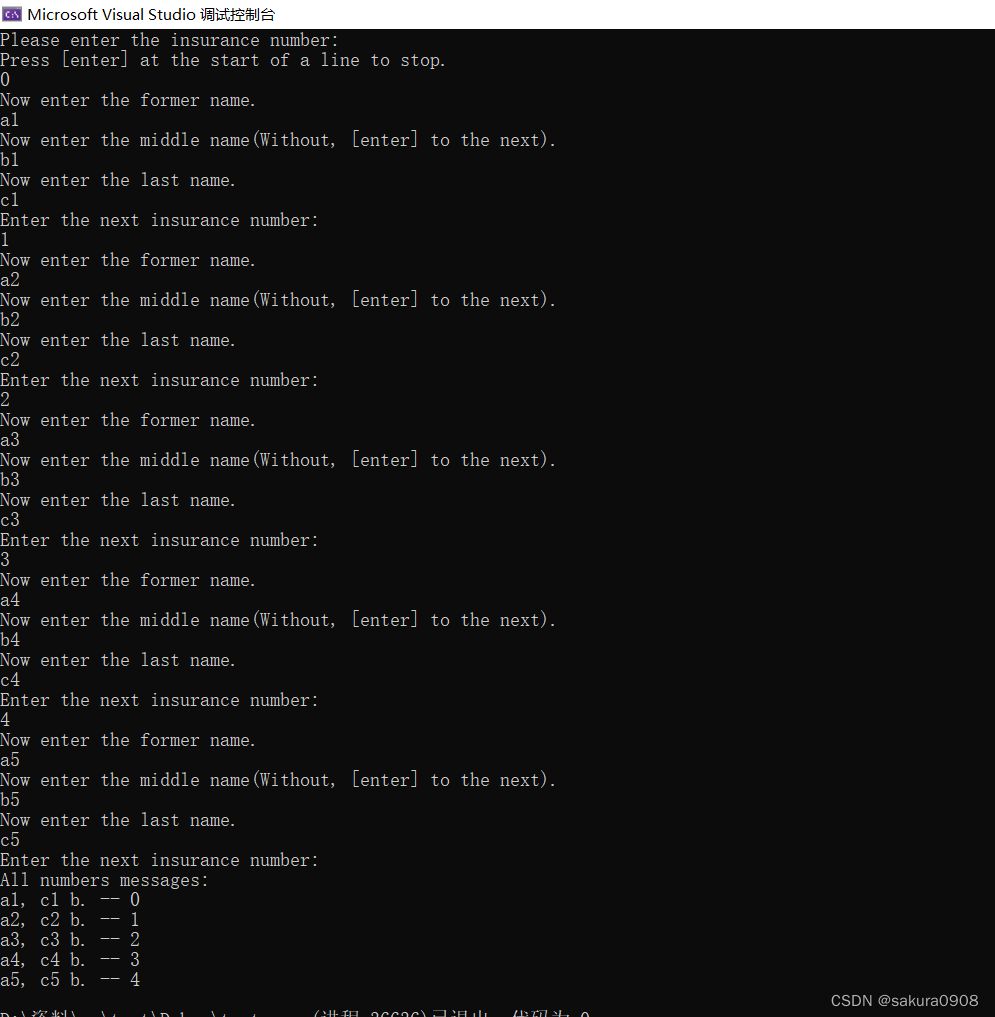
5.编写一个程序满足下面的要求。
a.外部定义一个有两个成员的结构模板name:一个字符串储存名,一个 字符串储存姓。
b.外部定义一个有3个成员的结构模板student:一个name类型的结构, 一个grade数组储存3个浮点型分数,一个变量储存3个分数平均数。
c.在main()函数中声明一个内含CSIZE(CSIZE = 4)个student类型结构的 数组,并初始化这些结构的名字部分。用函数执行g、e、f和g中描述的任 务。
d.以交互的方式获取每个学生的成绩,提示用户输入学生的姓名和分 数。把分数储存到grade数组相应的结构中。可以在main()函数或其他函数中 用循环来完成。
e.计算每个结构的平均分,并把计算后的值赋给合适的成员。
f.打印每个结构的信息。
g.打印班级的平均分,即所有结构的数值成员的平均值。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define LEN 15
#define CSIZE 4
#define SCORES 3
struct name
{
char fname[LEN];
char lname[LEN];
};
struct student
{
struct name mes;
float grade[SCORES];
float aver;
};
void set_students(struct student ar[], int n)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("Please enter three scores for %s %s:\n", ar[i].mes.fname, ar[i].mes.lname);
for (j = 0; j < SCORES; j++)
{
while (scanf("%f", &ar[i].grade[j]) != 1)
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
printf("Please enter a number: ");
}
}
}
}
void find_averages(struct student ar[], int n)
{
int i, j;
float sum;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (j = 0, sum = 0.0f; j < SCORES; j++)
{
sum += ar[i].grade[j];
}
ar[i].aver = sum / SCORES;
}
}
void show_messages(const struct student ar[], int n)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("\n%s %s's three scores: ", ar[i].mes.fname, ar[i].mes.lname);
for (j = 0; j < SCORES; j++)
{
printf("%g ", ar[i].grade[j]);
}
printf("\nAverage: %g\n", ar[i].aver);
}
}
void show_averages(const struct student ar[], int n)
{
int i;
float total;
for (i = 0, total = 0.0f; i < n; i++)
{
total += ar[i].aver;
}
printf("\nClass average: %g\n", total / n);
}
int main(void)
{
struct student classes[CSIZE] ={{"Flip", "Snide"},{"Clare", "Voyans"},
{"Bingo", "Higgs"},{"Fawn", "Hunter"}};
set_students(classes, CSIZE);
find_averages(classes, CSIZE);
show_messages(classes, CSIZE);
show_averages(classes, CSIZE);
return 0;
}

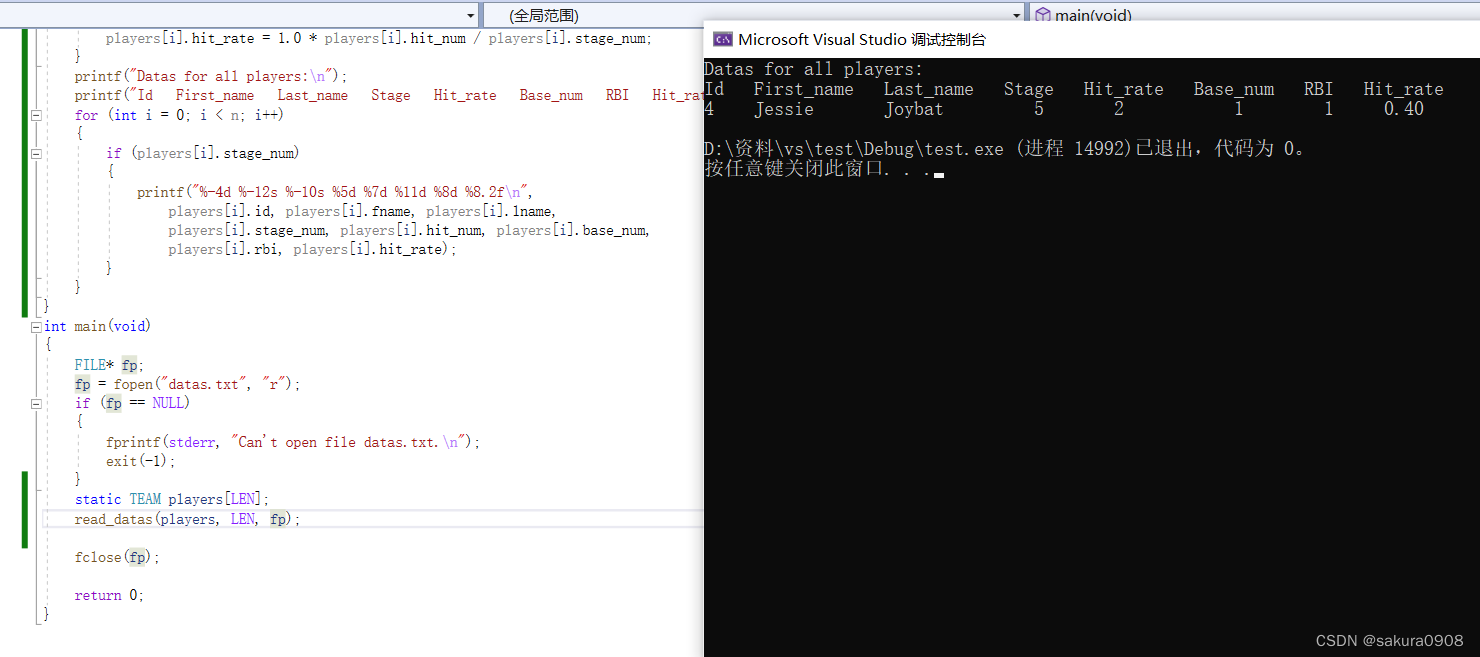
6.一个文本文件中保存着一个垒球队的信息。每行数据都是这样排列:
4 Jessie Joybat 5 2 1 1
第1项是球员号,为方便起见,其范围是0~18。第2项是球员的名。第3 项是球员的姓。名和姓都是一个单词。第4项是官方统计的球员上场次数。 接着3项分别是击中数、走垒数和打点(RBI)。文件可能包含多场比赛的 数据,所以同一位球员可能有多行数据,而且同一位球员的多行数据之间可 能有其他球员的数据。编写一个程序,把数据储存到一个结构数组中。该结 构中的成员要分别表示球员的名、姓、上场次数、击中数、走垒数、打点和 安打率(稍后计算)。可以使用球员号作为数组的索引。该程序要读到文件 结尾,并统计每位球员的各项累计总和。
世界棒球统计与之相关。例如,一次走垒和触垒中的失误不计入上场次 数,但是可能产生一个RBI。但是该程序要做的是像下面描述的一样读取和 处理数据文件,不会关心数据的实际含义。
要实现这些功能,最简单的方法是把结构的内容都初始化为零,把文件 中的数据读入临时变量中,然后将其加入相应的结构中。程序读完文件后, 应计算每位球员的安打率,并把计算结果储存到结构的相应成员中。计算安打率是用球员的累计击中数除以上场累计次数。这是一个浮点数计算。最 后,程序结合整个球队的统计数据,一行显示一位球员的累计数据。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define LEN 19
typedef struct
{
int id; //球员的编号
char fname[LEN]; //球员的名;
char lname[LEN]; //球员的姓;
int stage_num; //球员的上场次数;
int hit_num; //球员的击中数;
int base_num; //球员的走垒数;
int rbi; //球员的打点;
double hit_rate; //球员的安打率;
} TEAM;
void read_datas(TEAM players[], int n, FILE* fp)
{
int count = 0;
char fname[LEN], lname[LEN];
int m , stage_num, hit_num, base_num, rbi;
while (fscanf(fp, "%d %18s %18s %d %d %d %d", &m, fname, lname, &stage_num, &hit_num, &base_num, &rbi) != EOF)
{
if (players[count].stage_num == 0)
{
++count;
}
strcpy(players[count].fname, fname);
strcpy(players[count].lname, lname);
players[count].id = m;
players[count].stage_num += stage_num;
players[count].hit_num += hit_num;
players[count].base_num += base_num;
players[count].rbi += rbi;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
players[i].hit_rate = 1.0 * players[i].hit_num / players[i].stage_num;
}
printf("Datas for all players:\n");
printf("Id First_name Last_name Stage Hit_rate Base_num RBI Hit_rate\n");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (players[i].stage_num)
{
printf("%-4d %-12s %-10s %5d %7d %11d %8d %8.2f\n",
players[i].id, players[i].fname, players[i].lname,
players[i].stage_num, players[i].hit_num, players[i].base_num,
players[i].rbi, players[i].hit_rate);
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
FILE* fp;
fp = fopen("datas.txt", "r");
if (fp == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can't open file datas.txt.\n");
exit(-1);
}
static TEAM players[LEN];
read_datas(players, LEN, fp);
fclose(fp);
7.修改程序清单 14.14,从文件中读取每条记录并显示出来,允许用户 删除记录或修改记录的内容。如果删除记录,把空出来的空间留给下一个要 读入的记录。要修改现有的文件内容,必须用"r+b"模式,而不是"a+b"模 式。而且,必须更加注意定位文件指针,防止新加入的记录覆盖现有记录。 最简单的方法是改动储存在内存中的所有数据,然后再把最后的信息写入文 件。跟踪的一个方法是在book结构中添加一个成员表示是否该项被删除。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAXTITL 40
#define MAXAUTL 40
#define MAXBKS 10
#define CONTINUE 0
#define DONE 1
struct book
{
char title[MAXTITL];
char author[MAXAUTL];
float value;
};
struct pack
{
struct book books;
bool canceled;
};
int get_first(const char* str)
{
int ch;
ch = tolower(getchar());
while (strchr(str, ch) == NULL)
{
printf("Invalid data! Please enter again: ");
eatline();
ch = tolower(getchar());
}
eatline();
return ch;
}
int get_books(struct pack* pb)
{
int status = CONTINUE;
if (s_gets(pb->books.title, MAXTITL) == NULL || pb->books.title[0] == '\0')
{
status = 1;
}
else
{
printf("Now enter the author: ");
s_gets(pb->books.author, MAXAUTL);
printf("Now enter the value: ");
while (scanf("%f", &pb->books.value) != 1)
{
eatline();
puts("Please enter a valid value: ");
}
eatline();
pb->canceled = false;
}
return status;
}
void update(struct pack* item)
{
int ch;
struct book copy;
copy = item->books;
printf("============================================\n");
printf("t) modify title a) modify author\n");
printf("v) modify value s) quit, saving changes\n");
printf("q) quit, ignore changes\n");
printf("============================================\n");
printf("Please you enter to choose: ");
while ((ch = get_first("tavsq")) != 's' && ch != 'q')
{
switch (ch)
{
case 't':
{
printf("Please enter new title: ");
s_gets(copy.title, MAXTITL);
break;
}
case 'a':
{
printf("Please enter new author: ");
s_gets(copy.author, MAXAUTL);
break;
}
case 'v':
{
printf("Please enter new value: ");
while (scanf("%f", ©.value) != 1)
{
eatline();
puts("Please enter a valid value: ");
}
eatline();
break;
}
}
printf("============================================\n");
printf("t) modify title a) modify author\n");
printf("v) modify value s) quit, saving changes\n");
printf("q) quit, ignore changes\n");
printf("============================================\n");
printf("You can choose again: ");
}
if (ch == 's')
{
item->books = copy;
}
return;
}
char* s_gets(char* st, int n)
{
char* ret_val;
char* find;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
{
*find = '\0';
}
else
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
}
return ret_val;
}
void eatline(void)
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
return;
}
int main(void)
{
struct pack library[MAXBKS];
int count = 0;
int deleted = 0;
int index, filecount, open;
FILE* pbooks;
int size = sizeof(struct book);
if ((pbooks = fopen("book.dat", "rb")) != NULL)
{
while (count < MAXBKS && fread(&library[count], size, 1, pbooks) == 1)
{
if (count == 0)
{
puts("Current contents of book.dat:");
}
printf("%s by %s: $%.2f\n", library[count].books.title,
library[count].books.author, library[count].books.value);
printf("Do you want to change or delete this entry(y/n)?\n");
printf("Please you enter to choose: ");
if (get_first("yn") == 'y')
{
printf("Enter c to change, d to delete entry: ");
if (get_first("cd") == 'd')
{
library[count].canceled = true;
deleted++;
printf("Flag marked for deletion(The space for the next book).");
}
else
{
update(&library[count]);
}
}
count++;
}
fclose(pbooks);
}
filecount = count - deleted;
if (count == MAXBKS)
{
printf("The book.dat file is full.\n");
exit(-1);
}
if (deleted > 0)
{
printf("If you delete some books, you should enter books to replace.\n");
}
printf("Please add new book titles.\n");
printf("Press [enter] at the start of a line to stop.\n");
open = 0;
while (filecount < MAXBKS)
{
if (filecount < count)
{
while (library[open].canceled == false)
{
open++;
}
if (get_books(&library[open]) == DONE)
{
break;
}
}
else if (get_books(&library[filecount]) == DONE)
{
break;
}
filecount++;
if (filecount < MAXBKS)
{
puts("Enter the next book title.");
}
}
printf("Here is the list of your books:\n");
for (index = 0; index < filecount; index++)
{
if (library[index].canceled == false)
{
printf("%s by %s: $%.2f\n", library[index].books.title,
library[index].books.author, library[index].books.value);
}
}
pbooks = fopen("book.dat", "wb");
if (pbooks == NULL)
{
printf("Can't open book.dat file for output.\n");
exit(-1);
}
for (index = 0; index < filecount; index++)
{
if (library[index].canceled == false)
{
fwrite(&(library[index].books), size, 1, pbooks);
}
}
fclose(pbooks);
printf("Bye.\n");
return 0;
}
8.巨人航空公司的机群由 12 个座位的飞机组成。它每天飞行一个航 班。根据下面的要求,编写一个座位预订程序。
a.该程序使用一个内含 12 个结构的数组。每个结构中包括:一个成员 表示座位编号、一个成员表示座位是否已被预订、一个成员表示预订人的 名、一个成员表示预订人的姓。
b.该程序显示下面的菜单:
To choose a function, enter its letter label:
a) Show number of empty seats
b) Show list of empty seats
c) Show alphabetical list of seats
d) Assign a customer to a seat assignment
e) Delete a seat assignment
f) Quit
c.该程序能成功执行上面给出的菜单。选择d)和e)要提示用户进行额外 输入,每个选项都能让用户中止输入。
d.执行特定程序后,该程序再次显示菜单,除非用户选择f)。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define LEN 14
#define SEATS 12
typedef struct
{
int seat_id;
bool status;
char last[LEN];
char first[LEN];
} plane;
void eatline(void)
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
int get_first(void)
{
int ch;
do
{
ch = tolower(getchar());
} while (isspace(ch));
eatline();
return ch;
}
char* s_gets(char* st, int n)
{
char* ret_val;
char* find;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
{
*find = '\0';
}
else
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
}
return ret_val;
}
int getmenu(void)
{
int ch;
printf("To choose a function, enter its letter label:\n");
printf("a) Show number of empty seats\n");
printf("b) Show list of empty seats\n");
printf("c) Show alphabetical list of seat\n");
printf("d) Assign a customer to a seat\n");
printf("e) Delete a seat assignment\n");
printf("f) Quit\n");
printf("Please you enter to choose: ");
while (ch = get_first(), NULL == strchr("abcdef", ch))
{
printf("Invalid data! Please you choose again: ");
}
return ch;
}
void sort(plane* array[], int n) //按照ASCII码进行座位排序;
{
int i, j;
plane* temp;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (strcmp(array[j]->last, array[i]->last) < 0)
{
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[i];
array[i] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int openings(const plane pl[], int n) //显示空座位的数量;
{
int seat;
int count = 0;
for (seat = 0; seat < n; seat++)
{
if (pl[seat].status == false)
{
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
void list_assign(plane* ps[], int n) //显示按照字母序列排序后的座位表;
{
int i;
if (openings(*ps, n) == SEATS)
{
puts("All seats are empty.");
}
else
{
sort(ps, n);
for (i = 0; i < SEATS; i++)
{
if (ps[i]->status == true)
{
printf("Seat %d: %s, %s\n", ps[i]->seat_id, ps[i]->last, ps[i]->first);
}
}
}
}
void show_seats(const plane pl[]) //显示已分配的座位;
{
int i;
puts("Seats currently taken:");
for (i = 0; i < SEATS; i++)
{
if (pl[i].status == true)
{
printf("Seat %d: %s, %s\n", pl[i].seat_id, pl[i].last, pl[i].first);
}
}
}
void makelist(const plane pl[], char* str, int kind) //为分配和删除座位提供当前处理的座位数;
{
int seat;
char temp[LEN];
*str = '\0'; //清空str中的内容;
for (seat = 0; seat < SEATS; seat++)
{
if (pl[seat].status == kind)
{
sprintf(temp, "%d ", pl[seat].seat_id);
strcat(str, temp);
}
}
}
void show_empty_seats(const plane pl[], int n) //显示空座位的信息;
{
char seating[3 * SEATS];
if (openings(pl, n) == 0)
{
printf("All seats are assigned\n");
}
else
{
makelist(pl, seating, false);
printf("The following seats are available: ");
puts(seating);
}
}
void assign_seat(plane pl[], int n) //分配空余座位;
{
int ch, seat, flag;
char list[3 * SEATS];
if (openings(pl, n) == false)
{
printf("All seats are assigned. Can't assign again!\n");
}
else
{
makelist(pl, list, false);
printf("Available seats: %s\n", list);
printf("Which seat do you want? Please you enter from the lists: ");
do
{
while (scanf("%d", &seat) != 1)
{
eatline();
printf("Seats: %s\n", list);
printf("Enter a number from the lists: ");
}
if (seat < 1 || seat > SEATS || pl[seat - 1].status == true)
{
printf("Seats: %s\n", list);
printf("Enter a number from the lists: ");
flag = 1;
}
else
{
flag = 0;
}
} while (1 == flag); //本循环判断并处理用户的错误输入;
eatline();
printf("Enter first name:\n");
s_gets(pl[seat - 1].first, LEN);
printf("Enter last name:\n");
s_gets(pl[seat - 1].last, LEN);
printf("%s %s assigned to seat %d.\n", pl[seat - 1].first, pl[seat - 1].last, seat);
printf("Enter a to accept assignment, c to cancel it: ");
ch = get_first();
while (strchr("ac", ch) == NULL)
{
printf("Please enter a or c: ");
ch = get_first();
}
if (ch == 'a')
{
pl[seat - 1].status = true;
printf("Passenger assigned to seat.\n");
}
else if (ch == 'c')
{
printf("Passenger not assigned.\n");
}
}
}
void delete_seat(plane pl[], int n) //删除已分配的座位;
{
int ch, seat, flag;
char list[3 * SEATS];
if (openings(pl, n) == SEATS)
{
puts("All seats already are empty. Can't delete!");
}
else
{
show_seats(pl);
makelist(pl, list, true);
printf("Enter the number of the seat to be deleted: ");
do
{
while (scanf("%d", &seat) != 1)
{
eatline();
printf("Seats: %s\n", list);
printf("Enter a number from the lists:");
}
if (seat < 1 || seat > SEATS || pl[seat - 1].status == false)
{
printf("Seats: %s\n", list);
printf("Enter a number from this list:");
flag = 1;
}
else
{
flag = 0;
}
} while (1 == flag);
eatline();
printf("%s %s to be canceled for seat %d.\n", pl[seat - 1].first, pl[seat - 1].last, seat);
printf("Enter d to delete assignment, a to abort: ");
ch = get_first();
while (strchr("da", ch) == NULL)
{
printf("Please enter d or a: ");
ch = get_first();
}
if (ch == 'd')
{
pl[seat - 1].status = false;
puts("Passenger dropped.");
}
else if (ch == 'a')
{
puts("Passenger retained.");
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
int i, choice;
plane plane_seat[SEATS];
plane* ps[SEATS];
for (i = 0; i < SEATS; i++)
{
ps[i] = &plane_seat[i];
}
for (i = 0; i < SEATS; i++)
{
plane_seat[i].status = false;
plane_seat[i].seat_id = i + 1;
}
while ((choice = getmenu()) != 'f')
{
switch (choice)
{
case 'a':
{
printf("There are %d empty seats.\n", openings(plane_seat, SEATS));
break;
}
case 'b':
{
show_empty_seats(plane_seat, SEATS);
break;
}
case 'c':
{
list_assign(ps, SEATS);
break;
}
case 'd':
{
assign_seat(plane_seat, SEATS);
break;
}
case 'e':
{
delete_seat(plane_seat, SEATS);
break;
}
}
putchar('\n');
}
printf("Bye from Colossus Airlines!\n");
return 0;
}
9.巨人航空公司(编程练习 8)需要另一架飞机(容量相同),每天飞 4 班(航班 102、311、444 和519)。把程序扩展为可以处理4个航班。用一 个顶层菜单提供航班选择和退出。选择一个特定航班,就会出现和编程练习 8类似的菜单。但是该菜单要添加一个新选项:确认座位分配。而且,菜单 中的退出是返回顶层菜单。每次显示都要指明当前正在处理的航班号。另 外,座位分配显示要指明确认状态。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define LEN 14
#define SEATS 12
typedef struct
{
int seat_id;
bool status;
char last[LEN];
char first[LEN];
} plane;
int getmenu(int choice);
int get_first(void);
int openings(const plane pl[], int n);
void show_empty_seats(const plane pl[], int n);
void list_assign(plane *ps[], int n);
void assign_seat(plane pl[], int n);
void delete_seat(plane pl[], int n);
void show_seats(const plane pl[]);
void sort(plane *array[], int n);
void makelist(const plane pl[], char *str, int kind);
char *s_gets(char *st, int n);
void eatline(void);
void airline(int choice, plane *pl, plane *ps[]);
void init(plane *pl, plane *ps[]);
int show_airline_menu(void);
void confirm_seat(const plane pl[]);
int main(void)
{
int ch;
plane airline_102[SEATS];
plane airline_311[SEATS];
plane airline_444[SEATS];
plane airline_519[SEATS];
plane *ps_102[SEATS];
plane *ps_311[SEATS];
plane *ps_444[SEATS];
plane *ps_519[SEATS];
init(airline_102, ps_102);
init(airline_311, ps_311);
init(airline_444, ps_444);
init(airline_519, ps_519);
while ((ch = show_airline_menu()) != 'q')
{
putchar('\n');
switch (ch)
{
case 'a':
{
airline(ch, airline_102, ps_102);
break;
}
case 'b':
{
airline(ch, airline_311, ps_311);
break;
}
case 'c':
{
airline(ch, airline_444, ps_444);
break;
}
case 'd':
{
airline(ch, airline_519, ps_519);
break;
}
}
putchar('\n');
}
puts("Bye from Colossus Airlines!");
return 0;
}
void init(plane *pl, plane *ps[])
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < SEATS; i++)
{
ps[i] = &pl[i];
}
for (i = 0; i < SEATS; i++)
{
pl[i].status = false;
pl[i].seat_id = i + 1;
}
return;
}
int show_airline_menu(void)
{
int ch;
puts("There are some airlines for you to choose.");
puts("a) Airline 102.");
puts("b) Airline 311.");
puts("c) Airline 444.");
puts("d) Airline 519.");
puts("q) Quit the program.");
printf("Please you enter to choose: ");
ch = get_first();
while (strchr("abcdq", ch) == NULL)
{
printf("Please enter a, b, c, d or q: ");
ch = get_first();
}
return ch;
}
void airline(int choice, plane *pl, plane *ps[])
{
int ch;
while ((ch = getmenu(choice)) != 'f')
{
switch (ch)
{
case 'a':
{
printf("There are %d empty seats.\n", openings(pl, SEATS));
break;
}
case 'b':
{
show_empty_seats(pl, SEATS);
break;
}
case 'c':
{
list_assign(ps, SEATS);
break;
}
case 'd':
{
assign_seat(pl, SEATS);
break;
}
case 'e':
{
delete_seat(pl, SEATS);
break;
}
case 'g':
{
confirm_seat(pl);
break;
}
}
putchar('\n');
}
return;
}
int getmenu(int choice)
{
int ch;
if (choice == 'a')
{
printf("The airline 102 is being processed.\n");
}
else if (choice == 'b')
{
printf("The airline 311 is being processed.\n");
}
else if (choice == 'c')
{
printf("The airline 444 is being processed.\n");
}
else if (choice == 'd')
{
printf("The airline 519 is being processed.\n");
}
puts("To choose a function, enter its letter label:");
puts("a) Show number of empty seats");
puts("b) Show list of empty seats");
puts("c) Show alphabetical list of seat");
puts("d) Assign a customer to a seat");
puts("e) Delete a seat assignment");
puts("f) Quit");
puts("g) Confirm seat assignment");
printf("Please you enter to choose: ");
ch = get_first();
while (strchr("abcdefg", ch) == NULL)
{
printf("Please enter a, b, c, d, e, f or g: ");
ch = get_first();
}
return ch;
}
int get_first(void) //获取输入的第一个字符,丢弃剩余字符;
{
int ch;
do
{
ch = tolower(getchar());
} while (isspace(ch));
eatline();
return ch;
}
int openings(const plane pl[], int n) //显示空座位的数量;
{
int seat;
int count = 0;
for (seat = 0; seat < n; seat++)
{
if (pl[seat].status == false)
{
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
void list_assign(plane *ps[], int n) //显示按照字母序列排序后的座位表;
{
int i;
if (openings(*ps, n) == SEATS)
{
puts("All seats are empty.");
}
else
{
sort(ps, n);
for (i = 0; i < SEATS; i++)
{
if (ps[i]->status == true)
{
printf("Seat %d: %s, %s\n", ps[i]->seat_id, ps[i]->last, ps[i]->first);
}
}
}
return;
}
void show_seats(const plane pl[]) //显示已分配的座位;
{
int i;
puts("Seats currently taken:");
for (i = 0; i < SEATS; i++)
{
if (pl[i].status == true)
{
printf("Seat %d: %s, %s\n", pl[i].seat_id, pl[i].last, pl[i].first);
}
}
return;
}
void confirm_seat(const plane pl[]) //确认座位分配;
{
int i;
puts("Seats assignment lists:");
for (i = 0; i < SEATS; i++)
{
if (pl[i].status == true)
{
printf("Seat %-2d: assigned.\n", pl[i].seat_id);
}
else
{
printf("Seat %-2d: unassigned.\n", pl[i].seat_id);
}
}
return;
}
void sort(plane *array[], int n) //按照ASCII码进行座位排序;
{
int i, j;
plane *temp;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (strcmp(array[j]->last, array[i]->last) < 0)
{
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[i];
array[i] = temp;
}
}
}
return;
}
char *s_gets(char *st, int n)
{
char *ret_val;
char *find;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
{
*find = '\0';
}
else
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
}
return ret_val;
}
void eatline(void)
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
return;
}
void show_empty_seats(const plane pl[], int n) //显示空座位的信息;
{
char seating[3 * SEATS];
if (openings(pl, n) == 0)
{
puts("All seats are assigned");
}
else
{
makelist(pl, seating, false);
printf("The following seats are available: ");
puts(seating);
}
return;
}
void makelist(const plane pl[], char *str, int kind) //为分配和删除座位提供当前处理的座位数;
{
int seat;
char temp[LEN];
*str = '\0'; //清空str中的内容;
for (seat = 0; seat < SEATS; seat++)
{
if (pl[seat].status == kind)
{
sprintf(temp, "%d ", pl[seat].seat_id);
strcat(str, temp);
}
}
return;
}
void assign_seat(plane pl[], int n) //分配空余座位;
{
int ch, seat, flag;
char list[3 * SEATS];
if (openings(pl, n) == false)
{
puts("All seats are assigned. Can't assign again!");
}
else
{
makelist(pl, list, false);
printf("Available seats: %s\n", list);
printf("Which seat do you want? Please you enter from the lists: ");
do
{
while (scanf("%d", &seat) != 1)
{
eatline();
printf("Seats: %s\n", list);
printf("Enter a number from the lists: ");
}
if (seat < 1 || seat > SEATS || pl[seat - 1].status == true)
{
printf("Seats: %s\n", list);
printf("Enter a number from the lists: ");
flag = 1;
}
else
{
flag = 0;
}
} while (1 == flag); //本循环判断并处理用户的错误输入;
eatline();
puts("Enter first name:");
s_gets(pl[seat - 1].first, LEN);
puts("Enter last name:");
s_gets(pl[seat - 1].last, LEN);
printf("%s %s assigned to seat %d.\n", pl[seat - 1].first, pl[seat - 1].last, seat);
printf("Enter a to accept assignment, c to cancel it: ");
ch = get_first();
while (strchr("ac", ch) == NULL)
{
printf("Please enter a or c: ");
ch = get_first();
}
if (ch == 'a')
{
pl[seat - 1].status = true;
puts("Passenger assigned to seat.");
}
else if (ch == 'c')
{
puts("Passenger not assigned.");
}
}
return;
}
void delete_seat(plane pl[], int n) //删除已分配的座位;
{
int ch, seat, flag;
char list[3 * SEATS];
if (openings(pl, n) == SEATS)
{
puts("All seats already are empty. Can't delete!");
}
else
{
show_seats(pl);
makelist(pl, list, true);
printf("Enter the number of the seat to be deleted: ");
do
{
while (scanf("%d", &seat) != 1)
{
eatline();
printf("Seats: %s\n", list);
printf("Enter a number from the lists:");
}
if (seat < 1 || seat > SEATS || pl[seat - 1].status == false)
{
printf("Seats: %s\n", list);
printf("Enter a number from this list:");
flag = 1;
}
else
{
flag = 0;
}
} while (1 == flag);
eatline();
printf("%s %s to be canceled for seat %d.\n", pl[seat - 1].first, pl[seat - 1].last, seat);
printf("Enter d to delete assignment, a to abort: ");
ch = get_first();
while (strchr("da", ch) == NULL)
{
printf("Please enter d or a: ");
ch = get_first();
}
if (ch == 'd')
{
pl[seat - 1].status = false;
puts("Passenger dropped.");
}
else if (ch == 'a')
{
puts("Passenger retained.");
}
}
return;
}
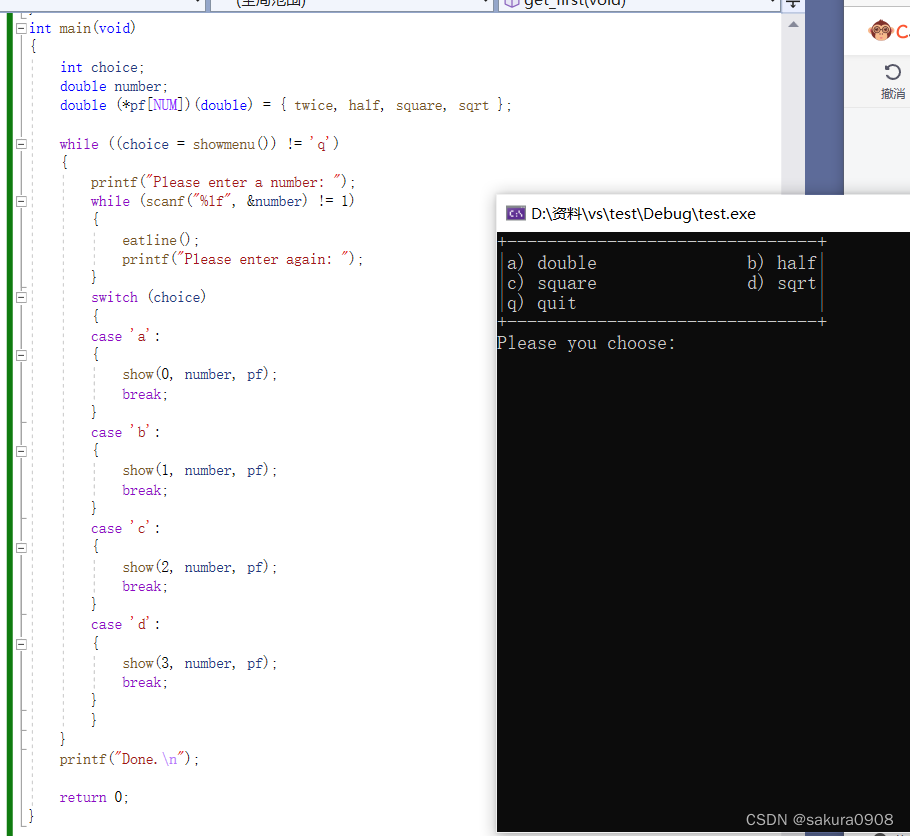
10.编写一个程序,通过一个函数指针数组实现菜单。例如,选择菜单 中的 a,将激活由该数组第 1个元素指向的函数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#define NUM 4
void eatline(void)
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
int get_first(void)
{
int ch;
do
{
ch = tolower(getchar());
} while (isspace(ch));
eatline();
return ch;
}
int showmenu(void)
{
int ch;
printf("+-------------------------------+\n");
printf("|a) double b) half|\n");
printf("|c) square d) sqrt|\n");
printf("|q) quit |\n");
printf("+-------------------------------+\n");
printf("Please you choose: ");
while (ch = get_first(), NULL == strchr("abcdq", ch))
{
printf("Please enter a, b, c, d or q: ");
}
return ch;
}
double twice(double x)
{
return 2.0 * x;
}
double half(double x)
{
return x / 2.0;
}
double square(double x)
{
return x * x;
}
void show(int i, double x, double (*pf[NUM])(double))
{
x = (*pf[i])(x);
printf("After operating: %g\n\n", x);
}
int main(void)
{
int choice;
double number;
double (*pf[NUM])(double) = { twice, half, square, sqrt };
while ((choice = showmenu()) != 'q')
{
printf("Please enter a number: ");
while (scanf("%lf", &number) != 1)
{
eatline();
printf("Please enter again: ");
}
switch (choice)
{
case 'a':
{
show(0, number, pf);
break;
}
case 'b':
{
show(1, number, pf);
break;
}
case 'c':
{
show(2, number, pf);
break;
}
case 'd':
{
show(3, number, pf);
break;
}
}
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
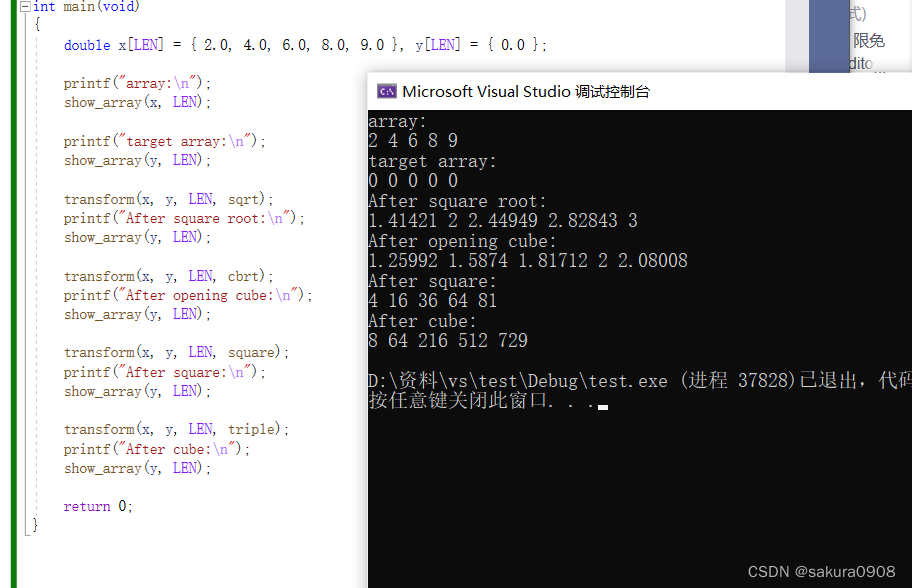
11.编写一个名为transform()的函数,接受4个参数:内含double类型数据 的源数组名、内含double类型数据的目标数组名、一个表示数组元素个数的 int类型参数、函数名(或等价的函数指针)。transform()函数应把指定函数 应用于源数组中的每个元素,并把返回值储存在目标数组中。例如:
transform(source, target, 100, sin);
该声明会把target[0]设置为sin(source[0]),等等,共有100个元素。在一 个程序中调用transform()4次,以测试该函数。分别使用math.h函数库中的两 个函数以及自定义的两个函数作为参数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define LEN 5
double square(double x)
{
return x * x;
}
double triple(double x)
{
return x * x * x;
}
void transform(double x[], double y[], int n, double (*p)(double))
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
y[i] = p(x[i]);
}
}
void show_array(double temp[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%g ", temp[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(void)
{
double x[LEN] = { 2.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0, 9.0 }, y[LEN] = { 0.0 };
printf("array:\n");
show_array(x, LEN);
printf("target array:\n");
show_array(y, LEN);
transform(x, y, LEN, sqrt);
printf("After square root:\n");
show_array(y, LEN);
transform(x, y, LEN, cbrt);
printf("After opening cube:\n");
show_array(y, LEN);
transform(x, y, LEN, square);
printf("After square:\n");
show_array(y, LEN);
transform(x, y, LEN, triple);
printf("After cube:\n");
show_array(y, LEN);
return 0;
}
![[深度学习]yolov7 pytorch模型转onnx,转ncnn模型和mnn模型使用细节](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fd2628d6ecbf45eca14ed7c0d096c7e3.png#pic_center)