系列文章
ProtoBuf 语法(一)
ProtoBuf 语法(三)
文章目录
- 八、更新消息
- 8.1 更新规则
- 8.2 reserved 保留字段
- 8.3 验证错误删除字段造成的数据损坏
- 8.4 未知字段及其获取方法
- 8.5 验证未知字段
八、更新消息
8.1 更新规则
如果现有的消息类型已经不再满足我们的需求,例如需要扩展⼀个字段,在不破坏任何现有代码的情况下更新消息类型非常简单。遵循如下规则即可:
- 禁止修改任何已有字段的字段编号。
- 若是移除老的字段,要保证不再使用移除字段的字段编号。正确的做法是保留字段编号(
reserved),以确保该编号将不能被重复使用;不建议直接删除或注释掉字段。 int32,uint32,int64,uint64和bool是完全兼容的。可以从这些类型中的一个改为另一个,而不破坏前后兼容性。若解析出来的数值与相应的类型不匹配,会采用与C++⼀致的处理方案,例如,若将 64 位整数当做 32 位进行读取,它将被截断为 32 位。sint32和sint64相互兼容但不与其他的整型兼容。string和bytes在合法UTF-8编码前提下也是兼容的。bytes包含消息编码版本的情况下,嵌套消息与bytes也是兼容的。fixed32与sfixed32兼容,fixed64与sfixed64兼容。enum与int32,uint32,int64和uint64兼容(注意若值不匹配会被截断)。但要注意当反序列化消息时会根据语言采用不同的处理⽅案:例如,未识别的proto3枚举类型会被保存在消息中,但是当消息反序列化时如何表示是依赖于编程语言的。整型字段总是会保持其的值。oneof字段:
- 将⼀个单独的值更改为新
oneof类型成员之一是安全和二进制兼容的。- 若确定没有代码⼀次性设置多个值,那么将多个字段移入⼀个新
oneof类型也是可行的。- 将任何字段移入已存在的
oneof类型是不安全的。
8.2 reserved 保留字段
-
如果通过 删除 或 注释 字段来更新消息类型,未来的用户在添加新字段时,有可能会使用以前已经存在,但已经被删除或注释掉的字段编号。将来使用该
.proto的旧版本时的程序会引发很多问题:数据损坏、隐私错误等等。 -
确保不会发送这种情况的⼀种方法是:使用
reserved保留字段将指定字段的编号或名称设置为保留项。当我们再使用这些编号或名称时,Protocol Buffer的编译器将会警告这些编号或名称不可用。例如下面的例子:
message Message
{
// 设置保留项
reserved 100, 101, 200 to 299;
reserved "field3", "field4";
// 注意:不要在⼀⾏ reserved 声明中同时声明字段编号和名称。
// reserved 102, "field5";
// 设置保留项之后,下⾯代码会告警
int32 field1 = 100; //告警:Field 'field1' uses reserved number 100
int32 field2 = 101; //告警:Field 'field2' uses reserved number 101
int32 field3 = 102; //告警:Field name 'field3' is reserved
int32 field4 = 103; //告警:Field name 'field4' is reserved
}
8.3 验证错误删除字段造成的数据损坏
现模拟有两个服务,他们各自使用⼀份contacts.proto文件,内容约定好了是⼀模⼀样的。
- 服务1(service):负责序列化通讯录对象,并写入文件中。
- 服务2(client):负责读取文件中的数据,解析并打印出来。
- ⼀段时间后,
service更新了自己的contacts.proto文件,更新内容为:删除了某个字段,并新增了⼀个字段,新增的字段使用了被删除字段的字段编号。并将新的序列化对象写进了文件。- 但
client并没有更新自己的contacts.proto文件。根据结论,可能会出现数据损坏的现象,接下来就让我们来验证下这个结论。
service 目录下新增 contacts.proto 文件:
syntax = "proto3";
package s_contacts;
// 联系⼈
message PeopleInfo
{
reserved "age";
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 age = 2; // 年龄
message Phone
{
string number = 1; // 电话号码
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts
{
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}
client目录下新增 contacts.proto 文件:
syntax = "proto3";
package c_contacts;
// 联系⼈
message PeopleInfo
{
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 age = 2; // 年龄
message Phone
{
string number = 1; // 电话号码
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts
{
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}
分别对两个文件进行编译,然后继续在service目录下新增service.cc,负责向文件中写通讯录消息,内容如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace s_contacts;
/**
* 新增联系⼈
*/
void AddPeopleInfo(PeopleInfo *people_info_ptr)
{
cout << "-------------新增联系⼈-------------" << endl;
cout << "请输⼊联系⼈姓名: ";
string name;
getline(cin, name);
people_info_ptr->set_name(name);
cout << "请输⼊联系⼈年龄: ";
int age;
cin >> age;
people_info_ptr->set_age(age);
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
for(int i = 1; ; i++)
{
cout << "请输⼊联系⼈电话" << i << "(只输⼊回⻋完成电话新增): ";
string number;
getline(cin, number);
if (number.empty())
{
break;
}
PeopleInfo_Phone* phone = people_info_ptr->add_phone();
phone->set_number(number);
}
cout << "-----------添加联系⼈成功-----------" << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION;
if (argc != 2)
{
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " CONTACTS_FILE" << endl;
return -1;
}
Contacts contacts;
// 先读取已存在的 contacts
fstream input(argv[1], ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!input)
{
cout << argv[1] << ": File not found. Creating a new file." << endl;
}
else if (!contacts.ParseFromIstream(&input))
{
cerr << "Failed to parse contacts." << endl;
input.close();
return -1;
}
// 新增⼀个联系⼈
AddPeopleInfo(contacts.add_contacts());
// 向磁盘⽂件写⼊新的 contacts
fstream output(argv[1], ios::out | ios::trunc | ios::binary);
if (!contacts.SerializeToOstream(&output))
{
cerr << "Failed to write contacts." << endl;
input.close();
output.close();
return -1;
}
input.close();
output.close();
google::protobuf::ShutdownProtobufLibrary();
return 0;
}
在client目录下新增client.cc,负责向读出文件中的通讯录消息,内容如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace c_contacts;
/**
* 打印联系⼈列表
*/
void PrintfContacts(const Contacts& contacts)
{
for (int i = 0; i < contacts.contacts_size(); ++i)
{
const PeopleInfo& people = contacts.contacts(i);
cout << "------------联系⼈" << i+1 << "------------" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << people.name() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << people.age() << endl;
int j = 1;
for (const PeopleInfo_Phone& phone : people.phone())
{
cout << "电话" << j++ << ": " << phone.number() << endl;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION;
if (argc != 2)
{
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << "CONTACTS_FILE" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 以⼆进制⽅式读取 contacts
Contacts contacts;
fstream input(argv[1], ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!contacts.ParseFromIstream(&input))
{
cerr << "Failed to parse contacts." << endl;
input.close();
return -1;
}
// 打印 contacts
PrintfContacts(contacts);
input.close();
google::protobuf::ShutdownProtobufLibrary();
return 0;
}
对代码分别编译完成后,进行⼀次读写操作:
[lhf@localhost service]$ ./service ./contacts.bin
./contacts.bin: File not found. Creating a new file.
-------------新增联系⼈-------------
请输⼊联系⼈姓名: 张三
请输⼊联系⼈年龄: 34
请输⼊联系⼈电话1(只输⼊回⻋完成电话新增): 131
请输⼊联系⼈电话2(只输⼊回⻋完成电话新增):
-----------添加联系⼈成功-----------
[lhf@localhost client]$ ./client ../service/contacts.bin
------------联系⼈1------------
姓名:张三
年龄:34
电话1: 131
确认无误后,对service目录下的contacts.proto文件进行更新:删除age字段,新增birthday字段,新增的字段使用被删除字段的字段编号。
更新后的
contacts.proto文件内容如下:
syntax = "proto3";
package s_contacts;
// 联系⼈
message PeopleInfo
{
string name = 1; // 姓名
// 删除年龄字段
// int32 age = 2; // 年龄
int32 birthday = 2; // ⽣⽇
message Phone
{
string number = 1; // 电话号码
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts
{
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}
编译
.proto文件后,还需要更新⼀下对应的service.cc代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace s_contacts;
/**
* 新增联系⼈
*/
void AddPeopleInfo(PeopleInfo *people_info_ptr)
{
cout << "-------------新增联系⼈-------------" << endl;
cout << "请输⼊联系⼈姓名: ";
string name;
getline(cin, name);
people_info_ptr->set_name(name);
/*cout << "请输⼊联系⼈年龄: ";
int age;
cin >> age;
people_info_ptr->set_age(age);
cin.ignore(256, '\n'); */
cout << "请输⼊联系⼈⽣⽇: ";
int birthday;
cin >> birthday;
people_info_ptr->set_birthday(birthday);
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
for(int i = 1; ; i++)
{
cout << "请输⼊联系⼈电话" << i << "(只输⼊回⻋完成电话新增): ";
string number;
getline(cin, number);
if (number.empty())
{
break;
}
PeopleInfo_Phone* phone = people_info_ptr->add_phone();
phone->set_number(number);
}
cout << "-----------添加联系⼈成功-----------" << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {...}
此时对client相关的代码保持原样,不进行更新。再进行⼀次读写操作:
[lhf@localhost service]$ ./service ./contacts.bin
-------------新增联系⼈-------------
请输⼊联系⼈姓名: 李四
请输⼊联系⼈⽣⽇: 1221
请输⼊联系⼈电话1(只输⼊回⻋完成电话新增): 151
请输⼊联系⼈电话2(只输⼊回⻋完成电话新增):
-----------添加联系⼈成功-----------
[lhf@localhost client]$ ./client ../service/contacts.bin
------------联系⼈1------------
姓名:张三
年龄:34
电话1: 131
------------联系⼈2------------
姓名:李四
年龄:1221
电话1: 151
- 这时问题便出现了,我们发现输入的生日,在反序列化时,被设置到了使用了相同字段编号的年龄上!!所以得出结论:若是移除老字段,要保证不再使用移除字段的字段编号,不建议直接删除或注释掉字段。
- 那么正确的做法是保留字段编号(
reserved),以确保该编号将不能被重复使用。
正确service目录下的contacts.proto写法如下:
syntax = "proto3";
package s_contacts;
// 联系⼈
message PeopleInfo
{
reserved 2;
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 birthday = 4; // ⽣⽇
message Phone
{
string number = 1; // 电话号码
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts
{
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}
编译.proto文件后,还需要重新编译下service.cc,让service程序保持使用新生成的pb C++文件,然后再次进行读写操作:
[lhf@localhost service]$ ./service ./contacts.bin
-------------新增联系⼈-------------
请输⼊联系⼈姓名: 王五
请输⼊联系⼈⽣⽇: 1112
请输⼊联系⼈电话1(只输⼊回⻋完成电话新增): 110
请输⼊联系⼈电话2(只输⼊回⻋完成电话新增):
-----------添加联系⼈成功-----------
[lhf@localhost client]$ ./client ../service/contacts.bin
------------联系⼈1------------
姓名:张三
年龄:34
电话1: 131
------------联系⼈2------------
姓名:李四
年龄:1221
电话1: 151
------------联系⼈3------------
姓名:王五
年龄:0
电话1: 110
- 根据实验结果,发现
王五的年龄为 0,这是由于新增时未设置年龄,通过client程序反序列化时,给年龄字段设置了默认值0。这个结果显然是我们想看到的。 李四的年龄依旧使用了之前设置的生日字段1221,这是因为在新增李四的时候,生日字段的字段编号依旧为2,并且已经被序列化到文件中了。最后再读取的时候,字段编号依旧为2。- 另外,因为使用了
reserved关键字,ProtoBuf在编译阶段就拒绝了我们使用已经保留的字段编号,通过上面的实验,也印证了我们的结论。
另外值得一提的是:
根据以上的例子,我们可能还有⼀个疑问:如果使用了 reserved 对 2 号字段进行了保留,那么service给王五设置的生日1112,client就没法读到了吗?答案当然是可以的,这就是下面未知字段的作用了。
8.4 未知字段及其获取方法
在上面的实验中,在service目录对contacts.proto文件新增了⽣⽇字段,但对于client相关的代码并没有任何改动。验证后发现新代码序列化的消息(service)也可以被旧代码(client)解析。并且这里要说明的是,新增的⽣⽇字段在旧程序(client)中其实并没有丢失,而是会作为旧程序的未知字段。
- 未知字段:解析结构良好的
Protocol Buffer已序列化数据中的未识别字段的表示方式。例如,当旧程序解析带有新字段的数据时,这些新字段就会成为旧程序的未知字段。 - 使用
proto3语法,在解析消息时总是会丢弃未知字段,但在proto 3.5版本中重新引入了对未知字段的保留机制。所以在3.5或更高版本中,未知字段在反序列化时会被保留,同时也会包含在序列化的结果中。
未知字段的获取:
- 了解相关类关系图
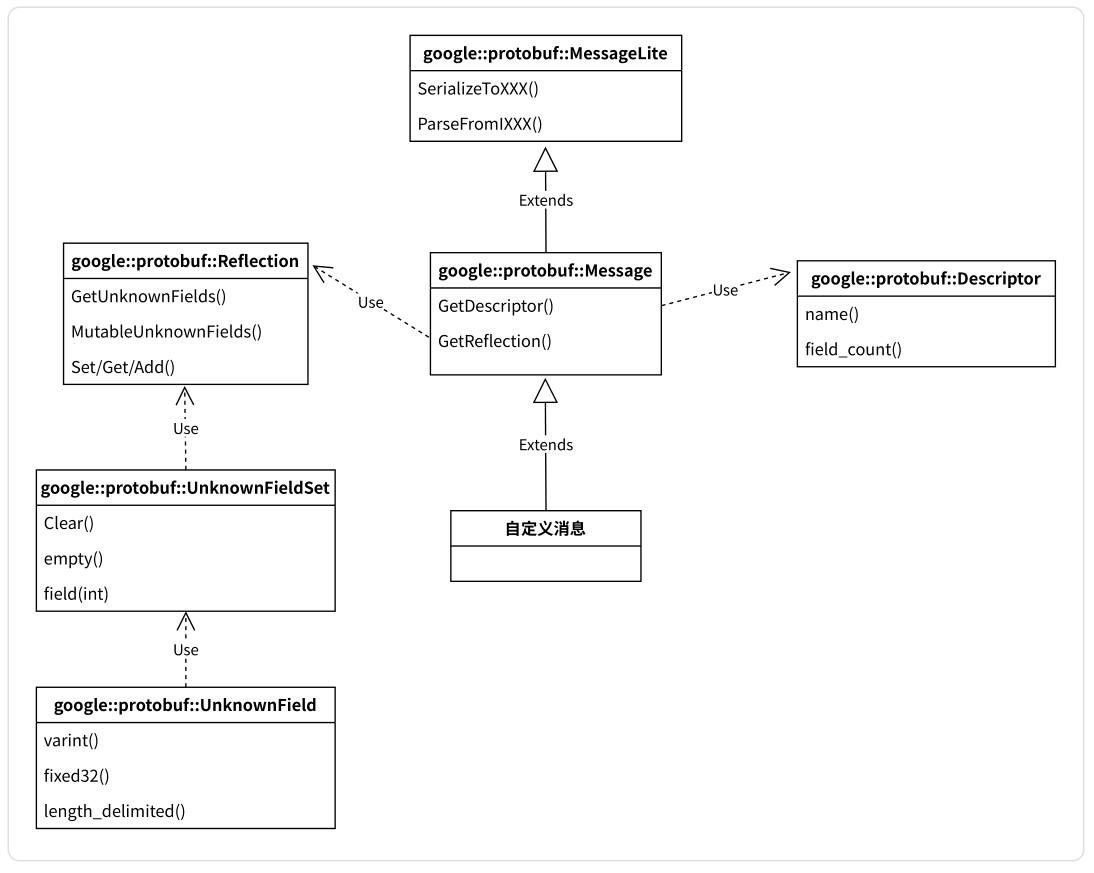
- MessageLite 类
MessageLite从名字看是轻量级的message,仅仅提供序列化、反序列化功能。- 该类定义在
google提供的message_lite.h中。
- Message 类
- 我们自定义的
message类,都是继承自Message。 Message最重要的两个接口是GetDescriptor和GetReflection,可以获取该类型对应的Descriptor对象指针和Reflection对象指针。- 类定义在
google提供的message.h中。
- Descriptor 类
Descriptor:是对message类型定义的描述,包括message的名字、所有字段的描述、原始的.proto文件内容等。- 类定义在
google提供的descriptor.h中。
部分代码展示:
class PROTOBUF_EXPORT Descriptor : private internal::SymbolBase
{
string& name () const
int field_count() const;
const FieldDescriptor* field(int index) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindFieldByNumber(int number) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindFieldByName(const std::string& name) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindFieldByLowercaseName(
const std::string& lowercase_name) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindFieldByCamelcaseName(
const std::string& camelcase_name) const;
int enum_type_count() const;
const EnumDescriptor* enum_type(int index) const;
const EnumDescriptor* FindEnumTypeByName(const std::string& name) const;
const EnumValueDescriptor* FindEnumValueByName(const std::string& name)
const;
}
- Reflection 类
Reflection接口类,主要提供了动态读写消息字段的接口,对消息对象的自动读写主要通过该类完成。- 提供方法来动态访问/修改
message中的字段,对每种类型,Reflection都提供了⼀个单独的接口用于读写字段对应的值:
◦ 针对所有不同的field类型FieldDescriptor::TYPE_*,需要使用不同的Get*()/Set*()/Add*()接口;
◦repeated类型需要使用GetRepeated*()/SetRepeated*()接口,不可以和非repeated类型接口混用;
◦message对象只可以被由它自身的reflection(message.GetReflection())来操作。 - 类中还包含了访问/修改未知字段的⽅法。
- 类定义在
google提供的message.h中。
部分代码展示:
class PROTOBUF_EXPORT Reflection final
{
const UnknownFieldSet& GetUnknownFields(const Message& message) const;
UnknownFieldSet* MutableUnknownFields(Message* message) const;
bool HasField(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
int FieldSize(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
void ClearField(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
bool HasOneof(const Message& message,
const OneofDescriptor* oneof_descriptor) const;
void ClearOneof(Message* message,
const OneofDescriptor* oneof_descriptor) const;
const FieldDescriptor* GetOneofFieldDescriptor(
const Message& message, const OneofDescriptor* oneof_descriptor) const;
// Singular field getters ------------------------------------------
// These get the value of a non-repeated field. They return the default
// value for fields that aren't set.
int32_t GetInt32(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
int64_t GetInt64(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
uint32_t GetUInt32(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
uint64_t GetUInt64(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
float GetFloat(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
double GetDouble(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
bool GetBool(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
std::string GetString(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
const EnumValueDescriptor* GetEnum(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
int GetEnumValue(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
const Message& GetMessage(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field,
MessageFactory* factory = nullptr) const;
// Singular field mutators -----------------------------------------
// These mutate the value of a non-repeated field.
void SetInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int32_t value) const;
void SetInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int64_t value) const;
void SetUInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
uint32_t value) const;
void SetUInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
uint64_t value) const;
void SetFloat(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
float value) const;
void SetDouble(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
double value) const;
void SetBool(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
bool value) const;
void SetString(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
std::string value) const;
void SetEnum(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
const EnumValueDescriptor* value) const;
void SetEnumValue(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int value) const;
Message* MutableMessage(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
MessageFactory* factory = nullptr) const;
PROTOBUF_NODISCARD Message* ReleaseMessage(
Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
MessageFactory* factory = nullptr) const;
// Repeated field getters ------------------------------------------
// These get the value of one element of a repeated field.
int32_t GetRepeatedInt32(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor*
field,
int index) const;
int64_t GetRepeatedInt64(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor*
field,
int index) const;
uint32_t GetRepeatedUInt32(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field, int index) const;
uint64_t GetRepeatedUInt64(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field, int index) const;
float GetRepeatedFloat(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index) const;
double GetRepeatedDouble(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor*
field,
int index) const;
bool GetRepeatedBool(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index) const;
std::string GetRepeatedString(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field, int index) const;
const EnumValueDescriptor* GetRepeatedEnum(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index) const;
int GetRepeatedEnumValue(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor*
field,
int index) const;
const Message& GetRepeatedMessage(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index) const;
const std::string& GetRepeatedStringReference(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index,
std::string* scratch) const;
// Repeated field mutators -----------------------------------------
// These mutate the value of one element of a repeated field.
void SetRepeatedInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, int32_t value) const;
void SetRepeatedInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, int64_t value) const;
void SetRepeatedUInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, uint32_t value) const;
void SetRepeatedUInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, uint64_t value) const;
void SetRepeatedFloat(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, float value) const;
void SetRepeatedDouble(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, double value) const;
void SetRepeatedBool(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, bool value) const;
void SetRepeatedString(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, std::string value) const;
void SetRepeatedEnum(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, const EnumValueDescriptor* value) const;
void SetRepeatedEnumValue(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, int value) const;
Message* MutableRepeatedMessage(Message* message,
const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index) const;
// Repeated field adders -------------------------------------------
// These add an element to a repeated field.
void AddInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int32_t value) const;
void AddInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int64_t value) const;
void AddUInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
uint32_t value) const;
void AddUInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
uint64_t value) const;
void AddFloat(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
float value) const;
void AddDouble(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
double value) const;
void AddBool(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
bool value) const;
void AddString(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
std::string value) const;
void AddEnum(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
const EnumValueDescriptor* value) const;
void AddEnumValue(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int value) const;
Message* AddMessage(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
MessageFactory* factory = nullptr) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindKnownExtensionByName(
const std::string& name) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindKnownExtensionByNumber(int number) const;
bool SupportsUnknownEnumValues() const;
};
- UnknownFieldSet 类
UnknownFieldSet包含在分析消息时遇到但未由其类型定义的所有字段。- 若要将
UnknownFieldSet附加到任何消息,可以调用Reflection::GetUnknownFields()。 - 类定义在
unknown_field_set.h中。
部分代码展示:
class PROTOBUF_EXPORT UnknownFieldSet
{
inline void Clear();
void ClearAndFreeMemory();
inline bool empty() const;
inline int field_count() const;
inline const UnknownField& field(int index) const;
inline UnknownField* mutable_field(int index);
// Adding fields ---------------------------------------------------
void AddVarint(int number, uint64_t value);
void AddFixed32(int number, uint32_t value);
void AddFixed64(int number, uint64_t value);
void AddLengthDelimited(int number, const std::string& value);
std::string* AddLengthDelimited(int number);
UnknownFieldSet* AddGroup(int number);
// Parsing helpers -------------------------------------------------
// These work exactly like the similarly-named methods of Message.
bool MergeFromCodedStream(io::CodedInputStream* input);
bool ParseFromCodedStream(io::CodedInputStream* input);
bool ParseFromZeroCopyStream(io::ZeroCopyInputStream* input);
bool ParseFromArray(const void* data, int size);
inline bool ParseFromString(const std::string& data) {
return ParseFromArray(data.data(), static_cast<int>(data.size()));
}
// Serialization.
bool SerializeToString(std::string* output) const;
bool SerializeToCodedStream(io::CodedOutputStream* output) const;
static const UnknownFieldSet& default_instance();
};
- UnknownField 类
- 表示未知字段集中的⼀个字段。
- 类定义在
unknown_field_set.h中。
部分代码展示
class PROTOBUF_EXPORT UnknownField
{
public:
enum Type {
TYPE_VARINT,
TYPE_FIXED32,
TYPE_FIXED64,
TYPE_LENGTH_DELIMITED,
TYPE_GROUP
};
inline int number() const;
inline Type type() const;
// Accessors -------------------------------------------------------
// Each method works only for UnknownFields of the corresponding type.
inline uint64_t varint() const;
inline uint32_t fixed32() const;
inline uint64_t fixed64() const;
inline const std::string& length_delimited() const;
inline const UnknownFieldSet& group() const;
inline void set_varint(uint64_t value);
inline void set_fixed32(uint32_t value);
inline void set_fixed64(uint64_t value);
inline void set_length_delimited(const std::string& value);
inline std::string* mutable_length_delimited();
inline UnknownFieldSet* mutable_group();
};
8.5 验证未知字段
更新client.cc,在这个版本中,需要打印出未知字段的内容。更新的代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <google/protobuf/unknown_field_set.h>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace c_contacts;
using namespace google::protobuf;
/**
* 打印联系⼈列表
*/
void PrintfContacts(const Contacts& contacts)
{
for (int i = 0; i < contacts.contacts_size(); ++i)
{
const PeopleInfo& people = contacts.contacts(i);
cout << "------------联系⼈" << i+1 << "------------" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << people.name() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << people.age() << endl;
int j = 1;
for (const PeopleInfo_Phone& phone : people.phone())
{
cout << "电话" << j++ << ": " << phone.number() << endl;
}
// 打印未知字段
const Reflection* reflection = PeopleInfo::GetReflection();
const UnknownFieldSet& unknowSet = reflection->GetUnknownFields(people);
for (int j = 0; j < unknowSet.field_count(); j++)
{
const UnknownField& unknow_field = unknowSet.field(j);
cout << "未知字段" << j+1 << ":"
<< " 字段编号: " << unknow_field.number()
<< " 类型: "<< unknow_field.type();
switch (unknow_field.type())
{
case UnknownField::Type::TYPE_VARINT:
cout << " 值: " << unknow_field.varint() << endl;
break;
case UnknownField::Type::TYPE_LENGTH_DELIMITED:
cout << " 值: " << unknow_field.length_delimited() << endl;
break;
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION;
if (argc != 2)
{
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << "CONTACTS_FILE" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 以⼆进制⽅式读取 contacts
Contacts contacts;
fstream input(argv[1], ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!contacts.ParseFromIstream(&input))
{
cerr << "Failed to parse contacts." << endl;
input.close();
return -1;
}
// 打印 contacts
PrintfContacts(contacts);
input.close();
google::protobuf::ShutdownProtobufLibrary();
return 0;
}
其他文件均不用做任何修改,重新编译client.cc,进行⼀次读操作可得如下结果:
[lhf@localhost client]$ ./client ../service/contacts.bin
------------联系⼈1------------
姓名:张珊
年龄:34
电话1: 131
------------联系⼈2------------
姓名:李四
年龄:1221
电话1: 151
------------联系⼈3------------
姓名:王五
年龄:0
电话1: 110
未知字段1: 字段编号: 4 类型: 0 值: 1112
值得注意的是:
未知字段的类型为 0,在前面的 UnknownField 类中提到了类中包含了未知字段的几种类型:
enum Type {
TYPE_VARINT,
TYPE_FIXED32,
TYPE_FIXED64,
TYPE_LENGTH_DELIMITED,
TYPE_GROUP
};
即,未知字段的类型为 TYPE_VARINT。