模型对象/材质
三维向量 Vector3 与模型位置
该类表示的是一个三维向量(3D vector)。 一个三维向量表示的是一个有顺序的、三个为一组的数字组合(标记为 x、y 和 z), 可被用来表示很多事物,例如:
- 一个位于三维空间中的点。
- 一个在三维空间中的方向与长度的定义。在 three.js 中,长度总是从(0, 0, 0)到(x, y, z)的 Euclidean distance(欧几里德距离,即直线距离), 方向也是从(0, 0, 0)到(x, y, z)的方向。
- 任意的、有顺序的、三个为一组的数字组合。
点、线、网格模型等模型对象的父类都是Object3D,如果想对这些模型进行旋转、缩放、平移等操作。如何实现,可以查询 Threejs 文档 Object3D。
Vector3 对象中具有 x、y、z,此对象还具有.set()等方法。
const geometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(100, 50);
// 材质
material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
color: 0x00ffff,
transparent: true, //开启透明
// opacity: 0.5, //设置透明度
// wireframe: true,//线条模式渲染mesh对应的三角形数据
side: THREE.DoubleSide, //两面可见
});
geometry.translate(50, 0, 0);
geometry.center();
mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
mesh.position.set(80, 2, 10);
scene.add(mesh);
const v3 = new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0);
console.log("v3", v3);
v3.set(10, 0, 0); //set方法设置向量的值
v3.x = 100; //访问x、y或z属性改变某个分量的值
console.log("v3", v3);
console.log("模型位置属性.position的值", mesh.position);
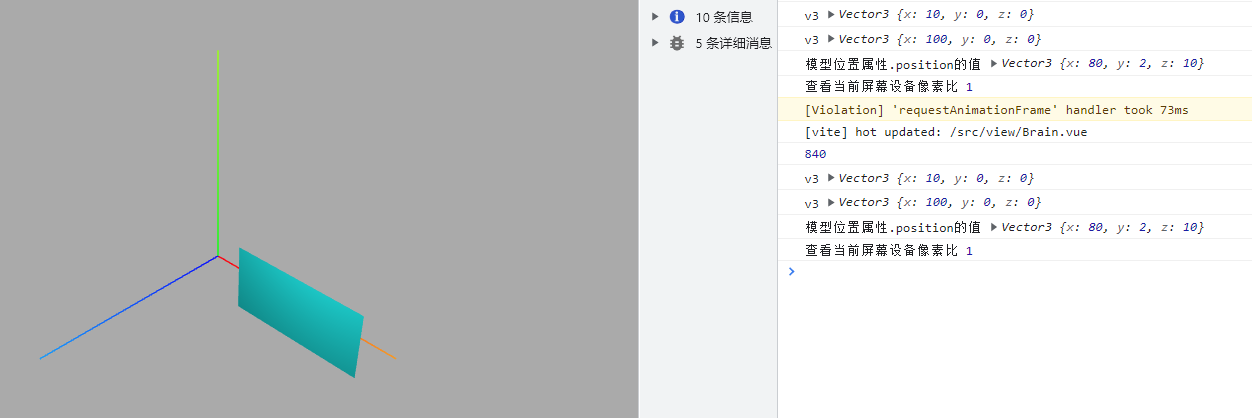
改变位置属性
通过模型位置属性.position可以设置模型在场景 Scene 中的位置。模型位置.position的默认值是THREE.Vector3(0.0,0.0,0.0),表示坐标原点。
设置模型 xyz 坐标
mesh.position.set(80, 2, 10);
平移
.translateX()、.translateY()、.translateZ()
mesh.position.set(80, 2, 10);
mesh.translateY(100);
欧拉角Euler
角度属性.rotation的值是欧拉对象Euler
//绕y轴的角度设置为45度
mesh.rotation.x = Math.PI / 4;
//绕y轴的角度增加0度
mesh.rotation.y += 0;
//绕y轴的角度减去90度
mesh.rotation.z -= Math.PI / 2;
绕着 xyz 轴分别旋转 45 度,0 度,90 度
旋转方法.rotateX()、.rotateY()、.rotateZ()
说白了其实.rotaition等价于rotate方法
mesh.rotation.x = Math.PI / 4;
mesh.rotation.y += 0;
mesh.rotation.z -= Math.PI / 2;
mesh.rotateX(Math.PI / 3); //绕x轴旋转π/3
这里rotateX会覆盖mesh.rotation.x
旋转动画
旋转动画的两种方式
// 渲染循环
function render() {
mesh.rotation.y += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(render);
}
function render() {
mesh.rotateX(0.01);
}
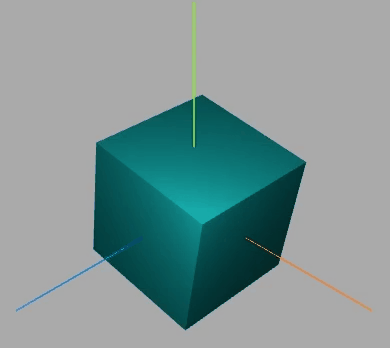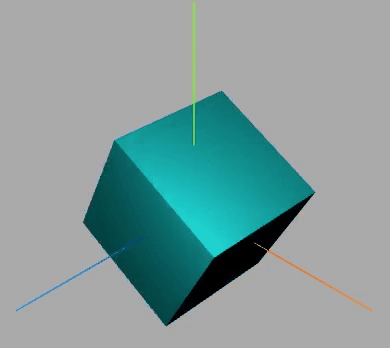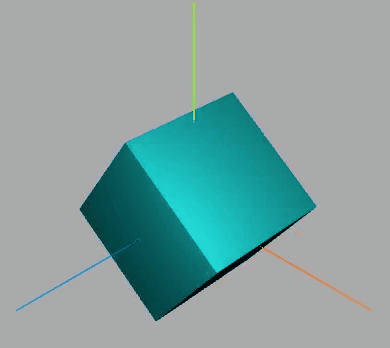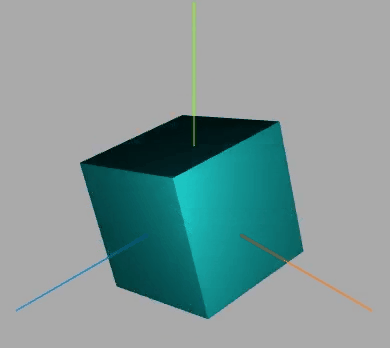
效果如下:
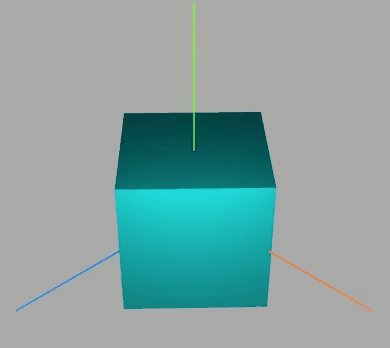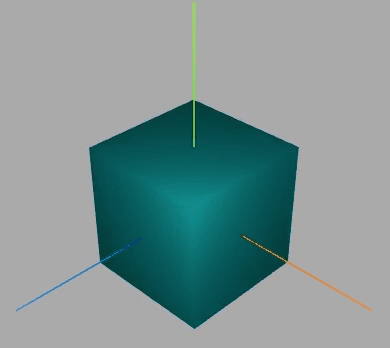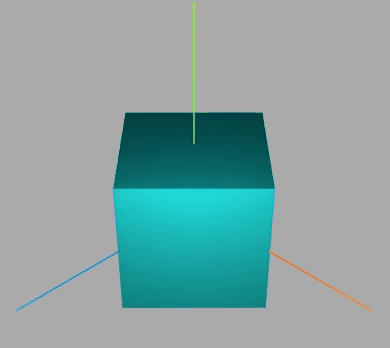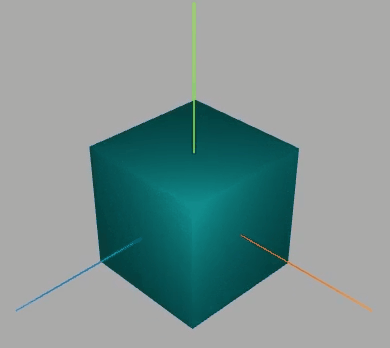
围绕某个轴旋转
此段代码放入动画中
网格模型绕(0,1,0)向量表示的轴旋转π/20。
const axis = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 1); //向量axis
mesh.rotateOnAxis(axis, Math.PI / 20); //绕axis轴旋转π/8
克隆.clone
复制一份和原对象一样的新对象,可以参考这种写法
const v1 = new THREE.Vector3(1, 2, 3);
console.log('v1',v1);
//v2是一个新的Vector3对象,和v1的.x、.y、.z属性值一样
const v2 = v1.clone();
console.log('v2',v2);
复制.copy()
这里不过多解释了
const v1 = new THREE.Vector3(1, 2, 3);
const v3 = new THREE.Vector3(4, 5, 6);
v3.copy(v1);
console.log(v3) // 1,2,3
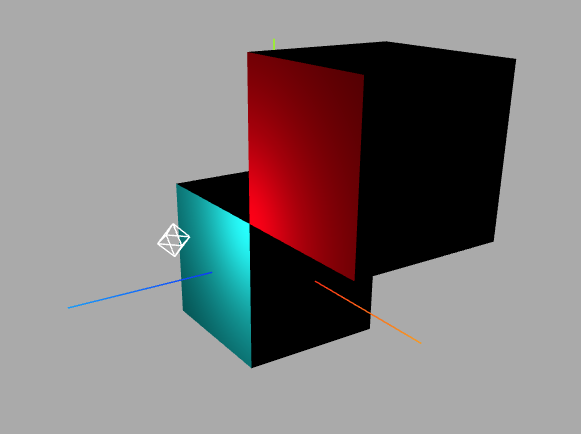
关于Mesh克隆.clone()
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(100, 100, 100);
// const geometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(100, 50);
// 材质
material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
color: 0x00ffff,
});
mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
const mesh2 = mesh.clone();
// 克隆几何体
mesh2.geometry = mesh.geometry.clone();
// 克隆材质
mesh2.material = mesh.material.clone();
// 更改mesh2的颜色
mesh2.material.color.set(0xff0000);
// 更改mesh2的位置避免重叠
mesh2.position.set(100, 100, 0)
scene.add(mesh);
// 添加进场景
scene.add(mesh2);



![[转]Github进行fork后如何与原仓库同步](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/190e5567244042808d3d45fdb52bfcfc.png)