C#实现凸包算法之Graham
文章目录
- C#实现凸包算法之Graham
- 前言
- 示例代码
- 实现思路
- 测试结果
- 结束语
前言
这篇关于凸包算法的文章,本文使用C#和Graham算法来实现凸包算法。
首先消除两个最基本的问题:
- 什么是凸包呢?
凸包是一个包围一组点的凸多边形。凸多边形是指多边形中的每个内角都小于180度的多边形。 - 凸包算法有什么用呢?
凸包算法的作用是找到这个凸多边形,并且使用最少的点来绘制出它的轮廓。凸包算法在计算机图形学、计算几何和机器学习等领域中有着广泛的应用。
示例代码
现在来看一下C#中的Graham算法是如何实现凸包算法的:
/// <summary>
/// 通过Graham算法获取围绕所有点的凸多边形的轮廓点<br/>
/// </summary>
/// <param name="points">点数组</param>
/// <returns>轮廓点数组</returns>
public static PointD[] GetConvexHullByGraham(PointD[] points)
{
if (points.Length < 3)
{
throw new ArgumentException("凸包算法需要至少3个点");
}
List<PointD> pointList = new List<PointD>(points);
// 找到最下面的点
PointD lowestPoint = pointList[0];
for (int i = 1; i < pointList.Count; i++)
{
if (pointList[i].Y < lowestPoint.Y || (pointList[i].Y == lowestPoint.Y && pointList[i].X < lowestPoint.X))
{
lowestPoint = pointList[i];
}
}
// 将最下面的点作为起点,并按照极角排序其他点
pointList.Remove(lowestPoint);
pointList.Sort((p1, p2) =>
{
double angle1 = Math.Atan2(p1.Y - lowestPoint.Y, p1.X - lowestPoint.X);
double angle2 = Math.Atan2(p2.Y - lowestPoint.Y, p2.X - lowestPoint.X);
if (angle1 < angle2)
{
return -1;
}
else if (angle1 > angle2)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
double distance1 = Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(p1.X - lowestPoint.X, 2) + Math.Pow(p1.Y - lowestPoint.Y, 2));
double distance2 = Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(p2.X - lowestPoint.X, 2) + Math.Pow(p2.Y - lowestPoint.Y, 2));
if (distance1 < distance2)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
return 1;
}
}
});
// 使用栈来存储凸包的点
Stack<PointD> hull = new Stack<PointD>();
hull.Push(lowestPoint);
hull.Push(pointList[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < pointList.Count; i++)
{
PointD top = hull.Pop();
while (hull.Any() && Cross(hull.Peek(), top, pointList[i]) <= 0)
{
top = hull.Pop();
}
hull.Push(top);
hull.Push(pointList[i]);
}
return hull.ToArray();
}
上面代码中定义了一个名为GetConvexHullByGraham的静态方法,该方法接受一个PointD类型的数组作为输入参数,并返回一个PointD类型的数组,表示围绕所有点的凸多边形的轮廓点。
补充一下,关于示例中使用到的Cross方法和PointD类型的源代码如下:
/// <summary>
/// 计算从 a 到 b 再到 c 的叉积
/// </summary>
/// <returns>叉积值</returns>
private static double Cross(PointD a, PointD b, PointD c)
{
return (b.X - a.X) * (c.Y - a.Y) - (b.Y - a.Y) * (c.X - a.X);
}
public struct PointD
{
public PointD(double x, double y)
{
X = x;
Y = y;
}
public double X { get; set; }
public double Y { get; set; }
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
if (obj == null || GetType() != obj.GetType())
{
return false;
}
PointD other = (PointD)obj;
return X.Equals(other.X) && Y.Equals(other.Y);
}
}
实现思路
- 检查输入的点数是否小于3个,因为凸包算法需要至少3个点才能计算出凸多边形。
- 找到数组中最下面的点,并将其作为起点。
- 对其余的点按照它们与起点之间的极角进行排序(这里使用了Atan2函数来计算点与起点之间的极角)。如果极角相同,则按照点与起点之间的距离进行排序。
- 使用一个栈来存储凸包的点。首先将起点和第一个排序后的点放入栈中。
- 遍历其余的点,如果遍历到的点与栈顶的两个点所形成的向量不是一个“左拐”,就将栈顶的点弹出,直到遍历到的点形成的向量是一个“左拐”。
- 将所有剩余的点都压入栈中,这些点就是凸多边形的轮廓点。
测试结果
用于测试的数据点:
static PointD[] points = new PointD[]
{
new PointD(0, 0),
new PointD(0, 10),
new PointD(10, 10),
new PointD(10, 0),
new PointD(1, 0),
new PointD(4, 3),
new PointD(5, 2),
new PointD(6, 5),
new PointD(4, 9),
new PointD(4, 2),
new PointD(5, 1),
new PointD(6, 5),
new PointD(1, 3),
new PointD(7, 2),
new PointD(8, 2),
new PointD(6, 7),
new PointD(8, 5),
new PointD(9, 3),
new PointD(7, 8),
new PointD(8, 9),
};
测试代码如下:
[TestMethod]
public void GetConvexHullByGraham()
{
Console.WriteLine("Graham 算法");
PrintPoints(ConvexHull.GetConvexHullByGraham(points));
}
private void PrintPoints(PointD[] points)
{
Console.WriteLine(points.Select(p => $" ({p.X}, {p.Y})").Join("\r\n"));
}
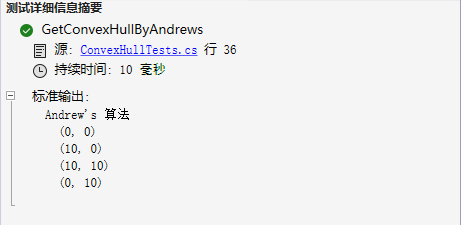
执行结果如下:
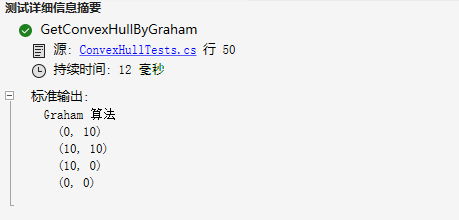
结束语
通过本章的代码可以轻松实现Graham算法并找到一组点最外侧的凸多边形。如果您觉得本文对您有所帮助,请不要吝啬您的点赞和评论,提供宝贵的反馈和建议,让更多的读者受益。