文章目录
- 一、CRUD
- 二、Create
- 1.插入基本语法
- 2.单行数据+全列插入
- 3.多行数据+指定列插入
- 4.插入时如果冲突则更新旧值
- 5.插入时如果冲突则替换
- 三、Retrieve
- 1.查找基本语法
- 2.全列查询
- 2.指定列查询
- 3.查询字段为表达式
- 4.为查询结果指定别名
- 5.查询结果去重
- 6.where条件
- 7.结果排序
- 8.将查找结果分页显示
- 9.插入查询结果
- 四、Update
- 1.修改基本语法
- 2.修改示例
- 五、Delete
- 1.删除基本语法
- 2.删除示例
- 3.截断表
一、CRUD
CRUD是增删查改的简称,C代表“Create”,即创建,也就是增加的意思;R代表“Retrieve”,即读取,也就是查找的意思;U代表“Update”,即更新,也就是修改的意思;D代表“Delete”,即删除。使用MySQL数据库,主要是对表中的数据进行一系列的增删查改,本篇文章将介绍MySQL对表数据的增删查改方法。
二、Create
1.插入基本语法
MySQL中向表插入数据使用的是insert指令,基本语法如下:
insert [into] 表名 [(列名 [,列名, ...])] values (value_list [,(value_list), ...]);
我们创建一张学生表,演示一下表的插入语法:
mysql> create table students (
-> id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
-> sn int not null unique comment '学号',
-> name varchar(20) not null,
-> qq varchar(20)
-> );
2.单行数据+全列插入
如果我们想插入单行数据,在values后面只需要带一行数据内容即可。如果我们想全列插入,在values前面可以不需要带列名。
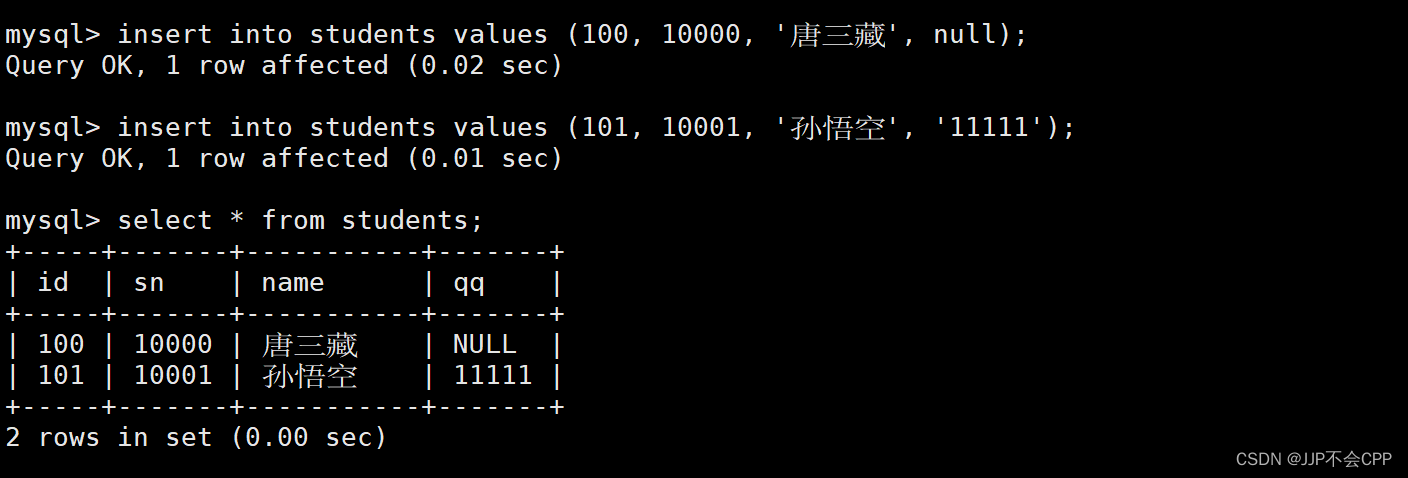
mysql> insert into students values (100, 10000, '唐三藏', null);
mysql> insert into students values (101, 10001, '孙悟空', '11111');
3.多行数据+指定列插入
我们可以一条语句插入多行数据,只需要在values后面加上多行数据内容即可。我们也可以不采用全列插入,而是采用指定列插入,这就需要在values前面指定需要插入的列名了。
mysql> insert into students (id, sn, name) values (102, 20001, '曹孟德'), (103, 20002, '孙仲谋');
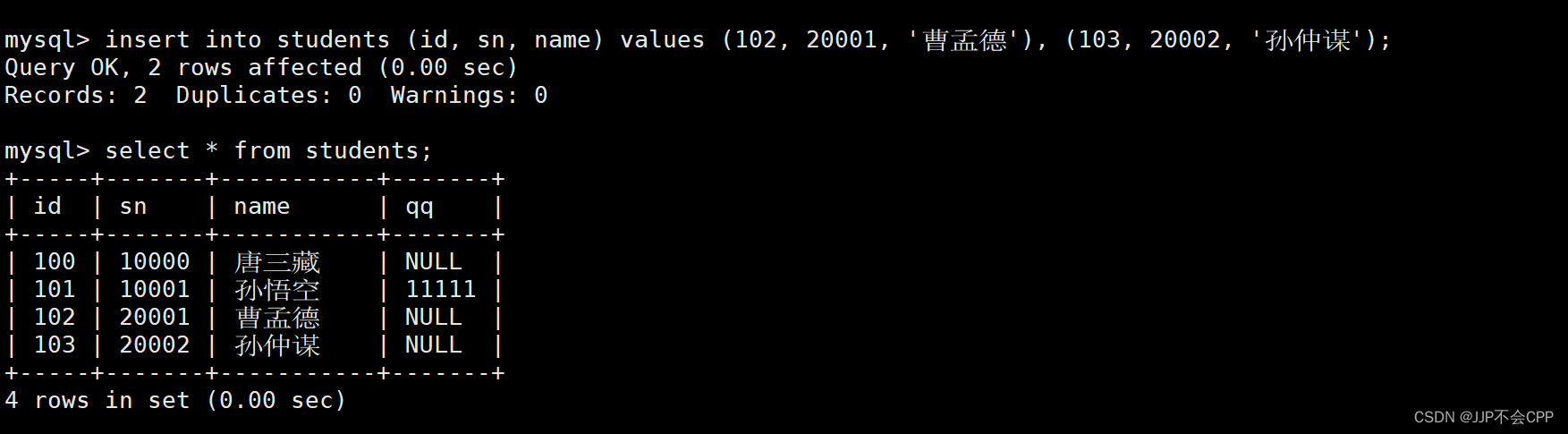
4.插入时如果冲突则更新旧值
由于表中有主键和唯一键,我们在插入数据的时候有可能会出现主键冲突或者唯一键冲突,即如果插入的主键值或者唯一键值已经存在,就会插入失败。但如果我们就想在发生冲突之后,将冲突的旧值更新之后再插入,就可以使用下面的语法:
insert ... on duplicate key update 列名=新值 [, 列名=新值, ...];
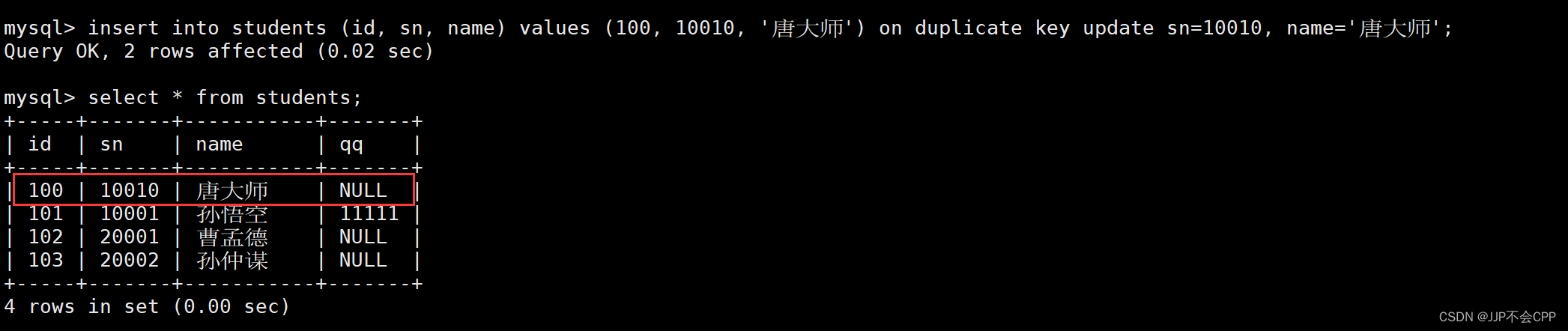
例如当前表中已经有了id值为100的数据,如果我们再插入一条id值为100的数据,但是不希望插入失败,而是希望发生冲突时更新旧值。
mysql> insert into students (id, sn, name) values (100, 10010, '唐大师') on duplicate key update sn=10010, name='唐大师';
5.插入时如果冲突则替换
除了上述的冲突时更新旧值方案,还可以采用替换方案。即如果插入时不会发生主键或者唯一键冲突,那么就正常插入。否则,就将冲突的旧值先删除,然后再插入新的值。此时需要使用到的插入语句是replace指令,基本语法如下:
replace into 表名 (列名) values (value_list);
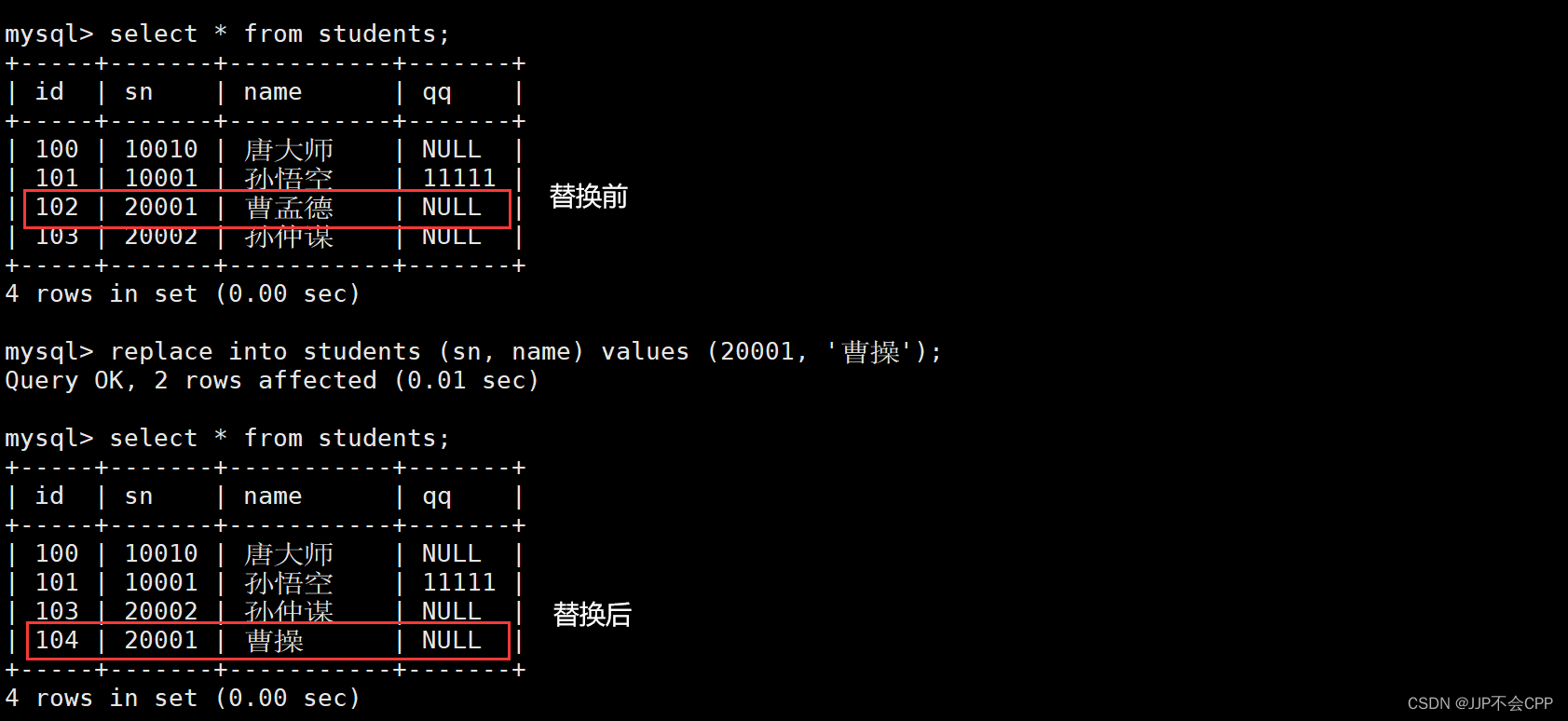
例如现在表中存在了sn为20001的值,如果我们再插入一个20001的值,希望将冲突的旧值替换成新插入的值。
mysql> replace into students (sn, name) values (20001, '曹操');
三、Retrieve
1.查找基本语法
MySQL中查找表中的数据使用的是select指令,基本语法如下:
select [distinct] {* | {列名 [, 列名, ...]}} [from 表名] [where ...] [order by ...] limit...
我们创建一张新的表,表名为exam_result,模拟记录学生的考试成绩,演示一下表的查找操作:
mysql> create table exam_result (
-> id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20) not null comment '同学姓名',
-> chinese float default 0.0 comment '语文成绩',
-> math float default 0.0 comment '数学成绩',
-> english float default 0.0 comment '英语成绩'
-> );
mysql> insert into exam_result (name, chinese, math, english) values
-> ('唐三藏', 67, 98, 56),
-> ('孙悟空', 87, 78, 77),
-> ('猪悟能', 88, 98, 90),
-> ('曹孟德', 82, 84, 67),
-> ('刘玄德', 55, 85, 45),
-> ('孙权', 70, 73, 78),
-> ('宋公明', 75, 65, 30);
2.全列查询
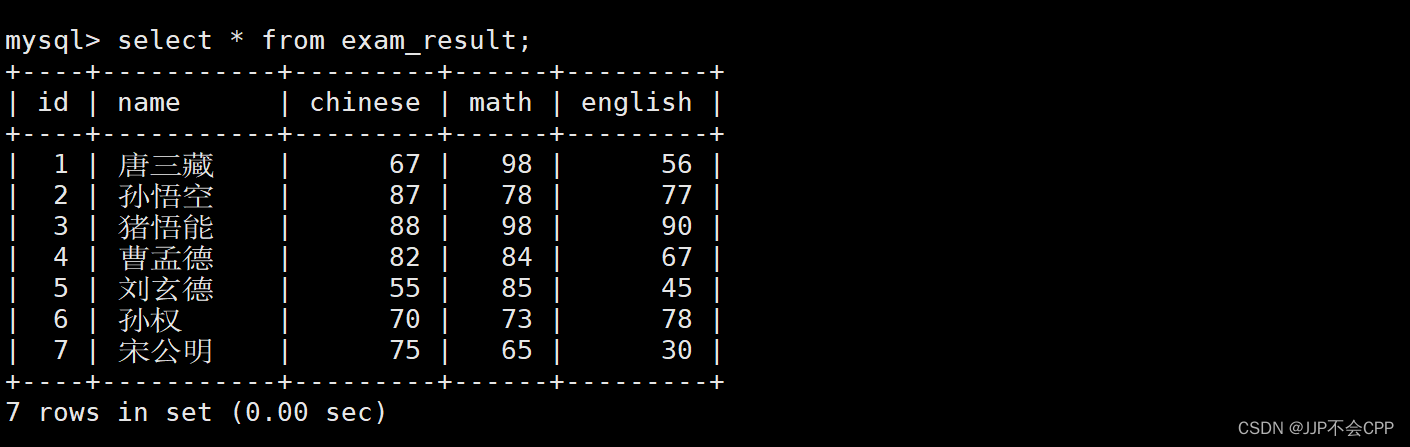
我们可以用如下语句进行全列查询:
mysql> select * from exam_result;
2.指定列查询
我们也可以指定列查询,select后面跟的其实是列名,如果我们指定了若干列就是进行指定列查询,如果是 * 则代表全列查询。
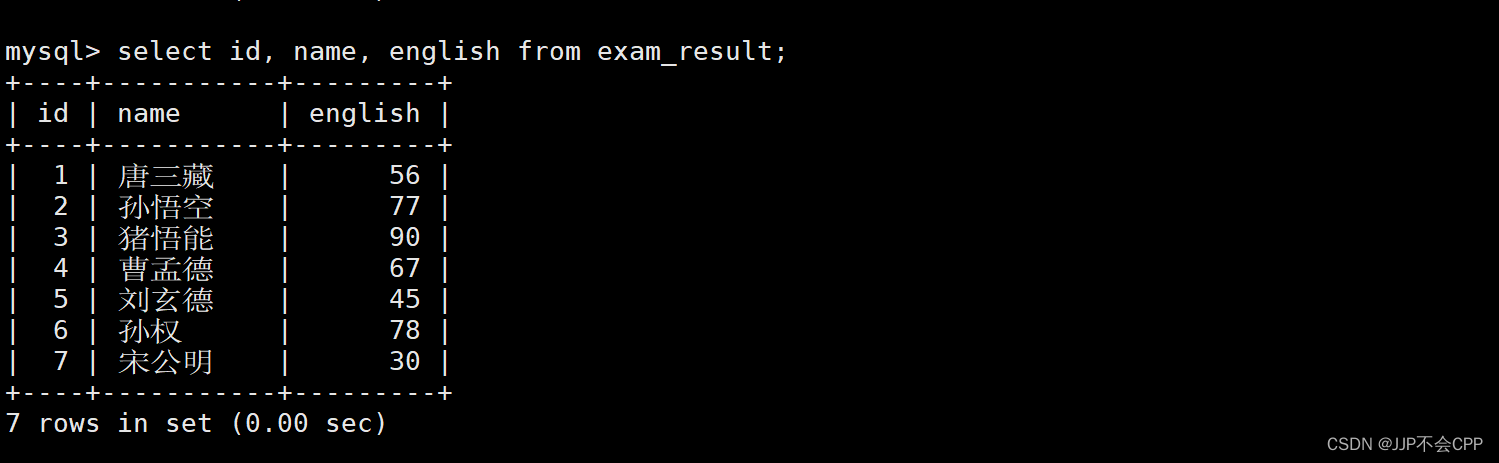
例如我们想要查询id列、name列、english列,输入以下指令:
mysql> select id, name, english from exam_result;
3.查询字段为表达式
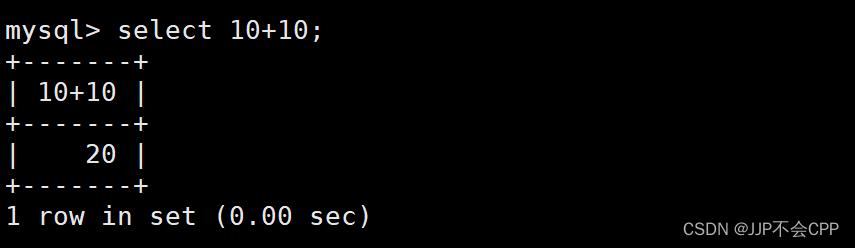
其实select的功能是比较多的,比如我们可以直接select后面接一个表达式,就可以得到表达式的结果:
mysql> select 10+10;
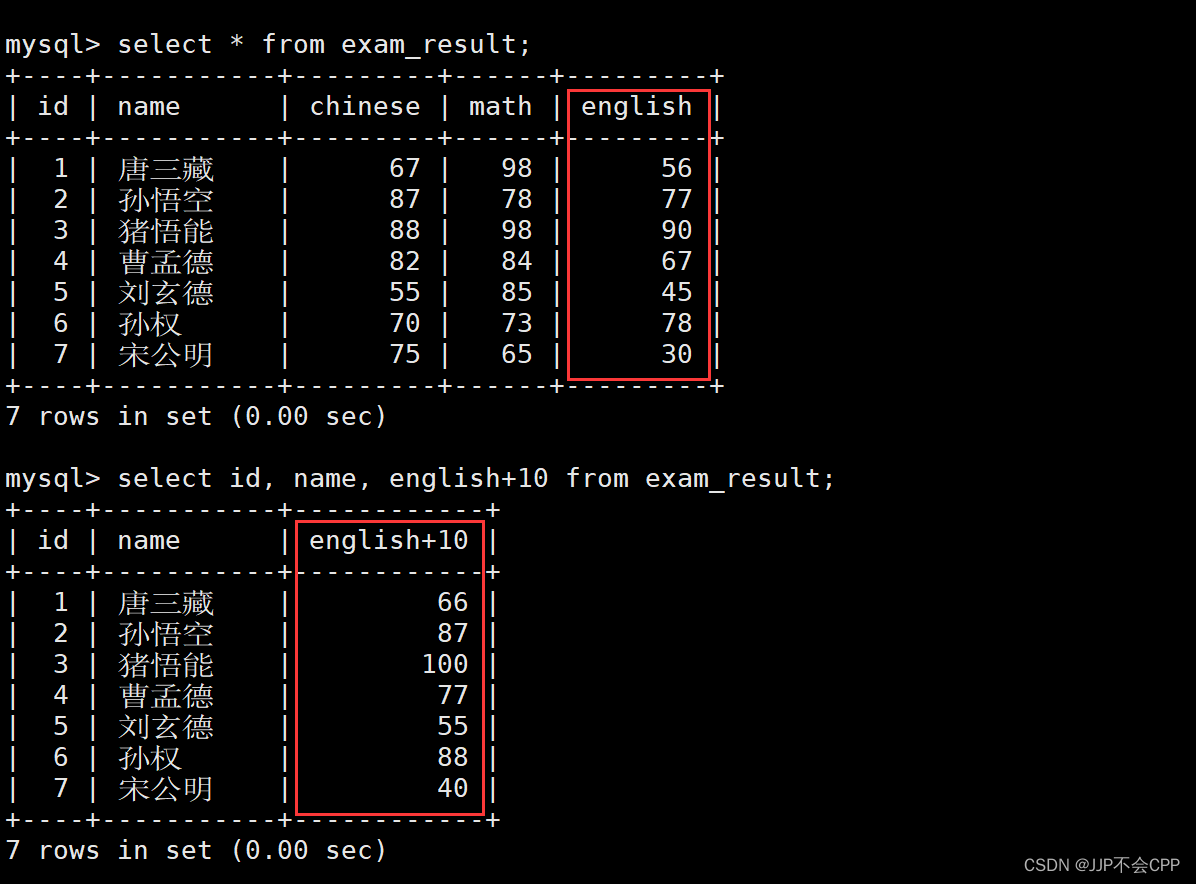
在用select查询表中数据时,也可以将列名换成表达式,例如我们想查询所有人的英语成绩加10分之后的结果,输入以下指令:
mysql> select id, name, english+10 from exam_result;
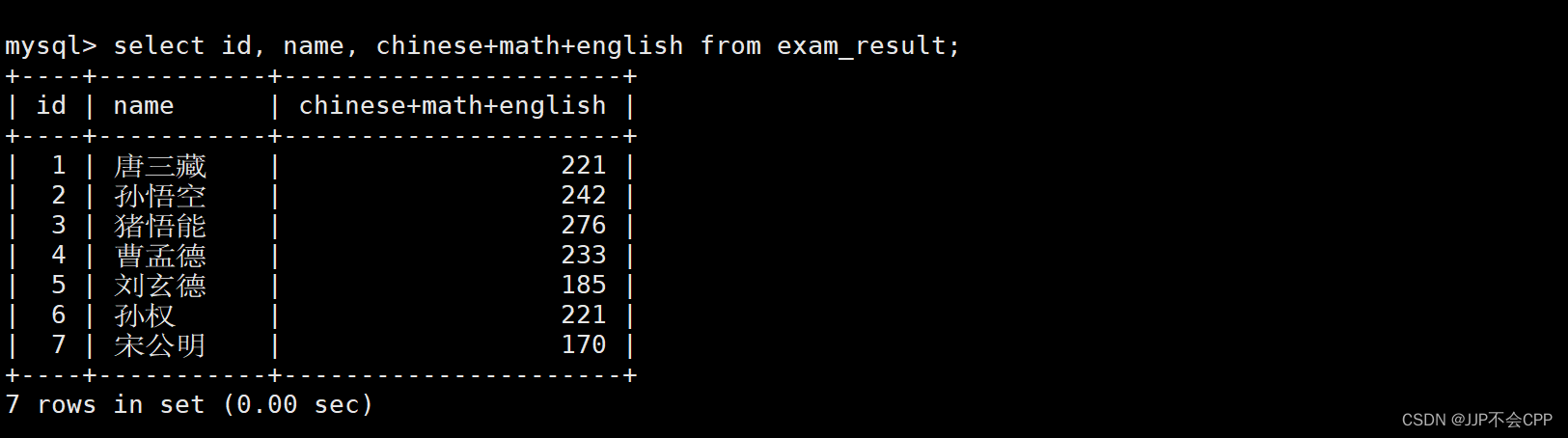
如果我们想查询所有同学的语文、数学、英语三个科目的总分,并需要显示对应的id和name,可以输入以下指令:
mysql> select id, name, chinese+math+english from exam_result;
4.为查询结果指定别名
我们可以为查询到的结果的列名取一个别名,基本语法如下:
select 列名 [as] 别名 [...] from 表名;
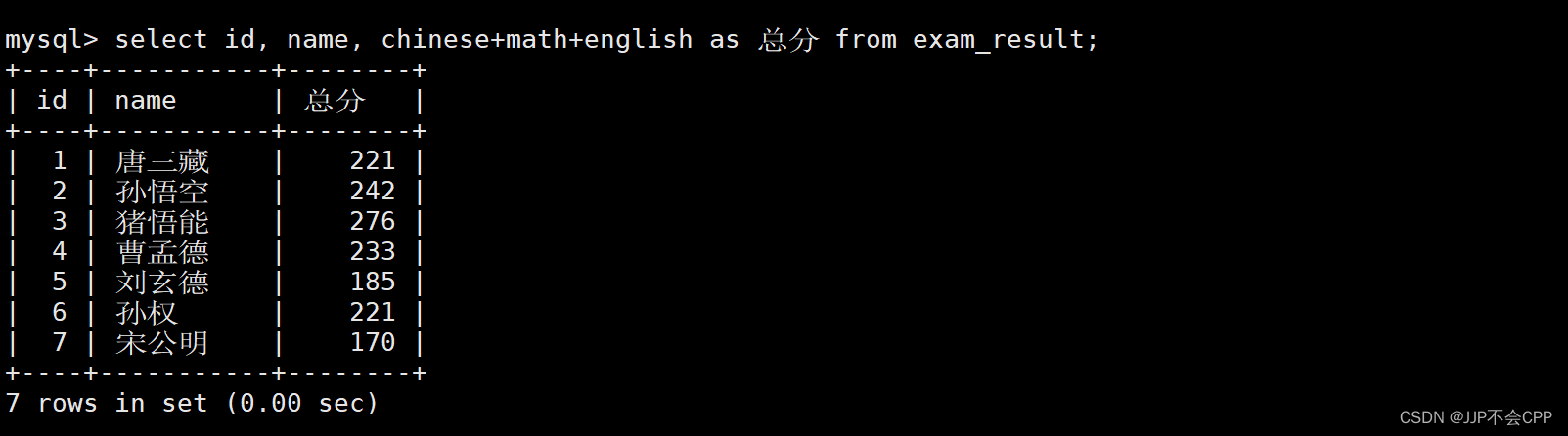
比如,我们上面查询了语文、数学、英语三个科目的总成绩,我们查出来的结果的列名是“chinese+math+english”,我们可以将其改成“总分”。
mysql> select id, name, chinese+math+english as 总分 from exam_result;
5.查询结果去重
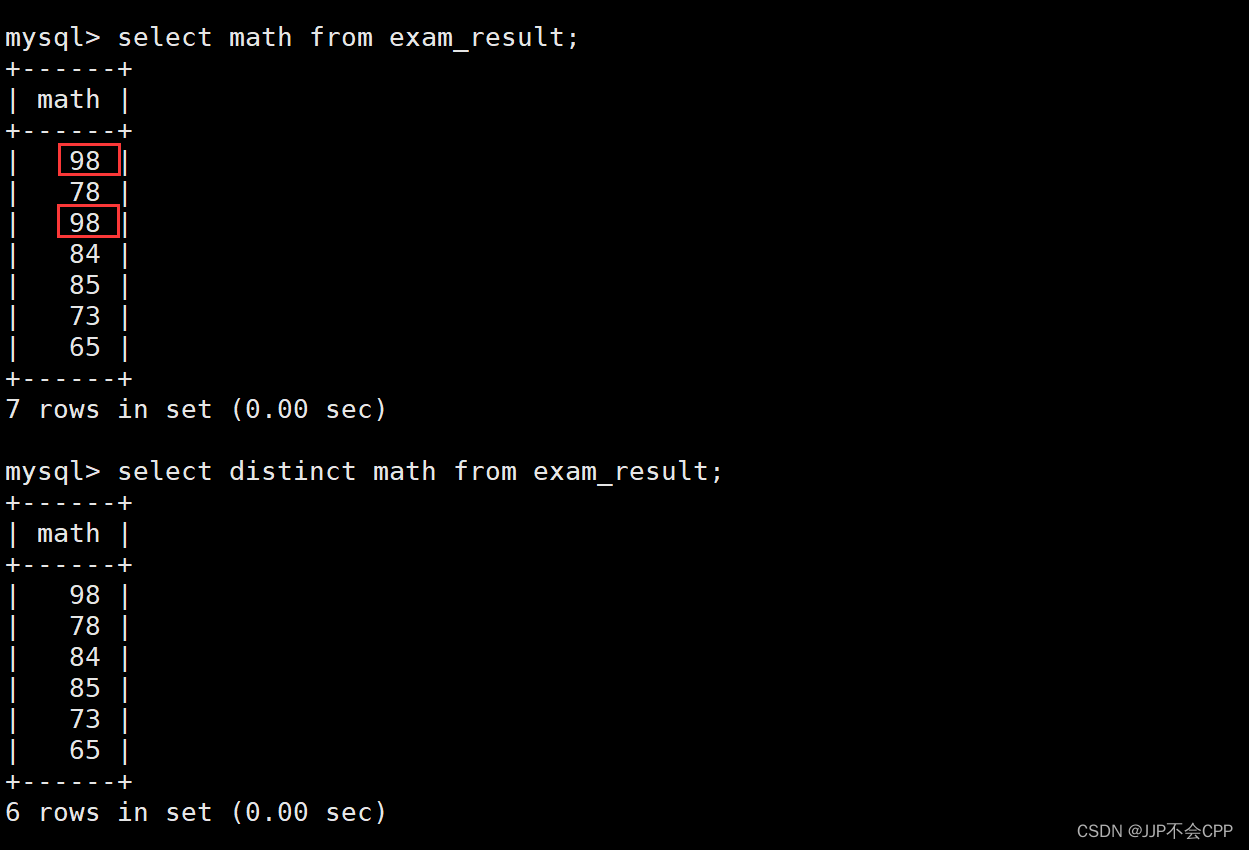
select语句支持将查询结果去重,只需要在select后面加上distinct即可。例如我们查询数学成绩时发现数学成绩有重复的数据,如果我们不想要这些重复的数据,可以使用以下指令:
mysql> select distinct math from exam_result;
6.where条件
我们在使用select指令对表中的数据进行查询时,可以指定查询的限定条件,比如我们想要查询所有同学中数学成绩及格的同学,这就是给查询加上了限制条件。
比较运算符:
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| >, >=, <, <= | 大于,大于等于,小于,小于等于 |
| = | 等于,null不安全,例如null = null的结果是null |
| <=> | 等于,null安全,例如null <=> null的结果是true |
| !=, <> | 不等于 |
| between a1 and a2 | 范围匹配,[a1, a2],如果a1 <= value <=a2,则返回true |
| in(option, …) | 如果是option中的任意一个,则返回true |
| is null | 是null |
| is not null | 不是null |
| like | 模糊匹配。%表示任意多个(包括0个)任意字符,_表示任意一个字符 |
逻辑运算符:
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| and | 多个条件必须都为true,结果才是true |
| or | 任意一个条件为true,结果都为true |
| not | 条件为true时,结果为false |
下面我们通过具体的例子来演示各种运算符的使用,使用的表依然是我们一开始就创建好的exam_result表,只对表中数据进行查找操作:
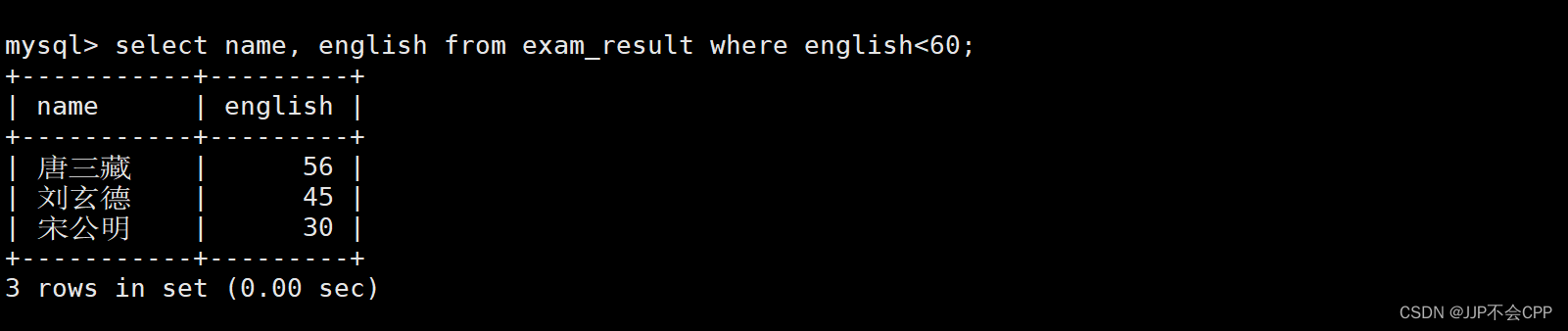
1. 查找出英语不及格的同学,并且显示学生姓名以及对应的英语成绩:
mysql> select name, english from exam_result where english<60;
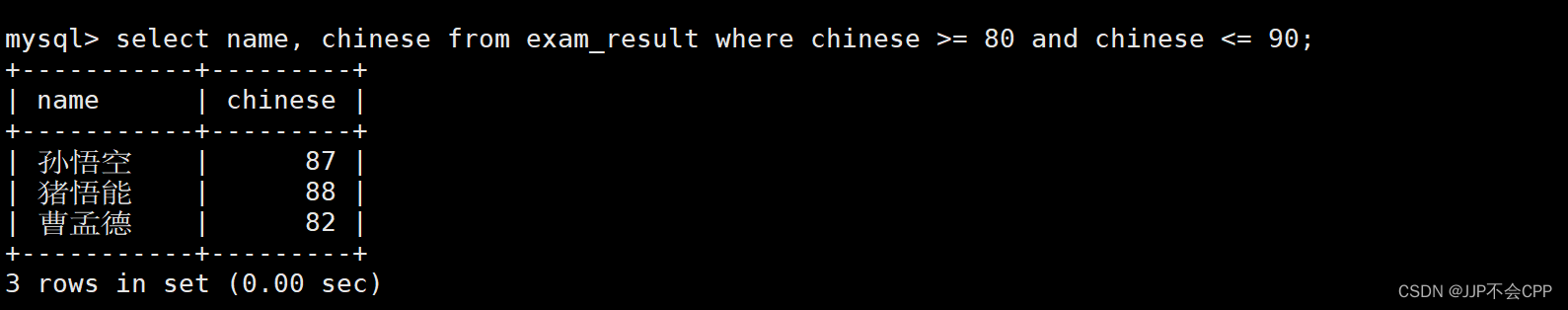
2. 查找出语文成绩在[80, 90]分的同学,并且显示学生姓名以及对应的语文成绩:
这里可以用两种方法来完成,第一种是使用and运算符来连接:
mysql> select name, chinese from exam_result where chinese >= 80 and chinese <= 90;
第二种是使用between and运算符:
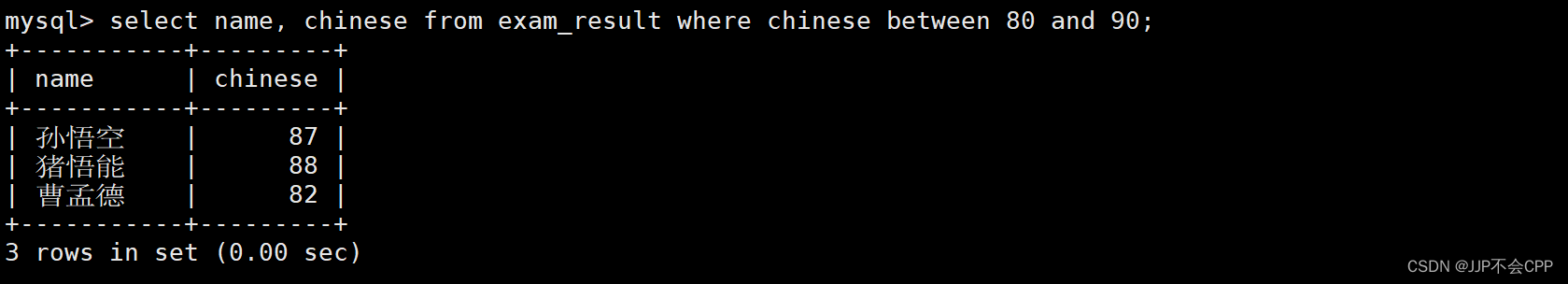
mysql> select name, chinese from exam_result where chinese between 80 and 90;
3. 查找数学成绩是58或59或98或99的同学,并且显示学生姓名以及对应的数学成绩:
这里也可以用两种方法来完成,第一种是使用or运算符来连接:
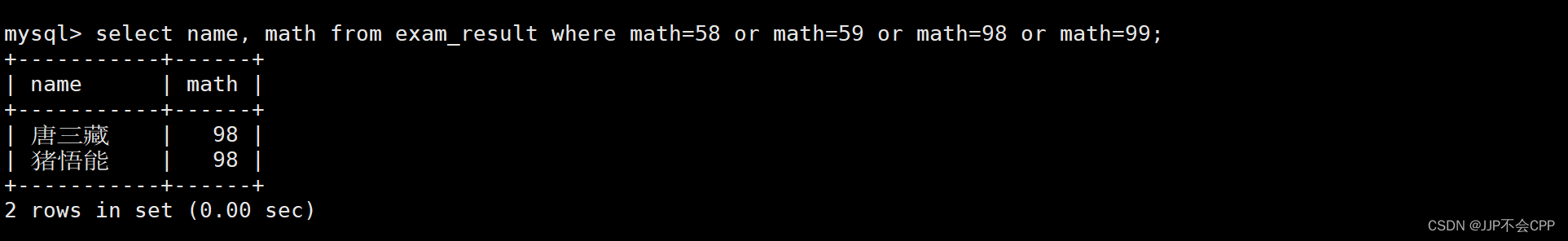
mysql> select name, math from exam_result where math=58 or math=59 or math=98 or math=99;
第二种方法是使用in语句:
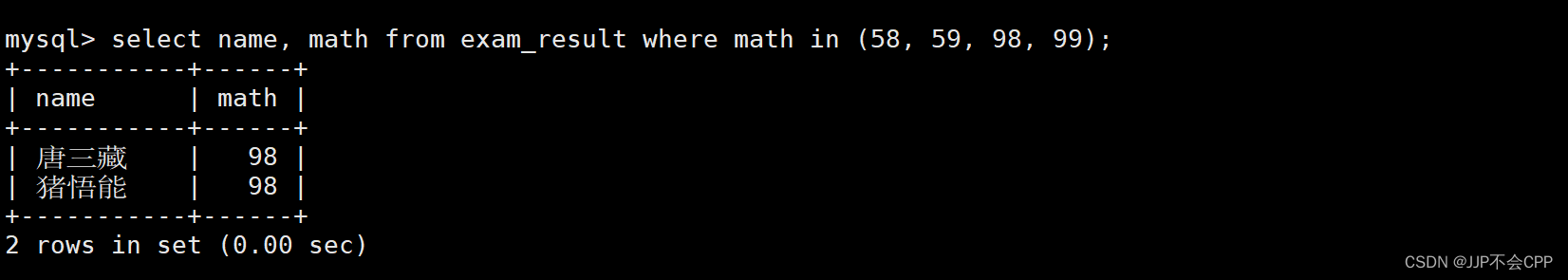
mysql> select name, math from exam_result where math in (58, 59, 98, 99);
4. 查找出姓孙的同学:
姓孙的同学有至少两种情况,可能孙同学的名字是两个字,那就是孙某同学,也有可能孙同学的名字是三个字,那就是孙某某同学,这里要求查找出姓孙的同学,就需要我们将所有姓孙的同学无论是孙某还是孙某某,都找出来。此时就需要使用到like模糊查找,并且应该使用%,表示匹配任意多个(包括0个)任意字符,具体使用如下:
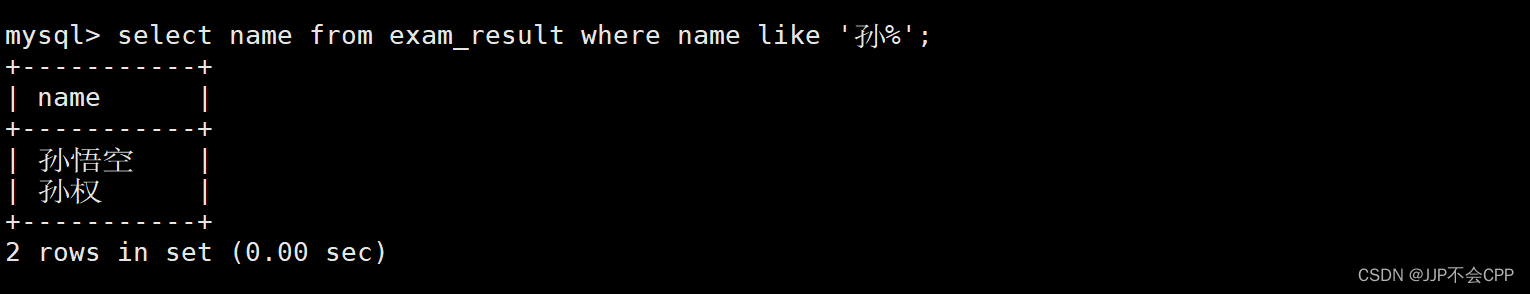
mysql> select name from exam_result where name like '孙%';
5. 查找出孙某同学
这里要查找出孙某同学,就不可以使用%的模糊查找了,因为%可能会查找出孙某某同学。此时就只能使用_模糊查找,它可以用来匹配严格的一个任意字符,具体使用如下:
mysql> select name from exam_result where name like '孙_';
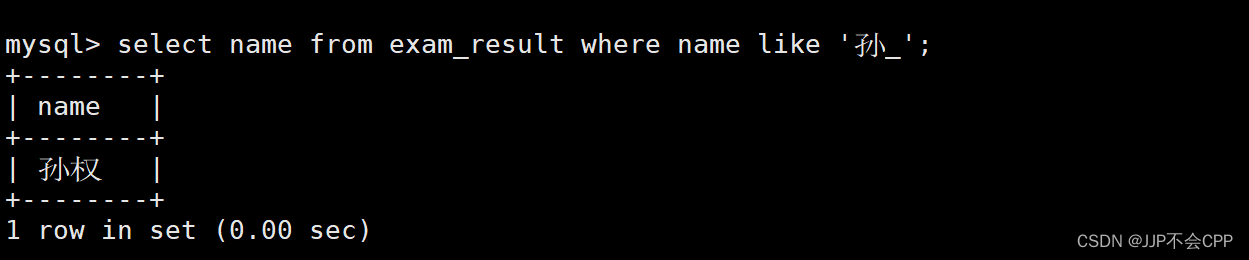
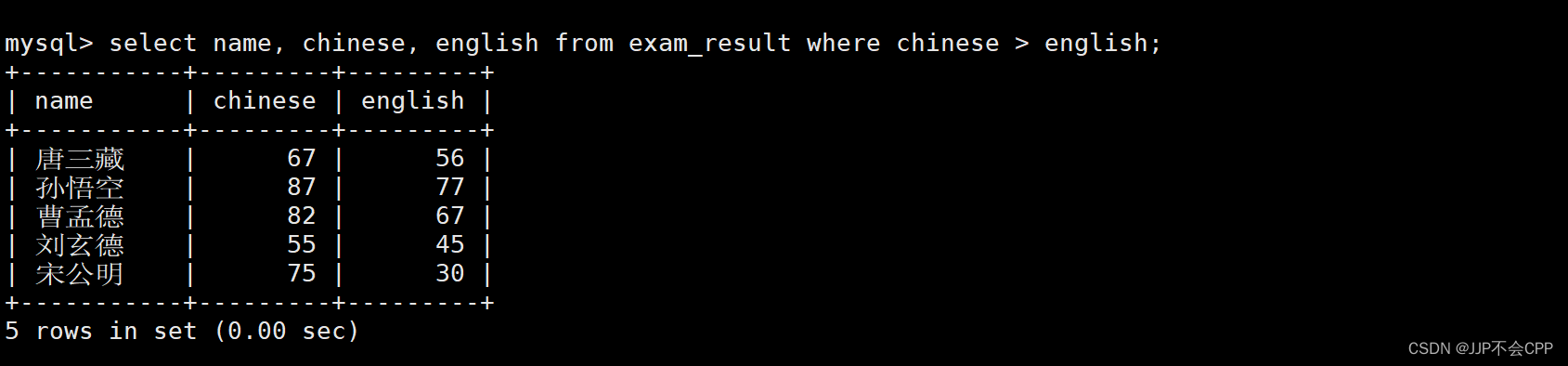
6. 查找出语文成绩比英语成绩好的同学,并将学生姓名以及对应的语文成绩和英语成绩显示出来:
mysql> select name, chinese, english from exam_result where chinese > english;
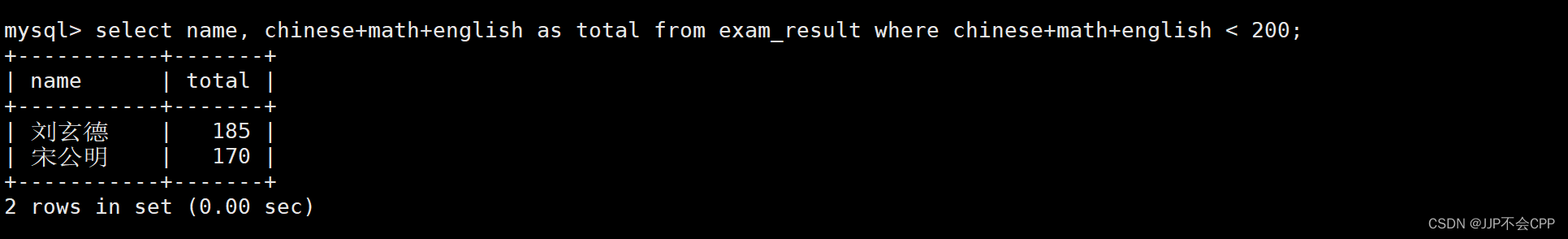
7. 查找出总分在200分以下的同学:
mysql> select name, chinese+math+english as total from exam_result where chinese+math+english < 200;
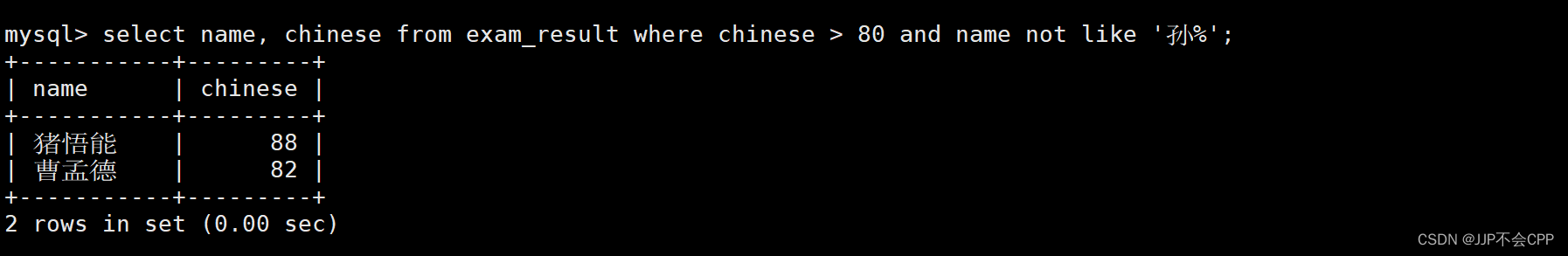
8. 查找出语文成绩大于80分且不姓孙的同学:
这里需要使用到and运算符和not运算符,具体使用如下:
mysql> select name, chinese from exam_result where chinese > 80 and name not like '孙%';
9. 查找孙某同学,否则要求总成绩大于200分并且语文成绩小于数学成绩并且英语成绩大于80分的同学:
这里的意思是找出所有的孙某同学,除此之外,如果不是孙某同学但是满足总成绩大于200分并且语文成绩小于数学成绩并且英语成绩大于80分的同学,也要找出来,具体查找如下:
mysql> select name, chinese, math, english, chinese+math+english as total from exam_result
-> where
-> name like '孙_'
-> or
-> (chinese+math+english>200 and chinese<math and english>80);
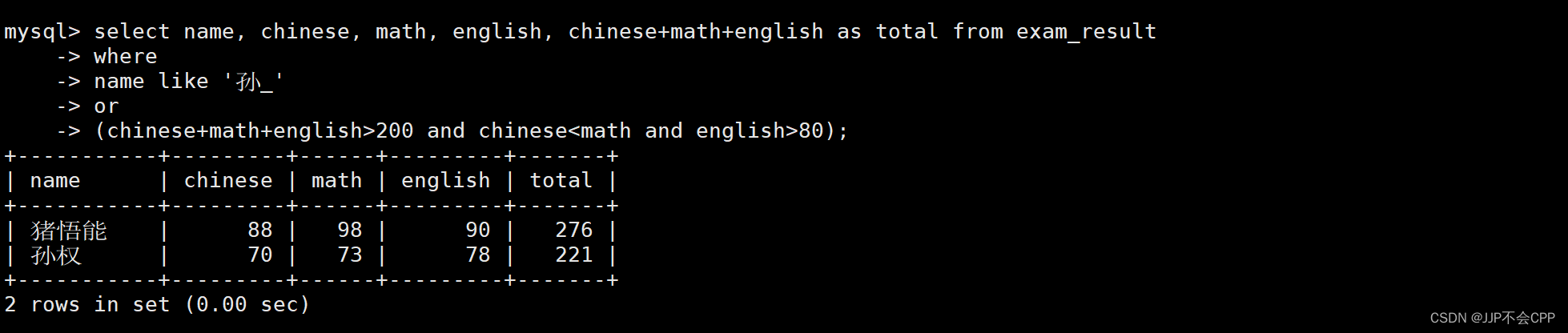
10. null查询
MySQL判断相等的运算符有两个,分别是=和<=>,前者是null不安全的,无论如何判断,只要=符号两边出现了null,查找的结果都是null。因为null是不参与运算的。但是后者是null安全的,举个例子就可以看出二者的差别,在students表中qq列有为null的:
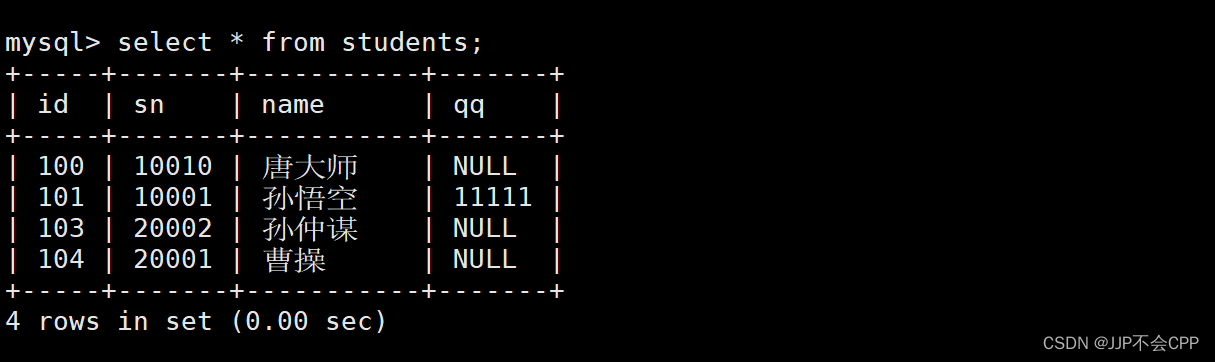
我们分别用=和<=>去查找为null的数据:
mysql> select name, qq from students where qq=null;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select name, qq from students where qq<=>null;
+-----------+------+
| name | qq |
+-----------+------+
| 唐大师 | NULL |
| 孙仲谋 | NULL |
| 曹操 | NULL |
+-----------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
所以如果我们要进行null查询,不要使用=运算符,而是要使用<=>运算符。除了这个运算符以外,还可以用is null来判断为空,和is not null来判断不为空:
mysql> select name, qq from students where qq is null;
+-----------+------+
| name | qq |
+-----------+------+
| 唐大师 | NULL |
| 孙仲谋 | NULL |
| 曹操 | NULL |
+-----------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select name, qq from students where qq is not null;
+-----------+-------+
| name | qq |
+-----------+-------+
| 孙悟空 | 11111 |
+-----------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
7.结果排序
我们可以使用order by来让查找到的结果按照顺序显示,其中ASC为升序,DESC为降序,默认是ASC升序排序。下面通过几个例子来演示以下结果排序的用法。
1. 查找所有同学的数学成绩,并且将数学成绩按升序排序:
mysql> select name, math from exam_result order by math;
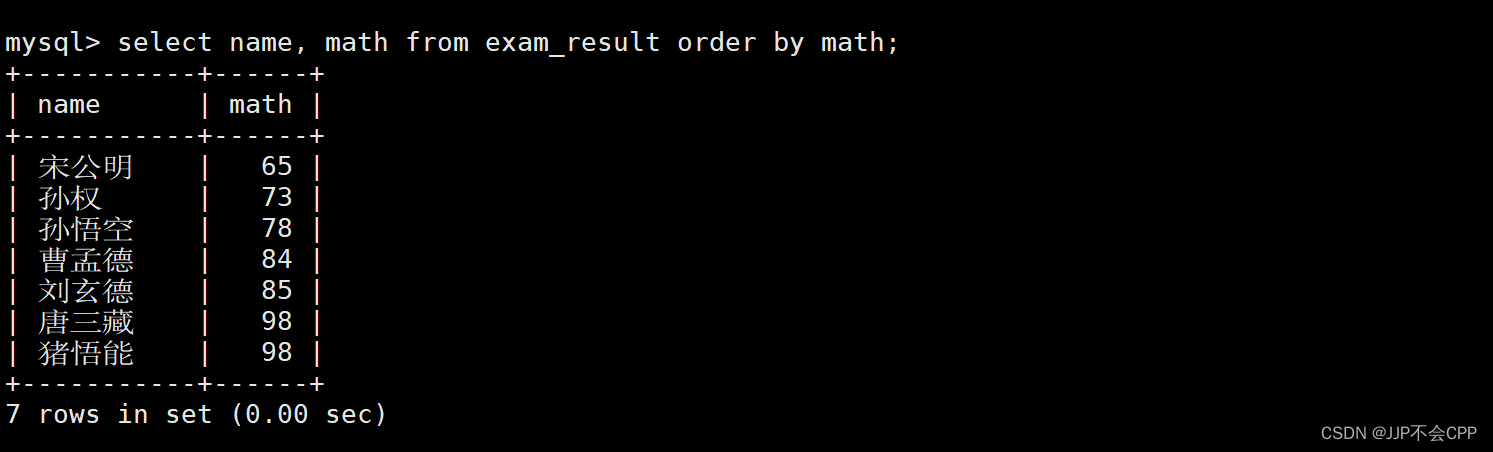
2. 查找所有同学的语文成绩,并且将语文成绩按降序排序:
mysql> select name, chinese from exam_result order by chinese desc;
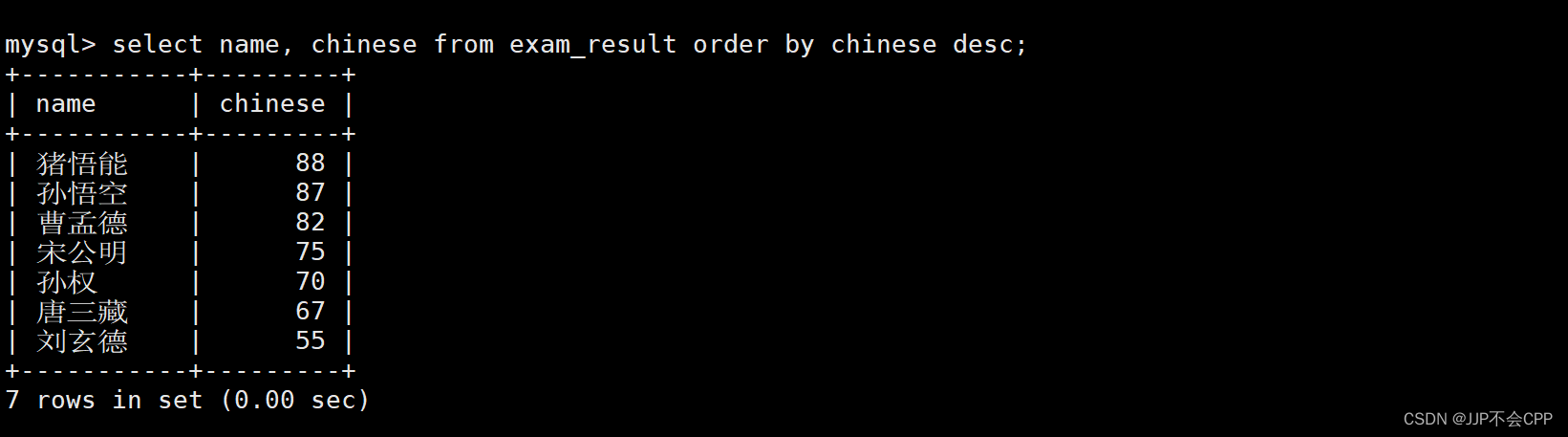
3. 查找同学的各科成绩,并且按照数学降序、语文升序、英语降序的方式显示:
mysql> select name, chinese, math, english from exam_result order by math desc, chinese, english desc;
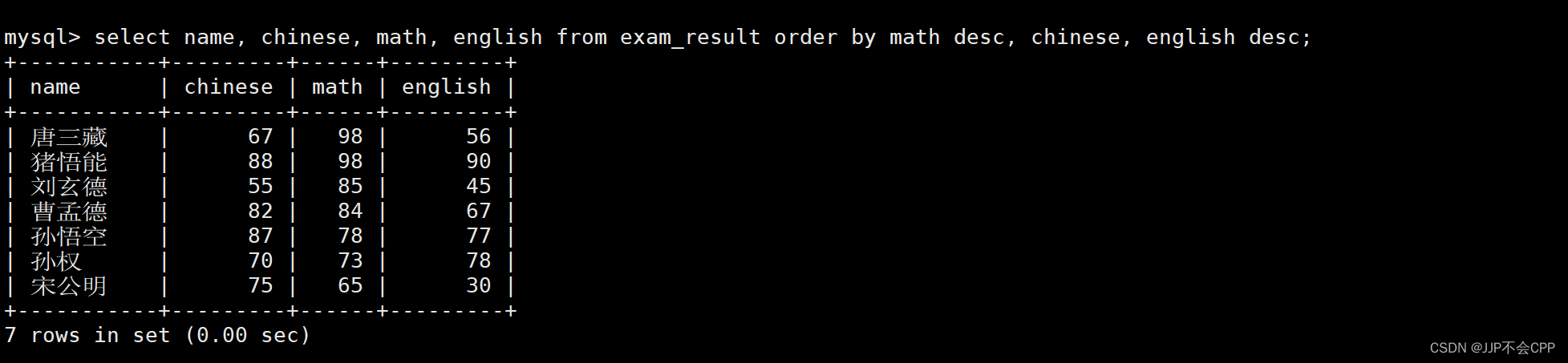
4. 查找所有同学的总分,并且将总分按照降序排序显示:
mysql> select name, chinese+math+english as total from exam_result order by chinese+math+english desc;
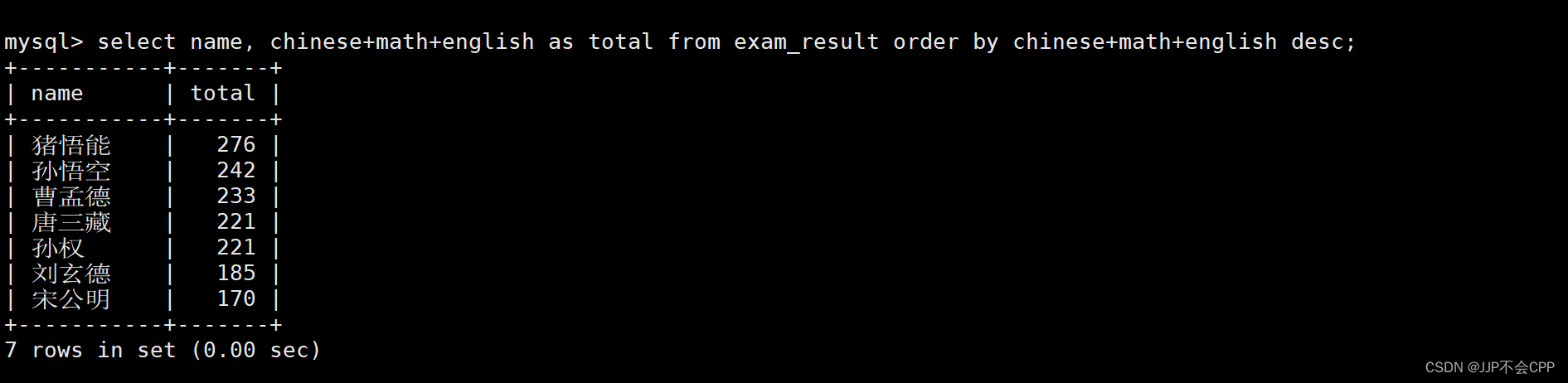
8.将查找结果分页显示
我们有些时候在对一些陌生表进行查询时需要将查询结果分页显示,因为有可能表的数据内容很多,查询全表数据有可能会导致数据库卡死。分页显示的基本语法如下:
-- 起始下标为 0
-- 从 0 开始,筛选 n 条结果
select ... from 表名 [where ...] [order by ...] limit n;
-- 从 s 开始,筛选 n 条结果
select ... from 表名 [where ...] [order by ...] limit n, s;
-- 从 s 开始,筛选 n 条结果,比第二种用法更明确,建议使用
select ... from 表名 [where ...] [order by ...] limit n offset s;
例如我们想查找exam_result表格,从2开始查找,一页存放4条结果:
mysql> select id, name from exam_result order by id limit 2 offset 4;
+----+-----------+
| id | name |
+----+-----------+
| 5 | 刘玄德 |
| 6 | 孙权 |
+----+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
9.插入查询结果
我们可以将一张表的查询结果插入到其它表当中,基本语法如下:
insert into 表名 [(列名 [, 列名 ...])] select ...
例如我们创建一个新的表new_exam_result,将exam_result表中的所有英语及格的同学插入到new_exam_result表中:
mysql> select * from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 唐三藏 | 67 | 98 | 56 |
| 3 | 猪悟能 | 88 | 98 | 90 |
| 4 | 曹孟德 | 70 | 90 | 67 |
| 5 | 刘玄德 | 55 | 115 | 45 |
| 6 | 孙权 | 70 | 73 | 78 |
| 7 | 宋公明 | 75 | 95 | 30 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> create table new_exam_result like exam_result;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> desc new_exam_result;
+---------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| chinese | float | YES | | 0 | |
| math | float | YES | | 0 | |
| english | float | YES | | 0 | |
+---------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into new_exam_result select * from exam_result where english>=60;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from new_exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 3 | 猪悟能 | 88 | 98 | 90 |
| 4 | 曹孟德 | 70 | 90 | 67 |
| 6 | 孙权 | 70 | 73 | 78 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
四、Update
1.修改基本语法
修改表中数据使用的是update指令,基本语法如下:
update 表名 set 列名 = 新值 [, 列名 = 新值 ...] [where ...] [order by ...] [limit ...]
2.修改示例
示例一:将孙悟空同学的数学成绩变更为80分
mysql> select name, math from exam_result where name='孙悟空';
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 孙悟空 | 78 |
+-----------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> update exam_result set math=80 where name='孙悟空';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select name, math from exam_result where name='孙悟空';
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 孙悟空 | 80 |
+-----------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
示例二:将曹孟德同学的数学成绩改为60分,语文成绩改为70分
mysql> select name, math, chinese from exam_result where name='曹孟德';
+-----------+------+---------+
| name | math | chinese |
+-----------+------+---------+
| 曹孟德 | 84 | 82 |
+-----------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> update exam_result set math=60, chinese=70 where name='曹孟德';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select name, math, chinese from exam_result where name='曹孟德';
+-----------+------+---------+
| name | math | chinese |
+-----------+------+---------+
| 曹孟德 | 60 | 70 |
+-----------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
示例三:将总成绩倒数前三的3位同学的数学成绩加上30分
要找出总成绩倒数前三的3位同学,需要使用order by将查找结果进行升序排序,然后使用limit从0开始取3个结果,就可以找到总成绩倒数前三的同学了。
mysql> select name, chinese+math+english as total from exam_result order by chinese+math+english limit 3;
+-----------+-------+
| name | total |
+-----------+-------+
| 宋公明 | 170 |
| 刘玄德 | 185 |
| 曹孟德 | 197 |
+-----------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> update exam_result set math=math+30 order by chinese+math+english limit 3;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 3 Changed: 3 Warnings: 0
mysql> select name, chinese+math+english as total from exam_result where name in ('宋公明', '刘玄德', '曹孟德');
+-----------+-------+
| name | total |
+-----------+-------+
| 曹孟德 | 227 |
| 刘玄德 | 215 |
| 宋公明 | 200 |
+-----------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
五、Delete
1.删除基本语法
删除表中的数据使用的是delete指令,基本语法如下:
delete from 表名 [where ...] [order by ...] [limit ...]
2.删除示例
示例一:删除孙悟空同学的考试成绩
mysql> select * from exam_result where name='孙悟空';
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 2 | 孙悟空 | 87 | 80 | 77 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> delete from exam_result where name='孙悟空';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from exam_result where name='孙悟空';
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 唐三藏 | 67 | 98 | 56 |
| 3 | 猪悟能 | 88 | 98 | 90 |
| 4 | 曹孟德 | 70 | 90 | 67 |
| 5 | 刘玄德 | 55 | 115 | 45 |
| 6 | 孙权 | 70 | 73 | 78 |
| 7 | 宋公明 | 75 | 95 | 30 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
示例二:删除整张表数据
mysql> create table for_delete (
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> insert into for_delete (name) values ('A'), ('B'), ('C');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from for_delete;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
+----+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> delete from for_delete;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from for_delete;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
3.截断表
截断表使用的是truncate指令,基本语法如下:
truncate [table] 表名
注意事项:
- 截断表只能对整表操作,不能像delete一样针对部分数据进行操作。
- 实际上截断表不对数据进行操作,所以比delete更快,但是截断表在删除数据时,并不经过真正的事务,所以无法回滚。
- 截断表操作后会重置auto_increment项。
下面我们创建一张临时的测试表来演示一下截断表的操作:
mysql> create table for_truncate (
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> insert into for_truncate (name) values ('A'), ('B'), ('C');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from for_truncate;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
+----+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> truncate for_truncate;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.07 sec)
mysql> select * from for_truncate;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
![[java]关于会话Session](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7473bf535abf4a39ae175154f049b46a.png)