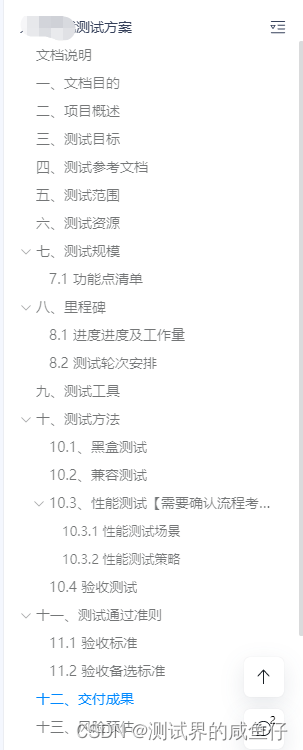
一、前言
Java8 新特性之一,其实现了Future<T>, CompletionStage<T>两接口,后者是对前者的一个扩展,增加了异步回调、流式处理、多个Future组合处理的能力,使 Java 在处理多任务的协同工作时更加顺畅便利。
二、CompletableFuture的使用方法
2.1创建异步任务
2.1.1 runAsync:创建没有返回值的异步任务
// 不带返回值的异步请求,默认线程池:ForkJoinPool
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
// 不带返回值的异步请求,可以自定义线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)示例1:
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("主线程-------------");
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
【执行结果】:
主线程-------------
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main
异步执行,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9示例2:
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("主线程-------------");
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,使用自定义线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}, ThreadPoolFactory.getExecutor());
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
【执行结果】:
主线程-------------
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main
异步执行,使用自定义线程池,当前线程名称:自定义ThreadPool_-1-thread-12.1.2 supplyAsync:创建有返回值的异步任务
// 带返回值异步请求,默认线程池:ForkJoinPool
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
// 带返回值的异步请求,可以自定义线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
示例1:
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("主线程-------------");
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "OK";
});
try {
System.out.println(future.get());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
【返回结果】:
主线程-------------
异步执行,有返回值,使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
OK
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main示例2:
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("主线程-------------");
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "OK";
}, ThreadPoolFactory.getExecutor());
try {
System.out.println(future.get());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
【执行结果】:
主线程-------------
异步执行,有返回值,使用线程池,当前线程名称:自定义ThreadPool_-1-thread-1
OK
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main【注】:在获取返回结果时,可以使用 get() 或者 fork()。区别在于:get() 方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException, 需要用户手动处理;join() 方法抛出的是uncheck异常(即未经检查的异常),不会强制开发者抛出。
2.2任务异步回调
2.2.1 thenRun / thenRunAsync
第一个任务执行完,执行回调,做第二个任务,不关心第一个任务的返回值,无入参,无返回值。
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("主线程-------------");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture future2 = future.thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println("future2 thenRun ……,当前线程名称:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
CompletableFuture future3 = future.thenRunAsync(()->{
System.out.println("future3 thenRun ……,当前线程名称:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
【执行结果】:
主线程-------------
异步执行,有返回值,使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
future2 thenRun ……,当前线程名称:main
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main
future3 thenRun ……,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9【注】调用thenRunAsync 方法执行任务时,子任务与父任务使用同一个线程,而thenRun不是。
2.2.2 thenAccept / thenAcceptAsync
第一个任务执行完成后,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,但是回调方法是没有返回值的。
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("主线程-------------");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture future4 = future.thenAccept((result)->{
result += 1;
System.out.println("future4 result最终的值为:" + result + "当前线程名称:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
CompletableFuture future5 = future.thenAcceptAsync((result) -> {
result += 2;
System.out.println("future5 result最终的值为:" + result + "当前线程名称:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
【执行结果】:
主线程-------------
异步执行,有返回值,使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
future4 result最终的值为:2当前线程名称:main
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main
future5 result最终的值为:3当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-92.2.3 thenApply / thenApplyAsync
第一个任务执行完成后,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,并且回调方法是有返回值的。
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("主线程-------------");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture future6 = future.thenApply((result)->{
result += 1;
System.out.println("future4 result最终的值为:" + result + "当前线程名称:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
return result;
});
CompletableFuture future7 = future.thenApplyAsync((result) -> {
result += 2;
System.out.println("future5 result最终的值为:" + result + "当前线程名称:"+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
return result;
});
System.out.println("future6 返回结果:" + future6.get());
System.out.println("future7 返回结果:" + future7.get());
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
【执行结果】:
主线程-------------
异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
future4 result最终的值为:2当前线程名称:main
future6 返回结果:2
future5 result最终的值为:3当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
future7 返回结果:3
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main2.2.4 exceptionally
第一个任务执行异常时,执行回调方法;将抛出异常作为参数,传递到回调方法。
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("主线程-------------");
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// return 1;
throw new RuntimeException();
});
CompletableFuture<String> future8 = future.exceptionally((e)->{
e.printStackTrace();
return "程序异常";
});
System.out.println("future8 返回结果:" + future8.get());
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
【执行结果】:
主线程-------------
异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
future8 返回结果:程序异常
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main
java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.RuntimeException
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.encodeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:273)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.completeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:280)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.exec(CompletableFuture.java:1582)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask.doExec(ForkJoinTask.java:289)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool$WorkQueue.runTask(ForkJoinPool.java:1056)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.runWorker(ForkJoinPool.java:1692)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinWorkerThread.run(ForkJoinWorkerThread.java:157)
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException
at com.zy.service.completable.CompletableFutureTest.lambda$main$0(CompletableFutureTest.java:16)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.run(CompletableFuture.java:1590)
... 5 more
2.2.5 whenComplete
第一个任务执行完,执行的回调方法,whenComplete方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是上个任务的结果。
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("主线程-------------");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future9 = future.whenComplete((result, e) -> {
result += 100;
System.out.println(result);
});
System.out.println("future9 结果:" + future9.get());
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
【执行结果】:
主线程-------------
异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
101
future9 结果:1
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main2.2.6 handle
第一个任务执行完,执行的回调方法,有返回值,handle方法返回的CompletableFuture 的 result是回调方法执行的结果。
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("主线程-------------");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future10 = future.handle((result, e) -> {
result += 100;
System.out.println(result);
return result;
});
System.out.println("future10 结果:" + future10.get());
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
【执行结果】:
主线程-------------
异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
101
future10 结果:101
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main2.3 多个任务组合处理
2.3.1 thenCombine / runAfterBoth / thenAcceptBoth
都表示两个 CompletableFuture 执行完,才执行的方法,区别在于:
thenCombine:会将两个 CompletableFuture 任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值
thenAcceptBoth: 会将两个 CompletableFuture 任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值
runAfterBoth 不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值。
另外:thenCombineAsync / runAfterBothAsync / thenAcceptBothAsync 相较于 thenCombine / runAfterBoth / thenAcceptBoth 的区别就是异步执行第三个 CompletableFuture。
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 2;
});
//有入参,有返回值
CompletableFuture<String> future3 = future1.thenCombine(future2, (s1, s2) -> {
System.out.println("thenCombine,s1=" + s1 + ",s2=" + s2 + ",当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "thenCombine";
});
//无入参,无返回值
CompletableFuture future4 = future1.runAfterBoth(future2, () -> {
System.out.println("runAfterBoth,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
//有入参,无返回值
CompletableFuture future5 = future1.thenAcceptBoth(future2, (s1, s2) -> {
System.out.println("thenAcceptBoth,s1=" + s1 + ",s2=" + s2 + ",当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
【执行结果】:
异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2
thenCombine,s1=1,s2=2,当前线程名称:main
runAfterBoth,当前线程名称:main
thenAcceptBoth,s1=1,s2=2,当前线程名称:main
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main
2.3.2 applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither
都表示:将两个 CompletableFuture 组合起来,只要其中一个执行完了,就执行第三个CompletableFuture。
区别在于:
applyToEither:会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值
acceptEither: 会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值
runAfterEither:不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值。
另外:applyToEitherAsync / acceptEitherAsync / runAfterEitherAsync 相较于 applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither 的区别就是异步执行第三个 CompletableFuture。
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 2;
});
//有入参,有返回值
CompletableFuture<String> future3 = future1.applyToEither(future2, (s1) -> {
System.out.println("applyToEither,s1=" + s1 + ",当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "thenCombine";
});
//无入参,无返回值
CompletableFuture future4 = future1.runAfterEither(future2, () -> {
System.out.println("runAfterEither,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
//有入参,无返回值
CompletableFuture future5 = future1.acceptEither(future2, (s1) -> {
System.out.println("acceptEither,s1=" + s1 + ",当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}2.3.3 allOf
所有任务都执行完成后,才执行 allOf 返回的 CompletableFuture。如果任意一个任务异常,allOf 的CompletableFuture,执行get方法,会抛出异常。
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("future1 -- 异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("future2 -- 异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 2;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2).whenComplete((s1, s2) -> {
System.out.println("future1, future2 执行完,才执行该处。");
});
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
【执行结果】:
future1 -- 异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
future2 -- 异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2
future1, future2 执行完,才执行该处。
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main2.3.4 anyOf
任意一个任务执行完,就执行 anyOf 返回的 CompletableFuture。如果最快完成的任务出现了异常,也会先返回异常,如果害怕出错可以加个 exceptionally() 去处理一下可能发生的异常并设定默认返回值。
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("future1 -- 异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// return 1;
try {
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("future2 -- 异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 2;
});
CompletableFuture<Object> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2).whenComplete((s1, s2) -> {
System.out.println("future1, future2 执行完,才执行该处。");
}).exceptionally(e -> {
System.out.println("异常:" + e);
return -1;
});
System.out.println("主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
【执行结果】:
future1 -- 异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
future2 -- 异步执行,有返回值,未使用线程池,当前线程名称:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2
future1, future2 执行完,才执行该处
异常:java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.RuntimeException: java.lang.Exception
主线程执行完毕,当前线程名称:main