目录
实验一 进程控制与进程调度
一、实验目的
二、实验内容
三、数据结构及符号说明
四、运行环境说明
五、代码段
六、 效果展示
实验一 进程控制与进程调度
备注:大二(下)操作系统实验一
一、实验目的
掌握进程状态的转变、进程调度的策略
理解进程控制的过程,进一步体会多道程序并发执行的特点
二、实验内容
利用简单的结构和控制方法模拟进程结构、进程状态和进程控制,进程调度采用时间片轮转调度算法
1、用PCB表示进程实体,利用随机数方法或键盘控制方法模拟进程执行中产生的事件,或者基于图形界面控制进程
2、定义PCB包括基本内容,如内部ID、外部ID、进程状态、队列指针
由于很难实现真正的进程创建功能,在实验中只需建立PCB节点,并用它代表一个完整的进程
每创建一个进程时,可动态分配PCB节点,对相应内容赋值,并链接到对应队列
可参考如下数据结构(C语言实现):
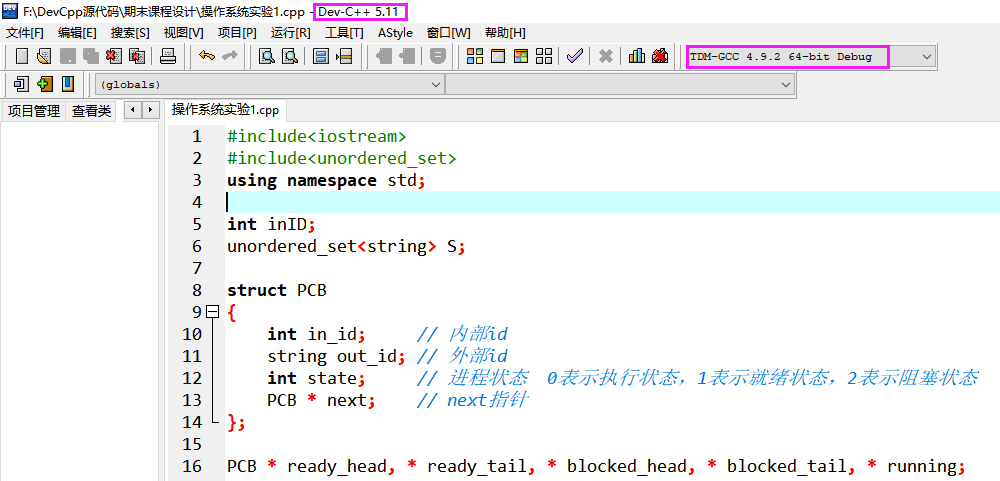
struct PCB
{
int inid; //内部ID 自动生成
char outid[10]; //外部ID
int state ; //进程状态 0表示执行状态 1表示就绪状态 2表示阻塞状态
struct PCB*next;
};
struct PCB *ready,*blocked,*running;
3、定义进程状态转换方式
真实的进程状态转换是由进程内部操作或操作系统的控制引起
由于模拟程序中无法实现这些功能,实验可以采用随机数方法或键盘控制方法模拟,并实现对应的控制程序
随机方法指产生1-5的随机数,分别代表(1)创建进程、(2)时间片到、(3)进程阻塞、(4)唤醒进程、(5)结束进程等事件;
键盘模拟方法指定义5个选项菜单代表以上5种事件
4、根据随机数或键盘操作处理就绪队列、阻塞队列和当前执行进程的状态
每次事件处理后应显示出当前系统中的执行进程是哪一个,就绪队列和阻塞队列分别包含哪些进程
5、编程语言不限,可以选择用C语言、Python或java
三、数据结构及符号说明
数据结构:
使用结构体PCB来表示一个进程使用链表实现就绪队列和阻塞队列,指针为 PCB * next
符号说明:
就绪队列头指针 ready_head就绪队列尾指针 ready_tail
阻塞队列头指针 blocked_head
阻塞队列尾指针 blocked_tail
当前运行程序指针 running
四、运行环境说明
五、代码段
#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_set>
using namespace std;
int inID;
unordered_set<string> S;
struct PCB
{
int in_id; // 内部id
string out_id; // 外部id
int state; // 进程状态 0表示执行状态,1表示就绪状态,2表示阻塞状态
PCB * next; // next指针
};
PCB * ready_head, * ready_tail, * blocked_head, * blocked_tail, * running;
PCB * PCB_creat() // 创建PCB
{
PCB * p = new PCB;
cout << "进程创建成功!" << endl;
return p;
}
void PCB_init(PCB * p) // 初始化PCB
{
string id;
p -> in_id = inID ++ ;
cout << "请输入进程外部ID:" << endl;
cin >> id;
while(S.count(id))
{
cout << "您输入的外部ID已被使用,请重新输入!" << endl;
cin >> id;
}
S.insert(id);
p -> out_id = id;
p -> state = 1;
p -> next = NULL;
cout << "进程初始化成功!" << endl << endl;
}
int insert_to_ready(PCB * p) // 插入就绪队列
{
p -> next = NULL;
if(ready_tail) ready_tail -> next = p;
ready_tail = p;
if(! ready_head) ready_head = p;
return 0;
}
void insert_to_blocked(PCB * p) // 插入阻塞队列
{
p -> next = NULL;
if(blocked_tail) blocked_tail -> next = p;
blocked_tail = p;
if(! blocked_head) blocked_head = p;
}
void change_process() // 切换进程
{
if(running) insert_to_ready(running);
running = ready_head;
if(ready_head) ready_head = ready_head -> next;
if(ready_head == NULL) ready_tail = NULL;
cout << "切换进程成功!" << endl << endl;
}
void block_process() // 阻塞进程
{
if(running)
{
insert_to_blocked(running);
running = ready_head;
if(ready_head) ready_head = ready_head -> next;
if(ready_head == NULL) ready_tail = NULL;
cout << "进程阻塞成功!" << endl << endl;
}
else cout << "当前系统没有运行当中的程序可供阻塞!" << endl << endl;
}
void awaken_process() // 唤醒进程
{
if(blocked_head)
{
// if(blocked_head == blocked_tail) blocked_tail = NULL;
auto p = blocked_head -> next;
insert_to_ready(blocked_head);
blocked_head = p;
if(blocked_head == NULL) blocked_tail = NULL;
cout << "成功唤醒阻塞队列队首进程!" << endl << endl;
}
else cout << "阻塞队列为空,没有可供唤醒的进程!" << endl << endl;
}
void end_process() // 结束进程
{
if(running)
{
S.erase(running -> out_id);
delete running;
running = ready_head;
if(ready_head) ready_head = ready_head -> next;
if(ready_head == NULL) ready_tail = NULL;
cout << "成功结束当前运行进程!" << endl << endl;
}
else cout << "当前系统没有运行当中的程序可供结束!" << endl << endl;
}
void show() // 显示
{
if(running) cout << "运行的程序是:" << running -> out_id << endl;
else cout << "没有正在运行的程序!" << endl;
if(ready_head)
{
cout << "就绪队列为:" ;
for(auto i = ready_head; i; i = i -> next)
cout << i -> out_id << " " ;
cout << endl;
}
else cout << "就绪队列为空!" << endl;
if(blocked_head)
{
cout << "阻塞队列为:" ;
for(auto i = blocked_head; i; i = i -> next)
cout << i -> out_id << " " ;
cout << endl;
}
else cout << "阻塞队列为空!" << endl;
cout << endl;
}
void check() // 检查(若当前没有正在运行的程序且当前就绪队列非空,则调度就绪队列队首进程)
{
if(!running && ready_head)
{
running = ready_head;
ready_head = ready_head -> next;
}
}
int main()
{
while(true)
{
int choice;
cout << "请选择系统模拟选项:" << endl;
cout << "1、创建进程" << endl;
cout << "2、当前时间片结束" << endl;
cout << "3、阻塞当前运行进程" << endl;
cout << "4、唤醒阻塞队列队首进程" << endl;
cout << "5、结束当前运行进程" << endl;
cout << "6、退出系统" << endl << endl;
cin >> choice;
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
{
auto p = PCB_creat();
PCB_init(p);
insert_to_ready(p);
check();
show();
break;
}
case 2: change_process(); show(); break;
case 3: block_process(); show(); break;
case 4:awaken_process(); check(); show(); break;
case 5:end_process(); show(); break;
case 6: exit(0);
default: cout << "您的选择有误,请重新选择!" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}六、 效果展示