目录
VL21 根据状态转移表实现时序电路
VL22 根据状态转移图实现时序电路
VL23 ROM的简单实现
VL24 边沿检测
VL21 根据状态转移表实现时序电路
题目分析:
1、使用三段式状态机,实现更为方便和简洁。
2、三段式和(一段式、二段式)对比:
优点:
(1)时序逻辑和组合逻辑分开,便于分析。
(2)利于综合软件的分析和优化。
(3)代码简介明了,便于维护。缺点:
(1)代码结构相较两段式复杂。
(2)采用时序逻辑输出避免了亚稳态,但是增加了触发器的使用。数字IC笔面基础,师傅领进门,修行靠个人——人人心中都有一个状态机(状态机简介及Verilog模板)_HFUT90S的博客-CSDN博客

三段式状态机模板:
第1段:描述状态转移(时序逻辑)
第2段:描述状态转移的条件和规律(组合逻辑)
第3段:描述状态输出(组合/时序逻辑)
代码实现:
module seq_circuit(
input A ,
input clk ,
input rst_n,
output wire Y
);
//三段式状态机
//状态定义
localparam IDLE = 2'b0; //初态
localparam s0 = 2'b01;
localparam s1 = 2'b10;
localparam s2 = 2'b11;
reg [1:0] CS; //现态
reg [1:0] NS; //次态
//描述状态转移(时序逻辑)
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
CS <= IDLE;
else
CS <= NS;
end
//描述状态转移的条件和规律(组合逻辑)
always @(*)begin
case(CS)
IDLE: if(!A)
NS = s0;
else
NS = s2;
s0 : if(!A)
NS = s1;
else
NS = IDLE;
s1 : if(!A)
NS = s2;
else
NS = s0;
s2 : if(!A)
NS = IDLE;
else
NS = s1;
default: NS = IDLE;
endcase
end
//描述状态输出(组合/时序逻辑)
assign Y = ((CS == IDLE)|(CS == s0)|(CS == s1))?0:1;
endmoduleVL22 根据状态转移图实现时序电路
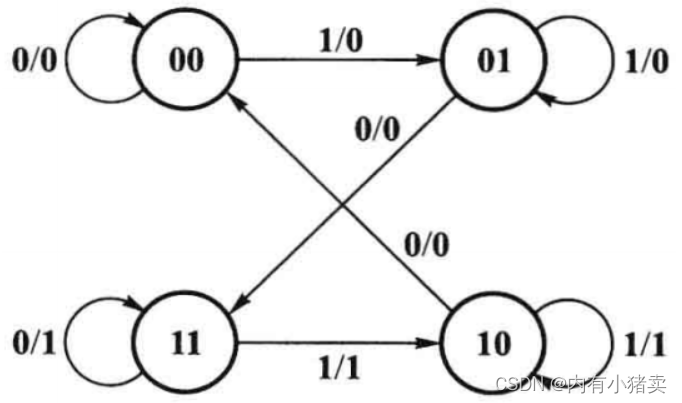
题目分析:
VL22和VL21同理,只不过从状态转移表换成了状态转移图,细心一点就没问题,用的还是三段式状态机。
代码实现:
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module seq_circuit(
input C ,
input clk ,
input rst_n,
output wire Y
);
//三段式状态机
//状态定义
localparam IDLE = 2'b0;
localparam s0 = 2'b01;
localparam s1 = 2'b10;
localparam s2 = 2'b11;
reg [1:0] CS; //现态
reg [1:0] NS; //次态
//描述状态转移(时序逻辑)
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
CS <= IDLE;
else
CS <= NS;
end
//描述状态转移的条件和规律(组合逻辑)
always @(*)begin
case(CS)
IDLE: if(!C)
NS = IDLE; //0
else
NS = s0; //0
s0 : if(!C)
NS = s2; //0
else
NS = s0; //0
s1 : if(!C)
NS = IDLE; //0
else
NS = s1; //1
s2 : if(!C)
NS = s2; //1
else
NS = s1; //1
default: NS = IDLE;
endcase
end
//描述状态输出(组合/时序逻辑)
assign Y = ((CS == s2) | ((CS == s1)& (C == 1)))?1:0;
endmoduleVL23 ROM的简单实现
题目描述:
①实现一个深度为8,位宽为4bit的ROM,数据初始化为0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14。可以通过输入地址addr,输出相应的数据data。
②使用Verilog HDL实现以上功能并编写testbench验证。
代码实现:
module VL23_rom(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [7:0]addr,
output [3:0]data
);
//定义一个深度为8 宽度为4的数组
reg [3:0] memory [7:0];
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
memory[0] <= 4'b0;
memory[1] <= 4'b0;
memory[2] <= 4'b0;
memory[3] <= 4'b0;
memory[4] <= 4'b0;
memory[5] <= 4'b0;
memory[6] <= 4'b0;
memory[7] <= 4'b0;
end
else begin
memory[0] <= 4'd0;
memory[1] <= 4'd2;
memory[2] <= 4'd4;
memory[3] <= 4'd6;
memory[4] <= 4'd8;
memory[5] <= 4'd10;
memory[6] <= 4'd12;
memory[7] <= 4'd14;
end
end
assign data = (addr == 8'd0)?memory[0]:
(addr == 8'd1)?memory[1]:
(addr == 8'd2)?memory[2]:
(addr == 8'd3)?memory[3]:
(addr == 8'd4)?memory[4]:
(addr == 8'd5)?memory[5]:
(addr == 8'd6)?memory[6]:
(addr == 8'd7)?memory[7]:0;
endmodule仿真文件:
module tb_VL23_rom;
// Inputs
reg clk;
reg rst_n;
reg [7:0] addr ;
// Outputs
wire [3:0] data;
// Instantiate the Unit Under Test (UUT)
VL23_rom uut (
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.addr(addr),
.data(data)
);
initial begin
// Initialize Inputs
clk = 0;
rst_n = 0;
addr = 0;
// Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish
#100;
rst_n = 1'b1;
#100;
addr = 4'd6;
#100; //#100 addr = 4'd5;
addr = 4'd5; //代表100ns后addr由上一个状态4'd6 变为此时的状态4'd5
#100;
addr = 4'd4;
#100;
addr = 4'd3;
#100;
addr = 4'd2;
#100;
addr = 4'd1;
// Add stimulus here
end
always #10 clk=~clk;
endmodule仿真图片:
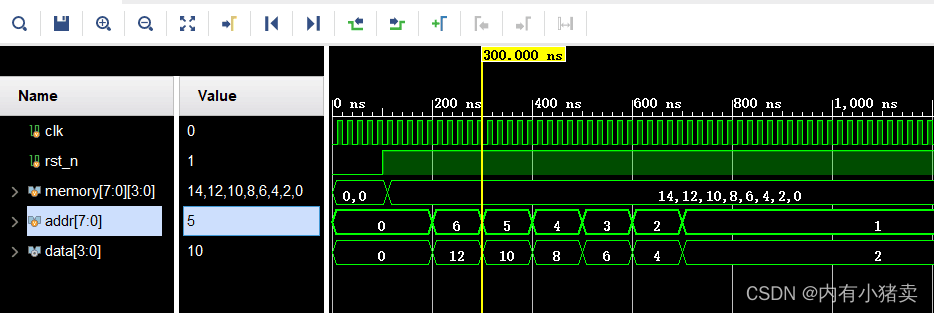
VL24 边沿检测
题目描述:
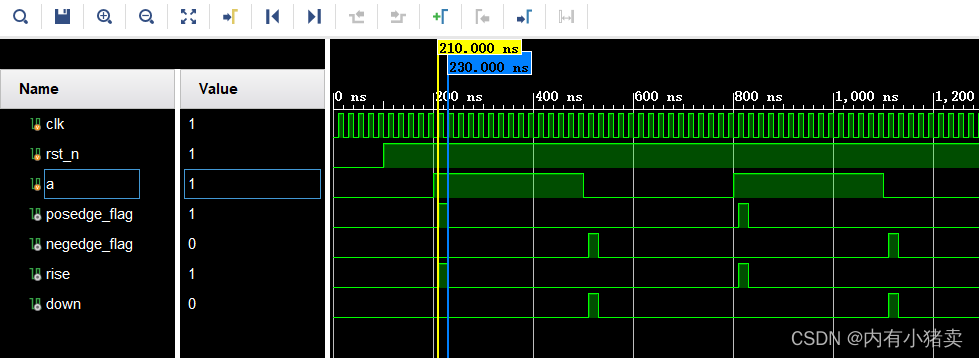
边沿检测:有一个缓慢变化的1bit信号a,编写一个程序检测a信号的上升沿给出指示信号rise,当a信号出现下降沿时给出指示信号down。
注:rise,down应为单脉冲信号,在相应边沿出现时的下一个时钟为高,之后恢复到0,一直到再一次出现相应的边沿。
代码实现:
module VL24_edge_detect(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input a,
output reg rise,
output reg down
);
reg b,c;
wire posedge_flag;
wire negedge_flag;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
b <= 1'b0;
c <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
b <= a;
c <= b;
end
end
assign posedge_flag = ~c & b;
assign negedge_flag = c & ~b;
always @(*)begin
if(posedge_flag)
rise <= 1'b1;
else if(negedge_flag)
down <= 1'b1;
else begin
rise <= 1'b0;
down <= 1'b0;
end
end
endmodule仿真文件:
module tb_VL24_edge_detect;
// Inputs
reg clk;
reg rst_n;
reg a;
// Outputs
wire rise;
wire down;
// Instantiate the Unit Under Test (UUT)
VL24_edge_detect uut (
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.a(a),
.rise(rise),
.down(down)
);
initial begin
// Initialize Inputs
clk = 0;
rst_n = 0;
a = 0;
// Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish
#100;
rst_n = 1'b1;
#100;
a = 1;
#300;
a = 0;
#300;
a = 1;
#300;
a = 4'd0;
// Add stimulus here
end
always #10 clk=~clk;
endmodule仿真图片:
哈哈哈,结束啦!